Production Features
Wood-laminated boards that can withstand prolonged exposure to moisture are designated as FSF according to GOST.
Waterproof plywood sheets are manufactured using specially selected substances. These substances protect the material from moisture. Drying oil is used to impregnate wood and paint. In some types, the coating is puttied with compounds using PVA, and fiberglass is used.
Already at the stage of forming the slabs, the degree of moisture resistance is set. This is done by adjusting the composition of the synthetic resins used to glue the layers. Therefore, knowing the substance that was used as glue, you can determine the degree of moisture of the material:
- Plates made using urea substances have a moisture resistance limit of around 5-10%. Such materials can withstand only short-term exposure to moisture.
- 10-15% resistance to moisture is ensured by the use of phenol-formaldehyde compounds. Plates of this type can be used for outdoor work.
- Waterproof laminated plywood is not subject to destruction under the influence of moisture. It is protected by a film applied to the surface of the slab.
Types of plywood
The following types of plywood are distinguished based on the adhesive base:
- FS – average moisture resistance. Glue – urea-formaldehyde resin.
- FSF – high moisture resistance. Phenol-formaldehyde resins are used in production.
- FOF – high moisture resistance with additional protection. The composition is the same as that of FSF, but plywood with this marking is laminated on both sides.
Birch plywood is made in all three versions. Coniferous is not suitable for lamination, so it is produced only in the FS and FSF types.
Advantages of the material and its disadvantages
The production method makes plywood durable and resistant to deformation. This is achieved through the presence of several layers and special adhesive compositions. Therefore, the following advantages of such plates can be highlighted:
- Moisture resistant. Waterproof plywood is not subject to destruction when exposed to moisture. It does not peel off into layers and is not deformed.
- Easy to use. The high strength of the material does not interfere with the processing process. Plywood is easy to process using a variety of tools. It is easy to install.
- Compatibility with other building materials. Most often, waterproof plywood is used as an additional material. It easily combines with natural and polymer building materials.
- Wear resistance. Plywood can withstand mechanical stress without compromising its integrity.
- Resistant to temperature changes.
- Wide scope of use.
- Aesthetics. Plywood has an original wood pattern and color in appearance.
- Affordable price. Plywood boards are cheaper than solid wood. And you can always save money by choosing a lower grade material.
The only drawback of the material is the presence of harmful substances included in the glue. We are talking about formaldehyde. Therefore, it is not recommended to use plywood in residential areas and where there are children or people with allergies.
Material of manufacture
Most often, there are 2 types of wood that are used to produce plywood: birch and coniferous wood (fir, pine, cedar or spruce).
- Birch is a noble material. The color of birch plywood is light, closer to white. It is dense, its strength reaches 30-80 MPa.
- Needles resist moisture better, but they are coarser and contain resin. The color of coniferous plywood is yellow. It is light and, as a rule, cheaper than birch, its strength indicator is 25-55 MPa.
- The moisture resistance of both materials is high, but birch is more susceptible to rotting and fungus.
Analyzing the data provided, we recommend using birch plywood for flooring, and coniferous plywood for walls and roofing.
Application area
Waterproof plywood is used in many industries. Most often it is used in construction. It is used in the following processes:
- Covering walls, floors, roofs.
- Interior decoration of buildings.
- For the manufacture of decorative elements.
- As a reusable formwork.
- For billboards.
- For the production of containers.
Due to its strength, reliability and low weight, waterproof plywood is used in the construction of ships, railway transport, and garden furniture. A separate type of it, made from peeled birch, is even used in aviation.
Selecting a material for specific applications
This approach is associated with a large number of factors. Products from China and Russia are presented on the domestic market, while material from the Middle Kingdom costs less, but nevertheless complies with GOST. Upon inspection, it was discovered that 80% of the laminated material is made from hardwood, or rather poplar.
If you familiarize yourself with state standards, then it is permissible to produce laminated plywood from some hardwood and softwood species, but only on the condition that the quality of the veneer does not affect the final technical characteristics. According to GOST, poplar can be used, but only for the inner layer, and not for the entire package.
