In our area, it so happened historically that for a long time the main building material for the construction of residential buildings was wood. And it’s not just that the country is rich in forests - it’s just that in the climatic conditions characteristic of most of the territory of Russia, wood was the optimal material for building the warmest houses possible. Add here ease of processing and accessibility - and everything will fall into place.
Today, wooden construction, one might say, is experiencing a rebirth, and this is largely due to the emergence of new technologies for processing natural wood. In particular, we are talking about profiled timber - a material that significantly simplifies the quick and high-quality construction of walls.
Which foundation to choose for a house made of timber
The popularity of this construction technology is growing, since with the relative lightness of the material itself, the simplicity and speed of installation work, the buildings are extremely durable and comfortable to live in. But there is still no escape from the problems of the “zero cycle” - the construction of a foundation for a wooden house must be approached with the same degree of responsibility as for heavier walls.
Therefore, the topic of today’s publication will be the question: what foundation to choose for a house made of timber.
Factors for choosing the type of foundation
The stronger and more reliable the support, the better, but excessive massiveness means extra costs that are not always justified.
Which foundation is best to choose for a house made of timber depends on many factors:
#1.
Weights and building designs.
#2.
The type of soil, its hardness, heaving, stability of behavior when moistened.
#3.
Groundwater level, precipitation, seasonal humidity fluctuations, topography.
#4.
Availability of a basement, availability of materials, economic calculations.
How to waterproof the foundation of a timber house
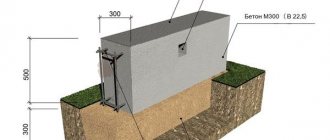
Bikrost TPP or ruberiod are materials for horizontal waterproofing of the foundation of a house. First, TechnoNIKOL No. 01 primer is applied, then roofing material or Bikrost TPP is applied, the edges are cut off. Waterproofing protects against moisture and the formation of cracks due to possible shrinkage of the house. Several rows of bricks are placed on the waterproofing layer.
The most reliable waterproofing is made of TechnoNIKOL weld-on material, fused with a gas torch using a bitumen primer
On the outside the masonry is solid with ventilation holes. Recesses are made inside for the floor joists. They must be at least 60 cm apart. Then the subfloor logs are installed. The ends of the beams are first impregnated with an antiseptic composition, then covered with roofing felt.
Vertical coating waterproofing of foundation surfaces in contact with the ground must be done with hot bitumen in two times or with special bitumen mastic such as AKTERM GidroDef BM, in two times.
How does the base influence the choice of foundation?
Before deciding which foundation to choose for a house made of timber, you should study the properties of the soil at the construction site. Load-bearing capacity, mobility, and heaving are important here. Based on their structure, foundations are divided into several types.
Rocky and clastic soils
Foundations in the form of rock or a dense embankment of solid debris have the highest bearing capacity, and their behavior is practically independent of moisture and groundwater levels. Strip and columnar shallow and non-buried foundations work well on them. In these soils it is very difficult, and often impossible, to build a basement under the house.
Sandy soils
Soils with a high sand content are stable and reliable foundations for a home. The good drainage qualities of sand practically eliminate frost heaving, except in cases of flooding above the freezing level. If the groundwater level is consistently low, any type of foundation can be used. In case of seasonal flooding, the best choice would be a pile or columnar one, with the base buried below the freezing depth.
Clay soils
Clay soil in a dry state has a load-bearing capacity comparable to stone. But its properties change dramatically when moistened. In addition, it has the property of heaving when frozen. If groundwater does not come close to the base of the foundation, and the surface layers are protected from precipitation and flood water, then any foundation on clay is equally effective, provided that measures are taken against frost heaving.
If rising groundwater or floods are possible, it is better to place the house on a monolithic reinforced concrete slab. If at the same time there is dense rock at an accessible depth that can serve as a support, then it is possible to make a pile foundation with a rigid frame that turns the pile field into a single structure.
Correct calculation when choosing the optimal foundation for a house made of timber
Calculation of the foundation support area will depend on the type of soil. The load should not be greater than the maximum value, which is specified in kg/cm2.
Let's consider several ways:
- Pebbles, gravel and crushed stone: medium density - 5 kg per cm2, high density - 6.
- Clay: medium density: from 1 to 3 kg per cm2, high - from 3 to 6.
