September 8, 2017
Why are some lumber called timber, others timber, others board, and how does a lath differ from all of them?
The large range of different types of lumber includes products with round, semicircular, sectoral cross-sections, sleeper-type cross-sections, as well as squares and rectangles. Each of them combines a whole range of building materials. But sometimes there is confusion, especially about square and rectangular lumber. How can you understand what you actually need to buy if we are talking about timber and timber, timber and board, board or slatted?
To distinguish some lumber from others, it is necessary to take into account several parameters:
- Section aspect ratio;
- Dimensions;
- The part of the log from which they are made is the cutting area.
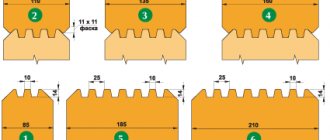
Dimensions.
Although lumber manufacturers most often supply them in a standard length - 6 linear meters, there are also non-standard sizes. However, for a material to be considered a beam, block, batten or board, only the section dimensions are taken into account:
- The timber has a thickness of 100, 150, 200 millimeters. Walls are made from it, load-bearing elements, beams, rafters, mauerlats, etc. are made.
- The bar varies in thickness from 50 to 100 mm. The strong material used for lathing is used during finishing and manufacturing of furniture, windows, and flooring.
- The thickness of the board ranges from 20 to 50 mm, and the width is more than 100. Depending on the type, it is used for the construction of internal non-load-bearing walls, in finishing, for the manufacture of flooring and joists, in roofing sheathing structures. Low-grade boards are used for the manufacture of formwork, fences, panels, walkways and in rough work.
- A product with a thickness of 10-15 mm and exceeding the width by 3-4 times is already a lath. A thin narrow board - lath is used in finishing, lathing, furniture making, etc.
The use of timber and boards in construction
Timber is mainly used for the construction of load-bearing structures: beams, columns, and so on. Walls are often made from profiled timber. Why is profiled timber better than regular timber, with a square or rectangular cross-section? Firstly, it is usually well dried, so it does not deform over time, and, secondly, thanks to the shaped profile, the timber is laid on the timber more tightly, improving the thermal insulation characteristics of the structure.
The difference between a timber and a board is that the board is used primarily for finishing or creating load-bearing structures intended for light loads: shelves, floors, wall cladding, and so on. The boards are as follows:
- edged (with both side edges sawn off);
- one-sided (only one side edge is sawn off);
- unedged.
Depending on the method of edge processing, a distinction is made between a board with tongue and groove (adjacent boards are connected to each other “ridge and groove”) and a board where the side edge is sawn off “into a quarter” - in the form of a step. Typically, such boards are used for flooring.
Board
Place of cut.
The timber is “mined” from the very core of the trunk. On the end sections, part of the annual rings of the cut tree is clearly visible. The block can be several centimeters away from the core itself and include only the inner annual rings in sectors. The board is cut mainly from the side parts of the trunk; some varieties have visible remains of bark (wane). The lath can generally be cut from the remains of a log, or the entire log can be folded into a lath.
Have you already decided what you need? Buy lumber cheaply from us! >>
Table
The table below summarizes the difference between timber and plank.
| timber | Board | |
| Section | 100 by 100 mm or more (may have a rectangular shape); profiled timber is a high-tech building material and, with a cross-section of at least 100 by 100 mm, has an arbitrary shaped shape | Thickness – no more than 100 mm, width – more than double thickness |
| Application | Mainly construction of load-bearing structures: beams, columns, walls, partially in the furniture industry | Wide range of applications in construction and furniture industry |
Which is better, profiled or laminated timber - table
Summary data on the compared parameters (what to choose, which timber is better, what is the difference and which one should be used to build a house) are included in the table
| Parameter | Profiled timber | Glued laminated timber |
| Feedstock | Solid wood | Prepared lumber glued under pressure |
| Drying | Natural or chamber | Chamber |
| Beam dimensions | Maximum section 200x200 mm Maximum length - 6 m.p. | Maximum section 275x275 mm Maximum length - 18 m.p. |
| Environmental friendliness | Does not contain harmful substances | The content of harmful components in the adhesive composition is within acceptable limits |
| Air exchange | Natural, inherent to the wood species | Violated |
| Humidity | 15-18% | 11-14% |
| Shrinkage | With chamber drying - 3-5% With natural drying - up to 8% | 0,4-1% |
| Strength | Low | High |
| Deformations | Allowed width no more than 1 mm | Likely. Depends on the quality of gluing |
| Biological resistance | High | High |
| Fire safety | Average | High |
| Aesthetics | Average. Dead knots and dark spots may occur | High |
| Finishing work | After 0.5-1 year or use casing boxes | Immediately upon completion of construction |
| Loss of properties during operation | Cracks appear that require caulking | No |
| Price | 30% lower than glued | High |
| Probability of counterfeit (fake) | High | Minor |
As you can see, the question of which is better, laminated or profiled timber, does not have a clear answer, and the choice is characterized by a fairly high degree of subjectivity.