Types of slabs
Taking into account the degree of moisture resistance, plywood is manufactured in several types:
- FC. This is a material that is made using urea-formaldehyde compounds. It has average moisture resistance. But it has good environmental friendliness. Used for interior work, furniture production and decoration.
- FSF has increased protection against moisture. Phenol-formaldehyde resins are used as an adhesive. This material is used to make subfloors, roof sheathing, containers, and advertising boards.
- FBS has the greatest protection against moisture and swelling. This is bakelized moisture-resistant plywood. It is used in shipbuilding and aircraft construction.
Based on appearance, waterproof plywood is divided into five grades (from 1 to 5). If the slabs are made from hardwood, the letter E is added to the numbers in front when marking. In the case of coniferous raw materials, the letter X is used.
According to the quality of surface treatment of the material, they are distinguished between unpolished (NS), with one-sided grinding (SH-1) and with double-sided grinding (SH-2).
There is also a classification depending on the amount of formaldehyde in the material. With a content of up to ten milligrams per hundred grams of material mass, they speak of emission class E-1. If the resin contains from ten to thirty milligrams, then class E-2 is indicated.
Moisture-resistant plywood - types, properties and applications
The moisture resistance of plywood is an extremely important indicator that you need to pay attention to in the store. It primarily depends on what timber and adhesive compositions are used in the production process. The ability of a plywood sheet to repel liquid is ensured by treatment with specialized impregnations.
The importance of the gluing process in timber processing cannot be overestimated. The main component of the adhesive composition for plywood production is synthetic resin, which is a solution of high-molecular compounds that can harden under certain conditions. The marking of plywood depends on the adhesive composition used. There are "FSF" - a material of increased water resistance, glued with phenolic compounds and "FK" - waterproof plywood, glued with urea compounds.
Finnish plywood is moisture resistant
Perhaps the largest European plywood producer is Finland, which produces plywood sheets in the 2440x1220 mm format from birch and coniferous raw materials. Quite often this material is called Finnish. Masters call it “large format”. Finnish companies, especially UPM, have a reputation for being craftsmen who guarantee consistently high quality products. Despite the fact that the technologies are the same, our enterprises lack high production discipline. It is as a result of constant quality control and strict compliance with technology requirements that Finnish plywood demonstrates stable characteristics.
Of course, today not all Finnish plywood is produced in Finland; it is produced in our country, but using special Finnish equipment. At the final stage of production, the plywood sheets are covered with layers of high-quality export laminated film. Often this film is brought from Finland. In principle, the result is high quality laminated plywood. Its main difference from the usual one is its increased moisture resistance, strength and resistance to acids. Finnish plywood is successfully used for formwork because it is a durable material and can be used many times. The decorative coating gives this timber a truly Finnish design.
Moisture resistant plywood sheet
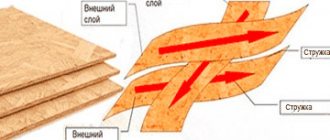
According to the Finnish plywood production technology, high-temperature drying and press under high pressure conditions are used, which prevents the entry of impurities into the veneer, namely, the accumulation of liquid. It is these measures that protect the surface from delamination and swelling. In addition to the large format, sheets are also produced: 1830X1525 mm and 3050 mm X 1525 mm, which are also called large-format. In the group of large-format sheets, subgroups are distinguished: longitudinal sheets - those in which the wood fibers of the outer veneer layers are directed in the same direction as the long side of the sheet; transverse sheets - those in which the fibers are directed in the same direction as the shorter side of the plywood sheet. The identification of these subgroups is very important, because the direction of the fibers is responsible for the physical and mechanical properties of the plywood sheet.
A sheet of plywood has a significant weight, for example, if the thickness of the sheet is 4 mm, then an ordinary laminated sheet of birch raw materials, measuring 2440x1220, will weigh over 8 kilograms. The same sheet with a thickness of 9 mm will weigh over 18 kilograms, and with a thickness of 21 mm the weight of the sheet will be 41 kg. Plywood weighs more than 50 kilograms with a thickness of 27 mm. The ability of plywood to resist the negative effects of moisture gives it the name moisture-resistant in the labeling. In domestic plywood production, this material is obtained by gradually gluing sheets of birch and coniferous veneer. Such plywood has several grades that determine the level of moisture resistance, which does not depend in any way on the raw materials, but only on the glue with which the layers are glued.
