Types of sequoia tree
There are three types of sequoia that are known to world botany.
Several species are native to North America:
- Redwood or coast redwood, which grows on the California coast.
- Gigantic is a growing area of the Sierra Nevada.
- Metasequoia, native to China.
The giant sequoia is the most popular in the world, the coastal one is called "Mahogany".
These species reach gigantic sizes: the coastal sequoia is the largest in height, and the gigantic in the thickness of the trunk. Metasequoia is no different from ordinary trees.
Preparing seeds for sowing
If you decide to grow sequoia, the first thing you need to do is find seeds. If you live close to their range, you can simply collect seeds from the nearest grove, giving preference to the tallest and oldest trees. In all other cases, you will have to order seeds online.
The best seed is harvested from the Sierra Nevada Mountains in California. They are specially collected from parent trees several thousand years old.
The chance of getting a strong, full-fledged sequoia from such seeds is much higher than from seeds from nurseries in Germany and Britain. It was brought to the botanical gardens of these countries a little over 100 years ago, and these trees are still too young to produce strong seeds. To grow sequoia from cuttings, it is much better to order seedlings from a European nursery, since a long journey from America can harm them.
The first step is to prepare sequoia seeds for planting. It is better to do this in early spring, so that by the onset of next winter the small plants have time to get stronger. To begin with, it is useful for the seeds to “overwinter” in the refrigerator for about a week. However, you shouldn’t put them in the freezer; a temperature of about 6°C is enough. Then you need to give them a “thaw” by soaking them in melt water at room temperature for a couple of days.
Coastal redwood
Redwood grows exclusively on the Pacific coast of the North American states. Trees of this species are the tallest on Earth, reaching a height of more than one hundred meters; the thickness of the Redwood trunk is six meters in diameter.
- Sequoia is a long-lived tree: there are trees on Earth that are about two thousand years old.
- The crown of the tree has a conical shape, and the branches grow horizontally to the ground.
- The thick but soft bark has a reddish tint.
- Young trees have elongated leaves, reaching a length of up to two and a half centimeters.
In old trees, in the upper part of the crown, the leaves look like scales, no more than one centimeter long. The seeds of the tree ripen in cones, about three centimeters long. When the seeds ripen, the cone dries out, after which it opens and the seeds spill out.
The maturation process lasts about nine months. Each cone contains from three to seven seeds.
Botanical description
This is the tallest tree on the planet, since the maximum height of a sequoia is up to 115 m and even more. It takes more than one century to reach this size, because the life expectancy of a long-lived conifer is over 2-3.5 thousand years (maximum up to 6 thousand years).
The evergreen sequoia or Sequoia sempervirens usually grows above 60 m, and its trunk has a diameter of about 6 m. Individual representatives measure above 115 m and their trunks reach a thickness of up to 18 m. The giant sequoiadendron or Sequoiadendron giganteum reaches a height of 70-90 m, and the diameter of its trunk does not exceed 37 m. In total, one tree can produce up to 2 thousand tons of wood.
Currently, the tallest specimen of sequoia is named Hyperion. It was found in 2006 north of San Francisco in Redwood National Park. The height of the tree is 115.5 m. By this time, only 15 trees have a height from ground level to the top. 47 has a height of 105 m. According to theoretical calculations, the maximum height for this species is 130 m; the plant will not be able to grow higher due to the inability to deliver water and nutrients to such a height. Numerous archaeological finds prove that sequoias grew throughout North America 150 million years ago.
The annual growth of a tree depends on weather conditions and can reach up to 1 m per year. Therefore, using a cross-section, you can get a fairly accurate picture of the weather map of the region over many centuries - an invaluable database for research. At the same time, it is not at all necessary to cut down relics. A thin section is cut out of the stem with a special tool, showing the growth rings, but not harming the plants.
