Watching this or that tree growing in the garden or walking in a forest among green spaces, we rarely think about their age. But some tree species can outlive humans for several generations.
Marvelous? Yes, that's Mother Nature. Having created favorable conditions for development for its “brainchildren,” it is not without reason that it creates one species at one end of the planet, and a completely different one at the other. After all, the lifespan of representatives of the plant world, including trees, directly depends on their habitat, that is, on whether it is related or whether it is necessary to adapt to it.
Maturation cycle
Oak is a tree that belongs to the evergreen plant species. Its crown may not change for several years. However, there are breeds whose leaves fall off with the onset of the first frost. The inflorescences of the tree are unisexual and small. It is worth noting that the crown cover is poorly developed during pollination. Only female flowers are strong; male catkins can fall off at the slightest breath of wind. It is noteworthy that oak is a tree whose pollination requires scales from two sexes at once. The ripening of the fruit occurs in a roller, which is a small saucer. Subsequently, an acorn grows in it. Each type of oak tree has different fruits and ridge shapes. In some species, acorns are elongated, in others they are round and small, in others they are nut-shaped. It is allowed to cross breeds, but this will most likely lead to a noticeable reduction in yield.
The tree grows extremely slowly, but can live for hundreds of years. The root system is formed during the first year, then constantly develops. It is interesting that after cutting down an oak tree, powerful shoots sprout abundantly from the stump after some time. Oak is a tree that is not too picky about soil, so the soil can be anything. Natural reproduction occurs by acorns. The height of the oak tree varies up to 40-45 meters. The volume of the crown depends on the breed and climate.
Factors affecting the lifespan of a tree
The main factor influencing the lifespan of a particular tree is the botanical species to which it belongs.
For example, fruit trees live the shortest - on the order of several decades. Coniferous and deciduous wild species are real long-livers, because they grow quite successfully for hundreds and even thousands of years (Figure 3). Since the lifespan of different species varies, it makes sense to consider the factors that determine the lifespan of certain tree species.
First, let's look at conifers and find out what factors can affect the duration of their existence:
- Soil: coniferous crops adapt much better to growing on poor soils and tolerate harsh climates more easily than deciduous trees.
- The nature of the terrain: the strength and direction of the wind depends on this. Accordingly, a pine tree growing on a plain will live much longer than a similar tree in the mountains.
- Diseases and pests: can weaken any crop and significantly shorten its lifespan.
In general, conifers live longer than deciduous trees for several reasons. Firstly, they have a very branched root system that can absorb moisture even from the deepest layers of soil. Secondly, they have a special crown shape, thanks to which the tree receives a sufficient amount of sunlight even in a very dense forest. Thirdly, the needles themselves play an important role. Its surface area is small, and each needle is covered with a special waxy coating. Falling to the ground in a dense layer, it helps retain moisture in the soil.
Deciduous trees live less than conifers for the following reasons:
- Soil nutrition: representatives of this group are very sensitive to the level of soil fertility and nutrient content in it. Accordingly, a tree will live much shorter on poor soils than on nutritious soil.
- Climate: humidity level, average annual temperature, wind strength and direction also play an important role.
- Forest density: the more trees are concentrated in one place, the shorter their life expectancy will be. In such cramped conditions, only the strongest specimens can survive.
- Location: We are talking about whether the tree grows in a forest or in an urban area. Naturally, in a city with high air pollution, the life expectancy of the crop will be much shorter.
Fruit trees live the least in gardens. But, if the gardener carries out pruning on time, feeds the crops and treats them for diseases and pests, then the lifespan will be several decades.
The question arises: why do forest deciduous trees live so much longer than garden trees? It's very simple: artificially accelerating the growth of fruit crops and stimulating high yields forces the tree to spend all its energy and nutrients on ripening the fruits. Naturally, in such conditions, a culture simply cannot accumulate enough strength for long-term existence.
