Elm wood, due to its physical properties, is durable, moisture-resistant and easy to process. Therefore, elm lumber is widely used in the manufacture of furniture and related wooden products. Elm can rightfully be called industrial wood. The scope of application of elm material is very wide. It is used in the furniture industry, the manufacture of souvenirs and toys, mechanical engineering and the production of industrial equipment. Plywood and chipboard are also made from elm trees.
Elm processing
When processing elm wood, standard carpentry equipment is used. But due to its properties of strength and hardness, elm is rarely cut to give rounded shapes. There is a technology for bending elm in which it is steamed and processed. Upon subsequent drying, it is restored to its original strength and holds its shape perfectly. Difficulties also arise when polishing elm. Therefore, it is often varnished or covered with decorative compounds. Elm tolerates chemical exposure well. The wood material adheres well and is “friendly” with metal parts.
Elm - material for beginner carpenters
Due to its prevalence and unpretentiousness, elm is ideal for novice carpenters and furniture makers. Elm with durable wood , almost completely corresponds to oak species. At the same time, it is easier to process, and the cost of the material is lower. The range of applications for vase lumber is varied. You can make both stools, so to speak, to get your hands on, and more complex furniture from elm using turning and carving. In both cases, the product will last a long time and reliably. Elm sapwood has a light yellow, uniform texture, so the product can be coated with any stains and varnishes. Thus, you can achieve the effect of a more expensive type of wood, and elm is certainly not inferior to it in terms of strength.
Solid Elm - the wealth of nature in your interior.
It is worth noting, delving into history, wood has always been a relevant highlight of all times and now fits into the concept of modern stylistic trends. Wood in the interior will be appreciated by people for whom family, warmth and comfort are the main values in life, who have good taste and clear life positions.
At the moment, there are a lot of offers of furniture made from solid wood, various species: pine, alder, oak, linden... They differ in color, texture, mechanical properties and shapes. ... Why do we choose the Elm massif or, as it is also called, elm? Elm is a tree of deciduous forests, growing together with maple and linden as an accompanying species; it is a long-lived tree that lives up to 500 years, or even more. Its diameter is up to 3 m and height up to 20 m. Elm wood is a valuable hardwood that is difficult to rot. In ancient times, weapons were made from it: clubs, stakes and shields, and also covered the hulls of old ships. Nowadays, due to the fact that wood is not afraid of water, it is even used in the construction of underwater structures, such as dams, locks and canals. It is this property that allows you to fearlessly use elm countertops in the kitchen and bathrooms. Elm also has excellent wear-resistant qualities that are not inferior to oak, beech, and ash. It is also worth noting the beauty of the wood texture - the uniqueness of the natural pattern. The preserved natural land gives exclusivity to products made from solid elm. Let's take a look into the workshop and find out what the technology is for producing products from Solid Elm. First of all, I would like to note that the production process is quite labor-intensive. Before processing, each workpiece undergoes a gentle drying process in special boxes, which takes from one to two months. Next, the saw cut is given an even plane on the machine, after which the edges are processed manually, cracks and irregularities are sealed with special compounds based on epoxy resin, then the tabletop is sanded in several stages and also covered with oil and wax in several stages.
To tint wood and give it properties that protect the tabletop from mechanical stress, special compounds based on natural oils and wax are used. Preference is given to leading European manufacturers such as Osmo, Borma, etc.
At the same time, impregnation with natural oils allows you to preserve the texture of the wood and its rings, emphasizing the uniqueness of your interior.
It is important to note that we do not use varnishes to paint wood, as they are harmful to health. Our furniture is environmentally friendly and natural.
Wood in the interior offers endless possibilities that come down to environmental friendliness, practicality and sophistication. It can be used to create any design in which an atmosphere of peace, warmth and natural richness is sure to reign.
If you want to add uniqueness to your interior, choose the product that you like: a table that will gather the whole family for an evening dinner, a mirror in the reflection of which you will see only smiles, a bed saturated with the smell of natural harmony.
Let this product become a family heirloom, passed down from generation to generation, which will keep the warmth of the soul of your home. SHARE:
Elm veneer
Elm, which grows in the vast expanses of the Eurasian continent, is called white elm. It is not suitable for veneering, as it is susceptible to disease. Due to the disease of the species, there is a risk of partial or complete destruction of the wood structure. But there is an alternative option for producing elm veneer. The so-called American elm or red elm is excellent for veneer production. At the same time, it has a reddish-brown texture, which makes it more exotic. This elm grows in both Americas and Canada. The use of solid wood is not economically feasible in our region. But it is beneficial to use veneer. It will not only create a beautiful visual effect, but will also perfectly protect cheaper types of wood from mechanical damage.
