The quality of the connection of individual wall elements affects the durability of the house, its reliability and appearance. Wooden buildings were one of the first to be erected by man, and since those ancient times he has known many ways to fasten timber together. They are still used today, along with modern methods that use special fasteners. Having studied all the known methods, you can choose from them those that seem to you the most durable and affordable.
Construction of a house from timber Source brusovoidom44.ru
Key points
When erecting walls, the task of joining arises in two cases: when building up (weaving) material along the length and connecting the corners of the building.
The joining of the timber in the corners is of greatest importance. During its implementation, the reliability of the house, its size, design and quality of the wall are laid down. There are two types of connections: without remainder and with remainder. The latter is based on the fact that the end extends to a set length beyond the corner fastening site. The peculiar wooden insulation of the corner, especially noticeable during windy times, is the main advantage of this method. In addition, thanks to this execution, an original design is created that has its own connoisseurs.
By interweaving without a trace we mean the arrangement of the ends at the same level with the plane of the wall. The main advantage is saving building materials and reducing the size of the building.
For any type of product, the connection rules are general; it can be profiled or laminated timber 150x150, dried or with natural moisture. During the installation of a log house, the same method should not be used. Different structural elements have their own fastening methods. When purchasing materials, it is worth remembering that samples for good insulation must have different sizes, in particular cross-sectional parameters.
Cross Lap Knit
Lap knitting is a universal connection of lumber, used when laying walls made of logs and timber. The workpieces are placed at right angles into cut-out grooves; the size of this groove depends on the size of the material used. Such a lock is used in the construction of log houses and ceilings, the construction of bridges, and the construction of canopies. The main methods of cross fastening:
- Half-tree connection;
- Quarter and third wood joint;
- Notch in one row.
The most widespread cross-shaped connection in half a tree is when cutting corners into a bowl; it is used in the construction of utility structures, residential buildings and baths. The structure is reinforced with building brackets, dowels and dowels.
Length extension
The length of industrially produced timber is determined by GOST 24454-80; of the many sizes of timber, 3- and 6-meter blanks are most in demand. When splicing, the ends of the joined beams are secured in various ways:
- Half-tree connection;
- On the root thorn;
- Straight patch lock;
- Oblique patch lock;
- Oblique cut.
The choice of fastening for the connected beams depends on the tasks at hand. For decking, a straight lock is used; for vertical supports, a half-tree or tenon lock is used; for the construction of 3D structures, oblique locks are used. Locks are reinforced with building brackets, dowels and dowels; bolted fastenings are used for load-bearing supports. In order to maintain the uniformity of the surface texture of the laminated veneer lumber, the length is increased using the toothed connection method or butt joints with a key, and the joints are reinforced with waterproof glue.
The longitudinal installation of timber roof rafters has its own characteristics - it is necessary to take into account the impact of multidirectional loads. For the connection, an oblique cut is used, reinforced with bolted fastening with a diameter of 10-12 mm.
Altitude bonding
When constructing wooden walls and partitions, masonry made from solid timber of natural moisture is reinforced with dowels, staples or “coupling” fastening. The corrugated timber has increased adhesion; reliable adhesion of the crowns is ensured by the tongue-and-groove connection.
The most common construction operation for height bonding is the construction of walls. Dowels with a diameter of 25-30 mm are used as connecting elements; one dowel holds together several crowns. To fix masonry made of corrugated timber, dowels are required 2-3 times less. The dowel connection is reliable and retains its properties throughout the entire period of operation of the structure.
With the help of fastening “on the coupling” they prevent deformation and the formation of cracks when the lumber dries, the screw tie creates an adjustable vertical tension.
- https://horoshidom.ru/postroit-dom/soedinenie-brusa
- https://brusder.ru/montazh/stroitelnyj-brus-sposoby-soedineniya
- https://www.stroikahome.ru/kir/brus-k-brusu.html
- https://m-strana.ru/articles/kak-krepit-brus-mezhdu-soboy/
- https://postroibanu.ru/steny/sposoby-soedineniya-brusa.html
- https://glavstroy365.ru/articles/osnovnye-vidy-kreplenij-brusa-mezhdu-soboj
- https://2proraba.com/stroitelnye-materialy/soedinenie-brusa-mezhdu-soboj.html
4 749
How to do it yourself?
