Ordinary timber is a high-quality and breathable material. But it has a number of disadvantages that increase construction time. Solid wood takes a long time to dry and can become deformed.
To avoid these and other disadvantages, glued laminated timber is used. But will it be warm enough, will it be necessary to insulate a house made of laminated veneer lumber from the outside during its operation, or is it better to do this in advance?
Is a house made of laminated veneer lumber cold?
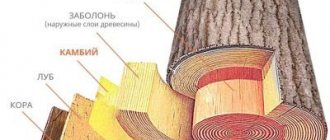
To understand this issue, you need to understand what the building material is. Glued laminated timber is a wooden product that looks like regular timber. It is made from wood material: cuttings from sawing a trunk, other beams. The raw materials are compacted and packed into lamellas (boards), which are dried and glued together into a solid beam.
Only high-quality raw materials are added to the finished product: without wane, rot, large knots and other wood defects. The result is a fairly durable and dry material. It is not inferior to ordinary timber in terms of thermal conductivity, and in some places even surpasses it. There are two types of laminated veneer lumber:
- Ordinary . Inexpensive material, without insulation.
- With insulation . A layer of insulation is laid between the lamellas. Quite an expensive product.
The first option retains heat well in the house, if construction technologies were not violated during the construction of the walls of the house. But it may require additional insulation from the outside. Building materials of the second type are installed as is. No additional insulation. Houses made from such laminated veneer lumber do not cool down and retain heat no worse than solid wood.
Regular timber is produced in sizes from 100 to 180 mm. The glued product can reach a height of 300 mm (for load-bearing walls of a house). On sale you can find laminated veneer lumber with insulation up to 270 mm thick. A house wall made of such building materials will retain heat much better.
Be careful when choosing building materials. Small businesses can skimp and add wood waste to the finished product. Check the structure of the tree and its geometry. The color of the timber should be almost uniform, without gray or dark inserts. The geometry is smooth, without twisting or chipping.
Manufacturing process of multi-layer wood products
At the first stage, the workpiece is cut into boards (lamellas). The resulting lamellas are then dried in a special chamber in which the humidity level is strictly controlled, usually from 8% to 12%.
After drying, the boards are carefully planed and sorted by strength. At the next stage, the rejected areas are marked and trimmed. Knots, uneven edges and cracks are considered defective.
The ends of the lamellas are milled with a toothed profile and glued together under a press to the required length. To glue the lamellas together, a thin layer of glue is applied along the plane. After applying a layer of glue, the boards are assembled in the form of a package, which is a blank of the required cross-section, and are pressed.
At the last stage, the finished glued product is profiled.
Glued wood production machine
Is this house ventilated?
In this case, we are talking about fistulas that can occur on a regular beam. The geometry of the tree changes over time. This happens due to two things:
- Shrinkage . Even a dry rounded log shrinks within 10-15%. Glued laminated timber will settle by a maximum of 1% per year. Its geometry will remain virtually unchanged.
- Bridges of cold. An ordinary beam has a flat surface, without grooves. Air easily passes through such a gap. The glued product has grooves. You can buy laminated timber with a “comb” to avoid direct cold bridges.
Glued laminated timber is fitted together like construction blocks. They fit tightly and do not shrink. All this minimizes the formation of cracks and drafts in the house.
Substances based on melanin or polyurethane are used as an adhesive base. It does not emit caustic fumes. “Chemistry” is not blown out of it, as some inexperienced experts believe.
Properties
The wood of different types of poplars has very similar properties and usually does not differ between types. The exception is aspen, which has no core and a slightly higher density. Poplar wood is generally very soft and, with its density ranging from 400 to 500 kg/m³ with a humidity of 12 to 15%, is one of the lightest domestic hardwoods and has correspondingly low absolute strength values. In terms of weight, however, the strength of poplar is comparable to other types of wood. This wood is resistant to cracking and is easy to chip compared to other hardwoods. Due to the surface compaction of wood fibers during friction, its wear resistance is quite high.
Aspen wood is weakly resistant to precipitation and under water. When fresh it has a high moisture content. In black and balsam poplars, the moisture content of the core is noticeably higher than in the sapwood; in white poplars it is approximately equal, which must be taken into account when drying. This wood dries slowly and is not prone to cracking or warping during the process.