Highlight:
- FC - this moisture-resistant plywood is produced by treating layers with urea resin. It is safe and can be used for interior decoration
- FSF - layers of this plywood are glued together with phenol-formaldehyde resin. This variety can be used outdoors, but only if there is a canopy.
- FBS – bakelite plywood. Its layers are glued together with a bakelite composition. This variety has the highest moisture resistance; it is used for the construction of ships, small aircraft and cars.
The most commonly used types of plywood—moisture-resistant (FC) and water-resistant (WSF)—are often confused. Let's try to figure out what the difference between them is.
For ease of comparison, we summarize the data in a table.
Comparative characteristics of FSF and FC according to physical and mechanical parameters
| Parameter | FC | FSF |
| Origin of veneer | Coniferous, deciduous varieties, birch | |
| Glue | Urea-formaldehyde | Phenol-formaldehyde |
| Phenol content | Not contained | 8 mg/100 g |
| Moisture resistance | Standard humidity level for residential or non-residential premises | Maximum level of humidity in external conditions, working with materials containing water |
| Surface treatment | Sanding on one or both sides, lamination | |
External differences between FSF and FC
It is quite difficult to distinguish FC plywood from FSF plywood by appearance; the only visible difference is the color of the material layers. For FC, in the production of which phenol-free glue is used, the interlayers are the color of the veneer, that is, the material is uniformly light in cut. FSF is characterized by a darker, reddish tone of the glue layers, which is explained by the phenol content. These differences are clearly visible in the photo.
Characteristics of FSF plywood
To make the outer layers of plywood, hardwood veneer is used: birch, alder, maple, elm, beech, aspen, poplar, linden. For the inner layers, in addition to those mentioned, softwood veneer is also used; pine, spruce, fir, larch and cedar. Moisture-resistant plywood FSF is considered to be made from the type of wood from which its outer layers are made. Plywood made from wood of one or different species is divided into homogeneous and combined, respectively.
In the outer layers of FSF plywood, wood defects and processing defects that exceed the limits established in the table are not allowed.
| Name of wood defects and processing defects according to GOST 30427 | FSF plywood with outer layers of veneer grades | ||||
| E | I | II | III | IV | |
| 1. Pin knots | Not allowed | Up to 3 pieces are allowed. per 1 m2 of sheet surface | Allowed | ||
| 2. Healthy fused light and dark knots | Not allowed | Allowed diameter, mm, no more | Allowed with cracks no more than 1.5 mm wide | Allowed | |
| 15 | 25 | ||||
| in quantity per 1 m2, pcs., no more | |||||
| 5 | 10 | ||||
| with cracks width, mm, no more | |||||
| 0,5 | 1,0 | ||||
| 3. Partially fused, unfused, falling out knots, holes from them, wormhole | Not allowed | Allowed diameter, mm, no more | |||
| 6 | 6 | 6 | 40 | ||
| in quantity per 1 m2 of sheet surface, pcs., no more | no quantity limit | ||||
| 3 | 6 | 10 | |||
| 4. Closed cracks | Not allowed | Allowed with a length of no more than 200 mm in an amount of no more than 2 pieces per 1 m of sheet width | Allowed | ||
| 5. Opened cracks | Not allowed | Allowed length, mm, no more | |||
| 200 | 300 | without limitation | |||
| width, mm, no more | |||||
| 2 | 2 | 10 | |||
| in quantity, pcs., no more | |||||
| 2 | 2 | without limitation | |||
| subject to sealing with putty | Allowed length up to 600 mm, width up to 5 mm, subject to sealing with putty | ||||
| 6. Light germination | Not allowed | Allowed | |||
| 7. Dark growth | Not allowed | Allowed in total with the norms of clause 2 of this table | Allowed | ||
| 8. Deviation in the structure of wood | Minor randomness is allowed, except for dark eyes | Allowed | |||
| 9. Healthy discoloration | Not allowed | No more than % of sheet surface is allowed | Allowed | ||
| 5 | |||||
| 10. Unhealthy discoloration | Not allowed | Allowed | |||
