5 / 5 ( 1 voice )
Botanical name: Warty birch (Betula verrucosa), drooping. Birch genus, Birch family.
Homeland of warty birch: Far East.
Lighting: light-loving.
Soil: well fertilized.
Watering: plentiful.
Maximum tree height: 30 m.
Average lifespan of a tree: up to 120 years.
Planting: seeds.
Warty birch: description of the tree
Warty birch is a deciduous tree about 25-30 m high. Young individuals are distinguished by brown bark, which becomes white by the age of 8. In older plants, cracks form in the lower part of the trunk, and the bark becomes black. Birch wood has a yellowish-white tint and is quite dense and heavy. The branches are covered with resinous glands - warts, from which the birch got its name “warty”. Young branches stretch down, this gives the crown a characteristic appearance, hence its second name “dangling.”
Kinds
The birch genus includes over 40 species. Today, many gardeners use birch for landscaping garden plots. Thanks to this, new varieties of wood were developed. Several interesting species of silver birch, which are especially popular, deserve special attention.
"Purpurea"
The highlight of this species lies in the shade of the leaves. They are dark red in color, which turns to a deep purple hue as they grow. They are shaped like a rhombus. The bark of the tree is quite dark compared to other species. It has a black-gray tint. The birch tree reaches a height of 10 m.
"Royal Frost"
It is distinguished by a pyramid-shaped crown and smooth, burgundy leaves. Young trees have bronze-colored bark. Over time it becomes white. This species is quite light-loving, but can also take root in darkened areas. Unpretentious in choosing soil. It develops well in soils of varying composition, density and acidity.
Youngii
This is a type of birch on a trunk. It is a small tree with an umbrella-shaped crown. Thin birch branches hang down, reaching the surface of the earth. Youngii grows up to 100 cm per year. In standard crops, the height depends on the grafting. The age of this species can reach 120 years.
Birch leaf
The leaves are alternate, long-petiolate, triangular-diamond-shaped, with a wedge-shaped base, smooth, 3.5-7 cm long, 2-5 cm wide. The edges of the leaves are double-toothed. The warty birch leaf has a weak aroma and astringent taste.
The buds are sessile. The flowers are small, inconspicuous, and have no decorative value. Collected in unisexual racemes - catkins: at the ends of the branches staminate, oblong, cylindrical, 6-10 cm long, yellow; on shortened side branches - pistillate, cylindrical, directed upward, 2-3 cm long, green.
The warty birch blooms from April to May.
The fruits are small winged nuts that ripen in late summer - early autumn. It begins to bear fruit at the age of 10, and in plantations at the age of 20-25.
Fruits and seeds
Birch blooms in April-May. The fruits appear in September. They are elongated oval nuts with two small wings. They are in an earring that can contain up to 500 nuts at once. Starting from the end of summer until mid-winter, the fruits of the birch gradually fall off.
In a natural forest stand, you can get a seed yield of up to 50 kg per 1 ha. Seed germination is 25 – 60%. In fruitful years, freshly harvested seeds have a germination rate of 70–80%. Their quality depends on weather conditions during birch flowering. If the weather is rainy during the flowering period, many empty seeds are produced.
Deciduous tree warty birch: root system
The warty birch tree is distinguished by a powerful root system, which, depending on the growing conditions, can be superficial or go deep.
The tap root quickly dies, the lateral roots develop at an accelerated pace and are overgrown with fibrous small roots. The root system lies almost on the surface of the earth, so the plant requires increased watering, especially on hot, dry days.
A burl on the trunk of a warty birch is a very common occurrence and a distinctive feature of the tree. This growth has a rougher and denser wood than the wood of the tree itself. A month before the leaves appear and flower, the birch tree begins to flow sap.
The release of sap begins in March; the most abundant release of birch sap is observed at the end of April; sap flow lasts 15-20 days. Birch sap has a pleasant sweet taste and beneficial properties.
Planting and care
Birch is not picky about soil and can grow and develop in any soil. To grow a curly tree in your own area, it is recommended to prepare moist and loamy soil. You should dig a hole into which the mixture is added in certain proportions: peat, sand, humus and ordinary garden soil in a ratio of 1:1:1:2. In order for the plant to take root better, the seedling must be placed with an earthen ball on the roots. After planting, you need to provide regular watering and fertilizing with complex fertilizers containing phosphorus and potassium.
Do not forget that in summer the tree absorbs a lot of water, so it is necessary to water it regularly, taking into account 1 bucket per 1 square meter. m.
Feed twice a year: in autumn and spring - with a nitrogen-containing solution or nitroammophos.
Prevention of diseases and pests is carried out annually. The plant is treated with a fungicide or insecticide.
Fluffy
Reproduction of warty birch
The warty birch, silver birch, reproduces by seeds. Seeds are sown during the period of browning of catkins, immediately after collection, in late autumn or spring.
Seeds left for spring sowing are stored in a closed container. When sowing, they are lightly sprinkled with earth and leveled. Straw or thin branches are laid on the surface of the ridge, through which watering is carried out. After pipping of the seedlings, the coating is removed, and the seedlings are shaded with shields. The warty birch is restored by stump growth formed after the death of young trees.