When assembling from finished profiled timber 150x150 or 100x150 mm, it’s easy to make a warm corner with your own hands. If the timber does not have locking grooves, you will have to make the correct cut of the required size according to the template. If the cutting is done with your own hands for the first time, it is done according to a stencil or template so that the dimensions of the grooves are the same.
Those who do not know how to work with an ax will have to file the grooves, guided by the drawings. Before starting work, you should master the technology of connecting timber “groove to groove” in crowns. Before installation, you need to do a little preparation by checking the fasteners and joints. The blanks from which dowels and dowels will be made are treated with an antiseptic and dried.
For the first three crowns, the most even timber without knots or other defects is used, with a geometry ideal for a strip foundation.
In this case, the beam rests with its end against the side surface of another log. In corner joints, metal brackets or pins help, which must be coated with drying oil before use.
A lock connection will be more reliable when a tenon is inserted into the groove. The installation in this case is more durable and airtight. Before this, using templates, grooves and tenons are created at the ends of the beams, which are then used to tie the crowns in the corners. To make the seam more airtight, you need to knit it using insulation, placing it between the logs. In this case, the groove must completely correspond to the tenon so that the masonry, for example, 18x180 mm, is airtight.
First you need to make a wooden template, with the help of which you can then mark the ends of the profiled logs for cutting. A groove and tenon are cut out on each beam using the created stencils. When laying timber, you should use a drawing that will indicate the alternation of the lock segments. Therefore, you need to draw a diagram that will indicate:
- serial numbers of the crown;
- the type of connection used at the ends;
- position of openings in the assembled wall.
Foundation preparation
For building a house, the optimal foundation is considered to be a strip foundation. To arrange it, stones and vegetation are removed, mounds and holes are leveled. When the site is leveled, the territory is marked. After this, a trench is dug, the depth of which depends on the height of the future building and the soil, the width is at least 25 cm. The profiled beam is quite light, so for a one-story building you can use a shallow foundation.
For multi-story construction or construction on unstable soil, the foundation must correspond to the freezing level of the soil. On average, this figure reaches 1.2-1.5 m.
The following materials are needed for the foundation:
- concrete, sand, crushed stone;
- formwork;
- reinforcing rods.
Any house begins with preparing the foundationSource penza-press.ru
The trench is filled with sand and crushed stone, and a mesh is laid with rods to reinforce the foundation. It is recommended to use tying wire rather than welding to connect the rods. The formwork is laid out, and then everything is filled with concrete. To make concrete mortar, cement, sand and crushed stone are used - all components are thoroughly mixed. The ratio of materials is 1:3:4, cement grade is at least 400. The foundation stands for about 2 weeks.
Types of corners in a log house
Corner joints can be “with remainder” or “without remainder”. The difference is in the ends of the timber, which will either extend beyond the frame or not.
Connecting corner beams with the rest is more expensive (material consumption increases). But the heat capacity and protective functions of such an angle are higher. The most used option for fastening timber with the remainder is “in the fat tail”.
Connection without residue
The splicing of timber without any residue is carried out using several types of knots: “into the bowl”, “into the okhop” or “into the okhryap”. The most common option is in a bowl.
Bowls in timber are made on a special bowl cutter or manually using a saw. The specialists have a mobile cup cutter that they can carry out work right on the construction site. The timber is laid one bowl on top of the other. Felt or jute insulation is laid between them.
The connection of the beam “into the clap” is similar to that “into the bowl”, but differs in the location of the drink. The bowl is cut from the top, not the bottom.
If we compare it with the main types, the connection “in the okhryap” is similar to the “in the paw”. Only in this design the end of the beam is removed, thereby forming an angle without a protrusion. The beam is connected to such a corner using dowels and crosscuts. This type of connection does not have high wind resistance, so often a straight cut is replaced with a trapezoidal one.