Elm is a tree that cannot be broken
November 7, 2022 Elms belong to relict tree species that appeared about 40 million years ago.
Their center of origin is Central Asia, from where they spread to most of the Northern Hemisphere: they settled throughout Eurasia and North America. Ten thousand years ago, when the climate on Earth was milder than today, Europe and the British Isles were completely covered with broad-leaved forests, dominated by oak, linden and elm. Then people came and started farming...
Now elms in Britain are found only in artificial plantings, but their Latin name “ulm” has English roots.
Botanical description of elm
Elm, or elm (Ulmus) is a genus of large trees widespread in mixed and deciduous forests of the central and southern European part of Russia. The tree extends beyond the Urals in the form of small “islands”. In total, the genus includes 30-40 species, the ambiguity of the number of which is explained by the difficulty of distinguishing them due to the ease of interspecific hybridization.
Some species in Russia are known under other names, for example, the word “berest” is used to describe the small elm (in the south of the European part of Russia, in the Caucasus), and “elm” (from the Turkic “ebony”) is the name for the squat elm (Volga region, Southern Urals, Caucasus).
The trees can be giants and reach 40 m in height, often their trunk bifurcates or is divided into many trunks. Less common are elms in the form of shrubs.
The bark of the elm is gray or brown, smooth in young plants, but with age it cracks and comes off in layers.
leaves are two-row, short-petioled, with early falling stipules. Their characteristic feature is the asymmetry of the leaf blade at the base. The leaves are oval or ovoid in shape with a pointed tip. The leaf length is from 4 to 20 cm. They are serrated or double-toothed along the edge, glossy on top and matte pubescent below. The leaf arrangement is alternate and so dense that the crown of the tree allows almost no light to pass through. In autumn, the leaves turn yellow or reddish-brown and fall off earlier than those of other species. But not all elms are deciduous trees; some of them are evergreen.
Elm grows very quickly; at about 60 years of age, its vertical growth slows down, but active thickening of the trunk begins, sometimes reaching 1 m in diameter. In terms of strength, elm can only be compared with oak, and also in terms of wood density (about 650 kg/m3).
The crown of the elm is ovoid with a truncated top, dome-shaped or almost spherical, and tolerates pruning well.
The roots are flat, disc-shaped, sometimes located at the base of the trunk. In most species, root system lacks a main root; it is usually powerful and deep. On strongly podzolic soils - superficial.
The tree is often dioecious, sometimes monoecious. Flowers are bisexual or unisexual. Pistillates can be solitary. More often, the flowers are collected in an inflorescence - a semi-umbrella, located in the axil of the leaves. Perianth petals 4-5, less often 3-8. There are as many stamens as there are petals or twice as many, pistil 1. Each individual flower hangs on a long thread-like peduncle, which, after fertilization of the ovary of the pistil, lengthens even more and the inflorescence takes on the appearance of a crumbly brush.
Elm blooms in April-May before the leaves bloom, like other wind-pollinated plants; in early springs it is valued as a honey plant. The exception is small-leaved elm, which blooms in the fall. The fruit of the elm is a nut or drupe, located in the center of the lionfish. Seeds are dispersed by the wind.
The tree grows well in fertile soils; some species of the genus tolerate salinity or dry habitats. All species are shade-tolerant, and with sufficient lighting they form a powerful crown. Thanks to the density of the leaf mosaic, they themselves form a dense shadow. They reproduce by seeds, stump shoots and root suckers.
Use of elm in economic activities
The average lifespan of elm is 80-120 years. 400-year-old specimens are known.
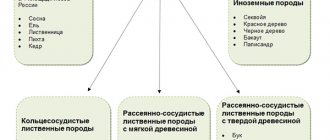
wood is hard, strong, viscous, elastic, easy to process, but difficult to split. Its heartwood is dark brown, the sapwood is lighter with a characteristic pattern of broken or parallel stripes, with narrow core rays. In water it resists rotting well, but this ability is lost upon contact with soil. A growing tree is often attacked by insect pests and parasitic fungi.