Planting silver birch
It is advisable to carry out this operation in spring and autumn. In extreme cases, in winter it is allowed to transship large trees with a frozen lump of soil to reduce the risk of destruction of the root system. Ornamental silver birch is planted according to general rules similar to most other ornamental plants. To create optimal conditions, it is better to use the following recommendations:
- Seedlings 5-7 years old take root better.
- Composition of the soil mixture: sand, peat, leaf soil in a ratio of 2:1:2.
- At the bottom of the pit you need to arrange a sandy drainage layer 15 cm thick.
- You can add 150-200 g of complex fertilizer to the hole, thoroughly mixing the fertilizer with the soil.
- The root collar should not be deeply buried.
- Young seedlings should be watered regularly, preventing the top layer from drying out.
- It is necessary to moisten the soil for the first 4 days.
Warty birch fruits
In open areas, the tree begins to bear fruit at 10-12 years of age. In plantings – from 20-25 years.
The birch fruit is a small, flattened nut with two membranous wings. The tree bears fruit annually and quite abundantly. The fruits ripen in July, the catkins open after the seeds ripen. One part of the seeds falls on the soil in the fall, the other in the spring. Seeds germinate on an empty, vegetation-free surface of the earth. They prefer soil rich in minerals and fertilizers. Thickets of grass and moss prevent the emergence of seedlings. In strong winds, warty birch seeds are carried at a distance of up to 100 m from the mother tree. The fruits do not open.
Growing
Agricultural technology
Silver birch is distributed throughout almost the entire territory of the country. We have about 120 species.
Silver birch forms derivative forests that arise on the site of cut down or burned pine, spruce, larch, and oak forests. It quickly populates the vacated territories and dominates them, creating only temporary groups; subsequently replaced by other tree species. It forms native stands only in forest-steppe and steppe regions, especially in Western Siberia, where it forms birch groves characteristic of the landscape of the forest-steppe zone. Often found in different types of forests as an impurity. Grows on dry and moist sandy, loamy, chernozem and stony-gravelly soils. Tolerates various climatic conditions, is highly winter-hardy (excellent), drought-resistant (good), therefore it grows from the tundra to the steppe zone. It grows quickly and renews well by shoots and self-sowing. The seeds are carried by the wind and easily take root in dry and moist soils.
It is almost not damaged by diseases and pests (good). Blooms and bears fruit regularly (good). The catkins bloom at the end of April, when the leaves bloom, the fruits ripen in August. Light-loving, but tolerates partial shade, prefers light, fresh soils.
Reproduction
Propagated by seeds.
Varieties
Along with silver birch, other types of birch are used to obtain medicinal raw materials: downy, flat-leaved and Manchurian.
Distribution of birch warty
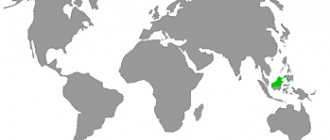
Warty birch is widespread in North America, Europe, North Africa, Western and Central Asia. It rises into the mountains to a height of 2100-2500 m above sea level.
Prefers areas with a temperate climate. In Russia it is one of the most common trees. It grows more often in the European part, Western Siberia, Altai and the Caucasus.
Birch forests are formed on the site of cleared or burned forests, often coniferous. Since birch is very light-loving, it is quickly replaced by other more shade-tolerant and larger trees. Grows in deciduous and mixed forests, steppes and forest-steppe areas.
It grows in forests as an admixture with the bulk of other trees in light areas. Birch plantations are found in gardens and parks.
Silver birch - care
During the season, the unpretentious tree practically does not cause the gardener any worries or troubles. The main agricultural activities are as follows:
- Loosening the soil to a depth of 3 cm simultaneously with weeding.
- Mulching tree trunk circles up to 12 cm thick with peat, wood chips, compost.
- Removing dry and diseased branches.
- Treatment with insecticides against chimney beetles and chafer beetles.
- Anti-rust treatment with copper oxychloride.
- Fertilizer application - stir 1 kg of manure, 10 g of urea, 1 g of ammonium nitrate into 10 liters of water. Young silver birch up to 20 years old requires 30 liters of feeding, older trees - 50 liters.
Pruning silver birch
When sanitary and decorative thinning of branches on this tree, a number of serious nuances must be taken into account. Let's look at the basic tips for pruning crops:
- The silver birch forms on a trunk exclusively at a young age of up to 15 years; later cutting down the crown to stimulate the development of lateral branches often leads to the death of the plant.
- It is recommended to prune in the fall in October-November before the onset of severe frosts at a temperature not lower than -3℃.
- It is strictly prohibited to trim birch trees after sap flow begins.
- For normal restoration, the birch tree is pruned after a year or at large intervals; annual pruning can be harmful.
- The maximum volume of cut mass is up to 20%.
- Be sure to remove dried and diseased parts of the crown.
- A few days after the operation, when the saw cuts are dry, they are treated with garden varnish.