Any connection must be discussed with specialists, since the choice must be based on the design features. For profiled timber, connections in length are allowed only according to certain parameters, in accordance with GOST 30974-2002 “Connection of corner wooden and log low-rise structures. Dimensions, design and classification."
Any connection breaks the tightness of the walls, so before installation you need to lay a special insulation and treat the joints with antiseptics, since this will be difficult to do in the future, especially with profiled timber.
There are two main types of log frame corners:
- "without a trace"
- "with the remainder."
When starting construction, you should decide what kind of building it will be, what load the foundation and walls will have to bear, and, accordingly, what kind of timber connection in the corners should be chosen in each specific case.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with: Warm floors in the bathhouse - do-it-yourself options
Considering that correctly set corners are the key to the strength and reliability of the entire structure, corresponding requirements are also imposed on them. This:
- Reliability of fastening. The corner of the house, regardless of how it is constructed, should not be made of lumber with cracks and splits. Wood for construction must be taken with a drying level of up to 20%, which ensures its ability to withstand deformation and environmental changes without damaging the structure.
- Air tightness. The absence of cracks that allow drafts to enter the home is the main requirement for wood corner joints.
Connecting corners to build a house made of timber is divided into:
- Angle with remainder.
- Angle without remainder
The corner connections of the house with the remainder are also called “in oblo”. The design of the unit is key, it can be assembled in several types:
- One-sided.
- Two-way.
- Quadrilateral.
Lap knitting is a universal connection of lumber, used when laying walls made of logs and timber. The workpieces are placed at right angles into cut-out grooves; the size of this groove depends on the size of the material used. Such a lock is used in the construction of log houses and ceilings, the construction of bridges, and the construction of canopies. The main methods of cross fastening:
- Half-tree connection;
- Quarter and third wood joint;
- Notch in one row.
The most widespread cross-shaped connection in half a tree is when cutting corners into a bowl; it is used in the construction of utility structures, residential buildings and baths. The structure is reinforced with building brackets, dowels and dowels.
A variation of the cross-shaped connection is the method of fastening the beams together without any residue; in this case, the two sides of the cross-shaped connection have no continuation. This connection is used when laying corners and is called “no residue in the paw.” Cutting a castle without leaving any residue does not require the use of special tools; the construction of a log house using this method is popular among individual developers.
A more complex method of corner mounting is dovetail installation; a dovetail lock is a reliable but complex fastening. Marking and complex cutting of such a connection requires professional skills; the technology is widely used in the construction of low-rise economy class housing.
Laying the first row
Frame of a wooden house made of timber.
For a log house, it is necessary to select only whole, even beams without visible defects. The first crown should consist of the strongest timber cut from the core of the tree. This can be determined by the density and location of the rings on the cut
It is very important that the wood is dry and light - beams with dark spots or gray sections are not suitable for a log house
During the installation process the following materials and tools will be needed:
- roofing felt;
- liquid bitumen mixture;
- antiseptic;
- wooden dowels;
- plane;
- drill;
- hammer;
- hacksaw.
The surface of the foundation strip is covered with liquid bitumen, on which roofing felt is laid. Such waterproofing reliably protects a timber house from moisture penetration from the foundation and extends its service life several times. The width of the roofing material should be 20-30 cm greater than the width of the foundation, so that its edges hang the same distance on both sides. At the joints, the material is overlapped by 7-10 cm, thickly coated with bitumen and pressed firmly.
Beam fastening.
When assembling the first row, you need to decide on the type of corner joints. The most economical option is a “half-tree” connection, when the upper part of the lower beam is cut out, and the lower part of the upper beam is cut out. With this method of fastening, less material is consumed; the ends of the beams do not extend beyond the corners of the building. Before assembly begins, all wooden elements must be treated with an antiseptic and dried, and then holes for the dowels are drilled. These holes should be located along the beam every one and a half meters.
