A long-lived tree, the walnut retains the ability to bear fruit for up to 400 years, which is one of the highest among horticultural crops. Nut kernels and the oil extracted from them are considered the most valuable product, but man has learned to use all parts of the plant to their advantage: wood, leaves, bark, pericarp, shell.
Characteristics of walnut
Processing: with the help of all types of tools, wood can be easily sawed both around the circumference and along the plane. The tree grows up to 30 m in height and up to 2 m in diameter. It has a cylindrical shape and a large crown.
Fast growing tree. The bark in youth is smooth, gray, darkening with age. The sapwood and heartwood are clearly separated. The core is in root stumps and branches, most often with a beautiful patterned pattern.
The color of the wood core, depending on age and living conditions, ranges from gray-brown to dark brown. The wood often has a wavy texture with a matte sheen.
The vessels in the early wood are distinct and larger than in the late wood. Annual increases of varying clarity. The wood is very decorative; when fresh it has a pleasant sour smell.
Varieties
The future size of the tree, yield, taste of the kernels, thickness of the shell, shape and shade of foliage depend on which variety the seedling belongs to.
Walnut Chandler
The Pancake week variety of walnut comes from California, where it was obtained in 1979 and named after the famous American botanist William Chandler. In the USA it is the most common. Seedlings bear fruit 3-4 years after planting. Flowering is later, which serves as protection against late return frosts. 1 hectare of plantings yields a harvest of up to 4-5 tons. Oval smooth fruits are up to 4 cm in diameter, in the shell they weigh up to 16 g (the almost white kernel weighs up to 6.5 g). The variety has very high drought resistance. For cross-pollination, varieties Franguette and Fernette are recommended.
Walnut Robert Livermore
This variety is one of those that bear fruit already 3-4 years after planting. The red walnut was introduced in the USA in 1999 and became the basis for other red-fruited varieties. The unusual shade of the skin of the kernels does not radically affect the taste, but it looks advantageous in desserts, for which it has gained high popularity in cooking. A tree up to 6 m high usually blooms in May, and the fruits ripen in August-September. Frost resistance – down to -37°C. The variety is characterized by consistently high yield (up to 60-90 kg per tree) and resistance to diseases. The weight of a large fruit is up to 30 g, the taste is pleasant and oily.
Canadian Chandler
A low-growing variety of almost dwarf walnut (on average 3-5 m tall), bearing fruit even in the climatic conditions of the Moscow region. Seedlings after planting give the first harvest in the 3rd year. Flowering occurs in May, and the nuts ripen in September. On average, the weight of the fruit is up to 30 g, the taste is sweetish and oily. The shell is easy to clean. The highlight of the variety is the beautiful bright yellow color of the foliage in autumn.
Description of walnut tree
The tree reaches a height of 30 meters and a diameter of up to 5 meters. It has a cylindrical barrel and a large crown. Refers to fast-growing trees.
- At a low altitude, the trunk branches into thick branches. The bark in youth is smooth, gray-ashy, darkening with age with a strong, longitudinally cracked bark. The leaves are twisted, complex, imparipinnate, petiole up to 5 cm.
- The number of cone-shaped leaves, oblong-oval at both ends, is 7-9, each up to 12 cm long. The leaves are reddish at first, then become greenish and dark green. Yellow-brown in autumn. It blooms in late April - early May, bears fruit in October.
The fruit hides a hard nut in a fleshy green shell with a tasty, edible core. However, it begins to bear fruit late, after 8-10 years. This tree has a strong root system that absorbs large amounts of nutrients, including lime.
Its bark greatly shades the ground, which prevents the growth and development of other plants underneath it. Refers to monoecious plants. Fresh leaves and fruits have an intense and pleasant aroma.
Planting and care
Walnuts are classified as heat-loving plants that require large amounts of sunlight for full growth and fruiting. The planting site is chosen on a slightly elevated sunny area with loose fertile soil, leaving 8 m between seedlings, and 10-12 m from nearby buildings. The optimal time for planting is the second half of April.
The land for planting walnuts is prepared in the fall. Dig a planting hole and mix the excavated soil with peat, humus, wood ash, and dolomite flour. Add 50 g of superphosphate. Planting holes are dug to a depth of 80-100 cm, and then filled back with refined soil and watered abundantly. In the spring in April, they are dug up again and a 15-20 cm layer of fine gravel or expanded clay is poured onto the bottom for drainage. A pole is driven into the bottom of the hole to secure a seedling 2 m high, since the tree grows quite quickly. The roots are sprinkled with fertile soil, the root collar is left 2-3 cm above the ground level. Water immediately, and the soil around the trunk is mulched with sawdust.