Description of English oak
This type of plant is considered to be ordinary, since it is the most common in the European part of the planet. An oak tree sprouts from an acorn in just six months. Then, over the course of 20 years, its trunk, crown and roots are formed. The oldest trees reach a height of 50 meters. The trunk and branches are thick, powerful, and can withstand even heavy winds. Under moderate conditions and a developed root system, pedunculate oaks can live up to 1000 years. The bark is dark brown, thick. The leaves are oblong, grow in bunches, have from 3 to 7 blunt lobes with slight teeth. Such trees bloom in late spring. Common oaks love the sun very much, as they are a heat-resistant plant. Acorns are up to 3.5 cm long.
When is it necessary to uproot old trees?
Field dog: brief description, fighting features and lifestyle
Trees are the lungs of our planet, which is why it is so important to preserve green spaces as much as possible. Unfortunately, sooner or later any tree ages and dries out irrevocably, and it has to be uprooted
Of course, owners of private houses try to keep trees alive for as long as possible by carrying out anti-aging pruning and proper care. But, if these procedures do not help, it is better to cut down the old trunk and plant a new young tree instead.
Foresters do much the same thing: they cut down only completely dry trees, and annually replenish the green spaces with new specimens. This is the only way to preserve a green forest and get rid of possible problems in the form of diseases that old trees can cause.
Features of downy oak
Most often, representatives of this breed are found in Transcaucasia, Crimea, as well as in Asia Minor and southern Europe. The trees reach only 8-10 meters in height. They are durable and heat resistant. It must be said that such oak species are significantly inferior to many other varieties in height. But they have a very winding thick trunk with spreading branches. Due to its small size and wide crown, the plant often resembles a large shrub from a distance.
The length of the leaves sometimes reaches 10 cm. They are variable in shape, grow in pairs, the blades are slightly pointed, dark green. Interestingly, the scales surrounding the acorn are very fluffy and soft.
Criticism of arguments - questions for alternative history
What were railroads and wooden buildings made of?
If about 200 years ago all the forests were destroyed, then what were railroad ties, buildings, ships, and stoves made of then? My relatives live in the Oryol region - a region not rich in forests, so they have practically no wooden buildings!
Fiction and painting
What about the mention of forests and logging in literature and paintings of the 18th and 19th centuries? Just ignore? Or were these masterpieces created by order of the secret world government in order to erase these events from people's memory? Seriously? Damn it, this theory is so crazy that it’s hard to find words from amazement: global catastrophes, nuclear war - and no traces of these events, except for “young forests” and “soil-covered” first floors of houses...
Holm oak structure
The homeland of the tree is considered to be the Mediterranean and Asia Minor. At the moment, they are actively cultivated in North Africa and Europe. This is an evergreen plant whose height is 22-25 meters. The trunk is gray, smooth. The crown is spreading and dense. The leaves themselves are small, variable in shape, shiny, bright green in color, and leathery. The fruits ripen only in the second year. Oak grows rapidly, regardless of the climate. It is suitable for frosts down to -20 degrees and heat up to +40. Shade-tolerant, drought-resistant. The breed is called stone due to the fact that trees mainly grow on rocks in mountainous areas.
What is ship timber
During the heyday of sailing shipbuilding, ships were made almost entirely of wood. For this purpose, the so-called construction timber was used, which had strict requirements for weight, strength, trunk shape and elasticity. The most difficult part was finding the right wood for the sailing ship's mast, since it had to be resistant to the serious loads that arose in strong winds.
Traditionally, oak, teak, larch and pine were used to make the main parts of a sailboat's hull. These types of wood were best suited for the construction of the ship's frame, its plating and deck flooring. For the manufacture of masts, a special ship's pine was most often selected, characterized by a straight trunk and sufficient girth. Other types of wood were used for the interior fittings and finishing of ships, which required less material: spruce, ash, valuable mahogany, acacia.
In a number of states where shipbuilding was one of the leading sectors of the economy, there were protected plantings and entire tracts of forest that were intended exclusively for the construction of ships. In Russia, the very concept of “ship forest” was introduced by Tsar Peter, who in the first years of the 18th century, by his decree, established ship groves, which were deciduous and coniferous. Here, under state control, especially high-quality species of pine, larch and oak grew. Regular commercial felling in ship forests was strictly prohibited.