- Wet sandy soil: medium density - 2 kg per cm2, dense - from 1.5 to 2.5 kg.
- Coarse sand: from 3.5 to 4.5 kg per cm2.
- Medium fraction sand: from 2.5 to 3.5 kg per cm2.
- Fine sand: from 2.5 to 3 kg per cm2.
During the first time after building a house, under the influence of its weight, the soil settles. If this happens unevenly, cracks may appear. Therefore, determining the bearing capacity of the soil depends on the settlement, which should not be greater than the standard specified in SP 45.13330.2017 “EARTH STRUCTURES, FOUNDATIONS AND FOUNDATIONS”.
The depth of the bottom mark of the base of the foundation for a cobblestone house should not be less than the depth of soil freezing.
In what case should one or another type of foundation be used?
There are different types of foundations. Each of them has its own area of greatest effectiveness.
Strip foundation
Structurally, this is the simplest foundation. It is located under all load-bearing walls and looks like a continuous strip. Thanks to its large support area, it has a high load-bearing capacity and can be used under heavy walls and structures.
Based on the depth of the base, strip foundations are divided into non-recessed, recessed and shallow-recessed. Recessed foundations are used under heavy structures and are laid below the soil freezing level to eliminate the effect of frost heaving on the base. A deep strip foundation forms the walls for basements and semi-basements.
For light structures, such as one- or two-story wooden houses, such a design is justified only in the case of a basement or ground floor under the building. A light structure resting on deep layers of soil places too little load on the foundation, which in some cases can cause a loss of stability. The influence of lateral and tangential forces of frost heaving on heaving soils is especially strong.
Shallow foundations are often used in rural housing construction. Under them, trenches up to 0.5 m deep are dug, a cushion of drainage materials is laid in them - coarse and gravelly sand, crushed stone, gravel, it is thoroughly compacted and a stone or concrete support “belt” is placed on top of it. This design is much cheaper both in terms of materials and labor costs. The drainage cushion compensates for vertical frost heaving, and lateral and tangential loads are insignificant due to the small contact area of the side surface with the ground.
Strip foundations are used on any sufficiently stable foundation. They should not be used on weak, heavily watered or flooded soils.
Columnar foundation
A columnar foundation is a series of supporting pillars made of stone, brick or concrete, connected by grillages.
This design allows you to significantly save materials and reduce the amount of excavation work. But due to the technical complexity of the installation of grillages, significant savings are obtained only with a sufficient vertical size of the foundation, at which a large difference in the volume of materials is achieved compared to the strip type. The lower frame of a timber house takes on the function of distributing the load on the pillars. This partially eliminates the problem of grillages and expands the range of economic benefits of columnar supports.
You can build a columnar foundation on clay soils, to the depth of freezing, if you plan to build a house without a foundation. If, due to the properties of the soil, climatic and hydrogeological conditions, the foundation is laid to a greater depth - 1.5 m or more, then the complexity of constructing pillars increases sharply. Here we enter the area of efficiency of pile foundations.
Pile-screw foundation
A screw pile is one of the types of piles used in construction. For private construction, screw piles are best suited because their installation does not require heavy special equipment. Depending on the diameter and depth of immersion, each pile can be installed by 2-3 people or using a compact power unit that can be easily transported to the construction site.
Screw piles hold up well on weak and swampy soils. They are insensitive to frost heaving, and the ease of their immersion allows the structure to be supported on deep, dense layers.
The foundation on screw piles can be used on clay and sandy foundations, in the vicinity of groundwater, in flooded areas, on the shore of a reservoir, on a coastal shallow. The only limitation for them is rocky and coarse soils.
Screw foundation construction technology.
Below are only general recommendations, since the specifics of constructing a house from wooden beams on a specific site cannot be foreseen.
1. Marking the territory.
It is produced in accordance with the project. To what extent it should be cleaned is decided on site, since no special leveling of the area is required before installing the screw base. But it is advisable to remove the turf (by 15 cm). This will prevent the appearance of a “garden/vegetable garden” under the house during its operation.
