If you decide to install the log house yourself, you need to think about connecting the timber in the corners. You will also need to understand how, if necessary, to join two logs or beams in length and insert a partition.
[toc]
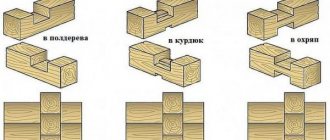
Regardless of what the frame is made of, there are two types of corner joints:
- with a remainder (or release) - this is when there is still some piece of log or timber behind the junction;
- or without any remainder.
When cutting with residue, there is a fairly large waste of material. Each remainder is at least 20-25 cm. These “tails” in one crown take 160-200 cm. The consumption is quite considerable. But on the other hand, such a cutting is called a “warm corner”, precisely because with normal caulking they do not dry out.
The corner in the log house can be with or without remainder
Cutting a log house without residue is more economical in terms of material consumption during the construction stage, but in this option the corner is the most freezing place. Also, with this method of connecting logs and beams in the corner, even small errors greatly affect the quality. Therefore, increased demands are placed on the quality of cutting bowls.
There is a big difference in the technology of constructing a log house from logs and timber. The logs have a round shape and without processing it is impossible to join them tightly. Therefore, a recess is made in the lower or upper crown - a groove, into/on which the next log is laid. This increases the surface of their contact. It is the width of the groove that is the actual thickness of the log wall. How warm the wall will be depends on the shape of the groove and the accuracy of its execution.
With timber everything is different. Since the planed one has almost the same dimensions, and the profiled and glued ones have no “almost”, and their edges are flat, no adjustment or groove is needed. Therefore, the entire assembly of a log house from timber consists of forming joints in the corners. Inter-crown insulation (jute, tow, moss) successfully copes with blocking small inconsistencies. As a result, a log house is built many times faster.
Connecting logs in corners with remainder
First, let's talk about log houses. Recently, they have become popular again, especially in suburban construction: they look attractive and are also natural. Moreover, even despite a significant overconsumption of material, the corners are made with a remainder. These methods of joining logs are traditional. They came to us from our great-grandfathers, this is how they built their houses.
Log house in a bowl
As has already been said, a longitudinal recess is made in each log - a groove. In the corners they are trimmed more, according to the shape of the log lying across. This notch is round in shape, which is why it is called a bowl, and the method of cutting a corner is called a bowl. The second name is “in the oblo”.
Marking the upper and lower bowl
Depending on the location of the bowl, there are upper and lower bowls. The upper bowl is so called because the log rests on top of the crown, clasping the lower one. This connection is also called “clap”. Remember: the bowl is upper, despite the fact that it is formed at the bottom of the log.
The work is carried out in several stages. The log is first placed in the log house and leveled. Then they outline the contours of the groove and the bowl, place it on a flat surface and process it there - cutting the bowls. When the excavation is ready, the log is raised again and placed in place, trying it on. If necessary, they are adjusted (removed again, trimmed where necessary) and only then laid on a compactor (tow, jute, moss). All these movements are compensated by the fact that with this method of cutting, sediment simply flows down the side surfaces of the wall, and they, as a rule, are well protected by several layers of impregnations and paints.
Types of bowls for joining logs in corners
The lower bowl can be molded directly in the log house: all manipulations can be done on the laid crown. When the walls are already raised high, it is very inconvenient to do this if you lack dexterity, so you still have to drag the logs up/down. Perhaps this is why this method is less popular.
It is easier to make a frame into a bowl: it allows you to correct almost all mistakes. In addition, despite all the apparent complexity, it is this type of joining of logs that is easier for beginners to do. All others require more carpentry skill.
How to make a joint from a log frame into the lower bowl is shown in the video below. The explanation is detailed, showing techniques for working with an ax and the full procedure. First you just need to talk about the tool that is used to draw the log. This is a carpenter's trait or scriber.
The device is very similar to a school compass. There is also a sharp stop on one side and a pencil on the other. Just like in a compass, the required distance is fixed with a screw. Having placed the ends at the required distance, the sharp part is guided along the log for which the bowl needs to be cut. Using a pencil, respectively, according to the one in which the groove and bowl will be cut. This produces markings, which are then drawn with a marker. It will become clearer when you see the process of marking the bowl in the video.
Actually, now a video about how to connect logs into the lower bowl. The first part deals with molding the longitudinal groove, the second directly deals with cutting the bowl.
Connection in okhryap
This type of connection consists of two semicircular bowls. In order for a corner folded using this method to be warm, considerable experience is required: even minor errors in the width of the groove or the thickness of the lintel will cause drafts.