Distinctive features of red oak
Most often found on river banks. Does not like stagnant water in the soil. North America, in particular Canada, is considered the birthplace of red oak. Such trees reach a height of 25 meters. Externally, the trunk is slender and smooth. The gray bark darkens and cracks over time. The oak crown is tent-shaped, green with yellowish tints closer to the ground. The leaves are large, sometimes their diameter reaches 25 cm. They have pointed blades. In autumn they turn red and fall off.
The fruits are small, spherical, no more than 2 cm in size. Ripe acorns are red, slightly brown. They ripen by the end of autumn; the first year is a poor harvest. Sustainable fruitfulness – up to 20 years. The tree is frost-resistant, calmly withstands strong winds and bright sun.
Interesting Facts About White Oak
The plant is native to the east coast of North America. Large stands are found in forests with limestone-rich soil. Easily gets along with other oak species. It is important that the habitat is no higher than a kilometer above sea level. White oaks do not tolerate severe frosts. The height of an adult tree is about 30 meters. The crown is powerful, tent-shaped, formed by spreading branches. The color of the bark is gray. Old trees hardly crack, unlike petiolate trees. The leaves are oval, large (up to 22 cm), have up to 9 lobes. During blooming they turn red, in summer they turn green, and closer to winter they turn purple and fall off. The length of the acorn is up to 2.5 cm. The fruits are almost not covered by scales, so they often fall from the tree from strong gusts of wind.
Description of large-fruited oak
These trees are a North American species. They grow up to 30 meters high. The trunk is thick, brown in color, and severely cracks after several years from the moment of germination. The tent-shaped crown shape is achieved by powerful spreading branches.
The foliage is oblong, lobed, dark green in color, glistening in the sun and after rain. In autumn, the entire crown falls off, sometimes along with thin branches. It is worth noting that the diameter of the leaves is 25 cm. The acorns are large, often reaching a length of 5 cm. They are oval in shape, covered by scales by a third. Large-fruited oak germinates at an average speed. The seeds are very moisture-loving and frost-resistant. Because of this, the breed is considered decorative.
Reserved chestnut oak
Widely distributed in Armenia, Iran and the north of the Caucasus. Cannot be cultivated. Most of the plantings are wild. In the mid-20th century, these trees were listed in the Red Book, so their felling is strictly prohibited. In the Hyrcanian Nature Reserve, they are monitored by specially trained people. Interestingly, the chestnut oak is a mixture of several wild species that grow primarily on ridge crests. Very light-loving, moderately resistant to frost, but does not tolerate drought.
When the oak leaves bloom, the tree looks like a huge chestnut tree, 30 meters high. The trunk is quite slender and thin, the branches are spreading. Large chestnut-shaped leaves further emphasize the grandeur of the tent-shaped crown. Acorns swell up to 3 cm in length.
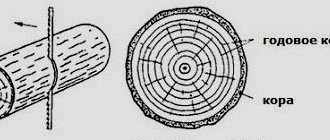
Tree rings
In places where periodic climate changes occur, trees develop circles in the trunk. The process occurs thanks to the cambium located under the bark. These are living cells that produce growth through division.
In winter the plant sleeps. Life processes in it are inactive. Vigorous activity intensifies in the spring and continues throughout the summer. At this time, the cambium forms many new cells, and the color of summer cells differs significantly from the color of spring cells. As a result, a thin light and wider dark stripe appears inside the trunk.
The dark circles represent growth rings. In some tree species they stand out more clearly, in others they are barely visible. Their thickness depends on the conditions in which the plant was located.
Swamp oak (pyramidal)
The southern regions of Canada are considered the birthplace of the breed. The tree reaches a height of about 25 meters. The crown from a distance resembles a pyramid. It is worth noting that the trunk practically merges with the leaves. The fact is that the bark of the swamp oak is completely green with an admixture of brown. The leaves are medium-sized and have deep notches and teeth. The crown color is green, but by autumn it turns purple. The fruits are spherical, sessile, about 1.5 cm in diameter. Oak seeds love water, just like mature trees. For additional moisture, the root system goes deep into the ground. The breed's habitat is marshy areas. The pyramidal oak grows quickly, but dies during prolonged frosts. Often large wild stands can be found on the shores of lakes and reservoirs.
Ship pine
Several types of ship pine were most often used in the construction of ships. These include yellow pine, which mostly grows in central Russia. Its elastic, durable and strong wood was used for the construction of above-deck structural elements, including masts, topmasts and yards.
