Plywood is a durable, multi-layer material made from natural wood. The physical and mechanical properties and technical characteristics of plywood are determined by the process of its production itself. Namely, an odd number of sheets of thin wood veneer are glued together using glue.
The veneer sheets are arranged in such a way that the direction of the wood fibers is perpendicular to each other. This makes the plywood very resistant to breaking, stretching and chipping (see table below).
Due to these parameters and affordable cost, plywood flooring is often used in construction.
Plywood for floor
Bending strength of plywood
Bending strength of plywood (birch, coniferous and combined)
Specification for plywood - table
Birch, coniferous, laminated and combined (TU 5512-001-44769167-02 and TU 5512-002-44769167-98).
Specification for softwood plywood
Specification for laminated plywood
Specification for composite plywood
Birch plywood specification
It should be noted that due to the fact that plywood for a long time remained almost the only material available to our compatriots, it was used everywhere. This, in turn, led to the emergence of different types and types of plywood.
Types of plywood
Types of plywood are determined by the scope of its purpose:
- construction;
- furniture;
- structural;
- industrial;
- packaging
Types of plywood depend on the glue used in production:
- FC – waterproof plywood. Kabamide glue is used in its manufacture;
- FSF – plywood with increased moisture resistance. Here the veneer sheets are glued together using phenol-formaldehyde glue;
- FBA is a non-waterproof plywood. In this case, albumin casein glue was used to glue the veneer. FBA plywood has little moisture resistance, but is highly valued by those who prioritize the environmental friendliness of the material;
- FB is a plywood that, thanks to the use of bakelite varnish, can be used in particularly damp conditions and in water.
And these are just the main types of plywood. There are many more stages of classification, depending on the thickness of the sheet, the number of layers, type of wood, grade, degree of finishing and type of additional processing.
Using plywood for flooring “+” and “-”
Advantages of plywood:
- plywood, unlike OSB and fiberboard, is a natural material and not recycled production waste. Therefore, it is more environmentally friendly;
- plywood moisture levels are in the range of 12-15%;
- plywood takes the brunt of variable loads. Thus, the screed retains its integrity, and the wood receives microcracks. However, they do not affect the quality of the floor;
- Due to the fact that plywood is made from wood, it has better contact with floor coverings. As a result, the service life of the latter increases;
- plywood makes it possible to obtain a floor that will meet the specified characteristics (flatness, surface quality) with less time and resources;
- laying plywood on the floor does not require special preparation and can be performed in several stages;
- plywood plays the role of a kind of insulation, allowing to reduce heat loss through the concrete screed and floor slabs;
- If there is a significant difference in height across the floor, the use of a screed is not recommended due to its high weight and cost. But plywood, on the contrary, would be an ideal option;
- Depending on the grade and quality of polishing, plywood can be used for rough and finished flooring.
But:
- plywood is not suitable for rooms with a significant temperature difference (for example, for dachas or houses of non-permanent residence), as well as with a high level of humidity (in a bathroom, bathhouse, sauna, swimming pool).
Comparison of characteristics
To choose the most suitable option for rough or fine finishing of a floor structure, it is necessary to take into account the main parameters of the product.
Environmental friendliness
Health safety is one of the main factors. The indicators of wood-based panel materials comply with the standards reflected in standardization documents.
- Plywood. Eco-friendly option. The most harmless products are those that are glued using natural resins.
- OSB. It does not pose a threat, but only if the production technology is followed. It is better to choose trusted manufacturers.
- Chipboard. This variety causes the most controversy regarding health hazards, since formaldehyde resins are used for gluing. Products must comply with standards (marking E1 or E0.5).
- Fiberboard. Does not pose a threat provided that high-quality raw materials are used.
- MDF. Eco-friendly material made using urea resins. These products must also comply with class E1 or E0.5.
Since the outside of all materials is finished, harmful fumes are minimized.