The bark is 30-80 cm thick. It is soft, its structure is fibrous, and is easily separated from the base. The branches are mostly thin, and begin to grow on the trunk at a young age, almost close to the soil. In old trees, their lower tiers dry out, leaving only a bare trunk with a conical crown at the very top. In closely spaced redwood trees, the top crowns are intertwined into a common, almost light-proof canopy. Branches usually grow almost horizontally, with only a slight downward slope. In young growth, the leaves are flat and elongated (15-25 mm long), and in adult sequoias they mainly depend on the light: in the shade the shape resembles an arrowhead, and in the light scales grow (5-10 mm long).
Both monoecious representatives of the genus reproduce by seeds. The fruit is an oval or spherical cone up to 2-3 cm in diameter. It is completely covered with scales that twist in a spiral. After pollination, which occurs in February, 3-7 seeds (length 3-4 mm) are sown in cones. The cones take 8-9 months to ripen, and by mid-October they open and scatter seeds, caught by the wind. The empty shells themselves remain hanging like “roses” on the branches for quite a long time.
Sequoia roots lie relatively shallow for their size. The plant holds tightly to the soil, since its root system has a high horizontal extension. All this helps the trees resist destructive hurricanes, which are not uncommon in this part of the Pacific Ocean. Specimens that have lost support due to waterlogging of the soil and erosion by precipitation fall.
In order to restore the previous population of sequoia in the remaining forests, ripened seeds are used, and in addition to them, green shoots from stumps left after cutting down. This growing method is not typical for conifers, but is 100% applicable to sequoia.
Surprisingly, sequoia is a tree adapted by nature itself to forest fires. The fire burns out low-growing vegetation, but cannot harm tall giants. The flame leaves scars on the thick bark, but does not destroy the plant itself. Over time, such scars become larger due to the fact that fungi inevitably settle in them. Sooner or later, such a tree falls, losing its former strength. At the same time, another process is taking place.
The burned spaces after a fire are quickly filled with young redwood trees. Under the ground, all these old and young trees unite into one common giant network, turning into a forest-tree. In this way, the species easily displaces competitors from the territories it captures. In such forests you can find special “white” sequoias, whose needles are practically devoid of chlorophyll. This happens due to the lack of light on the lower tiers. Such trees live thanks to the nutrition received from the roots of their neighbors.
Types of sequoia
A tree-type plant, sequoia (lat. Sequoia) is part of the Cypress family (lat. Cupressaceae). The sequoia genus consists of one representative: the evergreen sequoia (lat. Sequoia sempervirens), also sometimes called coastal or red sequoia. A separate genus: giant sequoiadendron (lat. Sequoiadendron giganteum), it also belongs to the Cypress family along with another genus: metasequoia glyptostroboides (lat. Metasequoia glyptostroboides).
Local residents in the United States and Canada call their trees mammoth trees, and sometimes, in their own way, California pines. The evergreen metasequoia, which grows in China, is not a tall sequoia, although its size is significantly larger than usual - a height of about 40 m, a trunk thickness of up to 2.5 m, and it lives only up to 600 years.
Sequoyah is not just a word, but the name of the leader of the Cherokee Indian tribe. He is known for his relentless struggle against the invaders of his homeland, the creation of the alphabet of the national language and the publication of the Cherokee Phoenix newspaper in it.
giant sequoia
This type of sequoia grows in the Sierra Nevada region of California. The tree reaches gigantic sizes, and the thickness of the trunk can be twelve meters.
- The oldest sequoia of this species is about three thousand years old; now there are about thirty groves with giant sequoias preserved on the planet.
- There is evidence that the breeding season for this species of sequoia begins after reaching four hundred years of age.
For successful tree propagation, high temperatures are necessary, so fires do not harm the trees. Sequoia bark is highly resistant to fire, absorbing moisture like a sponge.