Red pine, characteristic of the northern regions, with its dry wood, was used for paneling and also used for decking. White pine usually grows in swampy areas. It was of poorer quality, and therefore was used for those parts that did not require exceptional strength and did not carry a serious load.
The ideal ship's pine has a straight, tall, thick and very strong trunk, on which there are practically no flaws. The height of the tree may vary, but the tallest trees were used to make the masts, the trunks of which rose several tens of meters into the air.
Ship pine wood is usually moderately resinous, with a hard core. To achieve this state, the tree must grow for several decades in favorable conditions. The best specimens of ship pine reached the age of one hundred years, were up to 40 m in height and up to half a meter in diameter.
Growing and Reproduction
Seedlings of English oak and large-fruited oak are very demanding of moisture and mineral wealth of the soil. That is why they quickly emerge in floodplains and deep forest loams. It is not recommended to sow oak seedlings in podzol soil. In such soil, the sprouts will quickly die, since the roots will not be able to gain a foothold due to the high acidity of the humus. It is advisable to sow acorns in late autumn. The fruits must be fresh. If you allow the acorns to dry out at the slightest level, the germination rate will decrease significantly. Planting depth is from 5 to 8 cm. Before growing an oak tree, it is important to know that the soil must be fertilized when sowing. To protect the sprouts from pests, it is necessary to cover them with spruce branches. It is also important to maintain a stable soil temperature (at least +2 degrees).
Many gardeners wonder how to grow an oak if other trees, due to circumstances, do not produce acorns. For this, you can use the breeding procedure. Green cuttings should be rooted in the first half of summer. It would be a good idea to use special heteroauxins as fertilizer. In addition, you need to know that cuttings of young trees germinate much faster and easier than cuttings of old ones (more than 20 years).
Coniferous trees - counting the number of years lived by whorls and bark
The peculiarities of calculating the life time of some coniferous trees allow this to be done quite accurately and easily, without using mechanisms. For pine, spruce, cedar, and fir, it is enough to count the whorls located on the trunk.
How to determine the age of a tree in this way? Very simple! First of all, you need to know what a whorl is.
A whorl is a fan-like divergence of branches. They are on the trunk. Count them. Now you should add 3 to the existing value if the object of your attention is pine, 4 - for spruce, in the case of fir and cedar - 5 and 10, respectively.
These indicators indicate the age at which the first whorl is formed in a particular tree species. The number obtained as a result of summation should be considered the age of the tree.
An important sign of plant maturity is their bark. The structure and color matter. Young trees tend to have lighter and smoother bark. For pines and spruces, such a trunk surface is relevant for six to seven decades of life; it will be rough only in the lower part - to about a meter from the roots.
After another similar period of time - at the age of 130-150 years, the smooth bark will remain only on the upper half of the tree trunk, and in the lower half it will be covered with cracks. The bark of older plants is usually covered with lichens and moss.
Peculiarities of oak pruning
Representatives of this family of trees love careful care, despite the fact that they are considered wild. The pruning procedure especially affects the yield. Oak is a tree with monopodial branching. Therefore, the main stem must continue to grow for the rest of the plant's life. In this case, the top cannot be limited in height. It always dominates other shoots. Branch pruning should be done every few years. The optimal period for removing branches would be early spring or late winter. It is important that the air temperature is not lower than -5 degrees. Otherwise, frostbite will appear at the cut sites. By summer, these branches will dry to the ground. If there are a large number of them, the entire tree will die. Only new shoots, growths and diseased branches should be removed.
How to determine the age of an apple tree?
Sometimes gardeners buy a plot with trees growing on it. How to determine the age of the apple tree in this case? After all, maybe it is already so old that soon it will not bear fruit at all, and there is no point in feeding it and other measures related to increasing productivity. The most well-known method is to determine age by rings on a tree cut. But in the case of fruit trees, it will not work - because in this case they will simply die.
