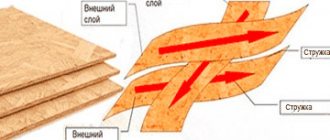
During construction and during finishing work, it is often necessary to create a coating with improved properties - even, moderately durable. Chipboard (chipboard) has the necessary characteristics. The sheets are made from wood, but the base is not solid wood, but shavings. The slabs are susceptible to moisture, but this disadvantage is outweighed by their advantages. When choosing, you should consider different options for materials; they differ in appearance, properties, and therefore are used under different conditions.
What is chipboard?
Chipboard (chipboard) is a composite material obtained from waste from the wood processing industry (sawdust, wood chips, etc.) by pressing under high pressure of 2.5 - 3.5 MPa at a temperature of 180°C, with the addition of an adhesive base - formaldehyde resins ( no more than 16-18%). The quality of the resulting chipboard directly depends on the quality of the sawdust itself, compliance with the technological process and the number of binding elements.
Chipboard
Chipboards differ in the pressing method.
Pressing methods
- Flat - this method is characterized by the fact that the press pressure is directed perpendicular to the sheet, which gives it greater strength. The formation of an endless carpet of shavings is carried out on belt conveyors by palletless hot pressing.
- Extrusion (extrusion) - pressure is distributed in parallel, directed towards the edge of the formation, which reduces its mechanical properties. This method is considered obsolete. The prepared chip mass is fed directly into the distributor between the hot vertical plates of the extrusion press.
Chipboard cladding
- Uncoated - used mainly in construction, repair work, as a backing for flooring.
- Lined with various decorative coatings (lamination with facing film or paper - laminated chipboard); PVC polymer coating; melamine coating (artificial veneer made of polymer film); natural wood veneer with varnish; tongue and groove coating made of waterproof polymer, etc.
Chipboard cladding
Types of chipboard coating
- Veneer is a thin section of wood obtained by sawing or peeling trees, usually rich species - oak, elm, maple, walnut, beech, alder, etc. The top of the veneer is additionally coated with varnish to protect it from mechanical damage. This chipboard looks like real wood, only the price is much lower.
- Laminate is a coating made of protective facing paper and polymer film exposed to high temperatures. The color range and structure of the coating of laminated chipboard (laminated chipboard) is very diverse, such a surface is not afraid of water and is resistant to mechanical stress, unlike non-laminated chipboard. Laminated chipboard has become widespread in the furniture industry. The laminate coating of such boards significantly reduces the release of formaldehyde.
Laminated chipboard - large selection of colors
- Melamine – the coating is provided by applying melamine resin to the board, which gives the surface greater wear resistance. Melamine coating is also called artificial veneer.
- PVC – surface covering with synthetic polyvinyl chloride film. The most popular and cheapest material for covering the surface of chipboard, it has fairly high strength characteristics, is resistant to moisture, and is easy to use.
- NPC – two-layer paper covering (1st layer – decorated paper, 2nd layer – transparent “over-lay” paper impregnated with special resin). This cladding is considered the most durable and abrasion-resistant.
- Laminated chipboard - the board is coated with a special glue, then a paper layer is applied, without the use of high temperatures and pressure in the technology. This type of chipboard finishing is considered the cheapest and fastest wearing.
Density and weight
One of the most important indicators used when assessing the quality of chipboard sheets is their density. And, if previously it was believed that the higher this indicator, the more durable and durable the material is, today it has been proven in practice that this is not entirely true.
In fact, the main role in ensuring the load-bearing capacity of chipboard is played by the condition of its surface, which is capable of holding fasteners, in contrast to its internal part, which has a looser structure.
