Chestnut tree
Chestnut is a member of the Legume family. Reaches a height of 30 meters. The characteristics clearly indicate greatness and superiority over other types of trees growing in its territorial area.
Description of chestnut tree:
- trunk more than 2 meters wide.
- The leaves are wide, oblong-lanceolate with pointed ends. The length is about 15-25 cm.
- The flowers are large, white, and upward-sloping flowers look like luxurious earrings created by nature. Each flower is divided into 6 petals and 6-15 stamens.
- The nut is interesting in appearance and content. Covered on the outside with a thick, prickly crust, it looks like a hedgehog. The fruit itself consists of cellulose, starch and sugar. It is brown in color and divided into two or three parts inside the peel.
Chestnut is a long-living plant. The age of the tree can exceed 1 thousand years.
And in the vicinity of the Sicilian volcano Etna, the legendary Chestnut of hundreds of horses was found. It blooms unusually beautifully and is the hero of an ancient Italian legend. It is worth noting that the specimen survived about 4 thousand years.
This video shows how chestnut blossoms in stages:
Distribution history
The spread and acclimatization of the chestnut tree goes back a long way. From the very beginning it was known during the era of the great Greek Empire.
Chestnut was valued for its qualities:
- nutritious fruits;
- the use of tree trunks as material for the production of ships and furniture;
- use of nut-based medicines;
- aesthetic aspect when the tree blooms.
The Greeks developed breeds to achieve specific purposes: for making Spartan black bread, flour or soups.
In the eighth century, the chestnut again began to enjoy popularity among members of high society, becoming a main ingredient in the production of sweets.
Japanese chestnut or crenate
Japanese chestnut or crenate chestnut (Castanea crenata) belongs to the genus Chestnut, of the Beech family. Deciduous tree or shrub, up to 15 m in height. The leaves are elliptical, long, up to 16 cm, sharp-toothed, oblong, lanceolate, dark green, on petioles up to 12 mm long. Young shoots are red-brown, pubescent, later glabrous. Plus with bare spines, up to 5.5 cm in diameter. Each plus has 3 fruits with a gray spot at the base, 2-3 cm in diameter. The tree grows quite quickly. It begins to bear fruit at 3-4 years of age. Demanding on soil and air moisture. Frost-resistant. Withstands temperatures down to – 20 °C. Under natural conditions it grows in the mountain forests of Japan, China and Korea. It has decorative value.
Used in group and single plantings as an ornamental and fruit tree. Japanese chestnut is not susceptible to pests and diseases. It has several decorative forms, differing in the shape of the crown and leaves.
The most common are: weeping - with a drooping crown and edible - with large fruits used for food raw and boiled. The fruits contain starch, fats, proteins, sugar and ash. It has been cultivated in Japan for more than 1000 years, during which time about 100 varieties with large, edible, palatable fruits have been bred. Several varieties were bred in America.
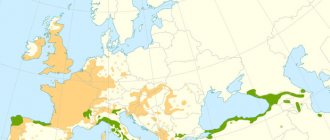
Where does chestnut grow?
The distribution area of the chestnut tree is wide:
- Spain;
- France;
- Part of Switzerland (Valais, Southern District);
- Italy, including Alpine valleys;
- Croatia;
- Balkan Peninsula;
- Asia Minor;
- Caucasus;
- Persia;
- South Africa.
Many species have spread as far as Japan and the United States of America. This is a typical forest tree, especially common on the Italian mountain slopes and also known in the Mediterranean Sea, with plantings reaching the Black Sea.
For fruitful growth you need:
- The soil . The chestnut tree does not live in isolation from other species. Loves siliceous soil or limestone. Chestnut blooms fruitfully in fresh soil, although it does not seek excess moisture. It is not planted in garden areas, as its size will become a serious problem for the development of other plants and species. The chestnut tree does not require special conditions for growth. Grows even in poor soil. The main thing is that it is a neutral layer of earth, with slight acidity, and does not contain clay.
- Temperate climate . Trees do not like constantly wet and compact soil, and also do not tolerate prolonged drought, especially in summer. In areas with high temperatures and dry climates, trees find their place in mountainous areas or among the hills, where the summer heat does not exceed dangerous levels.
- No low temperatures. Can withstand temperatures of -20 degrees in winter. But if this situation drags on for several weeks, the tree dies.
- High temperatures. It also tolerates heat normally if it does not exceed a short period. In this case, it is recommended to plant trees in a more ventilated area and with shade during the hottest time of the day. The chestnut tree is not afraid of drought, which does not last long and does not affect the period when the chestnut tree blooms.
