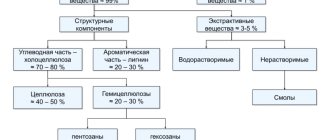
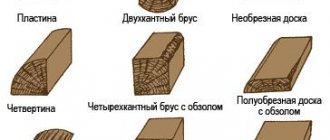
Types and differences of wood
There are many types of wood, and you need to choose them depending on the purpose. Differences may be in:
- degree of hardness, and therefore durability of wood;
- characteristics of rings;
- sensitivity to moisture;
- resistance to solar radiation;
- blossom.
There are three main types of wood: hardwood, softwood and exotic.
Fir
Similar to the structure of spruce - soft to process, little resin. However, the last nuance played a cruel joke on its ability to compete in the struggle for the construction of a log house - it is practically unprotected and is a tasty morsel for fungi and parasites. It is also impossible to make interfloor ceilings from fir - if completely dried, it is capable of breaking or, at least, cracking.
Soft and hard rocks
Softwoods are easy to work with, making them versatile. Soft wood mainly includes coniferous species such as pine, fir, and spruce. But hardwoods such as poplar and linden can also be found. These trees grow quite quickly and are available in our latitudes - hence their availability and relatively low price.
Hardwoods, in turn, are divided according to their degree of hardness. So, oak and walnut are medium-hard wood, ash or teak are hard, hornbeam is very hard. One of the hardest species is ebony. All hardwoods grow fairly slowly, making them more expensive than softwoods.
Cedar
Dry varieties are especially valued - those that grew far from the massif.
The hardness of cedar is inferior to larch, but it was also used in shipbuilding, where it is unlikely that they would use flimsy rock.
Another advantage of cedar is its good mechanical processing - it lends itself to any tool.
The main advantage that all coniferous wood for log houses has is the increased concentration of phytoncides - protective essential oils.
Cedar can boast of this in abundance. The disadvantage is the cost - this is an elite variety.
Hardwood
When it comes to hardwoods, oak is undoubtedly the king because oak wood is very hard and abrasion resistant, making it an ideal flooring material.
The only downside might be the price, but the durability of oak wood is such a huge and real benefit that it ends up convincing many buyers.
What other types of hardwood are there? In addition to oak, it is also worth highlighting the main hardwood species:
- Acacia;
- Beech;
- Sycamore;
- Ash;
- Alder.
Pine
An affordable and popular material for deciding which types of wood are suitable for a log house. With it you can build both luxury housing and an economy option. It has all the advantages of the varieties described above.
Pine is a relative of cedar, therefore it is also easy to process, beautiful and ideal for building housing for year-round use. It has a healing effect - the atmosphere will be filled with molecules of natural “spirits” throughout the entire period of operation.
Exotic breeds
Precious wood species due to their strength, hardness and high scratch resistance. Such wood can be so hard that it is difficult to hammer a nail into it, and this is by no means a fantasy.
Among the main representatives:
- Doussey;
- Kumara;
- Merbau;
- Teak;
- Iroko;
- Ipe;
- Wenge;
- Bangkirai;
- Denya.
Properties of valuable wood species
Valuable species are superior to common construction trees due to certain features, because they:
- stronger and have a longer service life;
- look more beautiful and noble;
- have a unique pattern and unique ring design.
What is the reason for the richness of patterns? Increased layer density.
Wood species and their applications
The presence of wood in homes is very common, from floors to furniture, kitchen countertops, all kinds of finishing accessories, wooden elements. Wood is used for interior design and, more recently, for wooden toys for children, which are non-toxic and biodegrade more quickly.
However, when choosing a tree for a home, a person must understand that, despite many advantages, wood also has disadvantages. Its ability to absorb moisture is undoubtedly one of them. The disadvantages include shrinkage or cracking of wood.
Fortunately, this can be corrected with proper maintenance techniques to prevent defects from occurring. This is important due to the fact that the use of appropriate impregnations, oils, and varnishes extends the service life of wood for many years.
Properties of fruit tree wood
Fruit trees are not often used in construction or applied business, and if they are used, they are wild trees. The properties of their wood attract the attention of craftsmen.
Pear
It has a pink or yellow-white color. Strong material, perfectly processed, regardless of direction. To impart hardness, the wood is soaked and then dried in the open air, protected from direct sun. It polishes well, does not crack or warp. There are pests in wood.
Apple tree
Easy to handle. When dry it bends a lot. Used in the manufacture of pads.
Plum
Characteristics similar to apple tree. Thanks to its special texture, it is used in the production of utensils, jewelry and furniture.
Walnut
Dense structure that can be easily processed. It has a very pleasant texture. Can be completely bleached using hydrogen peroxide. Well tinted and painted. Woodworkers create excellent furniture.
Most popular breeds
A few words about the main types of wood that are most often used in production.
Birch
Birch wood has high mechanical properties. Works very well on a wood lathe. Burns even when wet. It is used in the furniture, paper and woodworking industries.
Medium hard and heavy. It is used to make plywood, carpeting, and furniture. It is also used for dry distillation and for the production of charcoal.
Beech
Beech wood is hard and heavy. More detailed information can be found in the wood species table. It is an excellent furniture material and is also suitable for parquet, plywood and chipboard. It is used to make barrels, boxes, tools, machine parts, sports equipment and many everyday items.
