The current material for the foundation for a greenhouse will be timber. This is a durable and reliable material that will withstand the finished structure, and if desired, it can be moved to another location next year.
In order for the foundation to be reliable, it is necessary to become more familiar with the conditions of use of the material and the nuances of constructing the structure.
Advantages and disadvantages
Each base material has its own pros and cons. To begin with, it is recommended to consider the positive features of a timber foundation:
Minimum consumables. To secure a wooden base to the ground, you will need a small amount of hardware and parts, which will help reduce the construction budget.- Smooth geometry. The timber has smooth edges and precise dimensions. Thanks to this, it is possible to greatly reduce and simplify some of the construction processes.
- Fast construction. When the foundation is ready, you can immediately begin building the greenhouse frame - there is no need to wait for shrinkage and drying, as happens when using concrete and stone materials.
- Manufacturability. The wood is technologically advanced, which ensures easy fixation of the base components to each other, as well as trouble-free fastening of the frame to the foundation.
- Quick repair. If damage occurs, such a base can be lifted with a jack and parts that have become faulty can be replaced.
- Environmental friendliness. The timber is a safe material for humans, as it does not emit harmful substances into the atmosphere.
Note! Another plus is that such a base can be easily transported to another place on the site.
Despite the abundance of advantages, there are also some disadvantages to this design. For example, the service life is too short. One can argue with this statement, because houses made of timber have been standing for decades, and the foundation can always be repaired and continue to be used.
Also, some argue that such a base cannot support a large mass, but in this case this function is not needed, since greenhouses made of polycarbonate or film do not have much weight.
Advantages, disadvantages of wooden supports
On a wooden base, you can build both small greenhouses, used for beds and flower beds, which are easy to move without disassembling, and large stationary greenhouses. It is necessary to analyze the advantages of timber-based greenhouses.
The main advantages of lumber:
- low price compared to other building materials;
- speed of assembly and dismantling;
- mobility of small structures;
- availability of materials and basis for repairs;
- simplicity in calculations and construction;
- the ability to move the greenhouse to maintain crop rotation;
- spring cultivation of seedlings, after which the greenhouse is dismantled or transferred to the next section of the garden;
- does not emit toxic compounds that affect grown plants.
Despite all the positive aspects of a wooden support, it has a number of disadvantages that affect the construction and use of finished greenhouses. Such greenhouses require special protective measures against fungal infections of wood, insects that feed on wood fibers, as well as insulation from moisture, which causes rotting of the material.
If the wood is not treated with the necessary additives, this can affect the crops being grown, spreading pathogens among them, or poisoning the air in the greenhouse with their waste products, which will lead to a slowdown in growth, or the accumulation of toxic compounds in the fruits.
Terms of Use
The greenhouse must be installed on a frame, and if timber was chosen as the base material, then it is worth remembering several conditions for its use:
the weight that such a foundation can support is from 70 to 120 kg;- fastening of parts must be provided in such a way that in the future it can be disconnected and the greenhouse can be moved to another location;
- the greenhouse frame must ensure the rigidity of the entire structure;
- the timber must be treated appropriately to protect the soil inside from being washed away by rain;
- raw materials must be treated with antiseptics and impregnating materials to avoid rotting, attacks by rodents and insects;
- processing of the material should take place on a separate site to avoid chemicals getting into fertile soil;
- all cuts, places where beams and boards are fixed must be treated with antiseptics - this is done at the assembly site.
Important! To process the material, not only impregnations and antiseptics are used, but you cannot do without them. If you abandon the processing stage, then with constant rain and watering inside the greenhouse, the timber frame will become unusable very quickly.
Detailed instructions for installing a greenhouse on timber: diagrams and photos
Installation as follows:
- A ditch 30 cm deep and 20 cm wide is dug along the perimeter of the future building. The bottom of the trench is compacted, removing irregularities, and covered with a mixture of gravel and crushed stone. As a result, a layer 10–15 cm high is obtained. The gravel and crushed stone are covered with a layer of sand of the same thickness. The depth of the trench should be reduced enough so that the timber laid in it comes halfway out of the pit. The created sand cushion is carefully pressed. The bottom and walls of the trench are covered with waterproofing material.
Digging a trench for the foundation of the greenhouse, leaving no unevenness at the bottom
They prefer to fasten the foundation beams using the “half-tree” method
To fix the frame to the base of the beams, special metal supports are used
The wooden base of the greenhouse was placed on stones, and the frame was made of metal profiles
Types of timber foundations and selection criteria
Since a timber foundation is the most economical, it is chosen by most gardeners. But it is not enough to choose only the material; it is also important to choose the type of base. They come in these types:
- Tape. It can be deep or shallow. For a greenhouse, the second option is just right. It is a monolithic frame-ribbon made of wood. This option is reliable and economical.
- Columnar. It is represented by monolithic wooden pillars, which are installed in the corners of the future greenhouse. Such pillars are lowered into the ground to a shallow depth.
