Oak symbols
Oak is a mighty strong tree, a symbol of courage, fire, lightning and princely power. Oak is one of the most beloved and revered trees among European peoples. All the most important events took place among the Slavs under the sacred Oaks - meetings, wedding ceremonies, courts. In the sacred Oak groves, the oldest and most respected trees were surrounded by a fence, beyond which only priests could enter.
In prehistoric times, almost half of Europe's forests were oak forests. The man famously dealt with this wonderful tree. First, he cut down and burned the Oak , freeing up the land for arable land, and then chopped it down for firewood and building materials. Oak, unfortunately, was excellent for both. The result is sad - there are tens of times fewer oak trees (about 3% of all European forests).
Spring forest
The road lay in the Ryazan province, it was necessary to check the affairs in the son’s villages. The spring of 1809 turned out to be warm, Andrei indifferently looked at the green grass, young buds on the trees, which looked especially beautiful against the background of the bright blue sky.
It was especially warm in the birch grove, there was no wind here, it was getting hot, although earlier the remains of snow could be seen under the bridge. The purple flowers that decorated the meadows instilled faith in spring. The horses were sweating, and the birds and people on the goats rejoiced at the change of season.
The prince did not understand the reasons for human joy. He thought about the oak tree that stood by the road.
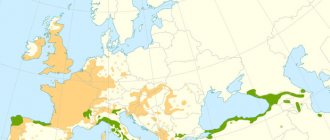
Where does Oak grow?
Oak is widespread in Western Europe and the European part of Russia. It reaches northwestern Russia as far as Finland. In the eastern direction, the northern limit of the Oak's distribution gradually descends to the south, and, approaching the Ural ridge, drops to 57° and somewhat to the south. The Urals are the eastern border of the English oak range.
Spreading
Towards the north it can spread up to and even beyond 60⁰ northern latitude. To the east - to the Urals, although there is documented evidence of survival both in Siberia and the Far East (Kamchatka, village, Milkovo, the oak tree near the house of the head of the administration is already about 30 years old, winter form).
Usually settles along river valleys and large reservoirs. In the hot steppe zone it prefers ravines and ravines. In broad-leaved forests and forest-steppe of Russia, it forms entire oak forests - oak groves. Can be found in Ukraine, Belarus, and the Caucasus.
What does Oak look like?
It is not difficult to distinguish an oak from other trees by its powerful stature.
Oak is a large tree, usually with a powerful crown and a powerful trunk. Reaches a height of 20-40 m. It can live up to 2000 years, but usually lives 300-400 years. The growth in height of Oak stops at the age of 100-200 years, the increase in thickness, although insignificant, continues throughout life.
The Oak crown is dense, spreading, with thick branches.
Oak bark is thick, durable, wrinkled and dark in color in an adult tree.
Oak leaves are oblong with large rounded teeth.
Oak slowly blooms its leaves - sometimes only by the beginning of June. And sometimes - on the second try, when the first leaves are eaten by the caterpillars.
Oak flowers are collected in long hanging earrings 2-3 cm long.
Oak acorns are usually oblong, growing from 1.5 to 5 cm. In summer, acorns are green, in autumn they turn yellow and fall off. The acorns are smooth and neat to the touch, which makes them want to be collected, especially by children. The acorn caps are also beautiful. Inside the oak acorn there are 2 segments of yellowish or reddish color, bitter in taste.
Acorns , the fruits of the Oak tree, sit in special “glasses” - pluses. Wild boars and domestic pigs love to feast on acorns, so already in the Middle Ages people grazed herds of thousands of pigs in oak forests. In Ivan Krylov’s fable “ The Pig under the Oak, ” an ungrateful pig, having eaten acorns, begins to undermine the roots of the tree, harming it. From a biological point of view, the fabulist is mistaken: by digging up the soil and destroying pests, pigs brought only benefits to the oak forests.
Widower, father, owner
Two years passed after the Battle of Austerlitz, Prince Andrei became a widower in Bald Mountains with his little son, father and sister. Sometimes he had to go on business to Kolenka’s estate, since he was the boy’s legal guardian.
Bolkonsky retired from military affairs and became a leading owner. In some villages, the prince transferred the peasants to the status of free cultivators. On other estates he replaced the serfdom of corvee with quitrent. Innovations had a beneficial effect on family income.
In his free time, Bolkonsky read a lot and kept notes on the reasons for the defeat of Russian soldiers in the war with Napoleon. Nothing pleased the soul of the thirty-one-year-old man. The emotional side of life did not fit into his daily routine.