The disadvantage is the lack of a basement (basement) floor. Consequently, the floor of the first will have to be additionally insulated, otherwise a house made of profiled timber is unlikely to be cozy. You can minimize costs both in terms of thermal insulation and labor costs. It is enough to excavate the soil (within 15 - 20 mm) on a segment along the contour of the foundation and pour a layer of expanded clay. Thermally treated clay granules will not allow the cold coming from the soil to pass through. But you shouldn’t make a traditional “pillow” from ASG. Sand intensively absorbs moisture, and there will always be dampness under the house. This will negatively affect the durability of the timber.
Where are screw piles placed:
- On the corners of a timber house.
- At the junction points of the walls; along the internal installation line.
- In places where the configuration of the foundation changes (relevant for buildings of complex architecture).
- For extensions, porches, verandas and the like.
- If you plan to install a powerful heating boiler, the base for it is mounted separately.
2. Screwing in piles.
Such supports are steel pipes, one end of which, with welded blades, is pointed. You can install the pile alone, although it is better to do this work together. One person twists, the other maintains the vertical direction.
- Pile installation depth.
It should be such that when the soil moves, it does not squeeze it out, that is, below its freezing level. This value can be easily clarified at your local weather service. Typically, products with a cross section of 108 mm are purchased.
- The height of the elevation above the ground.
This depends on the specifics of the site, for example, significant unevenness on it. In addition, the foundation can be built on a slope. There is only one criterion - the pile binding must be oriented strictly horizontally. The standard length of the samples is 1.65 (±0.15) m. If it is necessary to raise one side, it is easy to extend any knee.
3. Connection of piles.
This stage of arranging the foundation for a house made of timber can be neglected if the supporting frame is mounted from metal products - a channel, an I-beam. If timber is used for it, the piles are fastened together. Options are shown in the photo.
Which foundation is best for a house?
It must be installed in any case, otherwise there will be a constant draft under the house, which will affect the microclimate in the rooms on the 1st floor. A specific decision is made depending on what level from the ground the heads are located.
- Shallow trenches are dug between the supports (this is done at the stage of marking the foundation). You can fill them with crushed stone and pour the solution. Lay reinforced concrete beams or timber on top. But this is provided that the house is raised slightly.
- If the pile foundation is significantly elevated, the gap between the support frame and the ground is closed with brickwork (more expensive), boards, multi-layer plywood (FSF), chipboard, OSB and similar materials.
What is the best foundation for a house made of timber?
5. Installation of the support frame.
The photographs show what the result should be.
What is the best foundation for a house made of timber?
Installing this part of the foundation for a house made of metal products will lead to some difficulties in the future. First of all, there will be a problem with attaching the lower crown. From the point of view of ease of arrangement with your own hands, this is not the best choice.
It is much more convenient to tie the piles with timber. Which type of wood should I choose? Taking into account the specifics of use, it is better to purchase larch. It gradually hardens in damp conditions, and such a screw base will last at least 50 years without repair. How to fix the timber on piles? Heads with plates should be welded onto them, in which holes should be drilled in advance. Fixation - as in the photo - from below.
What is the best foundation for a house made of timber?
This is one of the options, and the simplest.
Pros and cons of a pile-screw foundation
After considering the main types of foundation, it would seem that choosing a pile-screw foundation is the most optimal, however, there are both advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages:
- Installation speed - just determine the freezing depth and order a drill, and literally within a day the piles will be installed;
- Simple process - does not require additional time or money;
- Versatility - good performance of this type of foundation was obtained on all types of soil, including peat;
There are only two disadvantages , but they must be taken into account:
- Calculation complexity - the heavier the building and the more complex its shape, the more careful calculations will be required;
- If a geological examination of the soil was not carried out before installing the pile field, then in the case of loose or peaty soil, a certain percentage of subsidence of the structure is possible - unfortunately, often uneven.
Pile field for a wooden house Source art-stroynn.ru
Types and features
The supporting system for a two-story building must be more rigid than for a small building. This is due to the high pressure of the house on the ground, exerted by two floors and a large number of interior partitions.
Photo - project of a strip foundation for a two-story house
There are several types of supports for a private home:
- Strip foundation;
- Columnar;
- Monolithic.
A pile foundation is absolutely not suitable due to its instability. Options on stilts can support a one-story brick house, but a tall two-story building, even made of timber, will be too heavy. Screw piles can be useful when installing a small two-story utility building, but they are not recommended for home construction - it will be difficult to legitimize the construction later.
