The density of wood is one of its most significant physical characteristics, which largely determines the suitability of the species for certain jobs. Every carpenter, joiner, turner and woodcarver has noticed the difference between linden and ash, as well as how his tool copes with them. Experienced craftsmen, only by twirling a piece of wood in their hands, can guess how it will bend, whether it is worth taking up processing with hand tools and what loads the resulting product can withstand. Density affects all this, but what kind of indicator is it and how is it determined?
How is the density of wood calculated (kg/m3)
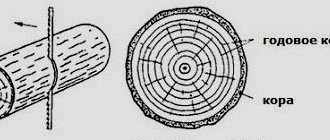
Density for any material is the ratio of volume and mass, or rather, an indicator of how much mass fits into a specific volume. In the case of wood, this indicator is not so easy to calculate, since it depends on the structure of the tree.
Wood is a heterogeneous material that consists of porous fibers. The pores may contain water or air, and this already significantly affects the weight of the wood and its density.
It is obvious that water is much heavier than wood, and air, on the contrary, is lighter. Therefore, dry wood will be much lighter, and therefore less dense, than wet wood.
Wood moisture content depends on many factors:
- Air humidity;
- Storage conditions;
- The date when the tree was cut down;
- The structure of the fibers of the tree itself;
- Age of the tree;
- The presence of resins in wood, as they prevent the absorption of moisture;
- Wood absorption, that is, the properties of a particular wood to absorb moisture.
Thus, a freshly cut tree will always be wetter than even the log that was lying on the ground next to it. Before any processing, the wood undergoes special drying.
But even after drying, the moisture content of the wood, and therefore the density, can change. Therefore, density is measured on dry wood.
There are several types of humidity:
- A wet tree with a moisture content of more than 50% is all freshly cut trunks. There is no point in measuring the density of such materials.
- Damp wood with a moisture content between 35-50% will be damp. These are, as a rule, felled trunks that have lain for some time in natural conditions.
- Semi-dry wood with moisture saturation in the range of 25-35%. These are materials that are kept in natural conditions in dry weather under a canopy.
- Dry wood has a water content of 12 to 25%. This is wood that has been dried indoors or industrially. It rarely deforms and is easy to transport.
- Absolutely dry wood, the moisture content of which is less than 12%. This wood is dried industrially and is used for construction and the production of furniture and crafts. It is this kind of wood that has its calculated density measured, which is then taken into account in any indicators.
To determine the density parameter, the following method is used: mass is multiplied by humidity, this number is divided by volume and again multiplied by humidity. Density is calculated in several parameters:
- Grams per cm cubed;
- Kilograms per meter cubed.
Important! Wood with high absorption will always be denser, since after drying it in any case takes moisture from the atmosphere and is saturated with it.
Oak
Oak wood is distinguished by its strength, strength, density of 720 kg/m3, hardness and heaviness.
An oak lives on average 1000 years. The trunk diameter can exceed 2 m. The older the tree, the higher the quality of its wood.
Our ancestors built wells from oak wood - the water in them did not “bloom”, it was cold and clean. In peasant farming, an oak table and an oak mortar were considered the best. Rims and runners were bent from oak, barrels, tubs, and bowls were made. Oak piles were also driven into the river.
Oak wood is very durable and difficult to cut. It bends well. It has a beautiful coarse texture. Easy to paint. When cut radially, the texture of an oak board is very beautiful. When processed with a chisel, it is fragile, requires a hard and sharp tool and caution, and withstands large threads well. For joinery it is necessary to use oak aged 150-200 years.
What does wood density affect?
The density of wood affects many more factors than it might seem at first.
What does wood density affect?
- Volumetric weight of the material, which is important for transporting and storing the material, as well as for calculating the final weight of the product. For example, a house made of oak timber and a house made of birch will require different foundations.
- Thermal conductivity. The lower the density, the lower the thermal conductivity, since the wood fibers contain more air space. So, less dense varieties are important for arranging a bathhouse.
- Flammability of the material. Less dense wood burns better because it contains more oxygen within itself. So birch and spruce will burn faster than oak or beech.
- Susceptibility to rotting. The denser the material, the less bacteria and fungi will spread in it. For dense wood, moisture content in the fibers is normal. It is for this reason that wood is often soaked in salted or distilled water, which makes it more durable.
- Stability. Denser material is stable with changes in air humidity - it does not swell when humidity rises and does not crack when humidity drops sharply.
- Possibility of processing. Denser wood is more difficult to carve.
The density of wood will help you make the right choice of species for specific purposes. For example, unloading costs vary depending on the type of wood, due to density and weight. The cost of creating carved products also depends on the type and density of the material.
What is the best firewood for burning?
Oak firewood is considered the most optimal in terms of calorific value, followed by birch, aspen and pine.
- Oak contains few resins, but emits a lot of carbon monoxide. The tart aroma of burning oak logs tones the body.
- Birch firewood burns for a long time and evenly, but has a lot of resinous substances and deposits soot in the chimney.
- Conifers are also used less frequently due to their high resin content.
- It is not recommended to use firewood from poplar, as it emits an unpleasant, bitter odor and produces little heat.
It is best to use hardwood firewood, which has a high specific gravity. It is advisable that the firewood be dry and not freshly cut. Let us remind you that when buying wet firewood, you pay more for weight, but get less heat.
Types of wood densities
All wood species are conventionally divided into three main groups according to their density. This takes into account different types of tree species and the structure of their fibers.
The density of wood often affects its value. Dense rocks have a higher price, as they are the most durable. But at the same time, even among inexpensive materials, you can choose a suitable option, taking into account its properties in everyday life.
Small
Low density is primarily characteristic of those trees that grow very quickly and are unpretentious to soils. The low density of wood ranges from 300 to 540 kg per cubic meter. meter. This group includes the following tree varieties:
- Spruce – 400-500
- Pine – 400-500
- Alder – 380 – 500
- Walnut – 450 – 600
- Willow – 460
- Linden – 320- 560
- Fir – 390 – 430
Varieties that grow in northern latitudes often have low density.
Average
This type of wood has a golden mean. This material is not too heavy, but not too soft either. It has low thermal conductivity, is easy to process and does not burn much.
This group includes trees with a density ranging from 540 to 750 kg per cubic meter:
- Birch – 600
- Beech - 700
- Elm – 670-710
- Chestnut – 560
- Cedar – 580 – 770
- Cypress – 600
- Ash – 660-700
As you can see, some types of trees can have different densities, depending on the variety.
High
Tree species that grow in southern latitudes usually have high wood density. Trees with a high density of sapwood and heartwood usually grow for a very long time, which is why they are considered very valuable. Their density is above 740 kg per cubic meter.
These types of wood include:
- Promotion – 830
- Bamboo – 870
- Wenge – 900
- Hornbeam - 820
- Oak – 900
- Larch – 950 – 1020
- Olive – 900
- Sandalwood – 900
- Plum – 800
- Ebony – 1100
Knowing the standard density of wood, you can choose the required species for construction, creating furniture, and finishing various rooms, including wet ones.
At the same time, you will be able to avoid overpaying both for the tree itself and for its transportation, unloading or processing.