After processing the building material, they begin laying the first crown. First, the first 2 beams are laid on the foundation from two opposite sides, then 2 more with cut grooves at the ends are lowered on top of them at right angles. The corners are adjusted tightly with a sledgehammer and the entire row is leveled; protruding areas should be corrected with a plane.
The main advantages of a log house
Many houses made of wood have a problem with cold corners. This is due to poor thermal insulation. It is quite difficult to eliminate this phenomenon during operation, so insulation should be taken care of at the time of construction. The warm corner of a log house can be done in several ways. The basic principle of connecting a corner is the absence of any additional fastening elements.
The design itself involves reducing the contact of the surface of the timber with the environment. How to do all this with your own hands will be discussed below.
The simplest and fastest way is to install a warm corner made of timber using profiled materials.
The advantages of this design include:
- Strength - if all the necessary conditions during construction are met correctly, then the stability of the house will be at a high level;
- Low costs – this applies not only to finances, but also to labor. The absence of fastening elements simplifies the assembly process;
- Speed - the technology for making warm corners from timber is simple and high-quality construction does not require a lot of time;
- Thermal insulation - the main property of a log house is considered to be heat preservation; if you compare it with insulation materials (mineral wool, polystyrene foam), then with the same wall thickness a wooden house will be warmer;
- Exterior – a house built from profiled timber looks very organic and does not require additional processing or insulation from the outside.
Material selection
Shrinkage is a proportional decrease in the linear dimensions of a beam under the influence of mechanical loads (primarily weight) and due to uniform loss of moisture.
And warping is the shrinkage that distorts the geometry of parts. It happens due to uneven drying, without regard to mechanical loads.
Shrinkage is standardized for different types of wood and different types of lumber. And warping is an unacceptable defect for high-quality commercial wood. Raw wood can be dried properly without warping. But seasoned wood, if stored incorrectly, can seriously fail the builder.
Considering all of the above, it is easy to conclude that a good house can be built from the following types of timber:
- Wild or wild wood. That is, from wood that had lain on the stock exchange for an indefinite period of time before sawing. This material is the cheapest, its humidity is not standardized, and its shrinkage is 10%. And we must keep in mind that if storage conditions are poor after purchase, it is not guaranteed against cracking and warping.
- Edged, seasoned. This one goes into sawing after being brought to air dryness (20%). Moreover, it is not much more expensive than wild timber, if we are talking about regions with a developed timber industry and active logging. However, its shrinkage is only 7%, its tendency to crack is normalized, and warping is not allowed under adequate storage conditions.
- Seasoned profiled. The properties of this material are almost the same as those of seasoned edged timber. But it is much more convenient to use. It is the most popular type of construction timber today, although it is more expensive than those described above.
- Glued. This timber is glued and pressed from individual lamella boards, pre-seasoned and impregnated. It can be profiled (more expensive) and seasoned (cheaper). In all technical and operational parameters it is superior to the above types of building timber and has only one drawback (for some it may be significant): the adhesive seams on such material are noticeable, and it becomes obvious that the house is not built entirely from natural wood.
- Rusk. That is, made from crackers - high-quality dead wood. The shrinkage of this building material is 0%. Cracking, warping and the formation of rot are also completely eliminated. However, cracked timber is very expensive, since the industrial production of cracked timber (that is, cutting the bark at the butt of a living trunk) is prohibited by law in all civilized countries. And Russia is no exception. The method is considered barbaric, and its use is criminally punishable and punishable under the relevant article of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation.
Half swallowtail
With this connection, the tenon is sawed down into a cone. The characteristics of the half dovetail connection do not differ from the knot described earlier. But the strength indicator increases. The conical cut securely holds the beams and prevents them from moving apart. This connection is used in the construction of walls with a length greater than the length of the beam.
There is no difference in the complexity of manufacturing when joining a half dovetail and a straight tenon. Both methods are performed with or without a template. For an experienced professional, the difference in the labor intensity of making these joints is almost imperceptible.