To choose the right option, you should pay attention to the type of soil. If it is rocky and not heaving, then you can safely choose pillars made of timber. For other types of soil, it is better to give preference to the tape option.
Protection of timber from damage
The timber in the greenhouse is in contact with soil and water, so certain protective measures are required to ensure that it lasts a long time. Thus, the main destroyers of wooden supports are insects, rotting, and fungal colonies. In order to secure the foundation, you can use both special industrial and home-made impregnations. The better the substance is suitable, the less often repair work will be required.
Of the factory ones, non-washable antiseptics are most suitable for treating greenhouses for outdoor use. Non-washable impregnations are used when wooden supports are exposed to aggressive environmental influences. Due to their composition, they remain in the wood and prevent mold and rot from appearing. Antiseptics for external use penetrate into the timber to a shallow depth, which is why if the top layer is damaged, fungus and mold may appear in scratches, which will spread under the treated layer.
For self-made protection, copper sulfate, used machine oil or firing and coating with bitumen are used.
The simplest homemade impregnation is a solution of copper sulfate, with the proportions of substance and water 1 to 100. You can apply it after the powder has completely dissolved; for this, the liquid is heated to 40-45 °C.
Mastic coated base
Used engine oil must be heated before being applied to the wooden frame. This method can be dangerous due to the substance getting into the products grown in the greenhouse, which will lead to deterioration of the harvest and harm to health.
Burn the base with a gas burner until charred. After completion of the heat treatment, bitumen or bitumen mastic is applied to all surfaces in 2-3 layers.
Once the wood is soaked, it must be allowed to dry completely before continuing with construction work. It is very important to cover the places where the greenhouse walls are attached to the base so that moisture does not get through them. This can be done either with bitumen or silicone sealant.
Choosing a wood type
The timber should be made from selected wood, but you should pay attention to its species.
Pine has an expressive pattern, but this is not the main thing when choosing a species for building a foundation.
This material has a density of 520 kg per cubic meter, it is rigid and elastic. Treating pine with impregnations will not be a problem. This is the most common lumber from which timber is made.- Spruce has a density of 430 kg per 1 cubic meter. It is light in weight, but has good stiffness and elasticity. It also lends itself well to treatment with chemical compounds. This raw material has a higher thermal insulation value and a low resin content. It is because of this that spruce is more susceptible to rotting than pine.
- Larch is often an alternative to oak, as it has good rot resistance. It is chosen for this advantage for foundations: larch is not afraid of dampness. It is strong, durable, widespread throughout the country - it is easy to find in almost any construction market, and larch is also low in cost.
- Cedar pine is not often used, since the timber made from it is expensive. The wood is dense and easy to process. This material is more suitable for decorative finishing. Than for the base for a greenhouse.
On a note. Considering the above, we can conclude that the best options for the base will be larch and pine.
Recessed option
Recessed columnar foundation for a winter greenhouse
A greenhouse or greenhouse is built on a wooden foundation even if it is necessary to grow vegetables and seedlings in the winter. It is usually buried 1 meter. This makes it possible to save on resources, taking advantage of the warmth of the earth. Despite the fact that the area of the walls transmitting light is reduced, this option allows you to save fuel.
The technology of the polycarbonate surface version differs not only in the design of the frame, but as for the base, it is created much more powerful. Using logs or semi-tips, semi-logs. Having removed the bark and carried out pre-treatment.
In these basics, the work goes like this:
- They excavate the soil to a given depth and level the walls. Lay a waterproofing layer of roofing felt on the outer wall.
- Drive the pointed end of the log into the ground around the perimeter. Pre-treating them with bitumen or mastic.
- Along the lower and upper parts of the finished log walls, staples 40-50 cm long are driven in and tightened.
- Level the top edge using a chainsaw. Then they place the top beam, screwing it to the ends of the logs.
- They compact the base near the pillars.
Every 5th log should be 50-60 cm longer than ordinary logs. For example, the burial height is 1000 mm. The row post is 1400 mm long, and the corner and intermediate post is 1800 mm long.
To build greenhouses made of wood or polycarbonate, you can use any of these technologies. The main thing is to determine the direction and purpose of the greenhouse. And to build a base from wood means choosing the optimal ratio of price and service life.
Material processing
Before using timber from the timber to lay the foundation, it is recommended that it be properly treated. It is worth considering several important nuances:
- the antiseptic must be intended for external use: compositions for internal use will be washed off at the first precipitation;
- the impregnation should be “friendly” with polycarbonate and not damage it during use;
- there should be no poison in the impregnation: it can penetrate the soil and infect the plants;
- the most optimal composition is water-based, which creates an invisible film on the surface of the raw material and protects it from rotting;
- Sometimes, instead of ready-made products, you can use a folk method: burning with a blowtorch, heated bit or machine oil works well.
You can also use copper sulfate - it is harmless to plants. For processing, each part is soaked in a solution and left to dry, but without exposure to sunlight. Drying usually takes about 3 weeks.
What will you need for the job?
To arrange the supporting structure, you need to prepare the following tools:
shovel;- roulette;
- level;
- hammer;
- drill;
- screwdriver;
- jigsaw or saw;
- screwdriver.