| 11. Rot | Not allowed | ||||
| 12. Tilt | Not allowed | Allowed in total with the norms of clause 3 of this table | |||
| 13. Overlapping in outer layers | Not allowed | Allowed length, mm, no more | Allowed | ||
| 100 | 200 | ||||
| in quantity, pcs., no more | |||||
| 1 | 2 | ||||
| per 1 m sheet width | |||||
| 14. Lack of veneer, defects in sheet edges during sanding and cutting | Not allowed | Allowed width, mm | |||
| 15. Presence of adhesive tape | Not allowed | Allowed in unsanded plywood | |||
| 16. Glue seepage | Not allowed | Allowed, %, no more | Allowed | ||
| 2 | 5 | ||||
| sheet surface | |||||
| 17. Scratches | Not allowed | Allowed | |||
| 18. Dent, imprint, comb | Not allowed | Allowed by depth (height) within the limits of maximum deviations in thickness | Allowed | ||
| 19. Fiber pullout | Not allowed | Allowed, %, sheet surface, no more | Allowed | ||
| 5 | 15 | ||||
| 20. Sanding | Not allowed | Allowed | |||
| 21. warped | In plywood with a thickness of up to 6.5 mm is not taken into account, with a thickness of 6.5 mm or more is allowed with a deflection of no more than 15 mm per 1 m of the diagonal length of the plywood sheet | ||||
| 22. Metallic inclusions | Not allowed | Non-ferrous metal brackets are allowed | |||
| 23. Gap in connections | Not allowed | Allowed width, mm, no more | Allowed | ||
| 1 | 2 | ||||
| in quantity, pcs., no more | |||||
| 1 | 1 | ||||
| per 1 m sheet width | |||||
| 24. Delamination, bubbles, zakorina | Not allowed | ||||
| 25. Waviness (for sanded plywood), hairiness, ripples | Not allowed | Allowed | |||
| 26. Surface roughness | Roughness parameter Rm according to GOST 7016, microns, no more: for sanded plywood - 100, for non-sanded plywood - 200 | ||||
| 27. Wood inserts | Not allowed | Allowed when sealed in quantity, pcs., no more | |||
| 8 per 1 m2 sheet | without limitation | ||||
| 28. Double insert | Not allowed | Allowed, pcs., no more than 2 sheets per 1 m2 | Allowed without restriction | ||
| Notes: | |||||
| 1. The rate of processing defect “lack of veneer” also applies to the inner layers of plywood. | |||||
| 2. Wood defects and processing defects not listed in this table are not allowed | |||||
In the inner layers of plywood, wood defects and processing defects are allowed that do not affect its quality and dimensions, the requirements for which are established in this standard.
With an even number of veneer layers, the two middle layers should have parallel grain directions. Moisture-resistant plywood FSF must contain symmetrically arranged layers of veneer, which must be made of wood of the same species and thickness. The thickness of the veneer used for the outer layers of plywood should not exceed 3.5 mm, and for the inner layers - 4 mm.
In the outer layers of FSF plywood, wood defects and processing defects that exceed the limits established in the table are not allowed.
Mesh plywood
Mesh plywood is also produced today - this is a transport laminated material with a mesh, the outer surface of which has a mesh structure. As a result of this, nothing slides on such material. Mesh plywood is used to create flooring in trucks, as well as: for the production of doors for car trailers for the construction of formwork for the temporary arrangement of subfloors. Most often, laminated mesh plywood is produced from 4 to 30 mm in thickness. Thin sheets are used to create even floors in cars and to line the walls of cabins in yachts. Thick ones can be used to create walls and doors. In our country, the production of mesh plywood began quite recently. Previously, it was imported from Finland. Laminated plywood sheets can be produced in 8 standard colors and quite a large number of shades. Any sheet can be made smooth or mesh. This material perfectly withstands the influence of natural factors, including precipitation, as well as chemicals and average mechanical loads.
It is used for:
- production of furniture sets
- interior work inside buildings
- construction, even capital
- car manufacturing
- car construction
- production of packaging material.
