How long do certain tree species live?
Let's first find out how long trees live under favorable conditions - if the tree grows in “its” climatic zone, without experiencing adverse effects.
Maple
The lifespan of a maple tree can reach 400-500 years. In Russia, such long-livers are rare. For example, the lifespan of the ash-leaf maple, imported from North America, does not exceed 100 years. Spreading tree with noticeable ornately shaped leaves.
Maple seeds can be carried very far - the two-winged fruits, falling, begin to rotate and, caught by the wind, fly away.
The height of maple plantations reaches 15-20 meters.
Beech
Beeches live 400-500 years. Widely distributed in European forests. Characteristic features:
- a smooth trunk that reaches a width of 2 m;
- maximum height – 30 m.
The tree grows slowly, but lives long. Beech has fruits that look like acorns. Moreover, they appear only in trees that have reached 40-50 years of age. Beech nuts have a unique ability to regulate metabolic processes.
Poplar
In nature, poplars grow for about 1000 years. This tree is actively planted in cities and along roads. If poplars have to grow in an unfavorable environment, they live less - 60-70 years.
Poplars can often be seen in industrial areas - they are planted here because of their ability to absorb radiation and harmful substances.
The height of poplars with columnar trunks reaches 35 meters. The leaves are round in shape. Poplar is a dioecious plant; there are female and male species. It is female trees that are the source of fluff, which causes allergies in many city residents.
Oak
Oak lives up to 1000 years. This is a well-known long-liver in our area. English oak (Quercusrobur) grows predominantly in Russia. There are approximately 600 species in the oak genus. Oak is easily recognized by its powerful trunk and spreading crown. Oak can also be unmistakably identified by the following characteristics:
- figured leaf of a uniquely beautiful shape;
- The original fruit is an acorn, which is adored by wild boars and pigs.
The tree is distributed throughout Europe. Oak wood is valued in furniture production.
Hornbeam
The hornbeam lives for about 300 years. It grows in Europe, less so in Transcaucasia and Asia Minor. It has a wide crown. Likes to grow in shaded deciduous forests. Growth is very slow. Belongs to the birch family. The leaves serve as excellent feed for livestock. Hornbeam fruits are used to obtain oil. Tree height – up to 30 m.
Linden
Linden lives on average 300-400 years, in some cases it can live 1000 years. There are many varieties of linden growing in Russia - Amur, Caucasian, large-leaved. The European linden can reach 40 meters in height. This beautiful tree is a source of linden blossom, which is actively used in cosmetology and medicine. Wood is easy to process - due to the softness of the fibers, it serves as an ideal raw material for carving.
Birch
The lifespan of birches is 100-150 years. If conditions are favorable, the tree can live 300 years. The distribution area of birch stretches from French lands to Altai. The most common species is the warty or weeping birch (Betula Verrucosa). Average indicators of birch:
- height – up to 45 m;
- trunk girth – up to 1.5 meters.
The tree has several dwarf subspecies.
A young tree has a completely smooth, light brown trunk. Birch acquires its famous trunk color – white with black stripes – only after reaching 8 years of age.
Birch leaves are small, in the form of rounded triangles, the edges are jagged.
Ash
The average lifespan of an ash tree is 500 years. Its fruits are in the form of lionfish, falling off in winter. It has sparse foliage that allows the sun's rays to pass through well. Peculiarities:
- tree height – up to 30 m;
- trunk width – up to 1 m;
Ash wood is particularly durable, which is why it is valued in construction. Ash bark, its fruits and wood sap are used in medicine.
Elm
On average, elms live up to 300 years. The tree can grow as a shrub. Young trees have smooth bark, which hardens with age. The leaves are elongated, the seeds are winged fruits. The height of the elm is up to 40 m.
It grows on plains and hills, in shady places and in open sunny heath.
Chestnut
Chestnuts live from 200 to 300 years. Differs in original flowers and leaves. The height of the chestnut is up to 35 m. The inflorescences are in the form of cones. In autumn the fruits ripen - they are in a spiky capsule. Painkillers are made from the fruit.
Aspen
Lives on average 80-90 years, rarely lives to be 150 years old. It has a columnar trunk. It reaches a height of 35 m. In diameter - up to 1 m. It burns poorly - it is not valued as fuel.
Alder
The lifespan of alder is about 100 years. This is a unique tree that can improve the soil - it is enriched with nitrogen fertilizers. Raspberries and other shrubs grow well near the alder. Height – up to 20 m.
