In conditions of moderate temperatures in most zones of Russia, such a well-known tree as alder, which is divided into several species, grows well. Due to its wide distribution and several distinctive quality characteristics, alder wood is valued in many areas of the wood processing industry.
The main features of alder wood
Alder belongs to the group of deciduous plants from the birch family. This tree grows and develops well near river banks, in swamps and in high mountain areas. Depending on the environmental conditions surrounding the alder, the type of soil, and temperature changes, the plant can be either a tree or a low-growing shrub.
Alder wood does not have a central core in its trunk, due to which the color of its cut is uniform. After cutting, the cut of the tree is whitish in color, but after lying in the air it gradually acquires a yellowish-red color.
Alder wood is valued for a whole group of its main qualities:
- This wood does not rot when used in water, and therefore it was widely used both in ancient times and now in the manufacture of piles and well foundations.
- Alder wood lends itself well to a wide range of joinery applications. It is easy to cut and plan, the wood produces products of various shapes; craftsmen use alder blanks to create unique crafts.
- The special texture of alder wood harvested according to standards allows it to be painted and processed using various paints, polishes, and stains. Thanks to this valuable quality, wood from different types of alder is used as a material that imitates, that is, copies, more expensive tree species. That is, the practicality of alder wood from this aspect of its use in production can be assessed as five points.
- Alder blanks dry practically without warping, which ensures high efficiency of working with this type of processed wood.
Alder blanks have increased resistance to external mechanical influences and deformation. Among soft-deciduous plants, alder rightfully occupies a leading position among trees that are highly resistant to rotting processes in water.
Photo of alder tree
Medicinal properties
Alder can be called a useful and even healing plant, which has great benefits for human health. The cones, leaves, bark and roots contain tannins, flavonoids, minerals and vitamins. Alcohol and water infusions, as well as decoctions, are made from medicinal raw materials of black or gray alder. The drugs help with colds, bronchitis, irritations and ulcers on the skin, inflammation of the mucous membranes, and bleeding. Alder has anti-inflammatory, astringent, hemostatic, and expectorant effects.
A decoction of cones is drunk for colitis, dysentery, diarrhea, bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract, nose and mouth. They are used to rinse the mouth for stomatitis and periodontitis. Tinctures from the root are recommended for women to normalize reproductive function and the menstrual cycle, and combat inflammation of the genital organs.
Typically, preparations made from alder have no contraindications, with the exception of an allergic reaction. However, moderation is needed in everything; it is not recommended to abuse or exceed recommended dosages, since certain components tend to accumulate in the body.
Types of alder and their description
According to some data, a little more than 40 species of alder trees grow on the planet. Only a few species of this deciduous tree are common in our state. The plant is unpretentious, grows well in areas with temperate climates, prefers moist soils.
Gray
Gray alder is a short tree, reaching a height of approximately 25 meters. In Russia, it grows in the northern regions, Karelia, western Siberia and most regions of Central Asia. Harvested wood from gray alder is used less often than from black alder.
This is due to the fact that gray alder often has a crooked trunk and takes a long time to reach the height required for felling. Despite this, gray alder wood is used to make plywood, particle boards, paper, and alder firewood. The environmental friendliness of the toys obtained from this tree species is rated five points. Various boxes and containers are made from prepared wood.
Photo of gray alder
Gray alder
Leaves, catkins and cones of gray alder
Black
Black alder has other names. Names often used for this type of plant are sticky alder or European alder. It grows almost everywhere in Russia. Trees growing on moist soils are especially valued, as they quickly reach the required height, have a smooth trunk and the least number of branches.
Black alder wood absorbs the least amount of water, it is coarse-grained and light. Black alder wood is well processed, therefore it is widely used in carpentry in the manufacture of furniture and the bodies of some musical instruments.
They are made from wood and containers for expensive products, such as tea and tobacco. Products in such packaging retain their quality for the longest period of time.
Photo of black alder
Leaves, catkins and cones of black alder
Black alder
Cordifolia
Heartleaf alder grows mainly in the Caucasus regions. During the first 40 years of its life, the tree quickly reaches a height of about 30 meters. This tree is used mainly for landscaping. If wood is harvested, its scope of use is almost identical to the scope of use of black and gray alder.
Alder is one of the most common trees in our state and therefore it is not surprising that the use of this wood is widespread. Low cost, fairly easy processing, the ability to manufacture various products - all these qualities make alder an irreplaceable wood species.
This is what a heart-leaved alder looks like in the photo
Reproduction methods
Alder is propagated by seeds, cuttings and root shoots. The most common method is seed and especially self-seeding. By autumn, ripe cones begin to open and release seeds. During November-March they fall into the ground and undergo natural stratification. After this, during the period of snow melting, the seeds are saturated with moisture and hatch. When planting, the seeds are embedded in melted soil to a depth of 2.5-3 cm. In the first year, only a small sprout will form and a rhizome will develop. Gradually, the seedlings become stronger and quite quickly turn into a lush bush or small tree. Every year it will increase in height by 50-100 cm.