Sequoia grove in Crimea
History of appearance
In the middle of the 20th century. Nikitsky Garden researcher Gennady Yaroslavtsev undertook an experiment on growing sequoiadendron in mountainous areas. The landing site - near Kutuzovskoye Lake on the slopes of the Chatyr-Dag plateau - was recommended by Anatoly Potapenko, an employee of the Alushtinsky forestry. The grove at an altitude of 850 m was planted in 1964 near a spring, which is the source of water for the lake. When choosing a location, the moisture-loving nature of these trees was taken into account.
To protect the seedlings from wild boars, deer, and people, Crimean pines were planted around them. The new trees were looked after by a forester who lived nearby, an acquaintance of Potapenko.
The experiment was a success. Now, in two sections of the grove, approximately 150 20-meter sequoiadendrons grow, which earned Yaroslavtsev a doctorate. The Crimean pines that once masked them are drying up, unable to withstand the competition. Kutuzovskoe Lake has also dried up almost completely.
How to get there
The grove is located on the southern slope of the Chatyr-Dag mountain plateau, near the Kutuzov Lake tourist site. First, by car or public transport, you need to get to the well-known trolleybus monument on the Angarsk Pass. A little higher, near the ski school, there is a parking lot.
From here starts a hiking route through the deciduous forest to the grove with coordinates 44.738158, 34.334936. The landmark on the way is a power line, after which you should turn south to the lake. The duration of the walking route, starting with a gentle ascent, is approximately 40 minutes.
Metasequoia
This type of sequoia grows in some Chinese provinces. The Chinese sequoia is not gigantic in size. This type of sequoia is listed in the Red Book due to extinction.
- Metasequoia can be found on mountain slopes.
- These trees reach a height of no more than 35 meters, the diameter of the trunk is only a few meters.
- Mature trees have a rounded crown, while young trees have a conical crown.
- Young trees have a reddish bark that becomes darker with age.
- The two-row leaves fall off during the winter season.
Spherical cones up to two centimeters in diameter appear in the sixth or ninth year of the plant’s life. The life span of one tree is about six hundred years. At the age of twenty, metasequoia reaches a height of about twenty meters, one and a half meters in volume.
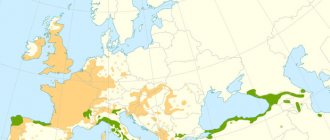
Spreading
Along a narrow line along the Pacific coast of the United States are quite significant redwood forests. They range from southwestern Oregon to the Santa Lucia Mountain Range in California. Trees prefer a height of 600-900 m above sea level. This explains why they can be seen in a belt 750 km long with an altitude of only 8-75 km above sea level. Single specimens can be found on the coast itself, and some grow in the mountains at an altitude of up to 920 m above sea level.
In addition to national parks and reserves in Oregon and California in the USA, redwood trees can be seen in the countries
- GREAT BRITAIN;
- Canada;
- New Zealand;
- SOUTH AFRICA.
- Hawaii;
- Italy;
To grow, this tree requires a humid maritime climate, as in its homeland, on the Pacific coast of the North American continent. This explains the range of the distribution. The seeds germinate and take root wherever the climate suits the redwood tree. Its frost resistance ranges from -12.1-17.7°C for young trees from American forests, but increases over time. The tree was brought to Europe only in 1853, after which it appeared in private gardens, as well as in parks and squares.
In Russia, sequoias are found in the mountains of the Western Caucasus and on the southern coast of Crimea. In Ukraine, 3 sequoias grow in the Berezinka arboretum in Transcarpathia. In forest conditions, trees over 30 m tall can survive winter temperatures down to -23.2°C.
"Hyperion"
Hyperion is the largest sequoia tree currently available. The giant was discovered fifteen years ago in one of the American national parks. This tree, 115.5 meters high, has far outgrown its relatives, which reach a height of no more than 90 meters.
- The approximate age of the tree is eight hundred years. Hyperion grows three centimeters every year.
- The slight increase in growth is explained by damage to the upper part of the trunk by woodpeckers, which is why the growth of the tree has slowed down.