Birch Fastigiata: description of the tree
Betula pendula Fastigiata is a species of silver birch. The crown is narrow, columnar. Its height reaches up to 20 m, width up to 5 m. The branches are directed upward. The leaves and trunk are the same as those of the warty birch. The leaves do not fall for a long time and remain on the branches until late autumn. The root system is powerful and wind-resistant. The height of the Fastigiata birch tree is about 10 m. The crown diameter is 2 m. It grows quickly, the annual growth is 40 cm in height. Life expectancy is up to 100 years. Flowers, flat, green, irregular in shape, 1 cm long. Leaves are diamond-shaped, bright green, yellow in autumn from 3 to 7 cm.
The silver birch Fastigiata has a decorative trunk and a beautiful crown. Used in single plantings and in groups to create alleys and parks. Photophilous, drought-resistant, not picky about the soil. Winter hardiness is high. The root system is superficial.
The plant is planted in open areas or partial shade. Soil mixture: turf soil, peat, sand. Fertilizing is necessary in early spring before the leaves appear and at the end of spring. Nitrogen-containing fertilizers are used: ammonia, urea, ammonium nitrate. In autumn, mineral fertilizers, nitroammofosk. Watering is required after planting and during dry periods. Loosening to a depth of 3 cm to control weeds and saturate the soil with oxygen. Drying branches are pruned in the spring.
Tree pests: birch sapwood, bucephalus corydalis, tubeworm beetle, chafer beetle, nun silkworm.
Recipes for various diseases
Prostate adenoma
Collection 1. Mix dried and crushed green onion feathers and May birch leaves (dry) in equal parts. Pour 2 tablespoons of the mixture into 0.5 liters of boiling water and leave in a warm place for 1 hour, then strain. Take 1/2 cup 2 times a day, preferably in the first half of the day: morning and afternoon. At the same time, take 1/2 teaspoon of pollen.
Angina
Collection 1. It is recommended to chew birch buds slowly after eating, after slightly kneading them. Gargle with birch sap.
Collection 2. Mix 1 teaspoon of birch ash with 1/2 teaspoon of table salt, grind well into powder. Wet your index finger with water, dip it in this mixture and rub the sore areas inside your throat. After 2-3 procedures, the throat disease usually goes away.
Collection 3. Crush the branches with birch buds, brew with boiling water and leave for 1 hour. Take 2-3 glasses per day orally.
Arthritis
Collection 1. For 1 liter of water, take 5 g of dry birch leaves and 15 g of oat grains, cook in a sealed container for 10 minutes, strain. Drink the decoction warm one hour before meals. The course of treatment is 10 days.
Collection 2. Pour 3-4 g of dry buds or 6-8 g of dry leaves (10-15 g of fresh) white birch with 0.5 liters of water, boil for 15-20 minutes. Drink 1/2 glass 3-4 times a day.
Collection 3. Pour spring birch leaves into a bottle, add vodka, leave in a dark place for one month, shaking the contents periodically. Store in a cool, dark place without straining. Rub the tincture, while taking it orally 20-30 drops 3-4 times a day 30 minutes before meals.
Collection 4. Place fresh (or steamed) birch leaves on the sore joint, bandaging it loosely with a woolen scarf. The procedure is especially useful if the compress is done all night.
Atherosclerosis, edema
Collection 1. Take 100 g of dry crushed birch bark and dry leaves of common ash, pour 1 liter of cold water, bring to a boil, cook in a sealed container over low heat for 5 minutes, leave, wrapped, for 10 minutes, strain. In the morning on an empty stomach, drink a glass of decoction, and drink the rest of the amount in small sips throughout the day.
Collection 2. Pour 1 tablespoon of crushed buds into 1.5 cups of boiling water, cook in a sealed container in a boiling water bath for 5 minutes, leave in the oven for 3 hours and, without straining, drink the entire infusion in the first and early afternoon for atherosclerosis.
Tracheitis, bronchitis
Collection 1. Pour 20 g of dry crushed birch buds with 100 ml of 70% alcohol, leave in a dark place for 3 weeks, shaking the contents periodically, strain, squeeze out the rest. Take 20-30 drops per 1 tablespoon of water 3 times a day 15-20 minutes before meals.
Phlebeurysm
Collection 1. In the morning on an empty stomach and in the evening, drink 1 glass of infusion of birch buds or leaves, prepared in a ratio of 1:10, with 2 teaspoons of apple cider vinegar and 2 teaspoons of natural honey. Additionally, you should lubricate the veins from bottom to top with apple cider vinegar in the morning and evening. Treatment achieves the fastest results if sweets are excluded from food.
Hair loss
Rub a mixture of birch sap, alcohol and burdock root decoction into the scalp.
Sinusitis
For sinusitis, it is useful to rub the skin over the sore spot with gruel or garlic juice, then rub in a mixture of birch charcoal powder and fresh burdock root juice for 20-30 minutes. Carry out the procedures 2-3 times a day until complete healing.
Haemorrhoids
Collection 1. Pour 5 liters of boiling water over 10 handfuls of birch leaves, leave in a tightly sealed container for 15 minutes, heat over low heat for 5 minutes, cool to 30°C and pour the decoction with leaves into the prepared bath. The duration of the bath is 15 minutes. Take baths 2-3 times a week.