The half dovetail tenon should not be more than 5cm at its widest point. Otherwise, a crack will appear in the timber with the groove. This happens due to uneven shrinkage. The picture shows this place.
Video description
This video shows how to make a groove on the end of a beam using a template and a chainsaw:
If the structure of spliced beams does not require the formation of smooth edges, they can be overlapped, tightened with nails on both sides or metal pins at several points. This is often done when you need to lengthen the rafters. Or get powerful logs or floor beams by merging two beams not only in length, but also in thickness. In such cases, before joining the timber, the joints must be shifted relative to each other.
T-shaped types of connections between timber and logs
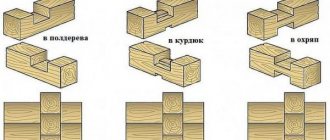
The connection with the remainder has three types of felling:
- In the oblo "in the bowl"
- In the heat of the moment
- In a huff.
Corner joints of logs “in the oblo” are done as follows:
- Half a tree
- Oval ridge
- In the fat tail.
Half a tree - easy to connect. To achieve stability of fastening, a longitudinal groove is made in the crown. We pre-fill the groove with insulation.
An oval ridge is a fastening with a remainder; here a small oval ridge is made on the bottom of the bowl; it is important that it exactly follows the shape of the laying groove. In this option, the longitudinal groove is cut not from the top but from the bottom of the log. Fat tail - more technically complex
A small protrusion (tail fat) is cut out at the bottom of the bowl, which is placed along the crown and across the bowl. In turn, a recess is cut out on the lower part, which coincides in shape with the protrusion (see picture:)
The fat tail is more technically complex. A small protrusion (tail fat) is cut out at the bottom of the bowl, which is placed along the crown and across the bowl. In turn, a recess is cut out on the lower part, which coincides in shape with the protrusion (see picture:)
In the oblo - this type of connection is almost the same as what we described above (“in the oblo”). The only difference is that the bowl is cut from above, and not on the lower part of the crown. The name oklop appeared because of the characteristic clap when rolling a log into a prepared corner.
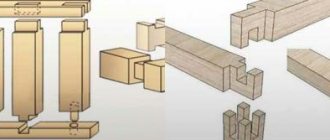
In addition to reliable tying of the corners of a wooden building, it is very important to ensure high-quality longitudinal joining of the beams or logs that make up the crowns. For timber, extensions are most often used using a direct or overlay lock. To further strengthen the overhead joint, vertical dowels or dowels are used
To further strengthen the overhead joint, vertical dowels or dowels are used.
In addition, it is convenient to make a longitudinal connection of the crowns “in half a tree”, cutting off part of the end of the connected beams. To increase the rigidity of the joint in the contact area, you need to install two dowel pins.
The connection with a root tenon is also quite acceptable for the longitudinal extension of beams.
The combined “half-tree” joint, on the upper protrusion of which is made of a “dovetail,” is well resistant to the longitudinal tensile forces that arise during the shrinkage of wooden crowns.
If such cutting seems too complicated to you, then make a longitudinal connection of the crowns with an ordinary dovetail, which reliably fixes the timber being built up and the log.
1. Key groove on the main tenon
2. Straight groove on the main tenon
3. The already familiar “dovetail”
Openings for doors and windows
The formation of a doorway begins with the 2nd crown, the height to the window is at least 70 cm. The formation of openings can be carried out in two ways. “Rough” opening in preparation for creating the opening. The opening itself is prepared for installation after the timber shrinks. The assembly of the structure is accelerated; beams are installed in the openings to secure the walls.
Openings can be arranged during the construction of walls. Source krsk.au.ru
In the second option, they immediately prepare for installation, installing decks that connect the beams and act as slopes. If metal-plastic windows are installed, then decks may not be installed. A vertical groove is made at the ends along the opening into which the rail is inserted. The slats/blocks are made 5-7 cm smaller than the opening so that it does not interfere with shrinkage.
