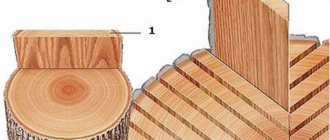
The cross-sectional shape and dimensions of railway sleepers are standardized and must strictly comply with the technical regulations of GOST 78-2004 for each specific type of sleeper product. The purpose of railway tracks and their capacity is the main criterion for classifying sleepers and determining their overall parameters and other technical characteristics.
Classification by type
All parameters of the rail support must meet the requirements of current interstate standards and technical specifications. Based on this, the VSP base element we are considering can be described and subdivided according to several properties at once.
With standard length and width, wooden sleepers are even today consistently used on the following classes of tracks:
- I-II – if they can withstand vehicle speeds exceeding 100 km/h and a load load of more than 5,000,000 t/km per year without deformation;
- III-IV - these mean intensively functioning access lines, as well as sorting and receiving-dispatch lines;
- Class V tracks, including those with little activity and for shunting and removal operations.
Strict standardization is also important here, which is why the above railway options are today designed and built with the active use of suitable rail supports. Types and sizes of railway sleepers are divided into:
- The first type (1) is for main paths (I-II class paths).
- The second (2) is for the entrance and station sections (III-IV).
- The third (3) is for organizing transport interchanges for enterprises and industrial facilities (V).
There is also a classification according to the type of section:
- trimmed - the section is a regular square;
- semi-edged - one corner is missing in the profile;
- unedged - opposite (relative to each other) edges have been removed, which is usually relevant for used VSP elements.
Theoretical weight of VSP materials | LLC ZhD Invest
| Name | Price with VAT | |
| Railway bolts | ||
| Mortgage bolt M22x175 | 0.635 kg | |
| Mounting bolt M22x175 assembled | 1.011 kg | |
| Terminal bolt M22x75 | 0.345 kg | |
| Terminal bolt M22x75 assembled | 1.204 kg | |
| Terminal bolt M22x75 with nut | 0.459 kg | |
| Butt bolt M18x88 with nut (R-24) | 0.262 kg | |
| Butt bolt M22x135 with nut (R-43) | 0.61 kg | |
| Butt bolt M24x150 assembled (P-50) | 0.806 kg | |
| Butt bolt M27x160 assembled | 1.128 kg | |
| Railway nuts | ||
| Nut M22 | 0.126 kg | |
| Nut M24 (butt) | 0.153 kg | |
| Nut M27 (butt) | 0.22 kg | |
| PC terminal | ||
| Intermediate terminal PC | 0.625 kg | |
| Railway crutches | ||
| Travel crutch 14x14x130 | 0.18kg | |
| Travel crutch 16x16x165 | 0.38kg | |
| Railway pads | ||
| Overlay 1Р-43 | 16.01 kg | |
| Overlay 1Р-50 | 18.77 kg | |
| Overlay 1Р65 | 29.5kg | |
| Overlay 2Р-65 | 23.78 kg | |
| Transfer beam | ||
| Railway chocks | ||
| Lining D-43 | 5.26 kg | |
| Lining D-50 | 6.2 kg | |
| Lining D-65 | 7.66 kg | |
| Lining DN6-65 | 8.44 kg | |
| Lining KB-50 | 6.85kg | |
| Lining KB-65 | 6.85 kg | |
| Lining KD-65 | 9.6kg | |
| Lining SD-50 | 6.5 kg | |
| Lining SD-65 | 6.97 kg | |
| Anti-theft | ||
| Anti-theft P-50 | 1.22kg | |
| Anti-theft P-65 | 1.36kg | |
| Rail insulation | ||
| Rails | ||
| Rails R-18 | 17.91kg/m | |
| Rails R-24 | 24.9kg/m | |
| Rails R-43 | 44.65kg/m | |
| Rails R-50 | 51.67kg/m | |
| Rails R-65 | 64.88kg/m | |
| ARS fastenings | ||
| Turnouts | ||
| Railway washers | ||
| Double-turn washer M22 | 0.12kg | |
| Single-turn washer M24 (R-50) | 0.068 kg | |
| Single-turn washer M27 (R-65) | 0.093kg | |
| Flat washer-bracket TsP-138 | 0.09 kg | |
| Wooden sleepers | ||
| Reinforced concrete sleepers | ||
| Railway screws | ||
| Travel screw M24x170 | 0.56kg | |
www.gd-snabjenie.ru
Length and other overall dimensions of wooden railway sleepers
They have long been standardized to provide practical advantages of rail supports, including:
- excellent processability of environmentally friendly material;
- maintaining high elasticity with relatively low weight;
- a serious margin of resistance to temperature changes and seasonal changes in heating/cooling cycles;
- interaction with the ballast cushion, which does not lead to destruction of the VSP;
- a wooden sleeper is a dielectric.
Application
Wooden sleepers can be used in any laying areas: link tracks with wider gauges, narrow gauge tracks, curves with a small radius (up to 300 meters), on swampy soils, in permafrost zones, on unstable soils, on tracks with high freight traffic.
The use of wooden sleepers is more effective than reinforced concrete sleepers on continuous continuous tracks that are intensive in cargo transportation.
Dimensions of wooden railway sleepers according to GOST
All dimensions under consideration are regulated by the interstate standard GOST 78-2004, approved for all countries of the customs union. It came into force in 2006 and stipulates the use of structures of all 3 section options described above, all five classes of track - for laying or restoring wide and narrow railway tracks and, in addition, for the construction of various buildings and structures.
The geometry and condition of the rail supports must also comply with GOST standards in order to maintain all operational advantages and, in general, the possibility of their safe operation. To extend the service life of VSP elements, they are coated with antiseptics.