Hypertension
Collection 1. Pour 1 tablespoon of high-quality tea into 3 liters of hot birch sap, leave in a tightly sealed container for 10 minutes, strain through multi-layer gauze, cool. Rinse the kombucha with lukewarm birch sap, place it in a wide-necked jar and pour in a cool infusion of tea in birch sap. Leave in a dark place at room temperature for 7-8 days, covering the jar with gauze to keep out dust. Before use, the infusion must be carefully filtered through multi-layer gauze. Drained and strained, it remains in bottles for a long time, acquiring an aromatic smell and a sour-sweet pleasant taste. It also helps with atherosclerosis. To prepare such a drink again, the “mushroom” should be washed again with warm birch sap and filled with tea and birch infusion.
Headache, migraine, insomnia
Collection 1. Pour 20 g of dry crushed birch buds with 1/2 cup of 70 percent alcohol, leave in a dark place for 3 weeks, shaking the contents periodically, strain, squeeze out the rest. Take 20-30 drops per 1 tablespoon of water 3 times a day 15-20 minutes before meals.
Jaundice
Collection 1. Take 1 teaspoon of birch charcoal powder 2 times a day, 20-30 minutes before meals, with water.
Gastrointestinal diseases
Collection 1. Pour 1 teaspoon of birch buds into 1/2 cup of boiling water, leave in a boiling water bath in a tightly sealed container for 15 minutes, cool at room temperature for 45 minutes, strain. Take the infusion in three doses throughout the day. Collection 2. A decoction of birch buds, take 1 tablespoon 4 times a day 30 minutes before meals for dysentery and stool disorders in children.
Collection 3. Pour 2 tablespoons of birch buds into 1 liter of water, cook over low heat for 20 minutes, leave. Take 1 glass sweetened in the morning on an empty stomach and an hour after meals. The course is 7-10 days for stomach pain.
Collection 4. A mixture of birch sap and the juice of young plantain leaves in a ratio of 2:1 has a beneficial therapeutic effect for stomach and duodenal ulcers, gastritis, and colitis.
Gallstone disease, kidney disease, articular rheumatism
Collection 1. Pour 2 tablespoons of crushed birch leaves with 2 cups of boiling water, leave in a tightly sealed container in a boiling water bath for 30 minutes, cool at room temperature for 10 minutes, strain, add bicarbonate of soda on the tip of a knife. Take 1/2 cup 2-3 times a day. The same decoction can be used to wash skin rashes, tumors, and various skin irritations.
Collection 2. Drink 2 glasses of birch sap per day.
Collection 3. Grind a piece of birch bark approximately 10x10 cm in size into powder and pour in 1 liter of boiling water, simmer over low heat until a glass of liquid remains. Cool the broth at room temperature, strain and take 1 tablespoon 3-4 times a day 15-20 minutes before meals for liver stones.
Urinary retention
Collection 1. Pour 1 tablespoon of birch buds with 1 glass of boiling water and leave for one hour in a tightly sealed container in a warm place. Take 1 time per day for 2 weeks. Its maximum elimination begins 1.5-2 hours after taking the infusion. The diuretic effect will increase if you add baking soda on the tip of a knife or 2 teaspoons of honey to a glass of infusion. Drink 3-5 glasses of birch sap per day (especially recommended in the postoperative period).
Collection 2. Pour 2 tablespoons of crushed birch leaves with 2 cups of boiling water, leave in a tightly sealed container in a boiling water bath for 30 minutes, cool at room temperature for 10 minutes, strain, add bicarbonate of soda on the tip of a knife. Take 1/2 cup 2-3 times a day.
Myocardial infarction
Collection 1. Drink 2-4 glasses of birch sap per day.
Cough
Collection 1. Mix 2 tablespoons of birch buds with 50 g of unsalted butter. Place on the fire, bring to a boil, but do not boil. Simmer over low heat or in the oven for 1 hour. Remove from heat and when cool but still warm, strain. Squeeze and discard the kidneys. Add 200 g of honey and stir well. Take this mixture 1 tablespoon 4 times a day.
Collection 2. Take 20 g of young birch leaves, pour 1 glass of boiling water, leave for 1 hour, strain. Boil 1 tablespoon of anise seeds and 1 teaspoon of honey in 1/2 cup of birch leaf infusion. Drink 5 tablespoons of decoction per day.
Anemia
Collection 1. Take birch leaves and stinging nettle leaves in equal proportions. Brew 2 tablespoons of the crushed collection in 1.5 cups of boiling water, leave in a tightly sealed container in a warm place for 1 hour, strain, add 1/3 cup of fresh beet juice. Drink during the day in 3-4 doses 20 minutes before meals. The course of treatment is 8 weeks.
Urolithiasis disease
Collection 1. Drink 3 times a day 1 glass of birch sap with 1 tablespoon of honey.
Collection 2. Pour 1 teaspoon of birch buds into 1/2 cup of boiling water, leave in a boiling water bath in a tightly sealed container for 15 minutes, cool at room temperature for 45 minutes, strain. Divide the infusion into 3 parts and drink the entire portion per day in 3 doses.
Collection 3. Pour 2 tablespoons of young (about the size of a penny) birch leaves with 1 glass of boiling water. Boil over low heat until half full. When cool, strain. Take one dessert spoon 3 times a day an hour before meals. The course of treatment is 3 months. Good for small stones. There will be pain, contractions, colic, nausea. We need to be patient. All the stones will come out.