The columnar one is installed under a regular ribbon one, as in the photo. This helps further strengthen the structure. In most cases, this option is used on moving soils or marshy areas.
Photo - pillar foundation
A strip foundation for a private two-story house is easy to make with your own hands; it is this type of construction that modern craftsmen most often resort to. The tape allows you to ensure correct distribution of loads between walls and nodes, and save a significant amount of money on concreting
When choosing such a design, it is very important to calculate the loads that will be exerted on the supporting system in order to calculate the optimal depth and width of the support and sole
A monolithic slab is the most expensive, but also the most reliable type of foundation for a private building. Despite its high cost, such pouring is often used in individual construction, because with the correct calculation of the size of the foundation, it provides a reliable foundation for the house. The reliability of such a foundation is undeniable; it is believed that even during earth movement (for example, during heaving or small tremors), a correctly calculated monolithic foundation will remain intact.
Photo - example of foundation design
Video: which foundation to choose
Studying the soil on the site.
The type of soil determines the loads that press on the side surface of the foundation. The heaving of the soil determines the increase in loads during the rainy season or during freezing. Increasing the volume of water in the soil increases the pressure on the foundation.
Based on their ability to retain water, soils are divided into:
- Non-heaving (soils containing gravel, medium- and coarse-grained sands);
- Heaving (fine-grained sands with a high content of dust fraction, loamy soils, clayey soils).
The level of groundwater is also of great importance. When the type of soil is determined, we proceed to calculations based on settlement. It should be minimal; the load is calculated based on the weight of the house, taking into account the standard temporary load, which depends on the climatic zone. When determining the weight of a house, the weight of the walls, ceilings and roof are summed up. These values are determined by their overall dimensions, type and materials from which they are made. These calculations should be made by specialists; only they will be able to fully account and analyze all parameters.
Self-production of strip base
Step one
The axes are marked and a trench is dug. Before starting work, the entire construction site is cleared of debris and dirt. The location of the axes is determined by the building theodolite. A trench is dug along certain lines. The work can be done manually or using a mini excavator.
Step two
A sand cushion is being built. Fine sand is poured into the dug trench. It is compacted thoroughly. The sand layer is covered with a 20 cm layer of gravel. The gravel is covered with cement, more than 10 cm thick. Don’t forget to put in reinforcement. Remember that the reinforcement in the middle of the cake is not doing any work. The main load lies on the lower and upper rows of reinforcement. Only reinforcement that has an anti-corrosion coating should be placed in the base.
We advise you to study - How to wash windows correctly and without streaks
Step three
The formwork is being constructed. For construction, you can use a variety of materials:
- boards;
- plastic;
- plywood;
- slate;
- metal.
Boards are attached to the walls of the constructed formwork along the entire perimeter. They play the role of strengthening the entire structure. For additional protection of the walls themselves, they are covered with a thick film. The film is secured with construction staples.
Step four
At the last stage, concrete is poured. The formwork is filled with concrete mortar. To prevent the formation of air bubbles, the surface is pierced in several places with a metal probe. You can also tap the entire surface with a wooden hammer. The hardened foundation must be watered every day. As soon as three weeks have passed, then the construction of the building itself can begin.
Video description
What are the pros and cons of a pile screw foundation? Is it possible to make a high-quality foundation for little money? Watch in this video:
Pile foundation - screw and concrete Source stroy-dom-pravilno.ru
See also: Catalog of wooden house projects presented at the Low-Rise Country exhibition.
Columnar foundation
The lowest financial cost is a columnar foundation, the basis of which is made up of concrete blocks with dimensions of 20x20x40 cm, bricks, asbestos-cement pipes, or concrete poured into the formwork. A sand cushion is installed underneath, and the pillars themselves are placed in those places where, according to the design, the greatest load is provided.
This option is relevant on freezing or heaving soil. The distance between the pillars is 1.2-2 m, the depth of penetration into the soil is 0.5 m, provided that there is a screed on a cement-sand base or a sand cushion 0.2-0.3 m high at the bottom.
The distance between pillars should be no more than 3 m
It is important to correctly calculate the number of supports and place them strictly in a vertical position, which will distribute the load coming from the building and protect the building from deformation, distortions and other defects
Laying and fastening the first row of timber to the foundation
Another important task that must be solved at the stage of creating the foundation is connecting the concrete base with the lower beam (creating a crown). If when building with brick or concrete everything is simple - adhesion is provided by the mortar, then in the case of timber this will not work, other solutions are needed here.