The first written mentions of elm date back to the Mycenaean period. The chariots used in the Battle of Knossos had wheels made of elm wood. In Ancient Greece, plows were often made from it. And elm burns excellently; its wood tends to ignite even when wet. Any fire can be easily lit from the logs of this tree. Yes, you can light a fire from logs, but cooking these logs is not so easy. However, we conducted an experiment: although elm does not famously scatter into logs, it is still not difficult to chop firewood from it if you get a good tool.
The Russian name of the tree speaks for itself - elm - from “knit” or “knit”. In the old days, sleighs, rims and other products were knitted from its bast. And for those who have chopped elms for firewood, the second meaning of this name is clear - if you drive an ax into a log with all your might, but it’s still intact, and you can’t even pull the ax out - it gets stuck. It is difficult to split an elm block because the layers of the tree's wood are uneven and difficult to separate from each other.
People use elm very widely:
- fruits - as a highly nutritious feed for pigs and other domestic animals. Young branches and bark are also used to feed livestock;
- for landscaping cities, since many of them are undemanding to living conditions. But in the steppes they suffer greatly from pests. In Europe and North America, the era of elm landscaping ended between World Wars I and II, when the trees were damaged by war and an outbreak of Dutch elm disease. The revival of plantings began in the 1990s. Then new, more resistant varieties of elm were developed. In total there are about 300 new varieties of wood. And the old pre-war varieties were lost;
- as an early honey plant;
- Due to its high density, elm is difficult to cut and split, but bends quite well. The smooth surface of the material tolerates polishing well. Fresh timber practically does not crack or warp when dried. A variety of bent products are made from it, for example, arches, rims, ship keels, etc., as well as small carpentry crafts. In ancient times and the Middle Ages, bows were made from elm when yew was unavailable;
- the bark is used for tanning leather products;
- Ropes and mats are woven from bast. They turn out to be very durable;
- water pipes were made from elm trunks, and the supports of the first London Bridge were made from them;
- wood is widely used in carpentry, furniture industry and mechanical engineering. Because of its density and viscosity, it was used to make wagon wheel hubs, baseball bats, gun butts, chair seats, wooden frames, parquet floors, door handles, etc. Now elm is mostly used in the form of veneer for refining lower-quality tree species or combined with other materials when finishing premises;
- Elm is edible! Its bark, cut into strips and boiled, sustained much of Norway's rural population during the Great Famine of 1812. Elm seeds are especially nutritious; they contain 45% crude protein and at least 7% fiber in dry weight;
- Chinese elm is popular for bonsai because it is tolerant of pruning.
In Russia, 10 species of the genus grow under natural conditions. The most common of them is the common or smooth elm (Ulmus laevis).
Interesting facts about elm
Elm has several names - elm, birch bark and elm. This plant has more than 30 varieties. Some plant specimens lived up to 400 years.
Our ancestors widely used elm for domestic purposes. In the Cheboksary Beer Museum there is a copy of a beer barrel, the rims of which are made of elm. Elm was also used to make skis for sleds and sleds. The flexibility of the species made it possible to bend the most bizarre shapes, and the strength of the wood allowed the products to serve for a long time. According to some sources, the elm sled was passed down to three generations, and later became a museum piece. American elm bark is used for medicinal purposes. A tincture of the bark is used to treat diseases of the throat and respiratory tract. Thanks to a special mucous substance, elm bark has excellent antiseptic properties.
The catchphrase “elm and grapes” denotes lovers who remain unshakably faithful to each other.
This is related to the parable in which a grape vine entwined itself around an elm tree, and during a severe drought it produced a wonderful harvest. This phenomenon can be explained from a biological point of view. The extensive foliage protects the grapes from the sun, and the deep bark system of the elm feeds the grapes with moisture. Tags: elm, wooden furniture, Elm furniture
Elm. Beneficial features
A decoction of elm bark is widely known and used in folk medicine, for diarrhea, to relieve the symptoms of gastritis, and helps in the treatment of ulcers.
Decoctions of elm leaves help against intestinal and kidney colic. Gruel from fresh elm leaves promotes wound healing. Compresses help with scabies and eczema.
Preparations based on elm leaves and bark have a beneficial effect on cardiovascular activity and normalize metabolic processes in the body.
Elm bark infusions are effective for cystitis.
The main effect of elm bark and leaves is anti-inflammatory.
Subscribe to our Yandex.Zen channel