- The tree grows on a slope, not in a valley, where there is more liquid and prospects for growth.
Before this place became a national park, there was active deforestation here, “Hyperion” miraculously remained untouched. Due to its height, the giant is a world celebrity and a landmark of Redwood Park.
Characteristics of the sequoia tree
The young tree has a wide and very dense crown. With age, the crown thins out and becomes more open. The branches grow horizontally to the ground, the roots lie shallow. The bark is very dense, but soft and has a fibrous texture.
- Non-flammable bark approximately 35 centimeters thick. New shoots grow upward, moving slightly to the side.
- Sequoia has thin branches and a deep green color. The leaves are flat, from one and a half to three centimeters in length.
- The pollination process begins at the end of the winter season, after nine months the seeds are fully ripe.
- The brown cone with a reddish tint bursts and the seeds scatter.
- Young shoots grow very quickly: the growth is more than a meter per year.
- The trees form huge forests that stretch along the Pacific coast, up to 75 kilometers wide.
Sequoias can grow close to the water, or at an altitude of up to one kilometer, as they love moist air. They also grow in ravines and gorges where the air is humid all year round.
In places with high humidity, sequoias reach enormous sizes. The dense crown of the sequoia practically does not allow sunlight to pass through, so only shade-loving plants that love moisture no less than the sequoia can grow next to it.
How to grow sequoia in the Moscow region
This topic has 5 replies, 3 voices, and was last updated.
Alexey 1 week ago.
Good afternoon. Tell me how to properly grow sequoia in the Moscow region (if possible)
Last year I bought sequoia seeds. On the advice of the seller, I planted the house in sandy-earthy soil, watered it moderately throughout the year, but nothing came up.
This year I bought seeds again from another place. They advised to put the seeds in the freezer for a month and then immediately plant them outside. “There’s no need to water it—it’s Canadian!”
Please help me fulfill my childhood dream - to grow the tallest tree =)
Alexey, you don’t need to put it in the freezer. It’s really worth planting directly into the ground, or into a seedling box, if you have one. A plastic fruit box can act as a seedling box. It is advisable to line the bottom and walls with a material that allows water to pass through, but which will not allow the soil to erode.
Having filled the boxes with soil, sow the seeds, water them abundantly and constantly monitor the soil moisture, in autumn and spring during germination. Sowing is done in the fall, October-November (middle zone).
Growing in apartment-greenhouse conditions is not advisable, because... you are unlikely to be able to create the necessary conditions, coolness, air humidity, and the sprouts will simply die.
Place the box with seeds in a shaded place, you can put it, for example, under apple trees.
In winter, make sure that the box, or in the case of direct sowing in the ground, the “bed”, is covered with snow. Without snow, especially in severe frosts, the soil will freeze and can destroy the seeds. Under the snow, the seeds will undergo the necessary stratification and in the spring, if the seeds were of good quality, you will get seedlings.
From this moment the painstaking work begins. The soil should be moist, not wet, so as not to rot the young plants. Young plants should be protected from bright midday rays. Therefore, if the plantings were in a box, leave them under the apple trees until the fall. The beds will have to be shaded with improvised means. Don’t forget to feed the sprouts once every 2-3 weeks; at the very beginning, you can water them with all sorts of growth regulators and preparations that improve root formation
In the fall, the seedlings from the boxes will still have to be transplanted into a shkolka, this is a bed where plants are grown. The school should be located in a place shaded from the midday rays; the morning and evening sun should not be a problem. If the sowing was immediately done in open ground, then we leave the plants in the ground. In this school, plants should live for at least another couple of years, and preferably up to 5 years. All this time, it is advisable to feed the plants, treat them with drugs against fungal diseases, and moisturize them, and not only the soil, shower the plants, but not with cold well water.
After the plants grow up, you can transplant the plants to the desired location.
Breeding period
Usually a lot of seeds ripen in sequoia, but only a few of them take root and produce young shoots. Young shoots are forced to survive in conditions of lack of sunlight.