Urinary incontinence in children
Collection 1. Pour 1 tablespoon of chopped buds into 1.5 cups of boiling water, cook in a sealed container over low heat for 5 minutes. Infuse, wrapped, for 1 hour, strain, squeeze out the rest. Take 1 glass 1-2 times a day 20 minutes before meals. The course of treatment is 2-3 weeks.
Collection 2. In the evening, put 1 tablespoon of birch buds in a thermos and pour 1 glass of boiling water. In the morning, strain, divide into 4 doses and take 1 hour before meals for enuresis.
Swelling of the eyelids
Collection 1. Pour 1 tablespoon of fresh birch leaves with 1 glass of cold water, leave for 8 hours, then strain. It helps well in the form of lotions.
Pericarditis
Collection 1. Fill a glass jar 2/3 of the volume with staminate (larger in size) birch catkins, fill them to the top with vodka, close and leave for 14 days. Do not strain. Take from 20 drops to 1 teaspoon 3 times a day 30 minutes before meals. When using this tincture, pain in the heart subsides, shortness of breath disappears, and vigor appears.
Cold
Collection 1. Brew birch buds as tea and drink warm throughout the day for a mild cold.
Collection 2. Drink 1 glass of birch sap 3-4 times a day before meals.
Collection 3. An old herbalist gives a recipe for making healing birch vodka that helps against colds: “For a bucket of strong and best grain wine, take half a pound of young birch leaves when it has just blossomed, preferably in May. You don’t need to take these leaves from the ends of the branches, but from the trunk. You can also take birch buds, not just half a pound, but a whole pound. Infuse in a warm place for 3 days, strain through cloth, squeeze out these leaves or buds and again add another half a pound of fresh birch leaves or buds to this light infusion. And so on up to three times. The next time, let it sit for 10 days and stir with an oar in the morning and evening. Pour into bottles through a canvas. This vodka has an effect on colds and fever, and on stomach pain. Heals wounds and all sorts of other injuries. And drink this vodka in the morning for a skinny heart and at dinner, one glass each” (1 pound corresponds to 409.5 g).
If you feel aches in your body when you have a cold, then at night you should rub yourself with an alcoholic infusion of birch buds - this will reduce the pain and cause heavy sweating. At the same time, you can drink tea from birch buds. After rubbing, the patient needs to lie under a blanket to sweat properly.
Go to bed, spread a thick layer of birch leaves on the painful parts of the body, cover yourself with a warm blanket and take a warm diaphoretic drink.
Prevention of colon and stomach cancer
Collection 1. 1st stage. Pour 1 glass of crushed birch buds into 0.5 liters of cognac (you can also use vodka in the same proportions) and leave for about a month in a dark place at room temperature, shaking the contents periodically. Then strain and squeeze. 2nd stage. Pass 5 kg of blue onions through a juicer, add 0.5 liters of birch bud tincture in cognac, 5 g mummy, 25 g birch mushroom powder - chaga. Shake the mixture thoroughly and leave for 3 days in a cool, dark place, shaking the contents occasionally. Take 1 tablespoon 3 times a day 20 minutes before meals. Be sure to shake before use. The course of treatment is 3 months, then you need to take a two-week break and continue if necessary.
Collection 2. Mix 50 g of tansy flowers crushed into powder and 20 g of sea buckthorn oil, pour in 0.5 liters of birch bud infusion. Let it sit for 2 weeks in a dark place at room temperature, shaking the contents occasionally, strain, and squeeze out the rest. Mix the drained tincture with the squeezed mixture and leave for another 3 days, then add 50 g of birch tar. Take 25 drops 3 times a day half an hour before meals. Shake thoroughly before use. The course is 6 weeks, then a two-week break.
Diabetes
Collection 1. Pour 2-3 tablespoons of birch buds with 2 cups of boiling water. Infuse in a warm place in a tightly sealed container for 6 hours, strain. Use within 24 hours.
Articular rheumatism
Collection 1. Take 800 g of unsalted butter and birch buds. Place butter in a glass, clay or enamel bowl (1-2 cm thick), on top - a layer of birch buds of the same thickness, and so on, alternating, 3-4 layers. Close the pan tightly with a lid, cover the gap with dough, then put it in a warm place, preferably in a cool stove or oven, for a day. After a day, cool slightly, strain and squeeze through cheesecloth. Add 5-10 g of camphor to the resulting mass and mix everything thoroughly. Rub the ointment into the joints once a day before bed.
Dry skin
Collection 1. Mix 1 teaspoon of sour cream or yogurt with 2 tablespoons of birch sap and 1 teaspoon of honey. Apply the mask to the skin for 10-15 minutes, then rinse with cool boiled water. In the morning, before washing, wipe your face with a cotton swab soaked in vegetable oil.
Furuncle
Collection 1. Take 1 part honey and 2 parts birch bud powder, mix until a thick, homogeneous mass is formed. If the honey is liquid, the amount of powder can be increased. The resulting “cakes” can be applied under the bandage, changing every 3-4 hours.