Young shoots often appear from the trunk. In just a year, their height can reach 1-1.5 m. In the spring, the offspring can be dug up and transplanted to a new place. It is recommended to keep a lump of old soil on the roots and not allow it to dry out.
In spring and summer, cuttings 12-16 cm long are cut from young shoots. They are rooted immediately in open ground. Plants treated with a root formation stimulator show better survival rate. Cuttings need to be watered regularly. By autumn, the plants will take root and become strong enough to winter without shelter.
Density
Alder, regardless of its type and place of growth, is a tree species with high uniform density. That is, the difference between the structure of the earliest annual layers of the plant compared to the most recent ones is insignificant. With a standard humidity of 12%, the average density reaches 525 kg/m3. After the complete drying process, the density reaches 595 kg/m3.
In terms of its main strength parameters, alder wood is superior by several considered indicators to such popular trees in logging as aspen and linden. Also, after proper processing at enterprises and preparation, alder is almost as strong as pine and spruce wood.
The average value of different density indicators at natural humidity of 125% is equal to:
| Features of the measurement | Indicators of density, elasticity |
| When measuring wood at the moment of static bending | 79 MPa |
| At the moment of stretching along the main fibers | 97 MPa |
| When stretched in the radial, that is, across the fibers, direction | 7.2 MPa |
| During compression along the fibers | 45 MPa |
| Modulus of elasticity of properly prepared alder wood during static bending | 14.2 GPa |
Response to flowering
The frequency and abundance of flowering depends on the breadth of cultivation and the type of plant. Most trees, including black alder, bloom in the second half of spring. Long catkins may form as the leaves bloom.
Alder wood and other wood are widely used in various industries. However, decoctions and infusions are strictly prohibited during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
Alder can cause an allergic reaction.
There have been cases of individual intolerance to alder.
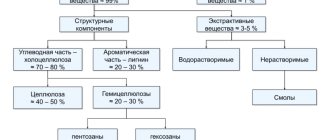
Chemical components
Alder wood, like most of the hardwood group, consists of organic substances and mineral compounds. Alder wood also contains unique tannins, referred to as polyphenols. After cutting down a tree, these polyphenols upon contact with air are oxidized and converted into phlobaphenes.
It is the phlobaphenes that determine the changing color of the tree from white to reddish. Phlobafens also give wood high resistance and strength in water. Alder wood is also rich in tannins; these compounds, when reacting with certain chemical reactions with heavy metal salts in water, form unique compounds that increase the strength of the wood.
Due to these elements and properties formed after cutting the trunk, alder wood is little subject to rotting under conditions of use in an aquatic environment and is resistant to the activity of many pathogenic microorganisms for plants.
Landscape use
The oval, openwork crown of the alder with moving branches and fluttering leaves looks very lively. Plants do not suffer from urban air pollution, so they can be planted along the road. Low trees or lush shrubs up to 3 m high are usually used as hedges. They are planted in a strip method quite densely and regularly shaped.
Large single-trunk trees are used in single plantings or in groups over a large area. They are planted along paths and alleys. Alder can also be used in compositions of shrubs and trees, combining plants with different colors and foliage structures.
Ignition temperature
The combustion heat of alder wood is 4.1 kWh/kg. Alder firewood flares up quickly enough, due to the lack of resin it does not emit fumes, burns for a long time and produces a hot flame. Alder firewood has a delicate aroma that lasts for years.
Due to its distinct smell, alder shavings are used for smoking meat and fish. Sawdust generated during the processing of alder is used to produce pressed briquettes used in fireplaces. The thermal conductivity of alder wood reaches the level of 0.15–0.17 W/(m×K).
Symptoms and consequences of hay fever for people at risk
The main reason for the development of seasonal allergies is considered to be a hereditary predisposition. If only the mother or father has this disease, then the probability that the child will have hay fever is 25%. However, if both parents have individual sensitivity to pollen, it increases to 50%. In the case where immediate relatives do not have a tendency to allergies, the risk factor is within 10%.
Attention!
There are 4 periods of danger for people with reduced immunity and a tendency to hay fever: flowering of trees, meadow grasses, cereals and weeds. The latter is considered the most dangerous.
You may be interested in: Schedule of holidays and weekends for November 2022 Calendar of weekends and holidays in June 2020 in Russia Schedule of magnetic storms in June 2022
Doctors advise studying flowering schedules for allergy sufferers by month and day in 2022 for people who are faced with the following features:
- live in regions with unfavorable environmental conditions;
- have allergies to food or medications.
- eat junk food with a high content of dyes and other synthetic additives;
- are constantly under stress;
- In childhood, I often suffered from diathesis.