Methods of propagation and planting of chestnut
You can grow a tree in different ways:
- Using seeds. In this case, you should not count on high germination rates, and you will have to wait quite a long time for the first shoots;
- Purchase ready-made seedlings from a store or nursery. The best age for a seedling to grow easily and quickly is from 7 to 10 years;
- You can use fruits. However, this method will be too long. He will require certain conditions for cultivation to be observed.
How to plant in autumn and spring
In autumn, the fruits are collected and kept in a cold place for 7 or 10 days. Only undamaged specimens need to be selected. You can learn from nature - throw a small pile of fallen leaves on the nut in the place that you have previously marked. In the spring it will be possible to find sprouted nuts that make good seedlings.
The cold-prepared fruit is planted to a depth of up to 3 times its diameter. The soil is watered. This method allows you to grow strong shoots, as they have time to undergo natural stratification in winter.
You can start planting when spring arrives. Until this moment, chestnuts should be kept in the refrigerator and only before planting they are placed in warm water for five days, which is changed twice a day. You need to wait until the nuts swell so that the sprouts can easily destroy the shell. The “blanks” are planted in moist soil.
You can plant the nut in a pot at the end of autumn. In winter it will begin to germinate, and in the spring it will be completely ready for planting.
How to properly plant seedlings
For seedlings to take root well, you need to:
- The area for one seedling should not be less than five meters in diameter;
- A hole is dug up to 0.5 meters deep. It should be shaped like a cube;
- Drainage is placed at the bottom of the hole. Its thickness should be at least 30 centimeters. Crushed stone or sand is well suited for this purpose;
- Soil is added to the hole and mixed with humus. If the soil has a high acidity level, add another 0.5 kg of dolomite flour;
- The root collar of a seedling planted in a hole should be at soil level;
- The planting hole is made 10 centimeters higher so that the trunk does not become exposed when the soil settles slightly;
- It is necessary to water the planted plant abundantly. Usually four buckets of water are enough;
- Support the young tree with a wooden peg, which will give it stability and help it withstand the pressure of strong winds. The support is removed when the root of the plant becomes stronger.
Chestnut does not require special care. It tolerates high temperatures well and does not need abundant watering. If the dry period lasts for too long a period of time, you need to water according to the following scheme: 10 liters of water per square meter of crown diameter (like a pear). Young growth should be watered regularly. What else is included in basic care?
- Pruning damaged or dry branches;
- Mulching the soil;
- Feeding;
- Removing young shoots from the trunk, as a slender and beautiful central trunk is formed.
As soon as spring arrives, you can start fertilizing. Usually organic matter is used for this. One kilogram of mullein and 20 grams of urea are mixed in 10-12 liters of water. If fed in the fall, also add 20 grams of nitroammophoska.
Peat, as well as wood chips or sawdust, are good for mulching. The mulch layer should not be less than 10 centimeters.
When does chestnut bloom?
The peculiarity of flowering is that it begins quite late compared to other fruit trees.
The swelling of the buds and the opening of flowers usually occurs in May.
This advantage avoids the risk of frost during bud opening and, as a result, loss of nuts.
And also a lot depends on the breed. Certain categories of chestnut fruit trees adapt to the required temperatures and begin to bloom when the climate becomes suitable for them.
Flowering lasts about 2-3 weeks, after which small green nuts are formed.
How does chestnut bloom?
An impressive moment in the life of this tree is the moment of flowering. With the arrival of spring, the tree comes to life after winter sleep. It transforms in such a way that it is impossible to take your eyes off its beauty and charm.
Description of chestnut flower:
- Flowers come in different shades depending on the specific type of wood.
- Often these are large white blooms with red or pink specks.
- The shape of the flowers resembles medieval candles.
- The structure is unusual and complex.
- Along the crown there are many individual flowers that form a pyramid.
- They reach almost 2 cm in diameter, surpassing any tree in size and beauty of flowering.
Photo gallery: flowering chestnut tree
Why doesn't it bloom?
Chestnut does not require constant care and is easy to grow. What factors influence the development of a chestnut tree and why does it not bloom?
Here are the main reasons:
- Age . Some species of this tree do not begin to flower until they reach ten years of age. There are also breeds that need longer time.
- Lack of space . The chestnut tree is a large specimen. It is important to have the space necessary for growth. When there is not enough space, the tree stops developing and stops blooming. It is important to ensure that there are no other trees within a radius of at least six meters from the trunk. When the chestnuts are close, it will be cramped for one. In this case, a strong tree will take away moisture and soil, and the other will die from lack of opportunity to grow.