This fact is confirmed by data on the density and thickness of boards manufactured by one of the leading manufacturers of particle boards, the Kronospan company:
| Plate thickness, mm | Sheet density, kg/m3 |
| 8 | 740 |
| 10 | 720 |
| 16 | 680 |
| 20 | 670 |
| 22 | 660 |
| 30 | 620 |
| 32 | 600 |
| 38 | 600 |
Having analyzed the information presented in the table, we can conclude that the density of the sheets in the thickest thickness of Kronospan chipboard is less than 700 kg/m3, but this in no way affects the quality of this material.
The weight of chipboard is proportional to its area and thickness and depends on the size of the sheet of material. For example, for a sheet with dimensions 2750 x 1830 mm and a thickness of 10 mm, it is 37 kg.
Advantages and disadvantages of chipboard
Advantages:
- Affordable price;
- A large assortment;
- Relative strength to impact loads;
- Easy to process and install;
- High rigidity index;
- Light weight;
- Easy to care for.
Flaws:
- The presence of formaldehyde in the composition, which can have a negative effect on human health.
- High water absorption. When swelling, the chipboard increases in size by 3 times.
- Zero flexibility, which does not allow the installation of chipboard on curved surfaces.
- Under constant dynamic loads, it collapses and crumbles at the place where fittings and hardware are attached.
Purpose
Chipboard is an environmentally friendly, easy-to-process, functional material, and also a high-tech alternative solution to solid wood. It is used to sheathe walls, roofs, make wall panels, create carpet or linoleum flooring, flooring, various partitions, make a wide variety of furniture, packaging, construct enclosing arrays, and decorate interior spaces. What is the production technology for chipboard? How is it made at home? Let's look at these questions later in the article.
Application area
Currently, the use of chipboard has expanded significantly. Chipboard has found its application in a variety of areas.
In construction:
- subfloor installation;
- installation of internal wall partitions;
- exterior decoration of building facades;
- frame covering;
- as formwork;
- for the manufacture of containers;
- temporary structures.
Scope of application of chipboard in construction
In the furniture industry (production of budget furniture):
- tables, shelves, racks;
- cabinets, cabinets, etc.
The use of chipboard in furniture production and as packaging
In addition to being used in construction and furniture production, chipboards are used :
- on personal plots for the construction of fences, garden houses and outbuildings;
- for installation of scenery in theaters and film venues;
- in instrument making;
- for the production of packaging for the transportation of valuable goods;
- for the production of interior doors, consumer goods, etc.
Advantages and disadvantages
Among the positive aspects are the following:
- Low price. Perhaps the most important advantage is that it can be used both in construction and for making furniture;
- Strength;
- Hold nails and screws satisfactorily without deformation;
- High resistance to moisture.
But, as in any other case, there are some disadvantages. The first, of course, is the use of formaldehyde resins in production. The environmental friendliness of the material is clearly not up to par. But here it is fair to note that there are two types of chipboard: E1 and E2.
The first among them meets the standards and is not so harmful, as evidenced by the fact that it is approved for use in the manufacture of various children's furniture. Panels made in German and Austria are traditionally considered the most environmentally friendly.
Another disadvantage is the inability to use the material for fine processing (for example, obtaining various shaped parts) due to its hardness. But this minus is not particularly critical.
A few more words about the advantages and disadvantages of the material:
Specifications
- Density from 610 to 850 kg/mᵌ (depending on the thickness of the sheet);
- Humidity 8±3%;
- Flexural strength 14-26MPa;
- Formaldehyde content ≤8 mg/100g;
- Swelling (over 24 hours) max 22%;
- Elasticity in bending 1200-1800 N/mm²
- Impact strength, 4000–8000 J/m2
- Hardness 20-40MPa
- Thermal conductivity 0.2 W/m*K
- Vapor permeability 0.13-0.24 mg/(m*h*Pa)
Chipboard sizes
Brands and classification of chipboard
Chipboard according to GOST 10632-2007 are divided into the following grades :
- P-A - high quality, improved strength properties, low swelling percentage, used in various fields where increased quality is required.
- P-B - lower quality compared to P-A, low cost, used for the production of containers, formwork, and in structures without special quality requirements.