Cystitis
Collection 1. Pour 5-10 drops of birch tar into 1 glass of warm milk and stir. Take 1/3 cup 3 times a day.
Collection 2. Pour 20 g of dry crushed birch buds with 100 ml of 70% alcohol or vodka, leave in a dark place for 3 weeks, shaking the contents periodically, strain, squeeze out the rest. Take 20-30 drops per 1 tablespoon of water 3 times a day 15-20 minutes before meals.
Scurvy
Collection 1. Preparation of vitamin infusion. 100 g of fresh leaves are poured with cold boiled water and left for 2 hours. Used as a good antiscorbutic remedy.
Eczema of the hands
Prepare a decoction of birch twigs along with leaves, cool slightly (it should be as hot as can be tolerated) and, without removing the twigs, put your hands in this decoction for 20-30 minutes. After the procedure, do not wipe your hands - let them dry. Carry out treatment 2-3 times a day, preferably at night. Moreover, the same decoction can be used repeatedly. In other liquids, it is advisable to wet your hands as little as possible during treatment.
Cervical erosion
Douche daily with a 20% decoction of birch buds.
Ulcers, wounds
Collection 1. Pour 10-15 g of birch buds with 1 glass of milk, cook for 5 minutes, strain and wrap the buds in gauze. Use as an external anti-inflammatory agent.
Birch warty
- (Betula verrucosa Ehrh.). Birch is a deciduous tree of the birch family, up to 25 m high with white bark. The trunk is straight, the branches are usually drooping. The leaves are oval or ovoid, sharp. White birch is not much different from silver birch; moreover, it often forms hybrid forms with it with characteristics of both species. Silver birch, or warty birch, is larger than downy birch and, as a rule, prefers dry places. Its branches hang downwards and, when young, are strewn with warty glands that form resin. The leaves are also larger. Downy birch, on the contrary, has pubescent young branches, and it grows in damp forests and swamps. Both species are used in medicine. Birch grows in most of the country. It is most abundant in Western and Central Siberia, as well as in the middle zone of the European part of the country. Buds, leaves, bark, wood, and birch sap are used in medicine. Birch buds are harvested in early spring, at the beginning of swelling. When dried, they should be dark brown in color, with a pleasant smell, bitter taste and shiny surface.
Young leaves are plucked off in the spring (May-June), when they have not yet hardened. Birch bark (the suberized outer layer of birch bark) is harvested mainly from growing trees, dead wood and from trees after felling.
Birch sap is extracted in early spring, before the leaves bloom. Infusion and decoction of birch buds are used as a diuretic and choleretic agent, as well as externally for cuts and abscesses. To treat acute and chronic eczema, make a hot bath from birch buds.
The leaves are used as a diuretic. Tar is obtained from birch bark by dry distillation, which is included in the Vishnevsky (thinning agent) and Wilkinson ointments (against scabies, scaly lichen and lice).
The use of warty birch in industry and in everyday life
The warty birch tree, the photo of which is located above, is quite in demand in industrial production. Due to its strength, elasticity and ease of processing, birch is used as a material for making furniture. It is quite easy to polish and sharpen; furniture made from its solid wood has a pleasant golden hue. Birch is used to produce plywood, fence boards, toys, skis, coal, souvenirs and much more. When processing birch wood, methyl alcohol, acetic acid, and turpentine are obtained from it. It is used in medicine and perfume production.
Many parts of this plant are used in everyday life: bark, wood, birch bark, birch sap. Birch firewood has been used as fuel for quite some time. They are good because they dry quickly, prick easily and burn for a long time. When burning, they emit much more heat than aspen or pine. They have medicinal properties. When burned, they fill the room with a special aroma that disinfects the air and has a beneficial effect on the respiratory tract, thereby preventing colds.
How does silver birch reproduce?
Not all methods of rooting material give positive results in this case. Practice shows that cuttings from silver birch are extremely rare. Even when using Kornevin, the yield of seedlings is very low. Normal results are obtained only with the Daurian variety of birch. It is much easier and more effective to use seeds.
Seed propagation of silver birch:
- In late autumn, prepare ripe brown earrings.
- Sowing seeds in early spring or autumn.
- When sowing in autumn, stratification is not required; for sowing in spring, you need to age the seeds for 3 months. at temperature 0-5℃.
- Scatter the seeds on the surface of the soil and sprinkle lightly.
- Water the planting site and sprinkle it with straw mulch.
- Water regularly through the shelter.
- When sprouts appear, remove the mulch.
- To shade the overgrowth, use shields or other non-hermetic fencing.
- Abundant watering is necessary until mid-August.
The use of warty birch in medicine
The leaves of the plant are used in folk medicine. Their infusion is an effective diaphoretic and diuretic. Fresh leaves are doused with boiling water and used as compresses for rheumatism and polyarthritis. To strengthen and grow hair, infusions and decoctions of birch leaves and buds are made. Birch sap serves as a general tonic. It is rich in vitamins, minerals and trace elements. Contains tannins, aromatic substances, sugar, malic acid.
Birch wood is widely used in traditional (scientific) medicine. Birch charcoal is obtained from it in the form of “Carben” tablets, which helps with food poisoning, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, high acidity, fermentation and flatulence.