Strength
To choose the most reliable option, you need to take into account the density and structure of the product:
- OSB and plywood. Oriented strand panels can withstand heavy loads well: the layers are placed in different directions and glued together extremely firmly. But wood-laminated board may have a significant disadvantage - the possibility of deformation due to non-compliance with the technology.
- Chipboard and fibreboard. They have sufficient hardness. Their areas of use are somewhat different. Wood-shaving parts are thick, and wood-fiber parts are very unstable in bending, so they cannot be used for leveling voids.
- MDF. A relatively soft material that is not used in places with high loads.
It is difficult to compare all products on this parameter, since they have different sizes.
Dimensions
The length and width of all varieties are approximately the same, so it is necessary to compare the thickness:
- Hardboard. The thinnest material. Its thickness can reach up to 7 mm, but the most common is 3.2 mm.
- Plywood. For the floor, products with a thickness of 12–15 mm are selected.
- OSB. Can be of different sizes, but for flooring options from 10 to 22 mm are used. If you need to level the existing base, then a thickness of 1 cm is suitable, but in order to lay the material on wooden logs, the parts must be more durable.
- MDF. Due to their softness, the recommended thickness of the slabs varies from 18 to 25 mm.
- Chipboard. For horizontal structures with increased load, a tongue-and-groove version with a thickness of 16–22 mm is used.
The thickness and structure of the parts also affects protection from sound penetration and heat retention. If the noise pollution is very strong, then it is recommended to give preference to medium-density fiberboards of maximum thickness. They also serve as additional thermal insulation, which is similar to OSB.
Price
The difference in the price of materials depends on many factors: production method, raw materials used, additional processing, size and even place of sale.
- The most expensive is high-grade plywood.
- The cost of MDF is calculated per square meter and depends on the manufacturing method.
- The price of OSB-3 and 2 corresponds to wood-laminated boards of grade 3 or 2 of a smaller size.
- The lightest and cheapest option is fiberboard.
To ensure that the total work budget does not amount to too significant an amount, it is necessary to immediately determine the scope of application of each type of product.
Easy to install
Laying wood boards is not difficult; it does not require professional skills or complex tools. The order of work depends on the specific situation:
- If a frame structure is being erected, then OSB would be the best option.
- The light weight and thickness of hardboard make processing the fastest, but it is not suitable for serious leveling.
- Chipboard and OSB panels are cut and fixed almost identically. They are much easier to trim than MDF, which due to its dense structure offers more resistance.
- The most labor-intensive material to process is plywood. It will take much longer to place the product. It is more difficult to drill or adjust to size due to the presence of layers of natural wood in the structure.
All floor slabs are mounted on glue or joists, the only exception is the fiberboard covering: these sheets are not intended for laying on joists, they need a flat and durable base
What kind of plywood to lay on the floor
To begin with, it is worth clarifying two important factors.
- The first point is what type of floor the plywood is intended for . After all, the floor, in fact, is a two-layer structure, which consists of a rough (underlay) and a finishing (front) layers of coating.
- The second point is in which room to lay plywood . So, for example, in a living room, and even more so in a bedroom or children’s room, it is permissible to use only FK plywood. It contains no formaldehyde. Consequently, its use is absolutely safe, with satisfactory moisture resistance. In a production area with good ventilation, it is permissible to use FSF plywood. But only 1st emission class. The class means that the formaldehyde content does not exceed 100 mg. per 1 kg. sheet of plywood.
Depending on the above points, the question of which plywood for the floor is better (which one to use for the floor) will be decided.