Pressler's drill
Using a Pressler drill, you can drill out a fragment of a tree with virtually no harm to it in order to determine its age. By looking at the rings, you can learn not only about the age of the apple tree, but also about the conditions in which it grew. If the size of the rings is wide, it means that the plant was well cared for and the climatic conditions were favorable. Narrow rings indicate periods of drought, attacks by harmful insects, excessive harvests and other negative factors. When counting, you need to distinguish between real and false rings. The former form a closed circle, the latter do not.
You can determine the age of an apple tree by cutting down the oldest branch on it. You need to add two years to these rings - this will be the age of the seedling.
You can look at the rings on the cut of an old tree branch to determine the age of the apple tree.
Useful and harmful properties of oak
For medicinal purposes, the bark and young branches of the tree, as well as acorns, and less often leaves are often used. The upper layers of the oak trunk contain a lot of resin, acids, sugar and pectin. The fruit contains useful substances such as organic oil, proteins, and starch. Young leaves contain tanning components, dyes and pentosan groups. Thanks to this, effective anti-inflammatory drugs are produced from the tree and fruits.
The antispasmodic properties of oak are also well known. For example, tree bark effectively helps with colitis, intestinal bleeding, gastritis, spleen and liver disease. Oak tinctures increase mental and physical activity, calm the central nervous system, and improve the patency of the vascular system. On the other hand, preparations based on this plant are contraindicated for children and patients suffering from constipation, hemorrhoids, nausea, and stomach ulcers.
Incremental Pressler drill (age-specific)
Our ancestors became concerned about how to determine the age of a tree by looking at its trunk without causing any significant damage to it back in the 19th century. If cutting down a plant is not necessary or impossible, you should use a special tool and take a sample of the wood with it.
The drill consists of a conical, hollow cylinder with a thread at one end. The other edge has four edges. It is on this side that the handle is fixed, simultaneously serving as a case. The tool also contains a plate with grooves.
A piece of wood taken for sampling is called a core. To extract such a fragment from a tree, the drill is placed at a right angle to the trunk, then screwed into it.
As the tool is immersed in the wood, the latter fills the cavity of the tube. After inserting the drill to the required depth, a grooved plate is inserted into the tool through the hole in the handle. By turning the drill in the opposite direction, it is removed from the trunk.
On the core, you can easily count the number of annual layers. However, you should always take into account the distance from the roots where the sample was taken. You can determine the age of a tree more accurately only by adding to the figure obtained by counting the rings, the number of years required to reach the height at which the core was taken. It depends on the breed of the plant and the conditions of its development.
The age drill allows you to extract a core up to 35 cm long, which means that in this way you can determine the age of a tree by a trunk diameter not exceeding 70 cm.
In representatives of breeds that grow very slowly, as well as in inhabitants of shaded zones densely populated with plants, the annual layers are thin and difficult to distinguish. In such cases, an optical taxation device (OTD) is used.
This device is equipped with an eyepiece and a lens. A core is placed in it and, focusing, the wood structure magnified by optics is examined.
There are also several ways to determine the age of trees without using any tools.
Resource usage
Oaks are mostly used in construction and cooking, as well as in light industry. Sawdust is used to make corks and furniture. The wood is optimal for surface vessels, fortifications, machine building, and barrel making. The boards do not swell, do not burn well, and are durable, hard and dense. When the oak leaves bloom and the acorns ripen, it’s time for the cooks. In North America, the fruits of the tree are often added to coffee, candy and the most delicious dishes. In Asia, acorns are eaten fried with spices.
The giant oak tree in France, in the hollow of which there is a room with a bench carved directly into the body of the oak tree, is more than two thousand years old. It is precisely because of their age and gigantic size that many oaks have become relics of cities and nations and are under protection. The Tsar Oak, the Kaiser's Oak, the 600-year-old Oak, the Chapel Oak, the Master's Oak have legends about each of them.
Oak is hardy and unpretentious, but despite these properties,
oaks do not grow in South America and Australia; in Africa they are found only along the Mediterranean coast.
In Russia, English oak grows with two varieties: summer oak and winter oak, differing in flowering time. Mongolian oak grows in the Far East and Amur region. Sessile oak grows on the Black Sea coast of the Caucasus.
In the 18th and 19th centuries, it was customary to decorate the clearings in front of the landowner's house with oaks; oaks were grown in palace and manor parks. Sometimes oak trees are planted to green cities; recently, gardeners have also begun to pay attention to this wonderful plant. Hence the logical question - how many years does an oak tree grow until the moment when it allows you to admire its beauty and grace?