The healing properties of Oak
Oak bark is of great medical importance , as it contains a significant amount (up to 20%) of tannins, as well as flavonoids, pectin, tannin, starch, mucus and other natural antiseptics. A decoction of the bark, due to its tanning properties, has a strong astringent and anti-inflammatory effect.
Oak bark is most valued and used in medicine . It is used mainly as an external remedy, sometimes internally, in the form of infusions, decoctions, and tea.
Oak bark and leaves have astringent, anti-inflammatory, anthelmintic, soothing, and hemostatic effects.
Oak bark infusion is taken for stomach diseases, diarrhea, gastritis, colic, intestinal inflammation, colitis, ulcerative colitis, gastrointestinal bleeding, liver disease, spleen. Warm infusion improves digestion.
Chemical composition
The beneficial and medicinal properties are determined by the components in the chemical composition of common oak. All parts of the plant contain tannins: in young bark - up to 29% (their amount decreases with age), galls (spherical growths on leaves) - 30%, acorns - 5-8%, wood - 4-6%.
In addition, flavonoids (quercetin, etc.), pentosans (13-14%), organic acids - gallic and ellagic (up to 1.6%), triterpenoids, pectins (6%), protein substances, phlobafen, levulin, sugar, mucus, starch. Vitamins are represented by vitamin B1, B2, B6, PP, C. The following macro- and microelements were found in the bark: potassium (1.4 mg/g), calcium (23 mg/g), magnesium (0.6 mg/g), iron (0.2 mg/g), as well as barium (537.12 μg/g), strontium (212 μg/g), manganese (142.6 μg/g), aluminum (116.08 μg/g), boron (74.8 µg/g), copper (12.3 µg/g), zinc (10.2 µg/g), etc.
The chemical composition of common oak acorns is as follows: starch (up to 40%), carbohydrates, proteins, fatty oil (up to 5%), sugars. The leaves contain flavonoids (quercetin, quercitrin), pentosans, triterpenoids, pigments, ascorbic acid (up to 0.2%), etc.
Application of Oak
A decoction of Oak bark and leaves (1:10) is taken for kidney diseases, kidney bleeding, bloody urine, frequent urination (in small doses), and inflammation of the urinary tract.
An infusion of Oak leaves is used for bedwetting (enuresis). Decoctions are also used for rinsing for inflammation of the oral mucosa, bad breath, inflammation of the tongue, for lotions for bedsores, frostbite of the hands and feet (baths), burns, wounds, skin inflammation, eczema, scrofula.
For sweaty feet, make baths from a decoction of the bark (2 tablespoons per 1 glass of water, boil for 1-2 minutes, leave until cool), and also pour crushed bark into socks for the day.
Coffee from Oak acorns: the acorns must be peeled, boiled, drained immediately, then coarsely chopped into pieces and fried until browned. Let cool and grind in a coffee grinder into powder. Brew like coffee, or can be used as a dietary supplement. This drink is given to children with diseases of the cardiovascular and nervous systems.
Traditional medicine recipes
Glaucoma
Burn the oak wood and sift the resulting ash thoroughly.
2 tbsp. pour 500 ml of ash. boiling water Mix. Cover with a lid and leave for a day. Strain.
Take 45 ml. (3 tbsp) three times a day half an hour before meals. The course of treatment is two weeks, then a break of 5 days and repeat the course.
The infusion is also recommended for increased intraocular and blood pressure.
Trichomonas colpitis
Young leaves are ground to a pulp using, for example, a meat grinder. The resulting mass is wrapped in gauze, a tampon is formed, which is inserted into the vagina.
Diseases and pests of Oak
One of the most dangerous diseases of Oak is powdery mildew . A characteristic white coating appears on the leaves, as if they had been doused with soapy water. The disease, noticed in an early stage, is easily stopped by spraying with a one percent solution of copper sulfate .
Leaf-gnawing insects and stem pests such as the large Oak Longhorned Beetle, the Green Oak Leaf Roller, and the Fruit Cap Moth are dangerous for Oak.
Collection of medicinal material
The bark is collected only from young oak trees, and only in the spring, when the active movement of sap in the tree begins.
And when it has a gray-brown color and a glossy texture, without vertical cracks. Oak trees are cut down completely to collect bark, since they will not survive after it is removed from the trunk. Dry the bark in a ventilated area, avoiding an increase in humidity. Bright light during drying is also not allowed. It is also advisable to collect leaves for brewing tanning infusions in the spring or early summer, when they are fully blossomed and formed.