Based on surface quality, chipboard is divided into grades 1 and 2 . On slabs of the 1st grade, chipping and coloring of corners, protrusions, depressions, and stains of paraffin or resin are not allowed.
Based on formaldehyde content and its effect on human health, chipboards are divided into emission classes :
- E0.5 - formaldehyde content per 100g should not exceed 3-4 mg. It is considered an environmentally friendly material, suitable for use in children's rooms and hospitals.
- E1 - the formaldehyde content per 100g should not exceed 8 mg. A relatively environmentally friendly material, it is used for interior decoration in residential premises.
- E2 - the formaldehyde content per 100g is more than 8-30 mg, has a strong pungent odor, is prohibited for use in the production of children's furniture, suitable only for external facade work.
By surface type : regular (O) and fine-textured (M).
According to the degree of surface treatment : polished (SH) and unpolished (NS).
According to hydrophobic properties: normal and increased water resistance.
Chipboard marking on packaging
According to GOST 10632-20073.2.2 - “The symbol of slabs must include: brand designation, grade, type of surface (for slabs with a fine-textured surface), degree of surface treatment (for polished slabs), hydrophobic properties (for slabs with increased water resistance), emission class formaldehyde, nominal length, width and thickness in millimeters, designation of this standard."
For example, a plate of grade P-A, 1st grade, with a fine-textured surface, polished, emission class E1, size 3500 x 1750 x 15 mm:
P-A, I, M, Sh, E1, 3500 x 1750 x 15, GOST 10632—2007
Each batch of slabs must be accompanied by a quality document , which must indicate :
- name, trademark (if any) and location of the manufacturer;
- national mark of conformity if the product is certified;
- symbol of slabs;
- sizes and number of slabs (in pieces, sq.m and mᵌ);
- date of manufacture of the slabs;
- stamp of the technical control department.
Classification
One of the first parameters that people pay attention to is the type of surface treatment. There are 2 options: sanded and unpolished slabs. They differ in the quality of the coating, which determines the area of application of the material. In addition, the slabs are distinguished by structure:
- ordinary (designated by the first letter – O);
- fine-textured (M).
The second option is used in the production of laminated boards. This is due to the fact that the film adheres better to the surface of such a product.
Surface quality
Slabs of different types are produced, differing in the number of defects:
- 1st grade – without changes in the structure of the material, defects;
- Grade 2 – a certain amount of damage is acceptable (regulated by regulatory documentation).
Due to average strength and moisture resistance, chipboard with more significant defects is not used, since it will not perform its main functions. The service life of the material will be significantly reduced.
Emission class
There are types of stoves that differ in the degree of danger to human health. They contain varying amounts of toxic components (in particular formaldehyde):
- E0.5;
- E1;
- E2.
Is chipboard harmful?
If you need to use the material indoors, only the first two options are considered. The concentration of formaldehyde in the structure of the binder component and when released into the surrounding space is minimal and is considered acceptable. However, the rule here is: the less, the better, so option E0.5 is preferable.
Strength level
There are types:
- P1 – general purpose;
- P2 – products intended for the manufacture of furniture and finishing work indoors.
The second option is more durable, so the scope of application of the slabs of this group is wider. P1 products are more often used for rough finishing, temporary structures or as auxiliary material. The strength of chipboard varies: 550-750 cubic meters. m. At the same time, the range of density values is also different: 0.5-1.0 g/cubic. see. Tensile strength is also taken into account:
- when bending – 10-25 MPa;
- when stretching - 0.2-03.5 MPa.
INTERESTING: Membrane roofing materials: types and installation technologies
Chipboard production
The raw materials for chipboard are:
- shavings from planing, matchmaking, plywood production;
- waste from sawmills;
- special chopped wood chips.
Basically, coniferous trees are used for the procurement of raw materials, less often - deciduous trees.