Installation of windows and doors with a “rough” opening is carried out by cutting it to the appropriate dimensions. The joints are sealed using insulation; it must be nailed at an angle. Then the window frame is inserted, fixed to the deck with self-tapping screws, there is a gap on top for shrinkage, it is filled with soft insulation.
When installing a window frame, be sure to leave gaps for shrinkage. Source patter.ru
Longitudinal connection
Such options are typical if the wall of the house has a non-standard length. The maximum length of laminated veneer lumber can reach 18 meters. But still, a situation is possible in which individual beams will need to be connected to each other along their length.
There are several types of joints in length:
- half-tree connection. half the thickness of both parts of the beam is cut off at a right angle. Additionally, you can strengthen the connection with screws.
- connection with a key. the connection itself can be made in half a tree, but dowels are pre-made and holes of slightly smaller diameter are drilled. The depth of insertion of the keys into the beams should be at least 2 cm and no more than 1/5 of the height.
- connection with the main tenon. a rather labor-intensive connection that requires great precision and serious carpentry skills.
- connection with an oblique lock. the most suitable connection when it comes to bending loads. Moreover, such a connection is quite simple to make.
- connection to a rim lock. The connection is quite complex in execution, which requires a difference in the plane of the connection to form a lock. in this case, the lock is cut out in both parts of the wood
To obtain large parts, you must use one of the following connection methods:
- longitudinal connection using a key and tenon;
- oblique lock;
- longitudinal connection of the timber to each other by the root tenon;
- butt connection;
- half-tree connection.
Type of longitudinal connection “half-tree”
General view of the connection. Connection elements.
This type of connection of wooden elements when constructing buildings from timber involves sawing out a corner in the timber to the middle of its cross section.
One part should have a bittern with a downward angle, and the second one should have an upward angle.
After the preparatory procedures, the wooden elements should be laid on top of each other. The most important disadvantage of this type of connection is that in the places of splicing, the wooden beam significantly loses its thickness, which means its performance indicators drop.
This method is the simplest. After splicing the timber, it should be additionally fastened with wooden dowels.
Type of longitudinal connection “oblique lock”
General view of the connection. Connection elements.
Experts call this splicing method the most difficult, but this design is very reliable.
It is necessary to cut out oblique elements from the ends of the wooden part. In this case, a certain angle must be maintained, the necessary bends must be repeated, and the dimensions must be fully consistent.
The result should be some kind of tongue and groove, which ultimately form an oblique lock. After this, the two beams must be connected by applying the treated areas to each other.
To achieve maximum reliability and strength of the connection, special wooden dowels are used.
Butt connections are made:
- root thorn;
- dowels.
Type of longitudinal connection with main tenon
General view of the connection. Connection elements.
The knot consists of a sawn tenon on one end of the beam, and a groove on the other. Connecting the root tenon is simple. During installation, insulation made of jute or felt is placed in the cut. When cutting out elements, you need to be precise, since the root tenon connection must be tight and airtight. This is the only way to avoid large heat losses.
Type of longitudinal connection with dowels
General view of the connection. Connection elements.
The principle of connecting timber:
Absolutely identical grooves must be made in two elements. After this, the processed parts are placed next to each other so that the grooves touch and a key is driven into this groove.
The key is an insert element, a kind of wedge, which is made of hard wood. For wooden beams, you should use an aspen piece. After falling into the prepared grooves, this element securely fastens the two beams to each other.
Keys can differ in geometric shape and be:
- straight;
- rectangular;
- with serrations;
- prismatic;
- in the shape of a dovetail.
Connection fastener
With the advent of modern fasteners made of durable alloy and galvanized steel, many construction processes have been simplified, including the installation of reliable connecting units in timber structures. Some of them have been used for a long time and are traditionally popular. Others appeared relatively recently, so they may be unknown to people whose profession and interests are not related to construction.
Traditional fasteners
The simplest and most reliable of them are dowels or dowels made of hard wood. They blend perfectly with the base material without causing it to deform, crack or rot. In combination with adhesives, they allow for durable fastening.