It’s a long time, but if you have the opportunity and space to plant an oak tree, be sure to plant it, and even if you don’t manage to admire the fruits of your labor, you will leave a memory of yourself for many generations.
At ten years old, you planted will outgrow the medium-sized fruit trees in your garden - apple and pear trees; at 20 years old the first acorns may appear on it , although oaks usually reach fruiting age at 40 years. Don’t be surprised, for an oak tree 450 years is the age, as they would say about a man at the dawn of his strength. The oak bears fruit with acorns approximately once every 4 years, but the oak is grown not because of the acorns, but for the strength and wisdom that it gives to its owners and this is not an allegory.
Plant the oak tree away from your home so that it doesn’t turn out like in this photo.
An oak tree in the body of which there is a chapel - France.
The soil for planting oak can be different; the density and strength of the wood and its durability depend on it. And oak can grow on sand and stones, along river banks, in lowlands in swamps and in elevated places, among bogs. The main thing is that the planted seedling is not burned by the sun, and the roots do not get wet in water in the first years of its life. Typically, oak grows up to 40 meters in height and up to 1.5 meters in width. The crown of the oak tree is gigantic, matching its height, so take care that in the future it does not damage your home and nearby buildings.
Lifespan
As strange as it may sound, trees are the witnesses of our history and evolution, therefore, if they could speak, they would make history. Oak, as a type of deciduous tree, is perhaps one of the most common in our region. Everyone knows what they look like: both adults and children. It is impossible to say exactly how many years oaks have existed on our planet, but these trees are already several thousand years old.
Having impressive dimensions, sometimes more than fifty meters in height and two in diameter, they have become full participants in our fairy tales and epics. This type of tree is very useful, it purifies the air well, evaporates a lot of water, has a pleasant aroma, an unusual leaf and fruit - an acorn. And how many medicinal properties this tree exhibits!
As for life expectancy, it is one of the highest in the world. How long does this majestic tree live? Some individuals even live up to 2 thousand years. It's hard to imagine, but it's true. Perhaps, if not for the rapid activity of man, their age would have been even higher. On average, the average city dweller lives to be 300-400 years old. Up to 150 it still grows in height, but its width increases throughout its life. It is by the diameter of the trunk that you can determine how old the tree is. Although this does not apply to all varieties, for example, the petiolate species lives on average only up to the age of one hundred years.
The oldest representative that lives in Europe is the Stelmuzhe oak, shown in the photo, which grows in the village of Stelmuzhe in Lithuania. Today, the age of this centenarian is more than 1500 years, although its height is only 23 meters. At the level of a person’s chest, the diameter of its trunk reaches 4 meters. Today the “old man” lives, he is as green as in his youth, although in 1955 Lithuanian scientists performed an operation on him to remove rot inside the trunk. Today, experts strictly monitor the condition of the old-timer in order to further extend his age.
How long does it take to grow an oak tree from an acorn?
It is better to plant oak trees with acorns; when transplanted, seedlings with bare roots do not take root well. If you are in a hurry to “live”, buy an oak tree from a skating rink, you can save 8 years or add them to your life, if it’s more pleasant for you to think about it that way. Plants with a closed root system take root and grow well, but unfortunately, an oak planted in this way will not be durable. Of course, it will be enough for your lifetime, but no more, this is due to the improper development of the root system of an oak seedling grown in a small vessel in the first years of life. By growing an oak from an acorn, you will lose a couple of years, but an oak grown in this way will grow for a long time and your children, grandchildren and grandchildren of your grandchildren will remember you.
Tree height growth rate
Typically, living things, including us, have a period of active growth when they are young, but as they age, growth slows down or stops altogether. The growth rate of trees in height has the same character. After a period of active growth in height, the growth rate of the tree decreases, and it begins to gain weight due to the trunk and side shoots. The figure shows the general nature of the relationship between the height of most trees and its age. The schedule is divided into three phases. 1 is the initial phase of slow growth, followed by a phase of rapid growth - 2. When the tree approaches a certain height, the growth rate drops - phase 3. Of course, time and height values will vary for each individual tree depending on the species and environmental conditions.