Pine
The tree lives on average up to 600 years. This is one of the most common trees in the forests of Europe and Russia. Widespread varieties of pine:
- Siberian cedar - lives up to 500 years;
- European cedar - lives up to 1200 years.
Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris) covers over 20% of the territory of the former USSR. Its height is from 20 to 40 m.
Spruce
Lives from 600 to 1200 years - depending on the species. Grows all over the world. There are species that grow in a certain area. They reach a height of 50 m. It has a cone-shaped crown. Seeds appear in the 20th year of life - they are contained in cones.
Fir
On average, they live 300-400 years. Can live up to 700 years. Coniferous plant with vertically growing cones. The tree is evergreen. The needles do not fall off even after the branches dry out. The height of the fir depends on the species.
Yew
Lives from 1500 to 2000 years. Under favorable conditions it can live 3000-4000 years. Yew berry grows very slowly. Height – 10-20, sometimes up to 28 m.
Thuja
Thuja lives 150-200 years. It is classified as a coniferous plant, but it does not have needles. This evergreen tree is unpretentious to soil, so it is one of the most popular ornamental plants. It reaches a height of 2.5 m. Thuja folded or giant can grow up to 6 m in height, thuja occidentalis - up to 20 m.
Juniper
On average, junipers live 200-300 years. There are species of juniper that live 500 years or more. Height and lifespan depend on the species. Maximum height – 8-12 m.
Apple tree
Life expectancy is from 100 years, depending on the species. This tree happens:
- fruity;
- decorative;
- growing wild.
The maximum height is 15 m; there are also low-growing shrubs among the apple trees. Trees vary in frost resistance and moisture needs.
Pear
Lives on average 70 years. Some species can live up to 150 years. Fruiting continues up to 50 years. There are approximately 60 species. Height - up to 20 m. Does not like to grow in places with high groundwater levels. To make the tree live longer, it should be planted at higher elevations
Plum
The plum tree lives no more than 20 years. The tree bears fruit already in the third year of life. Prefers moist soils. Doesn't like drafts. Reaches 15 m in height.
Cherry
The lifespan of cherries is 25 years. Does not grow higher than 10 m. Compact and productive. One cherry bears up to 20 kg of fruit. In wild conditions it lives up to 5 years longer.
Cherries
This heat-loving tree lives 25-30 years. Much more whimsical than cherries. Gives tasty and juicy fruits. It reaches a height of 8-12 m.
Apricot
Lives up to 100 years. It reaches a height of 5-8 m. It is not able to regulate fruiting - because of this, there is an overabundance of fruits. Drought resistant.
Rowan
Lives 50-80 years. It happens that some individuals live up to 200 years. There are 190 species. It comes in the form of a tree and a bush. Height – 8-12 m.
Aspen propagation
It only takes a few days for a sprout to emerge from an aspen seed. However, most of the seeds soon die after falling out of the boxes. In this regard, only fresh seeds that fell into nutritious soil this summer can germinate and form strong seedlings. In order for the seeds to hatch accurately, they need high humidity (rain) and bare soil. And since in the forest the surface of the earth is always covered with fallen leaves and dried grass, seed germination is observed quite rarely.
It doesn’t matter where the aspen grows, in the steppe or in the forest, you can always see a large amount of low young growth around it. If you dig a deep hole near a young aspen tree, you will be able to find a powerful root that extends almost horizontally from the mother tree. Such a plant produces abundant growth, because each root produces 10 shoots, which are located at a decent distance from each other. In the wild, aspen reproduces by seeds very rarely, mainly only by root shoots.
How to find out the age of a tree?
Receiving energy from the sun, trees grow at different rates, depending on solar activity. There are two ways to determine age - accurate and inaccurate, let's consider both.
Accurate – based on tree rings
To determine the exact age of a tree, you must first cut it down. Let's figure out why.
The trunk expands due to the cambium - a special tissue that creates cells in both directions - inside and outside the trunk. How the cambium develops depending on the time of year:
- Spring. The cambium produces cells characterized by large width and narrow walls. Such cells deliver nutrients more efficiently. Fabrics formed in spring have a lighter shade.
- Autumn. At this time of year, the cambium produces thick-walled cells that give the wood increased strength. The autumn layer differs from the spring layer in being darker in color.
By the number of stripes - light and dark, you can find out the age of the tree. To accurately determine the number of years lived, experts use:
- microscope;
- dyes.
If the dark stripe is wider than usual, it means that the tree survived a cold autumn and a long winter that year.