Assembling a log house on steel dowels Source remontik.org
Pins are also metal. Their main advantage is their high strength and durability, which is why they are often used to fasten timber crowns vertically.
Nails and staples, which used to be almost the only types of fasteners for wood, are now trying not to be used in the construction of permanent buildings, since the ferrous metal from which they are made is incompatible with wood. It corrodes easily, damaging the wood and gradually deteriorating. For the same reason, it is not recommended to use homemade dowels cut from reinforcing bars.
Modern fasteners
A wide variety of fasteners are made from perforated rolled steel with a thickness of at least 2 mm with an anti-corrosion coating. It is made from:
- plates of different lengths and widths with holes for screws and anchors. A large assortment of standard sizes allows you to solve problems such as connecting beams together along a length of 150 by 150, fastening rafters at the ridge part, or strengthening a sagging joint without lower support;
Galvanized connecting plate Source www.sibwindows.ru
Techniques for connecting corners from timber
In carpentry, there are several ways to make a corner connection; let’s look at those that can be used in building a house.
Straight tenon
This type of corner connection is well suited for small structures
It is important that more than one timber is not used per length of the building.
Having fulfilled this simple condition, you don’t have to worry about the reliability of the building; it can easily withstand any cataclysm, even an earthquake. With this connection method, the load is distributed evenly between all elements, so the weakened part of the beam will not be exposed to danger.
An important rule to follow is the ratio of the stud parameters. Its thickness and length should be in proportion 1 to 2 in relation to the main part of the beam.
Half swallowtail
If the house is long enough and it is not possible to use one beam to cover the entire length, a warm corner fastening method called half dovetail is used. Due to this, you can achieve greater strength of the entire house.
For a corner connection, part of one beam is sawed into a reverse cone, and an identical cut is made in the second. For a more precise fit of the tenon and mortise, use the same template. In terms of complexity of execution, this connection of timber into a warm corner is not much different from a straight tenon.
Corner tenon
This is an original, but not very effective way to connect a warm corner made of timber. Its disadvantage is its low strength. Although its tightness is still highly reliable. The manufacturing process is somewhat different from those listed above; the bevel should be cut using a chisel, or you can cut it out with a hacksaw.
This type of corner connection of bars is perfect for a bathhouse or a small shed, and other structures that do not carry a large load.
Half-tree connection
It is also called a claw joint; the peculiarity of this joint is that it is suitable only for the lower or upper layer of timber. This is due to the fact that a small gap is formed in this corner, which is provided by the technology.
Builders of log houses do not refuse to use this joint for the corners of the house. Due to its reliability and increased strength, the lower layer stands much stronger, and the upper one finally holds the entire structure together.
Important tips to keep the corner of a timber house warm, regardless of the connection method:
- A gap of no more than 5 mm should be left in the joint in order to use it for caulking;
- It is necessary to re-caulk the seams after 4-6 years; this should be done due to the fact that over time the wood shrinks, and the gaps in the joints may increase and begin to let air through;
- If the structure does not have architectural value, then for greater reliability the corners can be covered with thermal insulation film, this will help retain heat.
- By following the rules listed in this article, you can ensure that the corners of your log house will always be warm.
Basic information
One of the most proven methods of connecting two parts is considered to be a tongue-and-groove connection. This method of fastening wood products is the most widespread. It is used to fasten parts of window frames, doorways, various furniture elements, and the walls of wooden boxes. Each element of such products has a specially made tenon (or several pieces) or a groove (several grooves).
The types of main connections of parts made of wood are defined in GOST 9330-76. This document defines the following characteristics of such fastening of wooden parts:
- rules for abbreviation (abbreviation) of various compounds;
- drawings showing the appearance;
- permissible dimensions of each element;
- the procedure and rules for determining the size of each element;
- expressions for calculating the dimensions of the required cutting tool;
- formula for calculating the strength of assembled elements;
- inspection procedure and strength testing.