Chipboard production
Stages of chipboard production:
- preparing raw materials, cleaning them from impurities and inclusions by passing them through a special separator;
- grinding the raw materials to the required fraction, drying and mixing with the adhesive until a homogeneous consistency;
- formation of a carpet from raw materials at high temperature and pressure on the belt of pressing equipment, cooling;
- giving the required size, trimming edges;
- sanding and lamination (if necessary).
Chipboard layers
There are several technological methods for producing chipboard:
- single-layer;
- three-layer;
- five-layer;
- multilayer.
Single-layer chipboards are boards consisting of one layer of material. The chips in such a slab are the same size and uniformly distributed around the entire perimeter. It has not very good strength characteristics and a low price.
Three-layer chipboards - selected chips of a large fraction are placed inside the board, and the outer layers are formed from smaller chips with a large amount of binding glue. This enabled manufacturers to increase the strength of the material, remove brittleness at the ends and during bending, and improve the appearance (it became possible to perfectly sand the surface). Due to the use of large chips in the middle of the board, the price of the finished product is not much different from the price of single-layer chipboards. Therefore, three-layer chipboards are considered the best, optimal option when choosing the necessary building material.
Types of chipboard production - single-layer and multi-layer
Five-layer chipboard - consists of one inner layer of a large fraction of raw materials and a small amount of glue, two subsequent layers of a medium fraction of chips and a medium content of glue, and two outer layers of small shavings or wood dust using a large amount of binding glue. Accordingly, five-layer slabs have greater density and strength, as well as a higher price compared to single-layer ones.
In multilayer boards, the size of the wood particles gradually decreases from the inner to the outer layer, and the amount of bonding adhesive used increases accordingly. The only difference from single-layer, three-layer and five-layer is that the boundaries of the transition from layer to layer are not visible .
The production of five-layer and multi-layer particle boards is more expensive and is only possible on expensive production lines. Naturally, due to the increase in cost, the retail price of the finished material also increases, so this type of chipboard is not common in the construction market. It is mainly manufactured to order for serious manufacturing companies (for example, in the carriage building industry).
Chipboard, fibreboard or MDF - which is better?
All three materials are wood-based panels. Only in chipboard - wood chips are pressed, and fiberboard and MDF - wood fibers.
In the production of chipboards, coniferous wood is used , less often deciduous low-value species. Accordingly, the service life depends on the quality of both the chips themselves and the binder.
Fiberboard (fibreboard) - made by wet pressing. One of the sides of the fiberboard always remains rough, the other is made smooth by polishing well. In the production of fiberboard, no binders are used; in rare cases, formaldehyde resins are used in some types of fiberboard.
MDF (medium density fiberboard) is produced by pressing particles from very fine wood. Urea or melamine resins (lignin), which are environmentally friendly, are used as a binder.
Chipboard has become more widely used in our time than fiberboard and MDF. The scope of application of fiberboard is quite limited (the back walls of cabinets in the production of furniture, the bottoms of all kinds of drawers, etc.), and MDF is used mainly only in the production of doors and furniture.
Chipboard, fibreboard, MDF
In terms of physical and mechanical properties in terms of water resistance, chipboard is inferior to fiberboard and MDF. MDF can be used in rooms with humidity above 80%. Fibreboard, like chipboard, is afraid of moisture. In terms of strength, chipboard and fiberboard are inferior to MDF.
The cheapest material presented is chipboard, which is why it is most widely used in many industries. Chipboard is covered with many types of protective laminate coatings. Also, chipboard is easier to process compared to fiberboard and MDF.
Despite its shortcomings, chipboard is an affordable and cheap material. The main complaints from consumers are based on an incorrect approach to the choice of material, poor study of its features and errors during installation.
Features of the material, history of appearance
Previously, the issue of recycling wood chips obtained during production for various purposes often arose. It was solved thanks to the appearance of slabs made from this raw material. Wood-based products first began to be used in the thirties of the last century. They were used for commercial purposes later - in the 40-50s. XX century Since then, the material has been used more and more often, and annual production has increased several times.