It can be processed well with a sharp tool; it can be sawed, milled, peeled and cut. Fresh wood is easier to process than dry wood because the fibrous sawdust causes severe drift and heat in the saws. It is more difficult to achieve a smooth surface on wood with wide growth rings. Gluing is not difficult, connection with nails is satisfactory. The surface is easy to process, it can be stained well, but it is difficult to polish.
What is the thermal conductivity of wood compared to other materials?
It is worth making accurate calculations of the material in advance. Find out what kind of timber will be needed for a building in a given region, calculate the exact size of the walls of the house that need to be erected for year-round use.
Thermal calculation of walls
Accurate calculations are carried out at the design stage. You need to know all the introductory information in advance to make your house warm without throwing away a lot of money on heating. Thermal engineering calculation is carried out according to the formula:
R=a x GSOP+b
Where:
- R – heat transfer resistance coefficient;
- a, b – additional coefficients (Table 3 SP);
- GSOP is the product of the differences in degrees (inside the house and outside) and the days on which the room needs to be heated (SNiP 23-01 of 1999).
Let's look at an example. Let's take the city of Kazan. From SNiP we take the GSOP value for 215 days of heating, with an average temperature of -5.2 outside and +18 inside the house. We get GSOP=215x[18-(5,2)]=4988. The coefficients “a” and “b” for Kazan are equal to 0.00035 and - 1.4, respectively. Let's put it into the formula:
4988x0.00035+1.4=3.146 m2*S/W
The thermal conductivity coefficient cannot be directly related to the thickness of the walls of the house. You can find out the thickness of a building material through the heat transfer resistance coefficient.
Knowing the parameter R, you can calculate the thickness of the wall of a house made of laminated veneer lumber. To do this, you need to multiply R by the thermal conductivity coefficient of the laminated timber. The latter is equal to 0.1 W/m*S. For our example, we get a house wall of approximately 310 mm (0.35 m).
Let's look at the summary table for different regions of Russia:
| Region of residence | Recommended thermal resistance of walls | Recommended thickness of laminated timber walls |
| Stavropol region, Astrakhan | 2.1 m2*S/W | 210 mm |
| Moscow, Krasnoyarsk, Altai | 3.5 m2*S/W | 350 mm |
| Kamchatka, Khabarovsk | 4.9 m2*S/W | 490 mm |
| Yakutsk, Vorkuta | 5.6 m2*S/W | 560 mm |
If you doubt your own calculations, it is better to seek help from professionals.
What wall thickness is needed for year-round living?
The recommended wall thickness is an indicator that is tied to ideal conditions. In practice, things may be different. Heat retention is also influenced by: climate, presence of winds, location of the building, landscape.
All these factors can become additional conditions for heat loss. We offer another table, which is compiled taking into account certain climatic conditions. It indicates the most popular models of timber, as well as places of its application, taking into account year-round use.
Selection of cross-section of laminated veneer lumber depending on the geographical location:
| Material thickness | Usage | Regions |
| 240 mm | Year-round, minimal heating | Frosty and windy |
| 200 mm | Year-round, medium heating | Any with a temperate climate |
| 160-168 mm | Seasonal or year-round, subject to good heating | Any with a warm climate |
It is worth considering that only 33% of the heat escapes through the walls of the house. The main losses occur through: doors and openings (27%), basements and attics (21%), ventilation (19%).
Aspen combustion temperature, thermal conductivity
Like a number of other species of coniferous and deciduous trees, as raw materials for isothermal processes accompanied by the release of heat. In this regard, such an indicator as the calorific value of this tree is of particular importance.
In accordance with this criterion, defined as the amount of heat released by one weight unit of wood material during combustion, aspen can be classified as a low-heat species. That is, the amount of heat generated by it will be very small.
The burning temperature of aspen is 612 degrees. Firewood from this tree burns quite quickly, without the formation of charcoal residue. Because of this, they are not very well suited for heating purposes, since with their use it is impossible to maintain a constant operating temperature in the firebox.
However, such firewood is well suited for burning off soot and cleaning the chimney after using raw materials from softwood, which emit a large amount of soot and pollution.
The characteristics of aspen wood as a source of thermal energy are given in the following table:
It is also worth noting that, compared to other tree species, aspen has a high ability to absorb moisture. Its hygroscopicity limit is 21.8 - 22.9%.