Seasonal allergies can be recognized by four main symptoms: watery eyes, itchy and red eyes, and nasal congestion. Signs appear suddenly and are clearly defined. Additionally, shortness of breath, coughing, and wheezing may occur. Among the consequences, the addition of a secondary infection and anaphylactic reactions, which pose a serious threat to life, cannot be excluded.
Color shades and texture of alder wood
If you look at a cut of freshly cut alder, you will notice that its color is almost white. After the alder lies in the air for a while in this form, its color begins to change. At first, sawn and prepared wood turns slightly pink, then it acquires different colors of red, ranging from the lightest, yellowish to deep brown.
The color change occurs due to the release of polyphenols, which in air are converted into a coloring pigment - phlobafen. After alder wood has undergone the correct, standard drying process, its color changes to chocolate.
Alder wood is valued by specialists for its homogeneous structure; it does not have a pronounced core; the annual rings on the cut are practically not separated from each other by any visible effect. The rays emanating from the middle of the tree are also faintly noticeable.
Due to the softness of the wood and its special absorbent parameters, blanks from this plant can be painted in any color shades. With proper processing and preparation of wood, craftsmen receive unique wooden crafts and products that, in their external characteristics, completely imitate expensive types of wood.
Botanical characteristics
The average lifespan of an alder tree is no more than half a century.
An alder tree in its natural habitat can reach more than twenty meters in height. The crown often has an irregular shape. The culture prefers dense thickets. The trunk diameter of an adult tree is about half a meter. You can see depressions and humps on the trunk.
The tree is characterized by a rapid pace of development. At ten years the plant can reach adulthood. After maturation, the annual growth rate decreases significantly. The average life cycle of a tree is about fifty years. There are known cases of reaching a hundred years of age.
The superficial root system of alder is located in the uppermost layer of the substrate (at a depth of up to twenty centimeters). The main feature and value of alder for gardeners is the settlement of nitrogen-fixing bacteria on alder nodules. The plant is capable of saturating the soil with nitrogen.
Alder wood standards according to GOST
The grade of alder wood already in the process of harvesting is determined by several parameters. This is the smoothness of the trunk, the number of knots and certain malformations, the most important of which include cracks and curvature of the trunk.
The grade of harvested alder wood largely depends on where the harvested tree grows and whether all conditions for standard wood processing are met during the manufacturing of lumber from it.
The price of alder wood and lumber made from it is estimated by experts at 4 points. The cost of this wood makes it possible to obtain cost-effective products from it that are used in various spheres of human life.
Harvesting, drying and medicinal properties of alder:
WHERE THE FOREST DOESN'T GROW
Our most common type of alder is gray alder. It has a thin trunk covered with smooth gray bark. Oval, slightly jagged along the edges, the leaves are dull green in color and by autumn they do not become brightly colored, but fade and turn brown.
You can often find the definition of alder as a weed tree. But is it? Is alder really taking away space from more valuable species? Not at all. Alder usually settles where no decent tree is able to grow: on thin clayey and peaty soils, acidic and flooded by groundwater. Alder often grows in ditches, lowlands, and flooded river floodplains.
In other years, the bases of the trunks are constantly under water - and nothing, the trees do not rot or get sick, but continue to grow! In more favorable places, alder is quickly replaced by birch, aspen, and spruce. On dry sandy soils it practically does not grow at all, leaving the territory to pine trees.
So, if an alder has settled on your site, this is a signal about the immediate start of work to drain groundwater and improve the composition of the soil.
Care
In order for alder to live long and decorate the area, you must follow simple rules of care:
- Protect the plant from various pests and diseases. It is susceptible to fungal diseases. For treatment it is necessary to use special formulations. Diseased areas are immediately removed and burned. Alder can also be damaged by insects. Some of these pests are lancet, woodworm, cutworm, moth, and alder corydalis. If they arise, it is not easy to fight them. To do this, it is necessary to use chemical preparations. And for prevention, first of all, it is necessary to dig up tree trunk circles during the wintering period, and also install traps made from garden glue.
- Water. Alder loves water, so with the onset of a dry period it is necessary to water, but with warm water.
- Get a haircut. Regular pruning is not required if these are not decorative specimens. In the latter case, to do this you need to wait until the plant sheds all its foliage. You can remove diseased or injured branches in the summer. The main thing is to finish this before the frost arrives.
- Loosen the soil. This procedure is carried out before wintering or when there are a large number of weeds around the trunk. To simplify maintenance, gardeners also lay out mulch from peat or wood chips.
How long do trees bloom?
Flowering lasts about ten days; in central Russia it occurs at the end of spring.
Interesting materials:
How to unsubscribe from a group in contact? How to unsubscribe from Kviku? How to unsubscribe from Sea TV? How to unsubscribe from Yandex mailing lists? How to unsubscribe from emails sent to your inbox? How to send a long video on WhatsApp from an iPhone? How to send MMS photos? How to send a folder to telegram? How to send a parcel via Peak Point? How to send a parcel to Belarus?