GOST 9330-76 Basic connections of parts made of wood and wood materials. Types and sizes
1 file 285.82 KB
According to this standard, all connections are divided into the following categories:
- corner (end and middle);
- box (mainly belongs to the corner category);
- along the edge;
- the so-called “on the mustache” length.
For each of these categories, the standard has its own abbreviation (short designation). This marking consists of two capital letters of the Cyrillic alphabet and one number. For example, UK-2 means that we are talking about a connection with a double open end-to-end tenon, UK-9 is a “mental” connection with a plug-in non-through round tenon. The entire list is set out in more detail in the text of the adopted standard.
Any type is accompanied by a detailed drawing. Each of them shows frontal and profile projections indicating dimensions, formulas for calculating each element, and finished results. To obtain a strong connection, the standard defines tolerances that must be observed in the manufacture of each element. The parameters of the corner tenon (its length, pitch and bluntness) are given in detail. Based on the results presented, the guest developed recommendations for choosing the necessary cutting tools. Separate references are made to other documents (standards) that determine by what means each of the listed products must be secured.
Types of finger joints
Today, a wide variety of such methods for fastening wooden parts has been developed. All types of tenon joints are classified according to the following criteria:
- number of spines;
- their form;
- eye depth (through or not);
According to the first sign, tenon joints are: single, double, multiple. It determines the number of fasteners produced. The main forms of the spike are:
- rectangular (has different lengths, pitch and apex angle);
- round;
- triangular;
- so-called “dovetail” (one-sided or two-sided);
- gear (with different angles of inclination);
- angular.
The choice of shape and size depends on the material used and the level of load that the entire structure must withstand. A tenon joint with many rectangular tenons has become widespread. Its main advantage is considered to be ease of manufacture and the ability to use it for any wood.
Cross Lap Knit
Lap knitting is a universal connection of lumber, used when laying walls made of logs and timber. The workpieces are placed at right angles into cut-out grooves; the size of this groove depends on the size of the material used. Such a lock is used in the construction of log houses and ceilings, the construction of bridges, and the construction of canopies. The main methods of cross fastening:
- Half-tree connection;
- Quarter and third wood joint;
- Notch in one row.
The most widespread cross-shaped connection in half a tree is when cutting corners into a bowl; it is used in the construction of utility structures, residential buildings and baths. The structure is reinforced with building brackets, dowels and dowels.
Fastening with liquid nails
Using glue, the timber is laid on a cement screed; such floors are made in production workshops, shopping centers and warehouses for large-sized products. The reliable floor allows the use of electric cars and forklifts. In concert halls and entertainment centers, natural parquet is laid on timber floors - this is the best option for flooring in places with large crowds of people.
The choice of glue depends on the volume of work, the size of the wood and the characteristics of the mating surfaces. The affordable adhesives “Liquid Nails” and “Moment Joiner” are popular; for small volumes of work, polyurethane foam is used. Eco-friendly glue is used in residential and public buildings.
The most important operation is the preparation of the mating surfaces; the concrete screed is pre-primed - this operation will prevent excessive absorption of the glue into the porous structure and ensure a reliable connection with the glue. The surfaces to be bonded are cleaned of dust and degreased. The timing of complete polymerization of the glue is indicated in the instructions for use.
Designers believe that when decorating an interior with natural wood, it is better to choose liquid nails than to use a drilling and slotting tool.
Subsidiary variations of cutting timber into a bowl
Cutting profiled timber into a bowl, as shown in the photo, has always attracted attention due to its simplicity and relatively low labor costs. Although, if you do not make auxiliary locking elements, it will hardly retain heat. If you decide to build a summer bathhouse, then this is not a problem. If it is necessary to ensure the safety of heat for a warmer structure, then the cutting of timber walls should also be supplemented with a cut. In this case, the cutting method becomes somewhat more complicated, although heating technology will improve its parameters.
The most popular variations of chopping into a bowl are:
- chopping in the cold or, in other words, in the cold;
- bowl with ledge;
- chopping in the okhryap;
- clap with a cut;
- tail cutting.