Oak. Interesting Facts
On the leaves of the Oak tree you can see ruddy balls, like small apples , called galls or ink nuts. Galls on oak trees appear due to insects - Nutcracker. They lay an egg in the leaf tissue, and substances secreted by the larva cause the tissue to grow, resulting in the formation of a gall, and the larva receives a safe refuge.
The oak, defending itself from the parasite, deposits a very large amount of tannins
, which with iron sulfate form black paint, which was used in the
manufacture of ink , the same one that A.S. wrote with. Pushkin (!) and his contemporaries, by the way, are very persistent and durable.
Some Oaks live for more than a thousand years, reaching enormous sizes.
Contraindications
In order for the treatment to be beneficial, it is necessary to take into account not only the medicinal and beneficial properties, but also the contraindications of common oak that it has. Internal administration of bark preparations is contraindicated for constipation. The infusion of leaves should not be consumed by children.
Although there are recommendations to drink an infusion of bark for hemorrhoidal bleeding, other sources list hemorrhoids as a contraindication to the use of the drug. Therefore, if you have this disease, it is better not to take risks and consult your doctor.
Although common oak is not a poisonous plant and does not cause complications in recommended doses, nevertheless, when using plant preparations (bark, leaves, etc.) internally, care should be taken to avoid overdose.
So the maximum daily dosage of leaf preparations is two glasses. If you rinse your mouth with a bark decoction for a long time, your sense of smell may deteriorate.
Also, during a course of treatment, oak preparations should not be taken for a long time; breaks must be taken.
Sources:
V.S. Berry. Medicinal plants in dermatology and cosmetology.
V.V. Reshetnyak. Herbalist.
S.Ya. Sokolov, I.P. Zamotaev. Handbook of medicinal plants.
M.A. Nosal i I.M. Nosal. Medicinal plants and methods of their adoption among the people.
L.G. Dudchenko, A.S. Kozyakov. Spicy-aromatic and spicy-flavoring plants.
Rim Akhmedov. Plants are your friends and foes.
Advice from the traditional healer Evdokia. Herbalist, illustrated reference book.
Ivashin D.S., Katina Z.F. Medicinal plants of Ukraine.
I.N. Putyrsky, V. Prokhorov. Universal encyclopedia of medicinal plants.
Maznev N.I. Encyclopedia of medicinal plants.
A. Markova. Herbalist. Golden recipes of traditional medicine.
A.P. Popov. Medicinal plants in folk medicine.
Reproduction
A detailed description of oak propagation methods is described in the article. The culture reproduces with the help of acorns and petioles. Hybrid and ornamental varieties can also be developed by grafting, but this method is considered unconventional.
Most often, oak is propagated using acorns collected from the mother tree and planted directly into the soil in autumn or spring. Acorns are fairly easy to adapt and germinate, so there is no expense involved in getting a healthy, hardened plant. The disadvantage of this type of breeding is the fact that hybrid individuals rarely retain the characteristics of the mother plant.
Cuttings, as a method of oak propagation, are used no less frequently than sowing, since this method is effective and makes it possible to obtain several healthy seedlings at once. The cuttings take root within a short time, then they are ready to be transplanted to a permanent habitat.
Care
Caring for oak is simple - young seedlings need watering and periodic fertilizing with mineral fertilizers. Lack of care for young oak trees often leads to problems when gardeners do not understand why the oak tree does not grow or withers or begins to get sick.
The soil
To plant oak, use soil with neutral acidity or soil with a slightly acidic environment. Plants need feeding, so it is recommended to add some humus to the soil when sowing, mixing it with garden substrate.
Watering
Young oak trees, unlike adults, need regular watering. in the dry season, watering is carried out at least 2 times a week. With age, oak begins to cope with drought quite easily. However, with the onset of autumn, watering is gradually stopped, allowing the tree to prepare for a period of dormancy.
Top dressing
The first year after planting, the plant does not need fertilizing, so they begin to fertilize oak from the second year of cultivation. Mineral complexes are used as spring fertilizer. Manure and other nitrogenous fertilizers are also used as fertilizer. In autumn, a complex of mineral substances is also added to the soil.
Planting at home
Dwarf oak varieties are grown at home, as well as bonsai, which are so popular among gardeners. Small varieties such as northern oak or swamp oak are chosen for cultivation. Growing a decorative bonsai is quite difficult and requires a lot of patience and effort.