When choosing a material for building a residential building, wood is the ideal option. Wood has numerous benefits that make it the most used material in custom construction. The log house breathes, releases substances beneficial to the body, and has good thermal insulation ability. Recently, buildings made from various types of timber have become very popular, and manufacturers of both natural moisture timber and profiled timber are encouraging consumers to use their own products. Despite all the similarities between these materials, they have significant differences.
Production of ordinary (non-profiled) timber
This material is easy to manufacture, the procedure of which consists in edging a solid log on four sides, while all the properties of wood are preserved, the fibrous bonds do not break, almost all the resin is preserved inside, which has an antiseptic effect. The production process can be established at any sawmill. Mainly coniferous wood of natural moisture is used for production. For the construction of houses, lumber is produced in various sizes from 150x150, although 200x200 is ideal for building a foot.
Classification of construction board
Boards and timber are the most widely used materials offered to consumers by the woodworking industry. The main difference between a board and beams is its dimensions: a board is a product with a thickness of no more than 10 cm, and the width must be at least 2 times the thickness.
As a rule, the price list of any woodworking company includes the following types of construction boards:
- unedged - a part with unprocessed side edges (wane);
- trimmed - a part that has machined side edges strictly perpendicular to the horizontal planes;
- tongue and groove - a part with grooves cut into the side edges, facilitating the connection of boards during the construction of structures.
In addition, the boards can be planed or unplaned. Processing on planing machines gives the elements smoothness and eliminates all possible surface defects. Unplaned boards, as a rule, are used for the construction of structures that will subsequently be subjected to finishing.
Decorative boards, which include lining, imitation timber, slats, etc., are usually used for finishing work and are classified as a separate category.
Lumber of this type can be produced using several technologies:
- Using multi-saw processing. To obtain an unedged board, a log is passed through a machine with several cutters, which cuts the wood into several parts with a given thickness.
- Square sawing. First of all, the log is processed into timber, and then the timber is sawn into several parts.
- Sawing with milling. During production, cutters and band saws are used simultaneously, which make it possible to obtain edged boards with a clean and even surface.
Glued laminated timber or profiled timber - which is better to choose?
Let’s analyze the characteristics and properties to understand the difference between these materials, made from the same raw materials using similar technology, by comparing them according to a number of parameters:
Feedstock
Made from solid wood. The raw materials undergo screening, then a long process of natural or chamber drying, re-inspection for defects and processing using profiling equipment.
It is produced by gluing prepared, chamber-dried lamellas. This approach allows us to reduce the percentage of defects due to the ability to eliminate defects on part of the lamella. And also prevent cracking and twisting of wood.
To make timber, from two to five lamellas are used. This allows the manufacturer to vary the price by using different types of wood.
For example, the central slats can be made of pine, and the front slats can be made of larch or cedar. The material was prepared for the website www.site
Beam dimensions
The dimensions of the profiled timber are limited by the length of the wooden blanks. The standard length of the beam, as a rule, is 6 m.p. or multiples of 2 and 3 m.p.
Standard sections include: 100x100, 150x150, 200x200. Manufacturers also offer non-standard sizes made for a specific project, but their cross-section rarely exceeds 200x200, which is due to the complexity of drying. The thicker the array, the more difficult it is to ensure its uniform drying.
The dimensions of laminated veneer lumber vary over a wider range, and the maximum width reaches 275 mm. Due to the fact that the lamellas can be spliced along the length, in some cases the length of laminated veneer lumber can reach 18 m. This length is made to order (transportation to the construction site and the difficulty of working with a long beam leaves its mark on its length).
Note that the greater the width of the beam, the higher the thermal conductivity of the structure.
Environmental friendliness
Eco-characteristics are the main argument in the debate about what is the difference between profiled and laminated timber and which of them is safe for humans and the environment.