To successfully grow a walnut, a roller is erected from the soil around its trunk at a distance of about 50 cm, which does not allow water to spread after watering. For growth and fruiting, the plant requires a lot of moisture during the growing season. Mature trees draw it out from great depths, and young trees require watering every week (10-20 liters each).
Fertilizing is carried out twice a year. In the spring it is necessary to apply ammonium nitrate or superphosphate to increase green mass. In the fall, ammonium salts and calcium chloride are added for successful wintering; this is required even for frost-resistant walnut varieties - Chandler or Canadian.
Formative pruning is carried out on young trees in the fall to obtain a low-growing, spreading crown. To do this, in the first year after planting, only 3 main skeletal branches are left, and later, during the autumn pruning of the walnut, shoots directed vertically upward and thickening the crown are removed. In the spring, branches that have dried out during the winter and are broken are cut out. The root shoots of old trees are cut out or used for propagation. To protect against infection by diseases, all cuts must be coated with garden varnish.
Substances that the nut contains
All parts of the walnut: branches, bark, leaves and shell contain the substance juglone, which inhibits the growth of other plants. The ground around the tree is also saturated with juglone. Therefore, you should remove leaves that fall on flower beds or beds. They cannot be added to compost; it is better to burn them immediately.
The fruits contain a lot of oil, protein and vitamins (A, B1 and E), as well as iron and cobalt compounds. The leaves are also used as medicinal raw material. Sometimes fresh nuts, bark and roots are also used in medicine.
- Walnut leaves and green shells contain: pigments (flavonoids and carotenoids), organic acids, essential oils.
- They have anti-inflammatory, bactericidal, antihemorrhagic and antidiarrheal properties.
- They are used as a decoction against diarrhea in young children. They are believed to stimulate appetite and the secretion of digestive juices.
A similar decoction is also used to rinse the throat and mouth, wash wounds with it, and apply it as a compress to abrasions and bruises.
Interesting Facts
Walnuts were first named in Kievan Rus, where they came among other goods brought by Athenian merchants. In biblical Babylon, these trees grew in hanging gardens.
Among many peoples of the Caucasus, the walnut is considered sacred, and in Moldova there is a custom to plant this plant in the courtyard of the house when a child is born in the family.
The largest tree is considered to be a walnut tree, which existed on the territory of modern South Ossetia until the end of the 19th century. The circumference of its trunk exceeded 8 m, and several dozen horse riders could hide in the shadow of the crown. The average yield per giant was about 1.5 tons of fruit per season.
Walnut raw materials
Currently, walnut leaves and, less often, fruits are used as raw materials. Walnut leaves are harvested when they are fully developed, before spots appear and dry out.
They are dried at a temperature not exceeding 40 degrees Celsius. The fruits are harvested when the husks have not yet hardened, that is, in August, and are usually used fresh.
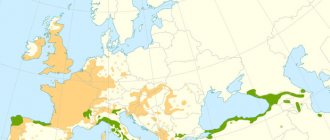
Spreading
Today, plantings of cultivated varieties are found almost all over the globe. To this day, relict groves with an area of more than 25 thousand hectares have been preserved, in which only walnuts grow - in southern Kyrgyzstan, in the southwest of Turkmenistan.
In Russia, walnuts grow in mixed forests of the Krasnodar Territory, Crimea, Rostov Region, Kabardino-Balkaria, and the south of the Volga region. Wild varieties grow freely in northern India and China, mostly on gentle slopes and in mountainous gorges.
Uses of walnut
Walnut makes hair color more saturated. Walnut leaf extracts are included in tanning products and hair dyes. Green fruits are sometimes used to dye brown and chestnut colors. Decoctions from the leaves have an astringent, bactericidal and fungicidal effect.
The oil obtained from its fruits, that is, nuts, is used in the food and cosmetic industries. It can be used as a body oil, for example for massage.
Walnut oil is one of the most valuable vegetable oils and is used to produce high quality soaps, inks and oil paints. The nuts are also used to make halva, ink and oil paints. The nuts are used in the production of halva, ink and oil paints.