The composition of the well-known ointments “Konkova”, “Vishnevsky” and others used for healing wounds and skin diseases includes birch tar. The bark effectively fights malaria, dropsy and pulmonary diseases. Essential oil is also made from birch bark and used for cosmetic purposes. An infusion of birch buds is effective as a choleretic, diuretic, antiseptic, and disinfectant. Warty birch sap is part of the Biomos preparation, which is used to heal wounds and burns. The juice is used to prevent vitamin deficiency, for colds and skin diseases, for kidney stones, venereal diseases, arthritis, rheumatism, for the prevention of caries and as an anthelmintic. Birch syrup is prescribed instead of glucose.
Warty birch leaves are collected in May, when the tree is flowering. Dry outdoors, away from direct sunlight. The shelf life of treated leaves is 2 years. Birch sap is collected during sap flow from trees intended for felling. The buds are collected from logging sites and tree felling sites. The best period for collection is early spring, when the buds are swelling. The branches cut in winter are tied into bunches, kept in the sun so that the buds swell and thresh them.
Chemical composition
Active ingredients
Various parts of birch contain biologically active substances.
The bark contains betulin, phytosterol, glycosides, saponins, resinous acids, tannin and essential oil.
In the kidneys there is essential oil, ascorbic acid, saponins, bitterness, tannins, resin, grape sugar and a yellow coloring matter.
The leaves contain essential oil, ascorbic and nicotinic acids, glycosides, saponins, triterpene alcohols and inositol bitterness.
Vitamins E and PP were found in the inflorescences (earrings).
The seeds contain a fatty drying oil.
Birch sap contains 0.5-2% sugars, organic acids, carbohydrates, glucose, fructose, vitamin PP, potassium salts, calcium, iron, and trace elements.
.
Birch tar
Birch tar has been used for a very long time. Its production was previously carried out by tar workers. Today, tar is produced in industrial production.
Treated birch bark is tightly placed in iron boilers and tar is distilled from it. To prevent a vacuum from forming in the furnace, the birch bark must be tightly clamped. Filled boilers are closed and heated. One distillation lasts up to 11 hours.
Decorative varieties and names of birch species
Silver birch (Betula pendula). The most popular and widespread type of classic birch in the landscape of the middle zone. A tall tree growing up to 30 m tall with long, thin, weeping branches. The species itself is rarely used in garden landscaping, but its low, graceful varieties have become sought-after plants in landscape design.
Varieties of this type:
"Trost's Dwarf" is a completely unusual low-growing variety with an openwork, airy crown of thin, needle-like leaves;
Birch "Yungi" (Youngii). One of the most popular low varietal forms. The height does not exceed 2-3 meters, but the growth of the tree can be controlled by pruning;
Variety "Yungi" on a standard
'Royal Frost' is a tree with showy chocolate-burgundy, glossy leaves that turn bronze in autumn. The crown is loose, pyramidal. It grows up to a maximum of 10 m. It develops well in almost all conditions and is most resistant to pests;
“Golden Cloud” is a small tree whose leaves are golden-green throughout the season, “Fastigiata” - the crown of the tree resembles the shape of a cypress or pyramidal poplar.
Paper or Canoe birch (Betula paperifera) from North America. Characterized by white bark with sparse dark stripes, sometimes shades of pink, cream or yellow are found. The crown is dense, not weeping. The bark of this tree was used by the Indians as paper. Variety "Renci" with a triangular crown and golden leaves in autumn.
Himalayan hybrid Jacquemont (Betula utilis var. Jacquemontii). It is distinguished by large leaves and smooth snow-white bark. Varieties: 'Doorenbos', 'Jermyns', 'Silver Shadow' and 'Grayswood Ghost'.
Popular articles Evening necklace for bustier dress
Varieties of the species Betula nigra:
"Little King" is a fast-growing dwarf form of a dense multi-stemmed tree with a wide, rounded crown;
Dwarf decorative birch of the Nana group (Betula nana). These are low bushes or trees, reaching a height of 50 cm to 1 meter. The branches are dark, covered with tiny round, glossy leaves. A magnificent hybrid on a standard with golden “Golden Treasure” foliage. Prefers peat soils.
“Magical Globe” is a new varietal on the trunk, originally from Australia, characterized by a spherical crown and dwarf growth. Feels good in the sun, prefers permeable, dry and rather poor soils.
History of the use of birch bark
In the past, birch bark occupied an important place in people's lives. It was used in the construction of houses to prevent dampness. Thanks to its antiseptic and moisture-repellent properties, it protected the home from rotting and mold.
They made toys, dishes and many other products from birch bark that were used in everyday life and at home. In a peasant hut, all the utensils were made of this material: baskets, tubs, bags, boxes, salt shakers and much more. Birch bark was used to make bast shoes, hats, feet and waders. They also made clothes from it. Children received birch bark toys: rattles, animal figurines, balls, small toy boats from a very early age.
It was also used to create musical instruments: pipes, horns, horns. In addition, birch bark was necessary for writing. Birch bark was the most accessible and cheapest material. To make the hard bark suitable for writing, it was boiled, and then letters were written on it with a sharp bone, and later with a metal rod. Adults wrote letters on birch bark or created scientific works, children learned to write on it, wrote letters, and drew.