Raw materials: chipboard
Chipboard is a type of board made from shredded wood. They got their name due to the type of raw material that underlies them (wood shavings). Particles of different sizes are used, they are held together with a binder of non-mineral origin (synthetic glue, often based on phenol-formaldehyde resins). This feature limits the scope of application. The material contains a certain amount of toxic components, their dose is minimal, it is regulated by standards, and therefore the sheets are not prohibited. They are often used, including in the production of various pieces of furniture, and when performing finishing work.
Choosing between chipboard and OSB boards
Many people confuse OSB and chipboard, although the difference between them is very significant. Above we have already figured out what chipboards are. In this paragraph we will talk about the difference between similar facing materials - OSB and chipboard.
Both materials are chip materials, but differ in the production method.
OSB is a three-layer oriented strand board, in each layer of which the chips have a different direction, which increases the longitudinal and transverse strength of the finished material. This is the main difference between OSB and chipboard, where the chips are located chaotically. Another indicator is that the size of the chips used in the production of OSB is much larger than that of chipboard. This affects the scope of application.
Chipboard and OSB
In terms of technical characteristics, OSB is also slightly different from chipboards:
- Strength - 18-20MPa;
- Modulus of elasticity in bending - 3500N/mm²;
- Density 500-600 kg/mᵌ;
- Thermal conductivity 0.14 W/m*K
- Vapor permeability 0.04 mg/(m*h*Pa)
OSB is a more durable, elastic and moisture-resistant material compared to chipboard, so its scope of application is wider. OSB has been used in frame construction for many years as the main load-bearing material. OSB can withstand high mechanical loads.
OSB house frame
OSB is divided into classes:
- OSB-1 - low strength, not moisture resistant, used mainly for furniture production;
- OSB-2 - quite durable, used for finishing interior spaces, for example, installing a subfloor;
- OSB-3 is the most common class, has high strength indicators, is resistant to aggressive environments, moisture resistant, and is used for both interior and exterior work;
- OSB-4 is ultra-strong, with ideal moisture resistance, the most expensive of all classes, applicable for facade and roofing work.
The disadvantage of OSB is its price, it is 2-3 times higher than chipboards. Therefore, if your budget is limited, choose high-quality chipboard. How to choose and what to pay attention to when buying is written in this article.
There is a misconception that boards labeled OSB and OSB are different. So, the only difference between them is the country of origin. Manufacturers focused on the Russian market designate particle board as OSB (oriented strand board), and OSB is also oriented strand board, only the abbreviation in English sounds like Oriented Strand Board . As we can see, this is the same board, produced in the same way from waste from the wood processing industry.
Selection rules
In furniture production, three-layer chipboards with different thicknesses are usually used. Products of 8–10 mm are suitable for the manufacture of facades, side panels, and drawers. These parts are not subject to heavy loads. 16–18 mm is used for furniture with medium load capacity. Thickness from 22 to 25 mm is used for high loads, and from thick slabs, from 28 to 38 mm, bar counters and tabletops are made.
You should choose smooth sheets without roughness, swelling or cracks. Furniture chipboard should be of higher quality than the options used in construction. It should not have a strong aroma. Please note that the odor can become noticeable in a warm room, so you should pay special attention to this when shopping on open trading floors. Products must be certified.
A three-layer board made in accordance with European standards is considered fire-resistant. It takes much longer to ignite, and burning particles do not scatter. Such products are painted red to distinguish them from regular versions.
Technologies do not stand still - today's high-quality and certified products are much better and safer than those produced several years ago. You can safely purchase chipboard sheets for furniture that you will make yourself, and ready-made furnishings for your own home.
Chipboard panels with a thickness of 8–10 mm are suitable for the manufacture of facades, side panels, and drawers.
Slabs from 28 to 38 mm are used for making countertops or bar counters
Furniture chipboard must be of higher quality than the materials used in construction
How to care for chipboard?