Where to plant
The material for planting oak at home is a regular garden substrate, to which organic fertilizers are added. Garden soil mixed with sand and peat, as well as with the addition of compost, is suitable as a substrate.
To grow the crop you will need a sunny area of your apartment or balcony. Indoor oak needs a long stay in a sunny place, but in the hot season and heat the crop is slightly shaded.
How to grow indoor oak
There are several ways to obtain a short indoor tree. The most popular is the sowing of acorns followed by caring for the crop. Another method of cultivation is cuttings, but this method is used quite rarely, due to the long engraftment of branches and low efficiency.
From seeds
It is not difficult to obtain oak bonsai from seeds; for this, acorns are prepared and placed in a loose nutrient substrate. For sowing, ripe and clean seeds are used, which are pre-soaked in water at room temperature. After soaking for a day, the acorns are thoroughly dried.
Acorns are planted in small pots, which are then covered with film. Periodically, the film is lifted and the soil is watered.
After the seedlings sprout, the pots are opened and placed in a bright place. When the seedlings give full roots and reach 15-20 cm in size, the trees are transplanted into deeper containers.
Cuttings
Bonsai, like garden oaks, can reproduce by cuttings. The procedure is carried out in the spring; for this purpose, healthy, strong young cuttings are cut from the mother tree with sharp pruners or a knife. To speed up the rooting process, gardeners recommend making oblique cuts. The bases of the cuttings are placed in a rooting agent and then buried a third of the way into pots of soil. The planting is watered abundantly and then covered with film to create greenhouse conditions.
When the plant takes root and the roots grow, the crop begins to actively develop, and the seedlings are transplanted to a permanent habitat.
How to grow oak in a pot
After the oak tree has matured, gardeners choose the style in which they will grow the bonsai. Many people settle on a classic tree, decorating it with rocky soil or creating the illusion of a garden area. To grow such a tree you will need regular care and timely pruning.
When forming an oak indoors, gardeners regularly prune the shoots of the plant. However, this procedure is carried out very carefully, trying to maintain a dome-like crown. In order not to damage the crop, pruning is carried out carefully, because there is a risk of overstraining the branches:
- When pruning shoots, initially remove large and heavy leaves;
- crown formation is carried out at least once a year;
- when cutting stems, they try to leave thin branches that are more harmonious in relation to the size of the plant;
- trim leaves, new buds and branches;
- Along with large branches and leaves, damaged parts of the plant are also removed.
Proper pruning of oak and regular formation of the same crown leads to the fact that the bonsai takes on a decorative and lush appearance.
When growing bonsai on your windowsill, regular pruning of the rhizome is considered an important condition for maintaining decorativeness. The procedure is carried out in the fall, at the same time as external pruning. Such actions ensure that the health of the crop is maintained.
The roots are pruned when the crop grows strongly. The procedure is carried out as follows:
- the plant is carefully removed from the pot;
- the rhizome is carefully but carefully cleared of soil;
- Using sharp scissors, heavily overgrown and damaged roots are removed, while healthy roots are cut off by a maximum of a third.
Experienced gardeners note that when carrying out the procedure, only the thickest roots are subject to pruning.
Growing seedlings
When growing oak indoors for the purpose of further transplanting into open ground, sowing is carried out in the same way as for growing seedlings. However, such oaks are not subject to mold pruning. The crop is placed in a permanent habitat 3-4 years after planting.
You might be interested in: Flax
Home care
Caring for a houseplant is quite difficult, since oak, in most cases, is a garden plant. Therefore, adherence to a certain regime for oak ensures not only the preservation of decorative properties, but also the health of the crop.
The basics of caring for indoor oak are as follows:
- high-quality lighting - oak requires long exposure to the sun. Some varieties are able to grow in partial shade, but they tend to stretch;
- high air humidity - in order to maintain high air humidity, the plant is regularly sprayed. Gardeners do not recommend placing a pot of oak near heating appliances;
- optimal temperature - for oak grown indoors, it is regularly maintained at 18-23 degrees. In summer, the trees adapt quite easily to garden conditions. During the dormant period, plants are placed in shaded areas where the temperature does not exceed 20 degrees;
- It is recommended to water the plant at least 2 times every 7 days. Ordinary tap water is suitable for oak, but preheated to room temperature.
Oak bonsai needs regular replanting into more nutritious soil. Replanting is carried out every season, since the soil quickly becomes poor. Mineral complexes and organic matter are used as fertilizer.