The best way to ensure a reliable connection between the walls and the foundation is with anchor studs. These are threaded metal rods that are placed into the body of the foundation before concrete is poured. After it hardens, you get a flat area with pins protruding from it.
The construction of walls begins with waterproofing. Two layers of roofing felt or other rolled material are laid on the foundation. Holes are drilled in the lower beam according to the diameter of the studs. The wood is impregnated with an antiseptic or bitumen mastic.
The beam is placed on a stud to ensure maximum strength of the connection; a nut and washer are used (you must first make a recess in the wood for them). Subsequent rows are laid in the standard way, with selections made at the corners.
Important! It is at the stage of assembling the lower crown that the shape of the building is set. The bottom beam must lie exactly in a horizontal plane. The slightest deviations must be corrected immediately with the help of slats; the resulting voids are subsequently filled with foam.
Columnar
A fairly simple way to independently mount the foundation for a house, which looks like separate monolithic pillars under load-bearing walls
It is important to ensure that there is a pole in every corner of the house. The materials for such a base can be stone, brick, rubble concrete or concrete blocks.
The pillars are installed on a pre-prepared sand cushion; their depth is relatively shallow. However, such a foundation cannot boast of its reliability. It is advisable to use it for a one-story light building on stable ground. This type of foundation is suitable, for example, for a log bathhouse or a small frame cottage.
Costs and speed of construction
The most inexpensive is a monolithic strip foundation of a shallow or non-buried type. The base does not require a large amount of excavation work, but after pouring the tape, you must wait 25-30 days for the concrete to harden. You can speed up construction by choosing a prefabricated strip foundation. Unlike monolithic, its tape is made from ready-made FBS reinforced concrete blocks, which are connected to each other. The cost of a prefabricated strip base is 20-30% more expensive than a monolithic one due to the purchase of ready-made blocks. It is also worth considering that it is impossible to install FBS yourself, so you will have to hire special vehicles. However, if the construction is carried out by a contractor, the increase in cost will be minimal.
A pile foundation will cost significantly more. Its cost depends on the type of supports used: metal piles will cost 30-80% more than bored piles. The cost of screw supports varies greatly and depends on the number of blades, length, metal and galvanization.
Video description
What are the features of concrete driven piles? We'll talk about pile foundations in our video:
Columnar: brick, block or concrete
Columnar foundations do exist as a separate type of foundation, but it must be noted right away that they cannot be used for the construction of a residential building.
In general, this is an inexpensive and easily erected foundation, which is a hole 50-70 cm deep, at the bottom of which sand and crushed stone cushions are laid, on top of which the pillar itself is built.
The methods for making “pillars” are completely different - bricks, pouring concrete into formwork, asbestos pipes, ready-made blocks. As with any technology that uses concrete, care should be taken to ensure that sand cushions, formwork and reinforcement are installed when making the bases on site.
Columnar foundation poured and made of blocks Source nauka-i-religia.ru
The distance between the pillars, regardless of unevenness, should not be more than 1.5-2 m; in addition, pillars must be present at the corners of the building and at the intersections and junctions of walls. Columnar foundations are installed almost everywhere, with the exception of floating areas (areas completely unsuitable for construction), using special device technologies - for example, TISE, where the pillars “expand” at the bottom, giving additional strength to the structure. But even when using this technology, you should also take care of additional insulation and waterproofing, and this work must be performed together with the construction of the walls (that is, the places where the pillars adjoin the walls are processed together).
Considering that columnar foundations are suitable exclusively for ultra-light buildings - gazebos and the like, it can be argued that they do not have many disadvantages. But in any case, such foundations are not suitable for complex soils - loose, with a large freezing depth.
No specialist would use such a foundation for a residential building. In addition, it is strongly recommended not to experiment with such a foundation when building a house through the efforts of “gray” construction crews, who do not care what they build, because they do not bear warranty obligations.
If the soil is even slightly mobile or susceptible to heaving (and usually it is), then eliminating the consequences will cost a pretty penny.
Incorrect use of a columnar foundation - the work will have to be redone Source stroy-dom-pravilno.ru
See also: Catalog of companies that specialize in foundation repair and design.