By the number of dark and light rings you can determine:
- how old is the tree;
- in what climatic conditions did the tree grow?
Inaccurate - based on indirect evidence
But how can you find out the age of a tree without cutting it down? In this case, a calculation is used based on average statistical indicators:
- Determine the circumference of the trunk at a level of 1.5 m from the ground.
- The resulting value is divided by 3.14 - the number “Pi”. The result obtained is the diameter of the trunk.
- The diameter is divided by the average annual growth of a particular tree in the region under study.
The result obtained is not accurate; the error may be 20-30%.
Advantages of planting aspen in a summer cottage
In villages, aspen trees outside the yard are a frequent visitor. It is not particularly bothered by shade and also grows well in the sun. People's beliefs speak of the ability of this tree next to the house to protect residents from evil spirits and negative energy. This belief is based on diseases affecting the tree trunk. If a tree is sick, it means it attracts all the bad things to itself - such conclusions were drawn in the villages.
Aspen forest on the canvas of I.I. Levitan
Today, the importance of aspen is consigned to history, and this tree is planted in the countryside for beauty and to improve soil fertility.
Soil improvement
All the leaves that this tree sheds in the fall decompose very quickly, increasing the looseness of the soil and turning into humus. Experienced gardeners know that aspen trees should be planted on clay infertile soils, because with its strong, deep roots the tree helps other plants and trees subsequently develop such soil.
Landscape design opportunities
Aspen trees are actively planted within the city as landscaping.
These trees hold back gusts of wind well and strengthen the banks near reservoirs. Even representatives of the fauna of the steppe zone are not particularly willing to penetrate the forest if an aspen tree grows on its border. If aspen is used as a material for landscape design of a holiday village, it is done not only because of the decorative qualities of the tree, but also because a number of aspens are fire-resistant plantings: the tree does not burn well. Decorative features boil down to the rapid leafing of the tree after pruning and beautiful autumn foliage. Breeders have developed several hybrids that have a pyramidal shape or weeping tiers.
Autumn alley of aspens
Tree life tables
The average lifespan of some deciduous trees is given in Table 1.
Table 1
| Name | How long does a tree live (average/maximum), years |
| Gray alder | 50-70 (150) |
| Black alder | 100-150 (300) |
| Aspen | 80-100 (150) |
| Birch warty | 150-300 |
| Common ash | 150-200 (350) |
| Smooth elm | 150 (300-400) |
| Rough elm | up to 300 |
| Small-leaved linden | 300-400 (600) |
| Beech | 400-500 |
| English oak | up to 1500 |
| Maple | 100 (300-400) |
| Poplar | 100 |
| Hornbeam | 300 |
| Ash | 300 |
| Elm | 300 |
| Chestnut | 300 |
The average lifespan of some common coniferous trees is summarized in Table 2.
table 2
| Name | How long does a tree live, years? |
| Norway spruce | 300-400 |
| Blue spruce | 400-600 |
| European larch | 400-600 |
| Siberian fir | 700 |
| Common juniper | 500 |
| Scots pine | 100 |
| European cedar pine | 1000 |
| Siberian cedar | 1000 |
| Thuja occidentalis | 150-200 |
| Yew berry | 1500-2000 |
The average lifespan of fruit trees is summarized in Table 3.
Table 3
| Name | How long does a tree live, years? |
| wild apple tree | up to 200 years |
| Homemade apple tree | 100-120 |
| Plum | 15-60 |
| Pear | 150 |
| Peach | 5-20 |
| Apricot | 100 |
| Rowan | 80-300 |
| Cherries | 25-30 |
| Cherry | 20-25 |
Features of wood processing
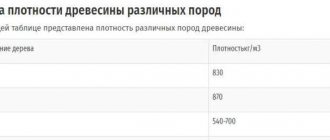
If you look at an aspen trunk in a cross cut, you can see that the wood has a nuclear-free structure. In general, the wood is soft compared to other deciduous trees, its density is 400-500 kilograms per cubic meter (with a humidity not exceeding 15%).
Aspen timber, like other lumber, is capable of absorbing large amounts of water, both in the atmospheric air and under water, which is a negative characteristic of this wood. Aspen wood dries slowly, over several months; when dried, it practically does not crack and does not change its original shape (does not warp). Dried wood splits easily in the longitudinal direction. In the outer part of the trunk, the wood has a high density, so wear rates during operation of aspen products are high.
The humidity in the central part of the tree trunk is much lower than in the peripheral areas. Lumber manufacturers take this feature into account when organizing the drying of timber and round timber.
