There are about 40 species of spruce trees in the world belonging to the pine genus. These are evergreen trees. The spruce reaches a height of 95 meters. Sometimes, more. The spruce species is a forest-forming species; sometimes the forest consists only of spruce. Spruce is also often present in mixed forests. The age of spruce reaches, on average, 200 years. Spruce loves fertile and moist soil. Shade-tolerant.
Spruce forms branches floor by floor. The first floor of branches takes 3-4 years. But in the future, clearly 1 floor of branches grows per year. Spruce trees are easily overwhelmed by winds because they have a very shallow root system. Spruce bark is typically light gray to dark gray in color.
Spruce is often planted in city squares and parks. It looks great in landscape design.
Lumber
general characteristics
Spruce is an evergreen coniferous tree belonging to the pine family. Today, up to 40 species of spruce are known to grow in temperate and moderately harsh regions of the Northern Hemisphere. Spruce is cultivated as an ornamental plant and as a source of high-quality wood. Some spruce species are grown as a source of cellulose, which is used in the paper industry.
The crown has a conical shape. The tree grows very quickly, from 15 to 28 cm per season, although some species can grow faster: 150 cm per year. On average, they reach an age of 250-300 years; it is rare, but older spruce trees are found. In Sweden, using radiocarbon dating, scientists determined the age of individual spruce trees. It turned out to be more than 9 thousand years old.
The tree grows on average to 25 - 50 m in height. The tallest spruce species is Sitka, 90 m high. The diameter of an adult tree near the butt can reach 1-2 m.
Spruce has needle-like leaves, arranged spirally on the branches. The leaves shed after 4-10 years. The branches of the tree grow almost at right angles to the trunk, so when viewed tangentially they are round.
Pollination occurs by wind transfer of pollen from male to female cones. The female cones open three years after pollination to release mature seeds.
In Russia, 30% of the taiga zone landscape is formed by spruce forests. This is 70 million hectares with estimated timber reserves of more than 10 billion m3.
Spruce
Spruce belongs to the pine family and has almost 40 species of evergreen trees, the height of which reaches 30 meters.
Spruce forests are in third place in terms of area among coniferous trees, second only to spruce and pine.
Pure spruce forests have a dense, dense and dark structure. Spruce wood is soft, light, does not have high strength, and is used as a building material (boards, beams), for small products, and also for processing into wood pulp.
The main feature of the structure of spruce is that it does not have a clearly defined core. The wood has a uniform white-yellowish color, rarely with a pale pink tint. Tree rings can be seen in any section.
The use of spruce as lumber occurs together with fir, because both species have similar qualities. Spruce wood is used to make boards, veneer, plywood, glued beams, chipboard and fiberboard.
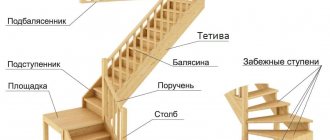
In home construction, spruce is used in the manufacture of roofs, wood siding, railings, stairs, wall and ceiling frames, floors, windows, doors and gates. Spruce boards are also used in the manufacture of window sills, flooring, cladding and decorative work. It has a pleasant smell, yellow-pink color with a creamy tint.
As a result of the presence of a high content of various resins, spruce edged boards do not rot, are moisture resistant and can withstand high temperatures. It can be used anywhere except for the construction of baths, because at high temperatures the resin will be released into the air.
Areas of application for spruce
Spruce wood is lighter than pine and chips well. In the past, it was widely used to produce chipped roofing materials: shingles and shingles. In terms of wood flexibility, spruce is superior to other conifers except juniper. Therefore, its wood is used for the production of bent products (arches, sleds, hunting skis, etc.).
The large length of the tracheids makes spruce wood a valuable raw material for paper production. The bark of spruce is thin and elastic when raw. It is used on the roofs of temporary buildings. There are many tanning agents in the bark, but their quality is worse than the tanning agents of larch and oak bark.
Valley spruce forests prevent water erosion and play a clogging role - they filter melt and rainwater from suspended solid particles, which protects reservoirs from silting.
| Scientific classification | Physical properties | ||
| Domain: | Eukaryotes | Average Density: | 430 kg/m³ |
| Kingdom: | Plants | Density limits: | 300-640 kg/m³ |
| Department: | Conifers | Longitudinal shrinkage: | 0,3 % |
| Class: | Conifers (Pinopsida Burnett, 1835) | Radial shrinkage: | 3,6 % |
| Order: | Pine | Tangential shrinkage: | 7,8 % |
| Family: | Pine | Radial swelling: | 0,19 % |
| Genus: | Spruce | Tangential swelling: | 0,36-0,39 % |
| International scientific name | Bend strength: | 68 N/mm² | |
| Picea A.Dietr., 1824 | Compressive strength: | 40 N/mm² | |
| Type species | Tensile strength: | 80 N/mm² | |
| Picea rubra A.Dietr. = Picea abies (L.) H.Karst.—Spruce | Fuel properties | ||
| 20.2 MJ/kg | |||
Types of spruce
Rod El
, according to the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, includes 37 primary species and 4 hybridogenic ones:
- Picea abies (L.) H.Karst. — Common spruce, or European spruce
- Picea alcoquiana (HJVeitch ex Lindl.) Carrière - Alcocca spruce, or bicolor spruce
- Picea asperata Mast. — Rough spruce
- Picea aurantiaca Mast.