Log in okhryap
Technology for assembling a log frame for a house or bathhouse
Organization of a workplace for assembling walls
To ensure the work progresses, the beams are laid out in a stack at a distance of 5-6 meters from the building on one or, better yet, both sides. Each layer of beams in a stack is placed on spacers made of boards.
A workplace for marking and cutting beams will be equipped next to the stack. A variant of such a workplace is shown in the figure.
It is convenient to mark the timber using a template at a height of 0.9 - 1.1 meters in the marking area, node A in the figure. After marking, the timber is lowered onto low pads into the cutting area. In this position, it is convenient and safe to cut the timber with a chain saw.
The cut timber is lifted onto the wall. To facilitate the ascent, slopes are arranged - inclined beams, whose upper end rests on the upper crown of the log house. The timber is moved along the slopes using a rope.
Wedge-shaped stops are nailed to the slopes, which make lifting the beam safer. In addition to safety, the stops allow you to get by with little force. Even one person can, if necessary, lift the beam, fixing it with stops at intermediate points.
It is most convenient to carry out work on assembling a log frame from timber with a team of four people. You can work together, but the work will just go slower.
Scaffolding is constructed to install the upper rims of the log house and the roof.
Three-tier scaffolding on the gable of the house.
1 — extreme racks; 2 - L-shaped scaffolding post of the first tier on the side facade; 3 - flooring; 4 — central racks; 5 — cruciform braces (shown conditionally); 6 - bosses
Assembly of the upper crowns of the log house is carried out from the level of the first tier. The flooring of the first tier is laid on L-shaped racks, pos. 2 in the picture. The racks are installed around the walls of the house and attached to the walls using bosses, pos. 6.
At the stage of constructing the roof (attic), on the facades where the installation of pediments is necessary, scaffolding has to be made in three tiers. To construct scaffolding racks, boards 50 x 150 mm are used. Flooring is made from the same boards.
Working from scaffolding is more convenient, faster and safer than from ladders - don’t forget about this.
Cutting logs with corners without residue
As we said earlier, the corners are colder without any residue, but they allow you to significantly save on building materials.
Angle "to the paw"
Among the joints of logs in the corners, the “paw” method is popular. It is easy to implement, and at the same time provides high strength and reliability of the connection. Also, the presence of inclined cuts makes it possible to achieve high tightness. The method has been tested for a long time, even GOST standards have been developed: size tables for each log diameter (see photo).
Table of foot joint sizes for different log diameters
All dimensions are plotted relative to the found middle of the log and a vertical line drawn from it (it is drawn using a plumb line).
Connecting logs without leaving any residue. Angle to paw
The order of work is as follows:
- Find the length of the cut part (called the block). It must be no less than the diameter of the largest log available (in the figure it is marked L). We set this value aside from the edge of the log (let it be 250 mm), draw vertical lines in these places. They will be the boundaries of the idiot.
- Let the diameter of the processed log be 200 mm. From the middle line, ½ of the value of A is set aside. D for a 200 mm log is 141 mm. We divide this value in half and put it on both sides of the center. We draw vertical lines.
- We trim (cut with a chain saw). As a result, you should get the same picture as in figure a).
- We take the appropriate dimensions from the table and mark them on the block.
- We trim off the excess (cut it off). The result should be a figure like in Figure b).
This is what the angle from the logs into the paw looks like (dovetail due to the fact that the connection is in the form of a trapezoid)
All logs are processed in this way one by one. As you can see, the dimensions depend on the diameters of the logs. In order not to have to worry about drawing every time, they make templates from thin plywood according to the diameters of the logs that are available (they label them). Then, having found the middle and made a block, they apply and trace a suitable template. With this order of work, there is less chance of making mistakes, and chopping bowls takes less time.
Comparison of manual and stationary cup cutters
It is impossible to say unequivocally which profiled timber with bowl cutting is of better quality: using machines or hand-held machines. However, many craftsmen prefer to order timber without locks and make them on the construction site using mobile devices.
Note! This equipment helps to achieve precise perpendicularity of the rows of timber when assembling a log house. Manual machines can be used both to create connections from scratch and to correct finished bowls if there was a manufacturing defect.
Experienced craftsmen use hand cup cutters to make high-quality locks.
For use in small woodworking enterprises, it also makes sense to purchase such devices. They are equipped with powerful cutters, with the help of which, with sufficient qualifications of workers, it is possible to carry out work with the same quality as on stationary machines.
It should be noted that the price for cutting cups varies from company to company. It also depends on the type of castle.