Which plywood to choose for the floor
When choosing plywood for the floor, you should pay attention to the following parameters:
- brand of plywood . As already noted, for residential premises it is better to purchase FK brand plywood. Its moisture resistance indicators fully meet the operating conditions in residential premises;
- plywood class (emission class). Only class E-1 is suitable for flooring;
- grade of plywood for flooring . Plywood is divided into 4 grades. In this case, the sides of the sheet may have different grades. It is marked as 1/1, 1/2, 2/2, etc. Plywood of grades 3 and 4 is suitable for the subfloor. For finishing – 1st or 2nd grade;
- humidity of plywood . A quality sheet is one with a moisture content of 12-15%;
- number of layers of plywood . The thickness of the veneer in a sheet of plywood ranges from 1.7 to 1.9 mm. Consequently, their number determines the thickness of the sheet. The more layers a sheet has, the more durable it is. However, the thickness of plywood is selected taking into account its purpose. So for a subfloor you need plywood with a thickness of 12-18 mm, for a finishing floor 10-12 mm. When using plywood in production - at least 25 mm. Please note that if plywood is laid in two layers, then the thickness of the sheet should be divided into two;
- plywood sheet size. There are format and large format plywood. The dimensions regulated by GOST 3916.1-96 and 3916.2 are given in the table;
The dimensions of plywood are more important for transportation and storage than for installation. After all, it is inconvenient to work with a large size, and any installation method involves adjusting the sheet to the required dimensions. The main thing is to number the selected sheets and not mix them up during installation. By the way, professionals advise laying the workpieces offset. Joining four corners significantly reduces surface quality;
- plywood manufacturer . European or domestic manufacturers offer good quality material. But Chinese-made plywood causes complaints from users and often does not meet the stated characteristics.
Requirement for distance between joists
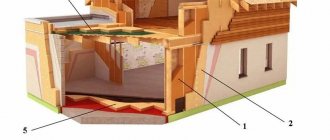
The main element when constructing a plywood floor is the frame. The logs are a wooden beam 2 m long with a cross section of 40x70 mm. When constructing the frame, you must make sure that the logs do not have serious defects, since this will directly affect the durability and reliability of the floor.
As for the distance between the logs, it is determined in accordance with the size of the plywood sheets, but a distance of 30–40 cm is considered optimal.
As practice has shown, plywood floors are highly durable and reliable. Although the installation of such a floor cannot be called a cheap option for a subfloor, it has a high degree of heat and sound insulation, allows the use of almost any type of finishing floor covering and is characterized by increased durability.
Laying plywood on the floor
4.1 Plywood for subfloor
Laying a plywood subfloor is the fastest, most affordable and easiest way, which also has several varieties.
Laying plywood on a concrete screed Laying plywood on a concrete screed . Sheet 10-12 mm thick. glued to the base. It is used when there is a smooth concrete screed of normal quality. The main thing is not to forget about expansion joints when laying. The gap is 3-4 mm. between the sheets, as well as between the sheet and the wall, will allow the plywood to play and adapt to its surrounding conditions.
Adjustable plywood floors This installation method can be used when there is a difference in height. It is enough to use special fasteners.
Adjustable plywood floors do not require the installation of joists, and height differences are leveled by fasteners located under the plywood.
Material prepared for the website www.moydomik.net
Installation of plywood on joists or floor beams. Installation of plywood on joists or floor beams .
Plywood, thickness over 12 mm. mounted on a prepared base. The method is labor-intensive, usually used when it is necessary to insulate the floor or raise it to a certain height.
Adjustable joists Adjustable joists allow you to install a sheet of plywood so that it can compensate for differences in height across the floor.
4.2 Leveling the floor with plywood
Leveling the floor with plywood A fairly common situation is when the floorboards have partially lost their appearance, but nevertheless do not cause any complaints. Then the flooring is laid on top of them.
But to prevent the finishing coating from becoming unusable, an intermediate floor (in this case, plywood) should be laid on the boards, which will level the surface.
Laying plywood on a wooden floor is carried out using hardware and is characterized by simplicity and high speed of work.
In order for plywood laid under laminate, linoleum or parquet boards to perform its functions for a long period, you must adhere to the following installation rules:
- securely fasten all sheets taking into account deformation gaps;
- “drown” the heads of the hardware into the sheet;
- remove irregularities using a grinder;
- fill in depressions and cracks;
- lay the substrate.