- Picea austropanlanica Silba
- Picea brachytyla (Franch.) E.Pritz. — Chinese spruce
- Picea breweriana S.Watson – Brewera Spruce
- Picea chihuahuana Martinez
- Picea crassifolia Kom.
- Picea engelmannii Parry ex Engelm. — Engelman spruce
- Picea farreri CNPage & Rushforth
- Picea glauca (Moench) Voss - White spruce, or Gray spruce
- Picea glehnii (F.Schmidt) Mast. — El Glen
- Picea jezoensis (Siebold & Zucc.) Carrière - Ayan spruce
- Picea koraiensis Nakai - Korean spruce
- Picea koyamae Shiras.
- Picea likiangensis (Franch.) E.Pritz. — Likiang spruce
- Picea linzhiensis (WCCheng & LKFu) Rushforth
- Picea mariana (Mill.) Britton, Sterns & Poggenb. — Black spruce
- Picea martinezii TFPatt.
- Picea maximowiczii Regel ex Mast. — El Maksimovich
- Picea meyeri Rehder & EHWilson - Meyer's spruce
- Picea morrisonicola Hayata
- Picea neoveitchii Mast. — El new Vicha
- Picea obovata Ledeb. — Siberian spruce
- Picea omorika (Pančić) Purk. — Serbian spruce
- Picea orientalis (L.) Peterm. — Eastern spruce
- Picea polita (Siebold & Zucc.) Carrière - Elegant spruce, or Japanese spruce (or Picea torano (Siebold ex K. Koch) Koehne, the legitimacy of the first name is still under debate)
- Picea pungens Engelm. — Prickly spruce, or blue spruce
- Picea purpurea Mast. — Purple spruce
- Picea retroflexa Mast. — Spruce bent
- Picea rubens Sarg. — Red spruce
- Picea schrenkiana Fisch. & CAMey.— Schrenk spruce Picea schrenkiana subsp. tianschanica (Rupr.) Bykov – Tien Shan spruce
Hybridogenic species
- Picea ×albertiana S.Br.
- Picea ×fennica (Regel) Kom. — Finnish spruce (Picea abies × Picea obovata)
- Picea ×lutzii Little
- Picea ×notha Rehder (Picea glehnii × Picea jezoensis)
Useful tables
Differences in the characteristics of wood and the main areas of application of pine and spruce
| Main characteristics of wood | Pine | Spruce |
| Color | Reddish or yellowish (ocher) tint | White |
| Color stability | Over time the shade becomes more intense | Natural light color lasts for a long time |
| Structure | Pronounced | Weakly expressed, high uniformity of fiber arrangement. |
| Density at 12% humidity | 480 kg/cub.m. | 430 kg/cub.m. |
| Resin content | High | Below average |
| Bitches | A small number, large and very large, oval-shaped, arranged in groups. | Large quantity, small, round |
| Resistance to rotting | High | Average |
| Resistance to blueing (freshly cut wood) | Low | High |
| Strength | High | Slightly smaller than pine |
| Properties relevant for machining | Soft, easy to process, does not crack when dry | Softer than pine, but knots make processing difficult, less susceptible to warping |
| Scope of use |
|
|
Hydraulic conductivity coefficient values (Dx1010 m2/s) for spruce
| Mature wood: | 200С | 600С | 800С |
| tangential e.g. | 2,65 | 9,05 | 17,7 |
| radial e.g. | 2,78 | 9,2 | 20,0 |
| Sapwood: | 200С | 600С | 800С |
| tangential e.g. | 3,16 | 12,1 | 19,0 |
| radial e.g. | 3,26 | 13,7 | 19,6 |
Applications of spruce wood
Spruce is used very widely in various industries due to its unique properties:
- The high flexibility of wood allows it to be used to make bent furniture and other things that require a certain forming;
- In construction, spruce is used for the construction of log houses, finishing ceilings, stairs, and decorating the house;
- Spruce is used to produce veneer, fiberboard, chipboard, laminated timber and high-quality plywood;
- Musical instruments are made from spruce (the soundboards of guitars, violins, cellos, etc.), the wood is considered resonant and transmits sound well;
- Spruce is widely used in the chemical industry for the production of rosin, alcohol, paper, cardboard, turpentine, etc.
Medicinal and beneficial properties of common spruce
The beneficial and medicinal properties of common spruce are as follows:
- diaphoretic,
- expectorant
- anti-inflammatory,
- antispasmodic,
- diuretic,
- choleretic,
- disinfectant,
- antimicrobial,
- bactericidal,
- wound healing,
- painkiller,
- desensitizing,
- vitamin,
- antiscorbutic,
- restorative.
What are the benefits of spruce in medicine?