When comparing manual cutting of joints and that carried out in a workshop environment, the following conclusions arise.
- In production conditions, with stationary cutting of locks, the human factor is reduced, but it does not completely disappear.
- With approximately equal advantages of manual and factory cuts, the determining factor in the quality of work is the qualifications of the hewer, the machine operator, as well as the foreman or head of the enterprise.
- The advantage of factory bowls is their configuration. However, an experienced craftsman can repeat their shape manually.
- The presence and quality of thermal locks when cutting bowls on stationary equipment depend, first of all, on the literacy of workers and the brand of machines.
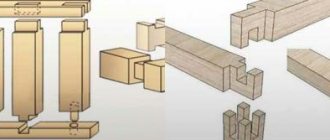
Joining the timber with the remainder
The easiest way to join timber in the corners of a log house is “into the floor of the tree”. A rectangular groove is cut, the dimensions of which depend on the thickness of the timber and are: The depth of the notch is half the thickness of the timber. That’s why it’s called “half a tree”.
Connecting the timber in the corners with the remainder - in half a tree, in a fat tail, in an okhryap
The “tail tail” method is distinguished by the presence of an additional tenon, which provides a stronger and more reliable connection, but requires more carpentry skill. More difficult is connecting the timber into an okhryap. Here you cannot make a mistake when calculating the width of the jumper, but it is much easier to implement than on a log: the geometry here is standard and you can use a template, which significantly speeds up the work, and then an error can only occur when cutting.
Connecting timber in a corner without leaving a trace
There are several types of connection. Traditionally, “half-tree” and “paw” are used for bathhouses and houses. They differ only in shape. Half a tree has smooth, parallel edges. It's easy to implement. When joining the timber “into the paw”, the shape of the tenons is made trapezoidal. It is a little more difficult to perform, but there is less chance of through holes occurring.
Joining the beam in the corner without leaving a trace: half a tree and a paw
There are several other types of butt joints for timber. They are not very reliable and do not provide proper tightness, although they are economical in terms of material consumption. They are rarely used for residential buildings, mainly for the construction of outbuildings.
A simple butt connection occurs with alternation. This makes the angle stronger. For reinforcement, you can use steel plates or knock down the beam with long nails at an angle.
Butt joint of timber
There are also methods for butt assembly with dowels of different shapes.
Another method of construction: using frame-timber technology. Then, in the corners and at the joints of the timber along the length, a vertical stand is placed with grooves formed in the required planes. At the ends of the beam, a spike is formed into the appropriate shape. When laying, you have to “put on” each element from above.
The advantage is that you can mold all the studs according to a single template, and then simply assemble everything like a construction set (not forgetting to lay inter-crown insulation). The connection turns out to be airtight and quite reliable, moreover, the joint itself is not visible and the appearance is very attractive.
Connecting timber using panel technology: quickly, warmly and reliably
Working principle of cup cutting machine
Scheme of a cup cutting machine.
To produce cups on profiled timber, various cup-cutting milling machines are used. Some of the most popular devices for making cups are the following devices:
- Makita 3612С;AEG 2050;
- Felisatti RF62/2200VE;
- Interskol FM-62/2200E and their analogues.
The cutter installed on the device has pads with two sharp edges. With the help of these cutters, wood is selected from the body of the timber used. To reduce the load on the device, the plates placed on the cutter are attached at an angle to the axis of rotation of the working tool. These plates are removable and are secured using special screws.
The cutter is mounted on a frame that can move along and across the log. A special device that provides lifting allows you to adjust the cup's depth. In addition, with the help of this device the depth of the manufactured groove lock is adjusted in accordance with the project.
A cup-cutting machine for timber on a frame is attached to the cleats on which the timber is installed. The cup cutter is fastened in the place where the cup cut is supposed to be placed. During operation, the frame of the device can move freely along the base of the device. Simultaneous movement of the cutter along and across the beam allows you to cut a groove of the required depth and width.
How to connect beads lengthwise
The easiest way is half a tree. Its configuration and shape are similar to those made when connecting a corner. But the disadvantage of this splicing method is that when longitudinal forces arise, which can occur during drying or movement of the soil, such a connection is easily broken. A continuous gap is formed.
Long beam connection
The oblique rim lock has the same disadvantage: it is easy to disengage. If you need reliable joining of timber, use a straight rim lock. As you can see, due to the protrusion, pressed by the crowns located on top and the weight of the roof, it will resist the forces of longitudinal tension (and compression too). It is more difficult to implement, but much more reliable.