The general nature of the dependence of the height of most trees on age
Different types of trees grow at different rates. Depending on the growth rate, trees are usually divided into groups. In tables 1 and 2, trees are divided into groups depending on the tree's growth rate per year. Trees gain such growth rates during the active phase (between the ages of 10 and 30 years).
Table 1: Fast and Moderate Growing Trees
Very fast growing
Fast growing
Moderately growing
Table 2: Slow-growing trees
Slow growing
Very slow growing
growth 0.25-0.2 m
Siberian cedar pine
Dwarf forms of deciduous trees (Dwarf willows)
Dwarf forms of conifers (Obtuse cypress)
Knowledge base
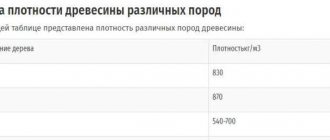
| Name | Height, m | Life expectancy, years |
| Homemade plum | 6–12 | 15–60 |
| Gray alder | 15–20 (25)* | 50–70 (150) |
| Aspen | Up to 35 | 80–100 (150) |
| Mountain ash | 4–10 (15–20) | 80–100 (300) |
| Thuja occidentalis | 15–20 | More than 100 |
| Black alder | 30 (25) | 100–150 (300) |
| Birch warty | 20–30 (35) | 150 (300) |
| Smooth elm | 25–30 (35) | 150 (300–400) |
| Balsam fir | 15–25 | 150–200 |
| Siberian fir | Up to 30 (40) | 150–200 |
| Common ash | 25–35 (40) | 150–200 (350) |
| Apple tree wild | 10 (15) | Up to 200 |
| Common pear | Up to 20 (30) | 200 (300) |
| Rough elm | 25–30 (40) | Up to 300 |
| Norway spruce | 30–35 (60) | 300–400 (500) |
| Scots pine | 20–40 (45) | 300–400 (600) |
| Small-leaved linden | Up to 30 (40) | 300–400 (600) |
| Beech | 25–30 (50) | 400–500 |
| Siberian cedar pine | Up to 35 (40) | 400–500 |
| Prickly spruce | 30 (45) | 400–500 |
| European larch | 30–40 (50) | Up to 500 |
| Siberian larch | Up to 45 | Up to 500 (900) |
| Common juniper | 1–3 (12) | 500 (1 000) |
| Common falsesuga | Up to 100 | Up to 700 |
| European cedar pine | Up to 25 | Up to 1,000 |
| Yew berry | Up to 15 (20) | 1 000 (2 000–4 000) |
| English oak | 30–40 (50) | Up to 1,500 |
| Baobab | 18-25 | 1000 (5500) |
* The height and lifespan of trees in particularly favorable conditions are indicated in parentheses.
Return to main page | Changes in European land cover over the last 150,000 years | Taxonomic units | Classification of wildlife | Biological resources of plant origin | Classification of cultivated plants | Centers of origin of cultivated plants (according to N.I. Vavilov) | Biological resources of animal origin | Lifespan of some animals | Duration of gestation and number of cubs born at the same time | Maximum sizes of some vertebrates | Brain mass, g | Brain mass in relation to body mass, % | Flight speed of some birds and insects | Egg and body mass of birds | Bird flight distance | Number of wing beats in birds (per second) | Oxygen requirement of some organisms | Upper hearing limit, Hz | Body temperature and pulse rate | Mammal class | Species of animals and birds that became extinct in the recent past | List of fauna objects that have disappeared in Russia and are excluded from the Red Book of the Russian Federation (as of November 1, 1997) | Objects of world cultural and natural heritage in Russia | Natural monuments of federal significance (as of 2000) | National parks of the Russian Federation | State natural reserves of federal significance under the jurisdiction of the Russian Ministry of Agriculture | State natural reserves of federal significance administratively subordinate to the Ministry of Nature of Russia | The largest botanical gardens in Russia | Record-breaking plants | Wood Density | The greatest depth of root systems | Preservation of seeds' ability to germinate | Poisonous plants | Diploid set of chromosomes of cells of some organisms (2n) | Genetic code | A complete "dictionary" of the genetic code for amino acids