The main emphasis is on the fact that in the production of laminated veneer lumber, glue is used, which contains chemical compounds. The slats are glued together using polyurethane or polyvinyl acetate glue. This gives grounds for opponents of laminated veneer lumber to argue that they have to forget about the environmentally friendly purity of laminated veneer lumber.
But, adhesive mixtures are not uniform in composition and are classified from dangerous (FC2) to safe (FC0). Timber manufacturers are required to provide a document containing information about what glue was used in production and confirming the level of formaldehyde content.
It is worth noting that profiled timber also undergoes additional treatment with antiseptics and fire retardants. In addition, in the production of timber, only the inner part of the log is used, which is freed from the protective bark and is more loose. This means that in order to maintain the performance characteristics of a house made of profiled timber, its walls must be periodically re-coated with special compounds designed to protect the wood from the harmful effects of ultraviolet radiation and other atmospheric phenomena.
Air exchange
The vapor permeability of profiled timber corresponds to the indicator for the type of wood from which it is made. Also, solid wood retains the ability to maintain a favorable microclimate, which is very important for a private home.
In glued beams this figure is much lower, because the lamellas are arranged in different directions, and there is also an adhesive layer that prevents the partially free movement of air through the pores of the wood.
Humidity
The natural moisture content of wood depends on the species and time of year of harvesting and can reach 40-50%. But, material with a humidity not higher than 15% +/- 3% is suitable for construction (for external work, according to GOST 8486-86).
To reduce the level of humidity, as well as to avoid torsion and cracking of wood, manufacturers subject the timber to drying: natural or forced (in chambers). The drier the timber, the less shrinkage the building constructed from it will have.
The optimal moisture content of laminated veneer lumber is 11-14%, and that of profiled timber is 15-18%. But we note that over time, both types of timber will draw moisture from the external environment and gradually their performance will be approximately the same.
Shrinkage
An indicator derived from humidity. Glued laminated timber shrinks 0.4-1%, profiled timber - 3-5%, natural drying - up to 8%.
Strength
In this indicator, glued is superior to profiled, because For its production, denser lamellas are used, cut from different parts of the log (core, heart-shaped rays, growth rings); in the production of profiled timber, only the core, the loosest part of the trunk, is used.
Deformation
Torsion of the beam when stored correctly is excluded. As for the appearance of cracks on an already finished structure, the likelihood of their appearance remains for both types of timber, both profiled (no more than 1 mm wide) and glued (depending on the quality of gluing).
Biological resistance
Both types of timber are treated with special protective compounds during the manufacturing process. Therefore, the likelihood of fungus, mold or wood bugs appearing is minimal.
Fire safety
Glued laminated timber burns much slower, this factor is very important for a bathhouse.
Aesthetics
Profiled and laminated timber has a high quality of processing of the front surface, which allows you to do without additional finishing, both internal and external. However, often, construction is carried out with timber 150x150 mm thick and there is a need for additional insulation.
As for the installation of window and door frames, the warm contour of a house built from laminated veneer lumber can be done immediately after construction (assembly). But the profiled one shrinks - you need to wait up to six months or use casing boxes.
Price
If we compare the initial costs, the cost of profiled timber is 30% lower than the price of laminated veneer lumber. But, during operation, higher costs are required to maintain the appearance of a house made of profiled timber.
Probability of counterfeit
Profiled timber is sold in large volumes. You can profile timber in artisanal conditions. The possibility of reliable installation will be provided only by material manufactured on high-precision equipment. It is more difficult to make counterfeit laminated timber, because... it is difficult to ensure the process of gluing the lamellas.
We learn to distinguish lumber: board, timber, block, log
Are you planning to build or renovate a house? Explore the supply market. Understanding the features and advantages of different types of lumber will allow you to build a reliable cottage and a durable bathhouse. Specialists from TD Stroy, a manufacturer and seller of timber, beams, boards and logs in Minsk, will help you understand the nuances of the construction market.
Are tempting offers always relevant?
In Minsk it is not difficult to find everything you need for construction. You can buy any lumber in the warehouse, the goods will be delivered quickly, it is possible that it will be of high quality and at a favorable price. It would seem that now the house should turn out great. But is it? Unfortunately, there are no guarantees...
The main thing that the master must do on the eve of construction is to choose the appropriate material. First of all, decide whether it is a beam or a log, a block or a board. The difference in lumber is significant; each variety is intended for specific purposes and this must be understood.