Despite its obvious shortcomings, aspen wood also has a number of positive qualities that deserve a rating of “five points” on a five-point rating scale. Namely:
- Decorative. Thanks to its pleasant silvery hue, it has been used by craftsmen since ancient times to cover the roofs of temples.
- Ease of use. Many products, including dishes, are made from soft and pliable aspen.
- Lack of resin. Because of this, it is often used to make baths.
- Environmental friendliness and safety for humans.
In what cases is it necessary to insulate a house made of laminated veneer lumber?
Glued laminated timber is warmer than solid wood or rounded logs. However, it also needs and can be insulated in a number of cases :
- When the building has already been erected. The house is very cold in the winter season. Heating is expensive and does not always save. Insulating the outside of the house would be an excellent option.
- With high heating costs. In this case, it may be enough to keep you warm. But the costs of even minimal heating will be too high. For example, when there is no gas main nearby, but an electric boiler is working. It makes sense to install insulation outside.
- When designing. Glued laminated timber is an expensive material. It may be easier to make the external wall of the house with insulation, rather than overpay for another layer of timber.
- When installing a ventilated facade. Additional insulation from the outside will not be superfluous, especially since the insulation will be hidden behind the external cladding.
It is up to the owners of the house to insulate the house or not. In any case, it is worth thinking about insulation at the beginning of construction.
Appearance
Aspen plywood
The wood of poplars is loose, has a light, whitish, reddish-brown to brownish color. The fibers are formed very evenly all year round, early and late growth are similar, so the wood looks uniform. However, the growth rings are clearly distinguishable, since the late wood forms a narrow, denser strip at the border of the growth ring. In poplars, sapwood and heartwood are clearly separated, with the exception of aspen, which is classified as a sapwood tree species. The kernel of black poplar and its hybrids in the fresh state has a color from light brown to greenish-brown; when dried, it becomes slightly red-brown and is equal in color to sapwood. The wood of aspen is off-white or yellowish-white, the heartwood of white poplar and gray poplar is dark, reddish-yellow to yellowish-brown. The sapwood of these species is whitish and similar to aspen wood.
How to choose thermal insulation for insulation
There are several options available on the thermal insulation market:
- Styrofoam.
- Expanded polystyrene.
- Polyurethane foam.
- Mineral wool slabs.
The first three are cheaper than mineral wool. They do not allow moisture to pass through, do not hold water, burn and do not breathe (they are not suitable for insulating the outside of a house made of laminated veneer lumber, or any other wooden house). The mineral plate easily absorbs liquid and condensate, does not burn, and allows air to pass through. For insulating the outside of houses made of timber, the latter option is preferable, since synthetic heat insulators do not allow the house to breathe.
Install wind and waterproofing to prevent mineral mats from absorbing moisture.
Usage
Material
To this day, poplar and aspen wood, due to its wear resistance, good workability and relatively low weight, is used, along with abacha, for the manufacture of prosthetics. However, wooden dentures are increasingly being replaced by artificial materials.
Wooden shoes are made in the Netherlands mainly from aspen
This wood comes to the market in the form of shavings and lumber, and is increasingly being recycled for energy (as a renewable fuel in thermal power plants).
In Germany, about 40% of aspen and poplar wood is processed into chipboard in various forms. The largest consumer of rotary-cut aspen veneer is the match industry, and rotary-cut veneer is also used for the production of plywood, glued blocks for bent parts, baskets for fruits and vegetables, and gift packaging. Sliced veneer is also made from this wood.
About a quarter of the wood produced in Germany is processed into sawn timber. It is used in the shoe industry, as well as for couches and benches in bathhouses. Pallets and boxes are also made from this wood.
Aspen is used to make charcoal, which is used for painting and in the chemical industry; the same wood is used to make drawing boards, household appliances, toothpicks and snow shovels. This tree is suitable for fiberboard and pulp and paper production.
Fuel
The calorific value of aspen, amounting to 19.8 MJ/kg, lies between spruce and beech, but due to its low density, the energy output per unit volume is less than that of other types of fuel wood.
Along with willows, poplars, as fast-growing trees, are the most important species for short-cycle forestry.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of insulating the outside of a house using laminated veneer lumber?