Photos of a birch tree are presented below the photo gallery.
Memorable image of a tree
The appearance of the birch is familiar to everyone; a large number of songs, poems, tales have been written about it, and many wonderful paintings have been drawn. This is the most famous tree, the symbol and pride of the Russian people. Very often, the description of a birch leaf becomes the main theme of many literary works.
Birch is always beautiful. Every season of the year makes it delightful and unusual. Everyone knows how beautiful she can be with green earrings, soft braids, silvery dew, and white bark. Very often there is a brief description of birch in school literature.
Numerous fairy tales, poems, and riddles that are passed down from generation to generation can show all the beauty and inimitability of a slender tree. This is probably why the description of birch for children, including in artistic skill, is very important for their spiritual development and education of patriotic feelings, the revelation of humanity, as well as the formation of love for all living things.
Photo gallery
Diseases and pests
Among the pests, trees of this species are particularly dangerous:
- Silkworm caterpillars eat the leaves, leaving only the veins. The caterpillars should be shaken off, and then the tree should be treated with an insecticide.
- May beetle, larvae - eats roots. Digging up the roots will help to eliminate all the larvae.
- The chimney beetle harms leaves and young branches. The affected parts of the plant are removed and burned, after which the trunk circle is dug up and everything is treated with an insecticide.
Birch often develops fungal diseases, for example, wood-destroying tinder fungi. The growths must be removed in a timely manner, and then the treated areas must be sprayed with fungicides.
Where does fluffy birch grow?
This tree grows in the European part of Russia, the Caucasus, Siberia, Transbaikalia and Europe, forming indigenous or together with coniferous and other deciduous forests.
It prefers moister soils and can grow in lowland swamps, watershed areas, forest edges, clearings, and in the mountains. On the plains of the forest-tundra, it forms sparse park birch forests and crooked forests, consisting of only birches or mixed with larch and spruce.
Method of using birch preparations
Decoction of birch leaves (20.0 - 200.0): brew 4 teaspoons of birch leaves per glass of boiling water; when the boiling water has cooled, add 0.2 g of soda to dissolve the insoluble betulorethic acid contained in birch leaves. Infuse well-brewed leaves for 6 hours, similar to infusions. Strain and drink in two doses, four hours apart.
Strong decoction of birch leaves (90.0 - 400.0): take 6 tablespoons of birch leaves in two glasses of boiling water, to take half a glass 4 times a day.
Decoction of birch buds: one teaspoon of birch buds in half a glass of boiling water; consume two tablespoons 3 times a day.
Tincture of birch buds with alcohol - 25.0: leave for 8 days; take 20 drops three times a day.
Tincture of birch buds with vodka: for 1 bottle of vodka, take half a bottle of birch buds, leave for a month; take 40 drops 3-4 times a day (for cholera - one glass each until vomiting stops).
Fresh birch sap is an excellent diuretic. Photo: Learning by doing
Take 3 glasses of fresh birch sap per day (as an anti-inflammatory and diuretic).
External use of birch leaves: ordinary baths - full and sitz, “dry bath” and warm compresses.
A “dry bath” consists of placing fresh birch leaves in a deep tub that replaces a bath, covering it to keep the leaves warm, and then the patient buries himself in them up to his neck or waist and remains in the “dry bath” for about an hour.
Warming compresses lasting one to one and a half hours can also be made from crushed birch leaves. In winter, you can (but with less effect) make the same compresses from dried birch leaves steamed with boiling water.
Class! Send Send
What you need to know about the characteristics of wood
Many types of birch trees are characterized by rapid growth and excellent adaptation to the environment. Wood is almost always easily processed and used on the farm.
Areas of application:
- production of parquet or plywood for renovation;
- creation of skis;
- turning production;
- furniture manufacturing.
Wood does not rot for a long time. You can find items made more than 500 years ago. Previously, trees were considered a symbol of prosperity; people tried to plant birch trees next to their houses.
Birch wood is used to make furniture. Items made from it are expensive and of high quality, but their production is limited.
Physical and mechanical characteristics of wood
Characteristics:
- Density. The material must have a proportional relationship between all parts. That is, if one is dry, the other should be at the limit of hygroscopicity. All types of birch trees used to make furniture have an average density. For later wood, the density is 2 times higher.
- Strength. The most durable is black wood. It resists external damage and has low humidity. Iron, weeping, downy birches have high strength.
- Hardness. On the Brinell scale, birch trees have medium hardness, but are considered wear-resistant. The wood is suitable for making parquet . The hardest is iron birch (82 MPa).
- Weight. The specific gravity of dry wood is 3–5% less than that of wet wood. Moreover, if the birch tree was cut down during the rainy period, the weight of the wood may increase by a third.
- Thermal conductivity. The material does not retain heat well and is susceptible to cracking. Wood is highly valued as lumber, and firewood can produce great heat.
- Humidity. Almost every type of birch is characterized by increased sensitivity to humidity. To prevent deformation of crafts, small products are made from wood. With the help of forced drying it is possible to reduce humidity to 12%.