- Unsuitable air temperature . A tree with inedible nuts always blooms, since it does not need a certain temperature. It is enough that it is not too high or too low. The situation is different with edible breeds. Often, they require 13 – 18 degrees above zero to bloom. In cold climates, chestnuts do not bloom.
Landing rules
As mentioned above, chestnuts have a very voluminous crown, so they require a lot of space. It is recommended to plant the tree in an area where there is a lot of sunlight. With insufficient lighting, flowering will be poor.
In order for the chestnut to develop well, there should be no buildings or vegetation at a distance of 5 meters from it.
If you plant a tree as a seedling, the optimal time is the beginning of spring or the end of autumn. When nuts are used as planting material, the best time is the end of spring, or they are left for the winter in the fall.
The root system of the tree does not go deep and spreads along the surface of the soil. To avoid water stagnation after watering, and the roots do not suffer from this, for this purpose, select soil with neutral acidity, or at most slightly acidic. There must be good drainage at the bottom of the planting hole. The optimal soil for the plant is black soil. If the soil is sandy, add a little clay to it.
Types of flowering chestnuts
Over the centuries, growing trends have changed and different types of wood are found. They vary in distribution area and in fruit quality, tree structure, longevity and use.
Chestnut
Popular view. Blooms in areas of constant rain and high humidity. The fruits are suitable for consumption with a pleasant sweetish taste. The main ingredient in the production of sweets and jams.
Chestnut
Fruits of chestnut
Horse chestnut
The horse chestnut, or common chestnut , is a centuries-old tree with roots in Western Asia and Eastern Europe. Popular all over the world. The horse species is used as an ornamental plant for parks and alleys. Nuts are not edible. The name suggests that horse chestnut was used mainly as food for horses.
Description of the species:
- Horse chestnut is similar to sweet chestnut in terms of tree structure, but their fruits are very different from each other.
- The horse variety is larger in size and the skin is much coarser than the sweet variety.
- The needles are wide and less frequent.
- Horse chestnut fruits contain a high percentage of saponins and glucosides, which are unpleasant to the taste.
horse chestnut
Horse chestnut fruit
Australian chestnut
This species does not take its name from its country of origin. The Australian species was brought to the mainland by emigrants. In particular, from Great Britain, Ireland and China, who arrived in Australia for the purpose of gold mining between 1850 and 1870.
The Australian chestnut differs from other breeds in its ideal shape. It amazes with its bright emerald hue and smooth leaves. Gets along great even at home. In favorable conditions, the height reaches 10 meters. The fruits have a sweetish, rich taste and are suitable for making jam.
Australian chestnut
Australian chestnut fruits
Japanese chestnut
Distributed on the mountain slopes of Japan. The tree blooms very early - already in the second year after planting. Selects clay soil and humid climate. The height of an adult specimen is about 15-20 meters. The branches fall to the ground and bear large edible fruits.
Japanese chestnut
Japanese chestnut fruit
Chinese chestnut
The species blooms mainly in China, Vietnam and Korea, creating entire chestnut forests. Chinese chestnut chooses soils rich in calcium. The flowering period begins quite late - in the fifth year after planting.
Flowers of the Chinese species are unlike any inflorescence of other species . These are the thinnest long flowers, shaped like the top of a reed. The fruits of Chinese chestnut are used in the food industry and construction activities.
Chinese chestnut
Chinese chestnut fruit
Red chestnut
A tree of the horse chestnut family, a rare species. It is fragile and grows in parks. Due to its bright pink flowers and pleasant scent, red chestnut is often used for decoration purposes. It begins to bloom in early spring and ends flowering at the end of the season.
Red chestnut
Guinea chestnut
Originates in the tropical forests of Central America. The biggest maintenance challenge is the large amount of water the tree requires to grow. The Guinea chestnut is a bright representative of the Baobab family. The shape resembles a bottle, since in the lower part the chestnut tends to accumulate moisture to saturate the trunk of the fruit.
In Russia, Guinea chestnut is used as part of home interiors . It adapts well to room temperature and does not exceed small sizes if the space is limited by a vase. Flowering Guinea chestnut at home is almost impossible.
Smooth chestnut
Another representative of the horse chestnut family, therefore the fruits of the subspecies are inedible. Smooth chestnut blooms mainly in areas of North America, Central Asia and Europe. Frost-resistant and light-loving breed.
forest chestnut
The tree originated in Turkey, after which it spread throughout Europe. Forest chestnut is popular in the United States, where it is part of the crops that decorate national parks and gardens with beautiful flowers. The tree cannot bear edible fruit. Therefore, it is used only for decorative purposes.
Varieties
Insects