Insulating the outside of your home has more pros than cons. So let's start with them:
- Insulating your home allows you to save on building materials.
- Insulating your home reduces heating costs.
- Less thickness of the walls of the house due to better thermal conductivity of the insulation.
There are only two global disadvantages:
- Additional cladding needs to be done. For example, install a ventilated facade, since the building will have an unpresentable appearance.
- Installation of insulation is done in dry times (if we are talking about mineral wool).
How do the conditions in the steam room affect the tree in it?
Resin leaks
Since we are now talking exclusively about shelves in a wooden bathhouse, let’s briefly go over the conditions that prevail in the Russian and Finnish steam baths, and how they affect the shelves, where, in fact, the steamer spends time.
So, in our sauna the temperature is high, around 90-110 degrees, and the humidity is somewhere around 5-15%. With such heat, all the bodies that are inside the steam room heat up. Including wood, although any type of wood has a fairly low thermal conductivity.
However, among the wood species there are conifers, the vessels of which contain resin. This is a thick liquid that flows out when the temperature rises, with a completely different thermal conductivity - it burns when touching the wood is quite bearable.
IMPORTANT! The presence of resin makes conifers completely unsuitable for making shelves for a sauna (and only for a sauna).
The low humidity of the sauna is good because it allows the use of wood that is more sensitive to humidity. Sensitivity in this case is swelling when wet and shrinking (often with cracking) when drying.
The Russian bath differs from the sauna in having higher humidity (55-60%) and lower temperature (40-60 degrees). Some breeds deteriorate more quickly than others under these conditions. However, this depends on their resistance not to moisture, but to rot, that is, to organisms that parasitize the tree and successfully reproduce in a warm and humid environment.
The same conifers, prohibited for saunas, are suitable for Russian baths (if the owner is not a fan of changing modes). And they would even be out of place here, because it is precisely due to resins (natural antiseptics) that they perfectly resist rot. And some coniferous species generally become stronger from water - larch, for example. (Some deciduous trees also grow stronger in water - oak is the same.)
So, how to choose wooden shelves for a bathhouse based on the temperature and humidity conditions in it?
ADVICE! For a sauna you need to look for wood with the lowest thermal conductivity, and for a Russian bath - resistant to rot and not prone to cracking and greatly changing dimensions when moistened/dried.
What are the rules for insulating a house made of laminated veneer lumber?
Installation of insulation requires compliance with a number of measures and rules:
- Be sure to install wind and waterproofing to transfer the dew point from the tree to the outside of the façade.
- Do not work during rain or other precipitation so that moisture does not remain between the insulation and the wall. It is especially important to comply with this requirement when working with mineral wool slabs.
- Wear protective equipment: a respirator and gloves if you work with mineral wool.
- Fasten the insulation tightly to the wall of the house. Don't skimp on fasteners.
Calculate insulation in advance. Take into account the calculated parameters with a small margin.
Use of aspen in furniture production
We found out the qualities of aspen wood above; based on them, the use of aspen in furniture production is clear: it is recommended for high indoor humidity. Combined with the fact that there will be no burns from touching hot wood, aspen furniture fits well into the decor of a bathhouse or sauna.
The price of aspen furniture is low, but it gives off a pleasant smell of calm. In addition, such a piece of furniture is difficult to get dirty. However, some people find furniture made from this type of wood unpresentable. If a diseased tree was used, then there is a possibility of the furniture rotting from the inside. We recommend aspen furniture to those who have chosen a country style for their home.
We hope that information about aspen wood, its use and properties was useful.
Aspen is a healing tree that can help in the unconventional treatment of diseases associated with inflammatory processes and diabetes. This is an accessible plant material that anyone can collect on their own if desired and make a medicine from it. Its main advantages are naturalness, mild action and proven effectiveness.
How much will it cost to heat a house?
Several factors influence the cost of heating:
- The thickness of the walls of the house and the presence of insulation.
- Climate, weather conditions, windiness.
- Area of heated premises.
- Presence of fistulas and fissures.
- Heat loss on: doors, windows, attic.
- Floor insulation.
- Type of fuel: gas, wood, coal, electricity.
- The cost of fuel in a particular region.
It is difficult to make accurate calculations. But one thing is certain. Heating costs will be lower than in a conventional log house, taking into account that the thickness of the walls of the house is the same.