This wood can be easily processed with mechanical and sharp hand tools, it is easy to saw and cut, it is easy to peel, split and mill. It is easier to process wet, not completely dry wood. When polishing wood, it is not easy to achieve a good smooth surface, although it is uniform and there are no obvious annual rings or knots in the wood. Aspen takes well to impregnation and staining. Dried wood is not difficult to glue; it can be used to make furniture, the parts of which are connected using screws or nails.
What affects lifespan?
The main factor influencing the lifespan of a tree is its type. Thus, fruit trees live the shortest - their lifespan is calculated in decades. But deciduous and coniferous trees can live for hundreds and even thousands of years - they are the basis of the “evergreen” forests of our planet.
Coniferous trees
Coniferous trees have a longer lifespan than their deciduous counterparts. Reasons for longevity:
- Representatives of coniferous species tolerate harsh climates more easily.
- Unpretentious regarding soil. They can grow on poor sandstones and clayey soils.
- Thanks to their branched root system, coniferous trees are hardy and absorb water from the soil well.
- Thanks to the special shape of the crown, they receive maximum solar energy even at high growth densities.
- The needles, unlike the leaves, have a small surface area and are covered with wax - this helps retain moisture in it.
The lifespan of coniferous trees can be influenced by the following factors:
- Genetics. Each plant has certain adaptation capabilities.
- Soil characteristics have a much smaller impact than on the growth of deciduous trees.
- Humidity and temperature have little effect - coniferous trees grow in their familiar environment. Their lifespan can only be affected by global climate change.
- Terrain – plain, slopes, mountains. The strength and direction of the wind depends on it.
- Forest density - coniferous trees are minimally affected, since their crowns are adapted to difficult conditions.
- Diseases and pests . Fungal and bacterial infections can significantly reduce the lifespan of any tree.
Deciduous trees
The lifespan of deciduous trees can vary greatly, even within the same species. The following factors may influence lifespan:
- Soil characteristics - its density, composition, saturation with nutrients and microelements.
- Climatic conditions - humidity, average annual temperature, wind strength and direction, other indicators.
- Surroundings – how close neighboring trees grow. If the growth density is high, then only the strongest individuals live long.
- Insects and other pests.
- Location – natural environment or urban conditions. It is clear that in a city where the air is polluted, trees live less.
Fruit trees
The lifespan of fruit trees is affected by:
- Type of fruit tree.
- Soil quality and fertilizing.
- Pruning, treatment, winterization and other care activities.
- Destruction of pests, especially bark beetles, which can destroy a tree in a couple of years.
Why, despite increased care, do fruit trees live so short? Large harvests are expected from fruit trees. By artificially accelerating the growth of a tree, a person forces the tree to waste its resources - it, having used up its reserve of strength, weakens ahead of time and dies.
A variety of coniferous trees
Coniferous plants live much longer than deciduous trees. This is explained by lower metabolism and serious ability to adapt to harsh climatic conditions. The shape of the crown of a coniferous tree allows you to extract the maximum amount of energy that the sun can provide.
A highly branched root system also helps to survive, as well as the fact that even in winter the needles continue to produce nutrients, albeit in minimal quantities. At the same time, the roots are able to get minerals and water even from frozen ground. In this case, the needles are covered with wax, which prevents water from evaporating.
Fir is the shortest-lived plant among conifers and can exist for up to 2 centuries. Spruce and pine, common among us, live up to 600 years. European larch lives up to 500 years, and its Siberian counterpart lives up to 900 years (a clear example of the influence of low metabolism). Cedar pine lives up to 1000 years, but the main long-lived tree is the sequoia, which lives on average 5 thousand years.
The oldest trees
Given favorable conditions and appropriate genetic capabilities, some trees can live for thousands of years:
- Pine Methuselah. The record holder for centenarians is growing in the western United States. Its location is California, National Forest, White Mountains. The tree is located at an elevation - 3000 m above sea level. Its exact location is a mystery. The staff of the reserve protect the tree from tourists who will definitely want to cut off a piece of bark from it or take a photo with it. The old tree needs peace.
The age of the Methuselah pine is 4580 years. This is the oldest tree on the planet.
- Sequoia General Sherman. Location: USA, California, Sequoia National Park. This is the oldest and tallest sequoia in the world. Her age is 2300-2800 years. The height of the tree is 84 m. In girth it reaches 31 m - at the base. The tree is always full of tourists.
The oldest sequoia in the world continues to grow - every year it adds 1.5 cm in girth.