Not everyone understands how important spruce is for medicine. However, the cones of the common spruce are used as medicinal raw materials. For these purposes, they need to be collected even before the seeds ripen, that is, in the summer. The cones contain tannins, resins and essential oils.
Ascorbic acid can be obtained from pine needles. Kidney infusion is also very useful. It has a desensitizing effect, relieves spasms, and inhibits the activity of many pathogens. Both infusion and decoction of cones are used to maintain normal functioning of the respiratory tract. These remedies are especially good for bronchial asthma.
The needles can also be used to prepare infusions that effectively treat scurvy. At the same time, the absorption of necessary microelements from infusions is much better than from most pharmaceutical preparations. In folk medicine, pine needle baths are also indicated for attacks of rheumatism.
The tradition of decorating a fir tree for the New Year
Many countries have a recognizable tradition of decorating a spruce tree for the New Year. There is a lot of advice on how to choose such a spruce, how best to install it, what needs to be done to prevent the needles from falling off longer. It is noteworthy that in Russia, ordinary spruce is most often used for these purposes. However, if you look into the question, there is nothing surprising in such a decision, since this tree is typical for the CIS and is found everywhere. It is also usually the cheapest to purchase.
As Norway spruce grows, it acquires branches that individually can resemble small trees. This feature is often used by sellers at spruce markets. They cut large trees into pieces and then sell them by branches. As a result, sellers increase the likelihood of selling more of the goods, and buyers get the opportunity to save money. Plus, in small apartments, massive spruce trees do not always look appropriate. Therefore, branches are most often taken.
It should be noted that there is a fairly popular misconception that you cannot buy food for the New Year, as this will lead to massive cutting down of plants. In fact, nurseries and even forestries get rid of the weakest plants in this way. They can be perfect for the New Year if they are still in excellent condition at the time of cutting down. They will look great.
However, experienced specialists see that such a tree may have some flaws, for example, in the root system, which will not allow it to fully develop and grow further. That is, such a tree would not have become part of the forest ecosystem in any case.
Also, spruce trees are often cut down for the New Year, which would still have to be gotten rid of one way or another as part of thinning. What are we talking about? The fact is that spruce seedlings in the first years of life are very fragile and painful. They can wither away from parasites, fungus, etc. Therefore, it is customary to plant a large number of seedlings in order to obtain the required number of trees in the future.
However, often everything takes root. Young Christmas trees begin to actively develop and stretch upward. But there's no room for everyone. Therefore, specialists who work in forestry have to deal with a task planned in advance - thinning. As a result, some of these trees end up at New Year's bazaars.
Also, do not forget that many nurseries specially plant fast-growing varieties in order to make money on this holiday. That is, this is the implementation of trees that were originally intended for the New Year. Therefore, if you start boycotting Christmas tree bazaars, then no one will plant such plants. Consequently, there will no longer be any more spruce in the forest.
In a word, when buying live spruce you do not harm the ecosystem. True, only if you purchase a New Year's tree from a nursery or from a seller who officially cooperates with them. On New Year’s Eve, “enterprising individuals” regularly appear who want to cut down spruce trees and make money from it. And so they can cut down healthy trees and touch those parts of the forest that do not need thinning. That is, really harm the ecosystem. Therefore, there is no need to encourage barbaric logging or buy anything from people who cannot provide documentary evidence of the legal origin of the trees.
The best option now is to buy a plant from an online store that cooperates with nurseries. You don’t have to go anywhere and, moreover, think about how to deliver a magnificent beauty home. After all, it often won’t fit inside the car. And even if you try to put it there, there is a risk of damaging the covers. In a word, it is best to entrust delivery and everything else to specialists.
Advantages and disadvantages of spruce lumber
Bathhouses and outdoor gazebos are traditionally built from soft, easy-to-process spruce. However, it is not used so often in the construction of houses, although its density is much lower compared to pine (about 400 - 450 kg/cubic m versus about 500 kg/cubic m). Due to the sparser arrangement of fibers, the thermal conductivity of spruce is low: only 110 mW/(m K) versus 150 mW/(m K) for pine.
The wood of the material is very light, almost white. Over time and under the influence of external factors, it does not darken or become stained, therefore it does not require special care or bleaching. But wood needs resins to protect it from harmful microorganisms, insects, and mold. Since spruce contains significantly less resin compared to pine, it is less resistant to negative external influences and is susceptible to blue staining. Spruce needs careful antiseptic treatment. In addition, over time, polymerization of resins in wood occurs, which gives the material greater hardness. Since pine contains more of these substances, it is more durable and reliable.
Gardening and landscaping
Common spruce is quite actively used in urban landscaping. This plant withstands smog and increased amounts of harmful substances in the atmosphere. Thanks to the lush needles, it actively traps dust and dangerous gases and reduces the amount of noise on the streets. Spruce trees are also used as snow-protective plantings, allowing savings on cleaning routes.
Spruce has found the widest application in landscape design. This plant has excellent decorative qualities. At the moment, a large number of different varieties have been bred, which differ in the size of the crown, the shade of the needles, as well as their crown. And while some have a very persistent and bright recognizable aroma, others will have a weak and delicate aroma.