- Walnuts have been widely used in folk medicine. The nuts themselves were once popular as a vision enhancer.
- An alcoholic tincture of green fruits and leaves was used for skin tuberculosis, and aqueous extracts were used for external bleeding, as well as for the treatment of diabetes, gout, exudative diathesis, and gastroenteritis.
- The leaves were also considered an insect repellent. It was used externally for compresses and rinses, as well as for ulcers and burns. An infusion of the bark and root was also used as a mild laxative.
The tree itself is used for the production of plywood, furniture, parquet, for turning products, for wood carving, for musical instruments, inlays, small fittings, and picture frames.
Benefits for the body
Thanks to its vitamin composition, the Far Eastern product helps to have a beneficial effect on the body. Mineral components relieve symptoms of many diseases, replace medications, and prevent the subsequent appearance of pathologies. What medicinal properties of the Manchurian walnut, its leaves and seeds when used can be noted:
- Relieves pain and has anti-inflammatory properties.
- Helps remove fungal infections.
- Has an antibacterial effect on open wounds and cuts.
- Dilates blood vessels and benefits the heart.
- Improves stomach function, removes toxins from the body.
- Strengthens human immunity in winter, prevents the occurrence of vitamin deficiency.
- Improves skin condition, fills it with moisture, and prevents aging.
- Restores hair structure, removes split ends and dullness, and gives curls a healthy shine.
- It has a preventive effect on cancer.
Manchurian nut has a general strengthening effect on the body, increases performance, and improves mood.
Manchurian walnut leaves - benefits
Due to the disinfecting and astringent properties of the leaves, they are excellent for compresses used in the treatment of such diseases:
- wounds that take a very long time to heal;
- boils;
- calluses;
- skin rash;
- fungal diseases.
Fresh and dried leaves are used in the preparation of oral decoctions that successfully combat the following diseases:
- stomatitis;
- gingivitis;
- periodontal disease
Tree diseases
Walnuts are often affected by the fungus Gnomonia leptostyla, which causes a serious disease called anthracnose. Anthracnose appears as yellowish, brownish round spots on the leaves.
- Initially, spots appear on the tips of the leaves.
- The spots then spread further.
- The infected surface dries out.
- Fungi appear on the underside of leaves.
- The fruit also has indented brown-black spots.
- Early infected fruits die.
Most infected fruits drop prematurely. The disease can be controlled by collecting and destroying infected fruits and leaves on which the fungus appears.
Reproduction
The most productive method of tree propagation is by seed. The seedlings obtained in this way are more easily adapted to the local climate and soil.
Before germination, ripe nuts are stratified . If the shell is thick, store at 0–5 °C for three months. Thin-shelled - at +10–12 °C for about 1.5 months. The material is then placed in wet sand for 1–2 weeks. When the valves open and the beginnings of sprouts appear, the nuts are planted in the soil to a depth of 10–12 cm. This is done when the soil warms up to 10 °C. When sowing large quantities, linear trenches are dug, placing the seeds 15 cm apart. To prevent young shoots from dying from the cold, they are transferred to greenhouses in the fall. After 2–3 years, the seedlings become suitable for open ground.
In warm regions, walnuts are propagated by grafting, placing a cut shield of the desired variety under the bark of the rootstock.
Photo of walnut tree
Contraindications
Despite a number of useful properties, the product has its contraindications and harmful properties. Who does not eat the product:
- Patients with allergies to substances in the composition.
- People with acute stomach ulcers.
- Hazel fruits are contraindicated for obese people.
During pregnancy and lactation, you should consult a doctor before consuming Manchurian nuts. What harm can the fruit cause to the body:
- Nausea, urge to vomit.
- Diarrhea, bloating, severe pain and colic in the abdomen.
- Irritation and rashes on the skin, excessive tearing, runny nose.
- General weakness, drowsiness, apathy.
Manchurian nut, the benefits and harms of which have been known since ancient times, can lead to intoxication of the body. If the above symptoms appear, you should think about poisoning and urgently consult a doctor.
Where does it grow
Manchuria, the forests of northeast China, is considered its homeland. The range extends to the Korean Peninsula, Taiwan, and the Russian Amur region. Thanks to successful cultivation, walnut plantations are found in the Southern Urals, near Moscow, in the Leningrad and Arkhangelsk regions - right up to the Solovetsky Islands. Single copies are found in many countries.