- Skhtorashen plane tree from Nagorno-Karabakh . Its age is 2000 years. The height of the plane tree is 54 m. At the base there is a giant hollow, its area is about 45 square meters. m. Plane tree leaves reach 50 cm in length. Crown area – 1.5 thousand square meters. m, so the old plane tree is visible to astronauts in orbit.
- Chestnut "Tree of a Hundred Horses" . Grows on Mount Etna, Sicily. The girth of the trunk is 58 m. Its approximate age is 2000-4000 years. The relic chestnut tree is located 8 km from the crater of the volcano; how it managed to survive so long is amazing!
- Cypress "Zoroastrian Sarv". Location: Yazd province, Iran. Age – 4000-4500 years. It was then, scientists believe, that the wheel was invented.
- Yew in the village of Hyangernyf, North Wales. Age – 4000 years.
- El Tikko. This tree is a clone of an old spruce tree, which is 9500 years old. Or rather, this is the age of its roots. The current spruce trunk is several hundred years old, its height is only 5 m. When the relict tree died, its roots sprouted.
Video about long-living trees. Watch an interesting video about the five oldest trees in the world:
Table 4 shows the life expectancy of long-lived trees:
Table 4
| Name | Average life expectancy, years |
| Sequoia | 5000 |
| Baobab | 5000 |
| Yew | 3000 |
| Cypress | 3000 |
| Cedar pine | 1200 |
| English oak | 1000 |
| Silver poplar | 1000 |
| Sycamore | 1000 |
Trees are priceless - they are the beauty of our planet, clean air and a source of all kinds of benefits. It takes years before a tree grows. The task of man is to increase natural and artificial plantings. When planting trees for a specific purpose - decorative or economic, it is useful to know how many years it will decorate your garden, yard, city, world.
0
0
Copy link
Application and significance of aspen
In the forest zone, both beavers and moose readily feast on aspen leaves and its young branches. Rot often forms inside its trunk in the core, in which, as a rule, a variety of pests live. Woodpeckers use them as food. If necessary, a woodpecker can hollow out a hollow in an aspen trunk, where it then lives. Old hollows can be used by various forest inhabitants to build their nests, for example: starlings, bats, owls and tits.
The opening of aspen flowers is observed in April. They attract large numbers of bees. The fact is that a large amount of pollen is formed on the inflorescences, which is processed into bee bread. Bees also collect glue from opening buds, which they use to produce propolis.
In ancient times in Rus', such wood was quite widely used in everyday life. Its wood was valued for the fact that it did not swell or rot in damp conditions, so it was often used to make well frames, cellar walls and various outbuildings. Logs were used to make matches and wood chips. The bark was used to extract tannins, and also to produce tar and vinegar. The remaining ash from the burnt bark was used to paint canvas, while the wood was used to produce green and yellow colors.
Aspen wood lends itself perfectly to carpentry, while the lumber practically does not crack and splits easily. Products made from it are resistant to abrasion. Also, high-strength shavings are obtained from aspen, characterized by excellent flexibility, which are used for a wide variety of weaves. The hardness of such wood is 1.86 Brinell, and its density is approximately 490 kg/m3. Aspen is also used for firewood, and it is valued in the same way as oak or birch. Its calorific value is approximately 1700 kcal/m3.
Traditional Khokhloma products are dishes made from aspen wood. It was also used to make flat planks, which were used to create the external cladding of residential buildings and church domes. If untreated aspen wood is exposed to the open air for only 2 or 3 years, then this will be enough time for it to acquire a pale gray color naturally. In addition, such wood is used to produce cellulose, plastics, methyl alcohol, viscose fiber, plywood, acetone, etc.
Aspen. Useful properties of aspen bark.
Average lifespan of a tree
There is no average indicator for absolutely all trees, since it depends on the growing conditions of a particular specimen and its type. But the lifespan can be given approximately, focusing on the botanical classification (Figure 1).
So, the duration of the life cycle for representatives of certain groups will be as follows:
- Fruit: among this group, wild apple and pear trees, which are found in forests, are considered to be the longest-living ones. Their wood does not rot, and the tree itself continues to bear fruit for 100-150 years. This figure is true for central Russia, and in regions with a mild climate the lifespan may be even longer. Peaches and apricots grown in our latitudes live no more than 20 years, but in Turkey and the Caucasus their lifespan can reach 100-300 years, respectively.