Since products and structures made of chipboard are afraid of moisture, and in the event of chipping and deformation of the edges, the surface must be washed with great care.
Do not use for cleaning:
- abrasives;
- hot water;
- steam plants;
- aggressive chemicals, wax, alkalis and oxidizing substances.
Chipboard care products
Wet cleaning should be done with a slightly damp cloth (microfiber cloth); after treatment, wipe dry. After wet cleaning, the room must be thoroughly ventilated to avoid the appearance of fungus and mold. It is allowed to use special furniture polishes.
Furniture made from chipboard should be stored and used in rooms with temperatures from +10°C to +30°C and relative air humidity from 45% to 70% . Failure to comply with these parameters, as well as sudden changes in temperature and humidity, lead to deformation and loss of performance of furniture elements, countertops, furniture components and fittings.
Influence of dimensions on application
To properly plan your purchase, it is useful to take into account all the features and characteristics of the sheets, including sizes, on which the recommended areas of use largely depend.
It is convenient to use chipboard with a thickness of 8 mm to 10 mm for the usual lining of rooms, the manufacture of furniture, and decorative fragments of the interior. The static load in such situations is not very high; there is no need for increased strength of the slabs.
When covering a floor on which linoleum or laminate is subsequently going to be placed, it is advisable to use products with a thickness of up to 16 mm and large other dimensions. This will ensure the strength of the substrate and a minimum number of joints on the surface.
Countertops, doors, furniture parts on which a large load can be concentrated should be made from chipboard sheets with a greater thickness, reaching 25 mm. The optimal length and width must be calculated taking into account the dimensions of future products.
Industrial floorings and work tables on which heavy units and devices are placed can serve reliably if they are made from chipboard with a thickness of up to 38 mm. In such situations, the foundation must be strong, since possible destruction will lead not just to minor troubles, but to emergency situations and injuries.
It should be remembered that the installation of large chipboard surfaces requires the installation of reinforced support structures that can support the weight of the slab and everything that will be placed on it.
Methods for treating chipboard from moisture
- Nitrocellulose varnish - does not require preliminary surface preparation before application. Varnished chipboard is often used as an independent floor covering.
- Drying oil - applied in two or three stages. To improve moisture protection, you can add bitumen varnish to the drying oil in a ratio of 1:5.
- Bitumen mastic for wood - will increase the resistance of chipboard to wear, has ideal moisture-proof characteristics, will simplify further cleaning, and protect the surface from pests and mold.
- PVA glue - to protect against moisture, before installing partitions and wall cladding made of chipboard, you must first treat it with PVA in two layers. The glue will also act as a primer for subsequent plaster.
Chipboard processing methods
- Special impregnation for wood - based on alkyd varnish, which forms a water-repellent film on the surface of the chipboard. It is used for processing chipboard during facade work.
- Spray paint - suitable for emergency, quick priming of a small chipboard surface.
- Acrylic primer with the addition of latex and antiseptic - has deep penetration into the material and protects the chipboard from mold and mildew.
- Epoxy resin - used to seal joints in chipboard flooring. A solution is prepared from resin and small wood shavings.
- Self-adhesive films are used for budget repairs of chipboard furniture surfaces. This method will also protect against moisture, especially on kitchen surfaces, and extend its service life.
Separation of impurities
The main classification of chipboard is based on the content of binder resins in it per 100g of composite. Class
- E0.5 - the release of chemicals will be less than 4%;
- E1 is safe for everyday use, even for children's and medical institutions, because the amount of impurities does not exceed 10%;
- E2 - resin content is more than 10%.
One of the myths is that laminated chipboard emits formaldehyde, which is harmful to health. Class E1 laminated chipboards contain a minimal amount of impurities that cannot cause harm to health.
In addition, the fully laminated and edged fabric does not allow substances contained in the material to pass out.