This operation is performed in autoclaves to protect against the harmful effects of moisture, fungus, mold, bark beetles and similar insect pests. Moreover, the quality of impregnation must comply with GOST 20022.5-93. The recommended penetration depth of the product depends on the type of timber.
Mechanical processing (if it is important) is carried out first.
Control methods.
3.1
Determination and measurement of wood defects and processing - according to GOST 2140.
Determination of the quality of impregnation of sleepers - in accordance with the requirements for impregnation of sleepers at sleeper impregnation plants.
3.2
The length of the sleeper should be measured at the shortest distance between its ends, the thickness - anywhere, but not closer than 380 mm from the ends, the width of the upper and lower layers - in the narrowest place in sections 400 mm long, spaced at a distance of 380 mm from the ends of the sleeper
3.3
The dimensions of the sleeper are measured with a metal tape according to GOST 7502 or a metal ruler according to GOST 427.
3.4
Control of pre-impregnation moisture content of sleeper wood - according to GOST 20022.14.
Transfer bars
Transfer bars are crossbars on the railway track at the places where switches are installed. The beams for transfers are laid on the upper ballast layer of the railway track.
Finished VSP elements of this type must comply with GOST 8816-70.
Below is a sketch of the cross-section of the beams for turnouts and a table with dimensions
| Type | Thickness h, mm | Cutting height, h1, mm | Dimension on the side without cut, b2, mm | Top plate width, b, mm | Bottom plate value, b1, mm | ||
| Normal, mm | Wide, mm | Widened, mm | |||||
| 1 | 180 ± 5 | 150 | 300 | – | 200-10 | 220-10 | 260-5; +20 |
| 2 | 160 ± 5 | 130 | 280 | 175-10 | – | 220-10 | 250-5; +20 |
| 3 | 160 ± 5 | 130 | 260 | 175-10 | 200-10 | – | 230-5; +20 |
According to their profile geometry and role, they repeat the classification of conventional rail supports made of wood, that is, they can be edged or unedged, used both on main and siding or access tracks, at receiving and sorting points.
The requirements for the moisture level of timber are the same - up to 22%, otherwise - allowance for drying. Attention, if we are considering a transfer beam, it is important to know its design, since different designs of turnouts are mounted on a corresponding set of beams having different lengths. It ranges from 3 to 6.5 m (not 2.75 m). Step – every 0.25 m. Such products are supplied in sets, in quantities regulated by projects.
Transfer bars are an equally important element of the canvas, in relation to which a number of requirements are also put forward. There are two key factors:
- Fitness for purpose:
from class I to class II should be used on branches with fairly high-speed transport (from 100 km/h) and high load intensity;
- III-IV - on access, acceptance, sorting, station lines;
- V - on low-income areas and on the basis of manufacturing enterprises.
Acceptance
2.1
A batch is considered to be any number of unimpregnated sleepers of the same type and one type of wood or impregnated sleepers of the same type, documented in one quality document.
2.2
The quality document must contain:
- — name of the organization whose system includes the supplier enterprise;
- — name of the supplier company and its location (city and conditional address);
- - for unimpregnated sleepers - type and type of wood, for impregnated sleepers - type;
- — number of sleepers in the batch, in pieces;
- — test results or confirmation of compliance with this standard;
- — designation of this standard.
2.3
The number of sleepers in a batch is determined by continuous counting.
2.4
The quality and dimensions of sleepers are checked by selective inspection.
The selection of sleepers for the sample is carried out according to GOST 18321 using the “blind” method in the quantity indicated in Table 4.
Table 4.
| Batch size | Sample size | Batch size | Sample size |
| Up to 90 | 5 | 281 — 500 | 20 |
| 91 — 150 | 8 | 501 — 1200 | 32 |
| 151 — 280 | 13 | 1201 or more | 50 |
The batch is accepted if all sleepers in the sample meet the requirements of this standard.
If unsatisfactory results are obtained, the entire batch is rejected.
Bridge beams
These track components are also subject to the strict requirements of GOST standards. And the key standard that they must comply with is an exclusively rectangular cross-sectional shape, one of two:
- 220 x 240 mm;
- or 220 x 260 mm.
Options 220 x 280 and 240 x 300 mm are also possible, but they are already manufactured individually and only with the consent of the customer.
The maximum deviations vary depending on the design: in the first case they are present in thickness (up to -2 mm), in the second they are not present at all, but are present in width (up to -3 mm). The maximum possible level of humidity without shrinkage is already 20%, the allowances are already your own - you need to choose them according to GOST 6782.1-75.
The length of bridge beams of a regular section is 3.25 m. The greater the distance between the axes of the longitudinal beams or trusses of the bridge (up to 2.5 m), the larger the cross-section of the bridge beams should be (up to 24x30 cm) and their length (up to 4.20 m).
Definitions.
In this standard, the following terms with corresponding definitions apply:
- 3.1 sleepers:
According to GOST 18288. - 3.2 edged sleeper:
According to GOST 18288. - 3.3 semi-edged sleeper:
Sleeper in the form of a three-edged beam. - 3.4 unedged sleeper:
According to GOST 18288. - 3.5 unimpregnated sleeper:
Sleeper not treated with protective agents. - 3.6 impregnated sleeper:
Sleeper treated with protective agents. - 3.7 deep-pricked sleeper:
A sleeper subjected to special treatment by deep pricking in order to increase the depth of impregnation with protective agents. - 3.8 sleeper top face:
The sawn longitudinal surface of the sleeper, which has a smaller width. - 3.9 sleeper bottom:
Sawed longitudinal surface of the sleeper, having a large width. - 3.10 sleeper side:
Sawed longitudinal side surface of the sleeper. - 3.11 wane part of a sleeper:
Uncut sections of the sleeper surface along the top surface and side.