A film is applied to FOF plywood, which is a special paper with maximum density. In addition, during sheet coating, the paper is impregnated with synthetic resin. Birch raw materials are used to make this material. Production is close to the production of the FSF grade (sheet of increased moisture resistance). This material is produced in two types: covered with a laminate, it has a smooth surface on both sides, covered with a smooth laminate on one side, and a mesh coating is applied to the other side. This plywood can be used in the production of cars, yachts, and boats. In terms of technical indicators, it is not inferior to other types of waterproof plywood.
It is worth noting that the term “moisture-resistant plywood” is not included in regulatory documents. You also need to remember that the moisture content of plywood should be within 5-10%. If the indicator is higher, this may negatively affect the strength properties of the material. It is also necessary to take into account the fact that during transportation, storage and use of plywood it can absorb moisture from the air.
Advantages and disadvantages
| Advantages | Flaws |
| Moisture resistance | Toxicity due to the use of formaldehyde in glue |
| Tensile and bending strength | High price |
| Possibility of repeated use |
Slab sizes
The average dimensions of the material are 1.22x2.44, 1.25x2.50, 1.52x3.05, 1.52x1.52 m. This is not all, but only the main dimensions according to which waterproof plywood is produced. The thickness of the slabs can be from 9 to 40 mm. It depends on the number of layers of wood. There can be from three to twenty-one.
- FK grade plywood is produced in lengths of 1.525 m. Its width can be 1.22, 1.27 or 1.525 m.
- FSF has a width of 1.22 and 1.25 m. Its length is 2.44, 2.5 m.
- The dimensions of FBS plywood vary in length from 1.5 to 7.7 m, in width from 1.2 to 1.55 m.
Manufacturer country
There are 2 main plywood producing countries on the Russian market: Russia and China. The quality of workmanship is almost the same today.
But we note that Chinese manufacturers have increasingly begun to use combined technology - this is when the front layers of plywood are made from expensive and high-quality veneer, and the inner ones from cheaper ones. Russian manufacturers are guided by GOST standards and use the same materials for all layers.
User reviews
According to consumers, waterproof plywood is a high-quality material that is not afraid of moisture and weather conditions. They also note the high strength of the material.
In addition, ease of installation and processing is noted. You can hammer nails into the slabs, tighten screws, make holes in them, and so on. And all this does not cause any difficulties.
Among the disadvantages, consumers note the difficulty of transporting plywood. This is due to its large dimensions. The dimensions of waterproof plywood are always more than one meter. Due to this, the slabs do not fit all types of equipment. Therefore, it is necessary to look for suitable transport to transport the material.
Comparative characteristics
The table shows the characteristics of all the above product brands:
| FC | FSF | FBK | FBS | |
| Density, kg/m3 | 660 | 700 | 700 kg/m3 | 1000 kg/m3 |
| Tensile strength, MPa | 10 | 14 | 28 | 32 |
| Sheet thickness, mm | 4-40 | 4-40 | 4-40 | 4-40 |
| Moisture absorption over 24 hours, % | Up to 24 | Depends on the type of wood | 1-2 | 0,92 |
As for sizes, they can be very different. The most common are square sheets 1525x1525 mm. In addition, you can find the following formats:
- 1525x1270 mm;
- 1220x1220 mm;
- 1220x2440 mm;
- 1830x1525 mm;
- 2500x1250 mm;
- 3000x1500 mm, etc.
Bakelite plywood is the strongest and most expensive
Differences between laminated plywood sheets by wood type
According to technical characteristics, maple, birch and alder woods are most suitable for creating laminated plywood boards, and the explanation for this is simple - large pores and a high level of lignin content. According to the characteristics of conifers, they even have large internal channels, but they contain hemicellulose substances and resins, and for this reason, phenol-formaldehyde-based varnishes will not penetrate well into the pores of the material.
Poplar is loose and light in structure, has hemicellulose substances in excess, and they also prevent the wood from being saturated with polymers. The substance is destroyed even with a small amount of moisture, and therefore poplar slabs are only suitable for disposable formwork or for finishing the inside of a room.
Sheets of laminated plywood produced at factories in Russia receive the following marking:
- The abbreviation FOB is indicated first.
- After this comes the grade of plywood based on the presence and type of laminated surfaces.
- Phenol class.
- Film size and density are indicated in g/m2.
At the end they write a designation according to GOST, which indicates the technical characteristics of the material.