You also need to purchase screws or other fasteners that will secure the frame. The materials you will need are timber of the selected species; it should have a moisture content of about 22%.
There are also nuances when choosing the thickness of the boards. For example:
- For a lightweight greenhouse frame, 5x5 cm beams are suitable.
- For a medium-sized structure on metal rods, it is important to take a beam of 5x10 or 5x15 cm.
- If the greenhouse frame is created from profile pipes or thick wooden boards, then it is better to take raw materials with a cross-section of 10x10 or 15x15 cm.
Monolithic slab foundation
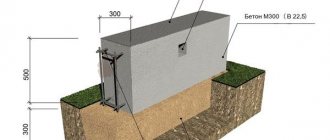
Are you interested in a design that can provide stability even on soft soils and at the same time protect the greenhouse from drafts, pests and hypothermia? Have you decided to build a very large building suitable for growing vegetables on an industrial scale at any time of the year? If so, then in such a case a monolithic concrete slab as a foundation is the best choice. This is the most expensive, but at the same time the most reliable and effective option. The design of a monolithic concrete slab has no fundamental differences from a shallow strip foundation; you can see it in the image below.
Monolithic foundation diagram
Now let's look at the stages of creating such a foundation.
Step 1. Mark using pegs and rope. Particular attention should be paid to controlling the diagonals and perpendicularity of the sides.
Step 2. Dig a pit at least 50 cm deep.
Foundation pit
Step 3: Add layers of sand and gravel. Their total thickness should be 25-30% of the pit depth. Compact them and, if necessary, cover them with geotextiles.
Step 4. Install formwork around the perimeter of the pit. Fill the space between it and the ground with gravel.
Formwork diagram
Step 5. Install fittings and drainage pipe.
Laying reinforcement
Step 6. Pour concrete to the edge of the formwork. This stage is very important and requires a professional approach - it is necessary to ensure a perfectly even screed. Insert anchor bolts or other fasteners for the greenhouse frame.
Fill
Step 7: Wet the concrete for a week.
Step 8: Next, let the foundation slab set. This usually takes 3-4 weeks, but in warm and dry climates the process will go faster.
Step 9. Remove the formwork and fill the gap between the slab and the surrounding ground with crushed stone.
Installing a greenhouse on a supporting structure
As an example, you can consider 2 options for step-by-step instructions: one for a strip foundation, the other for a columnar foundation.
To tape
Construction begins with clearing the site and marking it out. Pegs are inserted around the perimeter in the corners where the greenhouse will be. Then string is pulled between them. Also, do not forget that the timber must be treated with an antiseptic. Next step by step:
- Dig a trench under the base 10-20 cm deep.
- Make a sand cushion. Geotextiles are placed under the sand.
- Beams are laid on top of the geotextile.
- The corners are connected using dowels or corner plates.
- The beams are covered with roofing felt on top to protect them from moisture.
Attention ! Some builders recommend using roofing felt instead of geotextiles, which are wrapped around after laying the timber. But this method does not protect against moisture, because it has open joints, and does not prevent the development of mold. Moreover, due to lack of ventilation, the wood will rot faster.
The method of attaching the greenhouse to the foundation depends on the type of frame:
If the frame of the greenhouse is made of wood, then it can be fixed using special supports of a closed or open type. Vertical posts must be supported with slopes.- If the frame is metal, then it is attached to the beam with anchors. When the metal frame of the greenhouse is assembled, cellular polycarbonate is installed on it using special screws or another selected material.
On the pillars
This foundation is the most economical and simple. It is produced using the following technology:
- Clearing and marking the area around the greenhouse area.
- Digging a hole for wooden posts: their diameter should be 1.5 times the diameter of the beam.
- Filling the bottom with sand - then it needs to be watered and compacted tightly.
- Installation of a cross treated with an antiseptic on the sand.
- Installation of support pillars - pre-treat them or cover them with waterproofing.
Such a base will last for several decades with proper impregnation. The frame and covering of the greenhouse are also screwed onto the poles, depending on the raw materials used.
Greenhouse project
The first stage is project development. This includes determining the shape and dimensions, making a general drawing (sketch), detailing the elements and components of the structure.
The shape and dimensions of the greenhouse depend on the size of the site on which it can be located. And recommendations for choosing a location, in turn, depend on the design features. Although there are general provisions that guide the development of a project and linking it to the territory:
- The place should be open and well lit by the sun.
- Rectangular structures are oriented with their length from south to north.
- The location should be such that the greenhouse is protected from the wind as much as possible.
- Greenhouses made of timber are made with a gable or pitched roof. In the latter case, with a slope to the south.
- Optimal frame dimensions: height at the top point of the slope—2.5 m, height at the bottom point of the slope—1.7 m, width—3.5 m, length—up to 6 m.
In addition, take into account the following recommendations:
- convenient access;
- Possibility of access with a garden cart;
- proximity to the connection point to the water supply, if automatic and automated drip irrigation is provided.