But laying plywood under a wooden floor is absolutely not required. Due to the massiveness of the floorboard, it can be laid on joists or on a flat concrete screed.
4.3 Finish plywood floor
Craftsmen can create real palace parquet from plywood. In this case, special requirements are put forward for the quality of plywood. Only the first grade can be used; the surface of the front side of the sheet must be polished. To create a beautiful pattern, the plywood is treated with stain, and the laid plywood parquet is sanded and covered with several layers of parquet varnish.
Pattern on plywood floor
Plywood parquet
Plywood floor covered with stain
Features of plywood sheet coating
Plywood is based on a natural material that is highly hygroscopic, wood.
That is why plywood is not recommended for flooring in rooms with high air humidity. So, the permissible humidity should not exceed 60%. Failure to comply with this rule can result in rapid delamination of the plywood sheet and failure of the subfloor.
Stages of floor installation.
But if necessary, the moisture resistance of plywood can still be increased.
For this, a special putty is usually used, which is based on polyvinyl acetate, known as PVA. The plywood sheet is thoroughly coated with the solution, first on one side, ensuring that wet spots appear on the opposite side, then on the other. After the sheet has completely dried, the treatment must be repeated.
As a rule, it takes at least 72 hours for the material to dry completely. When the plywood has dried, it can be coated with any wood antiseptic or acrylic varnish can be used, which will give the material additional strength. Such specially treated plywood sheets can be used to construct floors in rooms where the humidity reaches 78%.
Plywood for flooring - protection, operation and storage
In order for a plywood floor to serve you faithfully for a long time, you need to provide protection for the sheets at the installation stage. When working with plywood you need to consider:
- plywood needs acclimatization .
Only the purchased material should not be used immediately. It needs to be given time to rest in the conditions in which it will be used. The holding period depends on where, how, in what position, at what temperature and humidity level the plywood was stored. The acclimatization period can be:
- day. If the difference in temperature and humidity at the place of sale and installation is minimal, and the sheets were stored in a dry room, on a flat surface in a horizontal position;
- 3-5 days. If the difference exceeds 5-8°C and 10% (temperature and humidity, respectively);
- over a week. If the deviations are significant or the sheets are slightly deformed. The latter can be eliminated by pressing down the stack of sheets with weights and using more hardware per 1 square meter. leaf.
- dampness destroys plywood . Rapid fluctuations in humidity can cause serious damage to the wood from which plywood is made. At the same time, constant humidity in the room cannot be higher than 70%, and short-term - 80%. Laying plywood on a wet base is unacceptable. To check the moisture level of a wooden base, use a special device. And concrete is covered with film for a day. The presence of condensation under the film indicates that it is worth holding off on installing the plywood;
- plywood sheets are laid at a temperature of 20-30°C . In this case, the leaf is in optimal conditions;
- additional processing improves the performance characteristics of plywood . For example, an antibacterial primer will protect the sheet from the effects of fungi and microorganisms. Impregnation with PVA-based putty will increase its moisture resistance. And applying acrylic varnish will increase the strength of the surface layer.
Features of plywood sheet coating
Plywood is based on a natural material that is highly hygroscopic, wood.
That is why plywood is not recommended for flooring in rooms with high air humidity. So, the permissible humidity should not exceed 60%. Failure to comply with this rule can result in rapid delamination of the plywood sheet and failure of the subfloor.
Stages of floor installation.
But if necessary, the moisture resistance of plywood can still be increased.
For this, a special putty is usually used, which is based on polyvinyl acetate, known as PVA. The plywood sheet is thoroughly coated with the solution, first on one side, ensuring that wet spots appear on the opposite side, then on the other. After the sheet has completely dried, the treatment must be repeated.
As a rule, it takes at least 72 hours for the material to dry completely. When the plywood has dried, it can be coated with any wood antiseptic or acrylic varnish can be used, which will give the material additional strength. Such specially treated plywood sheets can be used to construct floors in rooms where the humidity reaches 78%.