- Conifers: Live much longer than hardwoods. For example, larches whose age is estimated at 500-600 years have been discovered in Siberia, and in China there is a tree whose age is estimated at 1300 years. The common pine lives the shortest (about 100 years), although this period can be considered very impressive.
- Wild deciduous trees: among the representatives of this group there are also real long-livers. For example, in Europe, summer oak is found everywhere, which can successfully exist for up to one and a half thousand years, although ordinary oaks quite successfully live up to 500-600 years. Sequoia and baobab are also real record holders. For them, the average is 5 thousand years. In our forests, such long-livers are rare, although ordinary birch, ash or hornbeam can live up to 300 years under certain conditions.
Figure 1. Duration of existence depends on the specific type of tree
Given such impressive indicators, it becomes interesting how scientists determine the age of a particular tree, and what the duration of the life cycle of a particular specimen may depend on.
Which tree lives the longest on Earth: name, description
As you already understand, there are not very many long-living trees on our planet, and most likely, all of them are already known to mankind. Despite the fact that it is quite difficult to determine the age of a tree with an accuracy of one year, scientists still single out one winner in terms of life expectancy on Earth.
- So, primacy was given to the previously mentioned “Methuselah”. "Methuselah" is a specimen of bristlecone pine that was found and named by two scientists in 1957 during an expedition in the United States. On the same day, scientists calculated the age of the spruce and came to the conclusion that it lives 4789 years.
- It is worth noting that Methuselah did not immediately receive the title of the oldest tree, since at the time of its discovery, a tree older than it was growing on Earth. The long-lived tree was a pine called “Prometheus”.
Prometheus was the oldest tree
- Unfortunately, at the age of 4862 years, “Prometheus” was cut down, and the championship passed to “Methuselah”.
- Interestingly, the tree got its name in honor of the biblical long-liver Methuselah, who lived 969 years. There is information that the centenarian conceived his son at 187 years old.
- Another interesting fact is that not a single employee of the reserve where Methuselah grows will ever tell you its exact location. At the same time, no one forbids you to look for it and, if found, inspect it, but tearing pieces from the oldest tree in the world is strictly prohibited.
Tree care
Proper tree care involves choosing the right place to plant it and watering it. The plant is planted in the ground in the form of seedlings or seeds. Seedlings are transplanted in the spring to give them time to take root in a new location. Aspen is not picky and quickly takes root. It is planted away from residential structures, since due to the early appearance of rot in the trunk, the tree can easily collapse. The fluff during flowering causes an allergic reaction in some people.
Aspen seeds
The distance between each planting hole must be at least 2 meters. Otherwise, instead of trees, the seedlings will grow into a single bush. The recesses themselves should be shallow.
It is important to have an additional drainage layer of 8-10 cm from crushed stone or pebbles. With its help, the soil will retain moisture and create favorable conditions for aspen growth.
For the full development of seedlings, it is worth ensuring:
- correct choice of soil. Fresh, fertile and well-draining loamy or sandy loam soil is suitable;
- regular watering of the plant. Artificial cultivation of aspen requires periodic soil moisture. During dry periods, watering should be plentiful. The tree cannot tolerate dry soil;
- feeding It is applied at the stage of transplanting seedlings or planting them in the ground. Subsequent application of fertilizers is not required due to the powerful and well-developed root system. More often, mullein is used in a ratio of 1 kg per 20 liters of water and superphosphate - 20 g per the same amount of liquid;
- pruning thick branches from February to April. Young branches can be cut all year round;
- cutting down mature trees over 50 years old. Young shoots quickly appear around their stumps.
The soil at the site where the seedlings are planted needs additional loosening and weeding. Proper care will accelerate the growth of young aspen and its healthy development in the future.
What is the difference between aspen and poplar
If necessary, it is quite possible to distinguish aspen from poplar by certain characteristics, for example:
- At the beginning of the autumn period, a branch with buds that have not yet awakened is picked from aspen and poplar. Their lower part must be immersed in water in a glass. The poplar will be the first to begin to grow and open its adhesive leaf plates. The aspen branch begins to grow later, and its foliage does not have such a noticeable shine.
- The aspen is the first to bloom, and the poplar a little later. In this case, only on the poplar branch will a large amount of fluff be formed.
- Poplar has short leaf petioles, while aspen has longer leaf petioles, and they can easily be tied into a knot.
- Poplar branches are distinguished by their elasticity, which makes them extremely difficult to break. Aspen branches are more fragile, and breaking them will not be difficult.
- The foliage of these trees has a lot of similarities. However, the shape of the poplar leaf blades is more elongated and more pointed at the top.