- The lifespan of one tree is about three thousand years and slow reproduction will not affect the plant population in any way, but redwoods are periodically cut down and the recovery period is slow.
- Fortunately, forest fires have a positive effect on the reproduction process of redwoods. Young trees after a fire receive moisture, carbohydrates and nutrients. The tree is able to displace conifers and exist safely in its own shadow.
Sequoia is not picky about the soil; it loves moist air, but does not like swampy places and dry limestone soils.
Sprout care
As soon as sprouts appear, the film or cap must be removed immediately. Without free air circulation, they quickly die. A couple of days after pipping, the sprout sheds the dry skin of the seeds. If he has difficulty with this, you can gently help him.
Young sprouts love the sun, but they should be shaded from direct sunlight. Small sequoias should not be kept close to heating appliances. Dry air is harmful to them. 5 months after planting, you will already have a miniature Christmas tree.
Sequoia under the age of 3 years are recommended to be kept in a pot and watered regularly. Dry periods are stressful for her, as a result of which her growth slows down significantly. Biennial plants can be kept outside in warm weather. The tree should be brought indoors for the winter. Since spring, it can be left outside in a well-lit but not too hot place.
A plant 1-1.5 m high can already be planted in open ground. In European climatic conditions, sequoia can withstand frosts down to -18°C.
You can also grow other coniferous plants at home, such as cypress.
Where does the sequoia tree grow?
Sequoia predominates on the North American coast. This is where the largest trees on the planet grow, dense forests dominated by redwoods.
Redwood Park is dominated by coast redwoods, which have grown naturally here for many hundreds of years.
- California is rich in giant sequoias, namely the national park of the same name, Humboldt Park, Grant Grove and Mariposa Forest.
- These are the most popular places where giant trees grow. In our country, sequoia can be found in Transcaucasia, on the Crimean coast and in Ukraine.
In these parts, just as in China, sequoias do not reach enormous heights; their height varies around thirty meters. Sequoia is able to survive frosts down to minus 17 degrees, and frost resistance increases with age.
Sequoias with a tunnel in the trunk for cars and pedestrians
In January 2022, it became known that the most famous sequoia with a tunnel in its trunk, the Pioneer Cabin Tree, had fallen in California. This giant sequoia in the United States became famous for its tunnel in the trunk through which a car could drive. A tree that grew in Calaveras Big Trees State Park was toppled by a violent storm, making worldwide news and sparking unprecedented interest in redwoods.
The original tunnel at the base of this giant sequoia was made in the late 1980s at the request of the owner of the Murphys Hotel. It was a tourist attraction, because people of that time were incredibly interested in walking and even driving through the trunk, and then telling all their friends about it. So more and more people learned about this interesting place and they increasingly came to the park and stayed at the hotel.
This particular tree was chosen to cut the tunnel because it already had a huge scar from a forest fire. To be fair, it must be said that the idea of a tunnel was not new and, according to the hotel owner’s idea, this sequoia tree was supposed to compete with the already well-known Wawona tree in Yosemite Park (Yosemite’s Wawona Tree) in the USA, in which the tunnel was made much earlier, in 1881, with the goal of attracting as many visitors to the park as possible. And although the Wawona sequoia in Mariposa Grove stood for much less time (only until February 1969), some older Americans still remember the road tunnel in it.
Interesting fact: The tunneled sequoia tree that fell on January 8, 2022 was not the only one in California. At the turn of the 19th and 20th centuries in the western United States, it was very fashionable to make such tunnels in giant trees in order to attract general attention and develop automobile tourism. After all, it was possible not only to walk or ride a bicycle through it, but also to drive a car inside the sequoia. However, this trend caused irreparable damage to nature and was quickly stopped.