Manufacturers of chipboards in Russia
- , Sergiev Posad;
- CJSC "Cherepovets FMK", plywood and furniture plant, Cherepovets;
- LLC "Sheksninsky KDP", Sheksna;
- , Novgorod;
- JSC "Murom", Murom;
- LLC "Syktyvkar Federal Plant", Syktyvkar;
- , Dubrovka village;
- Vokhtozhsky DOK LLC, Vologda;
- JSC "Karelia DSP" Medvezhyegorsk;
- PC “Shatura-slabs”, Moscow region, Shatura;
- OJSC "MEZ DSP and D", Moscow region, Khimki;
- LLC "DSP", Yekaterinburg;
- OJSC "Dyatkovo DOZ", Bryansk region, Dyatkovo;
- CJSC Skhodnya-plitprom, Moscow region, Podrezkovo village.
- OJSC “Zheshartskiy FC”, Komi Republic, Balezino village;
How to choose the right chipboard
- When choosing chipboard for interior spaces, you should choose only chipboard of emission class E1 , since the amount of harmful phenols released in this case is within the normal range (in Russia this figure is no more than 0.1 mg/cub.m). This is one of the most important points when purchasing chipboard.
- The color of the material will also give you a lot of information about the quality. It is necessary to pay attention to the light beige tones of the slabs (it is important that there is a single color scheme throughout the entire batch/packaging). If the color of the chipboard is dark , this indicates non-compliance with the temperature conditions during production (burnt board), if the color is red , the raw materials for the production of this board were rotten, damp. Moisture-resistant chipboard will have a greenish tint at the end due to impregnation with melamine resins and hydrophobic polymer additives.
The difference between moisture-resistant chipboard and regular chipboard
- When purchasing, you can check the strength of the slab . To do this, you need to insert a metal rod (key, screw, etc.) into the surface of the chipboard. If the rod goes in easily, without any additional force on your part, the quality of the slab leaves much to be desired.
- Consider the end of the chipboard . If the middle of the slab consists of larger chips, and the outer layers are made of small chips, such a slab is more durable and less brittle and will hold fasteners perfectly.
- Try crumbling a chipboard corner . If it crumbles easily, the slab is of poor quality. A deviation in thickness of more than 0.3 mm (if the curvature is visually noticeable) also indicates a low-quality product.
- Ask the seller for a certificate of conformity , check the markings on the packaging or on the chipboard sheet itself.
RESULT
- Chipboard is quite safe for people in terms of ecology, if you correctly approach the issue of choosing and studying its characteristics. Emission classes must be taken into account.
- Chipboard has many positive qualities: it is easy to use, easily amenable to any type of processing (drilling, cutting, etc.), withstands temperature changes, and is less demanding on the installation of fasteners than, for example, wood. If all technological rules are followed, chipboard can last for many years without losing its basic properties.
- Chipboard is the most common, inexpensive structural and finishing material, the main advantage of which is its availability and price. The area of application of chipboard is where the use of more expensive material is not feasible from an economic point of view.
The article was written for the site.
Tags:Wall panels
Color spectrum
Laminated and veneered boards do not differ in the abundance of colors. Paper film is usually painted in the color of various types of wood, although brighter products, often monochromatic, are offered for sale. Veneer gives the furniture status; it looks no worse than options made from natural expensive materials.
But a laminated board can be painted in completely different colors, shades, stone imitation, or a funny pattern. It all depends on consumer preferences. The matte or glossy surface of the facades looks different and can make the interior original. Modern laminated chipboard is visually difficult to distinguish from MDF. But the latter is easier to process. When choosing whether to purchase MDF or chipboard for making furniture, you should consider:
- difference in quality;
- purpose of the room where the product will be used;
- Cost of materials.
To reduce costs, manufacturers and ordinary consumers often combine two types of boards, making only facades from MDF. If high-quality components of both types of material are selected, the furniture will last a long time and be functional. And bright colors or an original surface pattern will add color to the room.