The chemical industry produces paper, wood vinegar, charcoal and tar oil from beech. Suitable for turning.
Oak
Relatively heavy and hard, oak wood is commonly used for carpentry and furniture. Its abrasion resistance makes it ideal for flooring boards.
Over time, oak products naturally darken from water, and due to the tannin content, they easily react with chemicals, especially paints (salts, acids, alkalis).
During severe frosts, oak cracks due to high internal stresses. This wood is ideal for interior carpentry, but is very risky for exterior work, especially windows and doors.
Ash
Ash wood is hard, flexible and heavy and is used in carpentry, furniture and violin making. Dark ash is harder and more durable than oak. Available in 16 wood shades. The darker the wood, the harder it is.
Pine
Pine wood is easy to process, elastic and has good mechanical strength. It was previously used as a material for utility poles or railroad sleepers.
Commonly used in carpentry and in the production of paper, plywood and wood wool. Scots pine wood is suitable for cladding interiors, windows and doors, floors or furniture.
Properties of coniferous trees
Coniferous trees are characterized by high resin content and a pungent odor. They differ from deciduous trees in a more pronounced structure.
Pine
This tree is the most famous among woodworkers. Stroyles has a color from almost white to brown. Trees growing at higher elevations with little moisture have a harder and stronger structure.
- Pines growing in moist soils have a looser structure.
- Dry pine material is easy to process - you need to plan along the grain and saw across it.
Furniture, structural bases, windows, doors, and stairs are made from pine.
Wood is perfectly decorated with varnishes and paints.
Spruce
Softer than pine, but difficult to process due to the large number of knots. It has an inexpressive texture.
- Spruce is more susceptible to rotting, but warps less.
- The material is poorly processed, but it glues easily.
- The knotty nature allows it to be used as a mosaic.
Spruce is used in structures that do not experience serious mechanical loads.
Fir
It is less durable than spruce, with the same scope of application.
Larch
The strength of larch exceeds that of oak. The wood has a red-brown color.
- Moisture-resistant material, easy to process.
- The highly resinous fiber quickly coats the processing parts of machine tools.
- The lumber does not warp, but with accelerated drying, cracks appear.
- Used for carpentry and carving work.
Paints well with nitrocellulose varnishes.
Cedar
The material is rot resistant. At the same time, it is not particularly strong. Endowed with a beautiful texture of various shades. It depends on the place of growth.
- Cedar is not susceptible to wood pests.
- The tree has a sharp, unique smell.
- Used to create wooden furniture frames.
- Suitable for cutting tools.
Typically, cedar is not polished, but coated with wax.
Juniper
The shrub has a trunk diameter of up to 10 cm. It has durable wood, with thin layers. The material is easy to process and has a special smell. Serves as a raw material for the manufacture of small items, mosaics and wood carvings.
Cypress and thuja
Trees with properties similar to juniper. They have wider dark wood. Successfully used for wood carving. Cypress does not develop defects during drying.
Yew
Contains red-brown wood with white sapwood. Hard and strong rock with many knots. Unaffected by insects and atmosphere. Easily amenable to carpentry tools, polished and painted. Good for cutting and making mosaics.
There is no universal breed
There really is no one type of wood that is right for every project. It all depends on what needs to be done.
There are other interesting woods in the furniture industry such as elm, alder, acacia and birch. There are also many exotic wood species, it is impossible to list them all.
In general, hardwoods dominate over softwoods in the furniture industry. This is because these woods are harder and have a more interesting grain.
Which wood will be chosen should depend, first of all, on the type of product, its purpose and the place where it will be located. This should be taken into account when choosing wood of different species.
The role and importance of wood in construction
It is known that, according to their intended purpose, wooden building materials are quite clearly ranked into general construction and finishing. The former are used to build walls, ceilings and other structures, while the latter are used for decorative purposes. The areas of interchangeability are extremely limited. For example, walls are not covered with thick boards even for reasons of improving sound insulation. And a frame is not assembled from thin lining. Of course, there are deviations from the rules, but the implementation of exclusive solutions is always expensive and not always justified. It is equally important in construction, in addition to this classification, to clearly understand the properties of wood and the advisability of its use in a certain situation.
The valuable construction properties of wood determine the areas of its effective use. The low density of dry wood with relatively high strength and rigidity (along the fibers) makes it advisable to use wooden structures in coverings of public, industrial and agricultural buildings. Environmental friendliness makes wood especially suitable for the construction of private housing. In the enclosing parts of heated buildings, the low thermal conductivity of dry wood across the fibers is well used.
The importance of wood in construction
For load-bearing structures, pine, spruce, larch, fir, and cedar are used. Deciduous trees - aspen, birch, alder, linden and poplar - are used only in the construction of temporary buildings and structures, as well as for formwork, scaffolding and scaffolding . Glued-laminated timber structures best meet the requirements of modern construction. They make it possible to improve the quality of construction and widely use prefabricated parts of any shape and size. Glulam structures are the most economical in terms of wood consumption.
The use of new materials such as waterproof plywood, particle boards and fibreboards, laminated plastics and fiberboard makes it possible to use wood and waste that is of little use for construction. Industrial production from dried material and the use of the necessary structural and chemical measures to protect wood from rotting and fire hazard create conditions for a significant increase in the capital value of wooden structures.