More than a century has passed since then, and almost all the trees with car tunnels have collapsed. The giant sequoia Pioneer Cabin Tree was the last of its kind, and now it too has fallen. However, it is still possible to find a couple of giant sequoias with pedestrian tunnels on the West Coast of the United States and three coastal sequoias with vehicle tunnels.
California Tunnel Tree
Tunnels in giant sequoias:
- California Tunnel Tree in Mariposa Grove (Yosemite National Park). The tunnel was built in 1895 so that a horse-drawn carriage could pass through this giant sequoia. Today, the tunnel can only be walked or cycled.
- Dead Tunnel Tree in Tulumne Grove, also in Yosemite National Park. This was the very first growing giant sequoia through which a tunnel was made (previously, tunnels had already been made in fallen tree trunks).
Tunnels for vehicles in the coastal redwoods:
- The Chandelier Tree is the most famous tunnel tree in the United States and is located in the Drive-Thru Tree Park in Leggett, California. Its height is 96 meters. The tunnel was made in the late 30s of the 20th century, its width is 1.8 m and its height is 2.06 m. Anyone can drive through the sequoia in a car and take a photo of their car inside the tree for 5 US dollars. See the website for all details and directions.
- Two other coast redwoods with tunnels grow along US 101 in northern California in Klamath and Myers Flat.
Application of wood
Due to the large amount of resins contained in sequoia wood, it is not susceptible to fungi, mold and other diseases characteristic of coniferous species. Sequoia absorbs moisture during its life, but when dried, it dries out a little and does not crack.
- The popularity of this type of wood lies in its reddish tint. The habitat of a tree affects the quality characteristics of the wood.
- Thin and loose wood with a beige tint - the tree grew in an area with high humidity.
- Reddish and light brown hue is found in sequoia wood that grew in an area with moderate humidity.
- The structure of a young tree is loose, consisting of straight fibers.
Wood does not have a specific odor, so it is preferred in the manufacture of caskets and boxes for storing food products.
In addition, sequoia is used in the manufacture of furniture, as well as in finishing and construction work. Wood is a unique material due to its fire-resistant qualities and lack of odor.
Interesting facts about the sequoia tree
- The breeding period of the giant sequoia begins at the age of four hundred years.
- Wood is resistant to fire due to its ability to absorb moisture from the air.
- Fires have a beneficial effect on the opening of cones and the spread of seeds.
- Metasequoia was first discovered as fossilized remains.
- About three thousand trees with a trunk volume of two to eight meters grow in the Chinese province of Hubei.
- Scientists examined the remains of a redwood tree found in the ground and stated that they were about fifty million years old.
Sequoiadendrons and metasequoias from seeds!
The greatest delight among tree lovers are giant sequoias (sequoiadendron) and metasequoias. A very obvious consequence of this delight is the desire to grow such a tree at home. Further, the seeds that are bought are by no means the cheapest and, upon receiving them, a logical bewilderment follows: “How to grow a hundred-meter tree from these tiny seeds. »
Well, it's quite possible.
Below are step-by-step instructions for growing huge trees from far from the largest seeds.
We take the seeds (in this case, metasequoia in the photo), soak them for 2 days in settled water at room temperature. We change the water at least 1-2 times a day
Sequoiadendrons and metasequoias from seeds
After two days, we fish the seeds out of the water, shake them out onto a paper towel and dry them a little so that they don’t stick together when sowing.
Sequoiadendrons and metasequoias from seeds
Next, take a box, fill it with soil (mix it yourself or buy it for conifers 1:1 with universal soil). We water the soil. We distribute the seeds evenly over the surface. Water again (with a sprinkler!).
If you are going to plant plants almost immediately, you can sow thickly, as in the photo. In any other case, sow less often 4-5 times.
Sequoiadendrons and metasequoias from seeds
You can sprinkle a little earth on top, but in a very thin layer - metasequoias do not like being buried deep in the ground. Layer just a couple of millimeters so that with watering the seeds will appear on the surface again. Afterwards, water it from a spray bottle.