Types of timber
Timber specifications may vary. They have different purposes, requirements and production methods. Round products are made in the form of sections of tree trunks of various species. There is a high-quality cleaning of the workpiece from twigs, branches and leaves. The round cross-section is ensured by means of a round cut. Products are made peeled from bark or with it.
Round timber
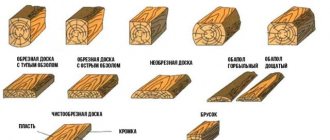
The range of timber products differs in the type of processing. There are:
- edged products. Characterized by the presence of parallel front or back edges. Edge trimming is performed perpendicular to the axis. Sawing deviations are regulated by GOSTs depending on the type of material;
Edged
- unedged products. A distinctive feature is the presence of sawing on the front and back sides. Longitudinal edges are filed completely or partially. Defects are regulated by the corresponding GOST.
Unedged
Important! It is allowed to trim lumber from one edge.
Processing method
After sawing from a tree trunk, the lumber can undergo additional processing.
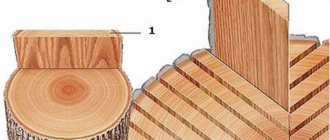
Unedged - minimal processing when the edges are not trimmed. There may be wane left on them.
Wane is a defect when an untreated area with remnants of bark remains on the lumber. Where the wane is located, rounded ribs are usually obtained. Unedged lumber with wane requires additional processing.
Edged lumber - the edges are cut so that they are perpendicular to the faces, and the amount of wane does not exceed the permissible values.
the planed material undergoes another stage of processing. A small layer of wood is removed from at least one face and two edges. Planed materials are used for finishing surfaces.
Profiled lumber - the product is given a complex cross-sectional shape to improve joining. Docking can be done according to the “tenon and groove” principle, when a tongue and groove is cut out on one side and a groove on the other.
Varieties
The widest range of lumber is presented:
- plates in the form of a half log obtained by cutting a tree trunk along the axis;
- quarters produced by sawing logs in two diameters. A perpendicular relationship is maintained, allowing cutting into 4 even parts along the axis of the workpiece;
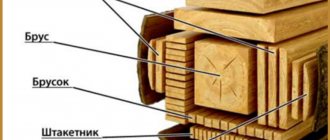
- beams whose thickness and width exceed 100 mm;
- wood sleepers presented in the form of timber with a round cross-section. The main scope of application is the construction of railway tracks;
- boards up to 100 mm thick and no more than 200 mm wide;
- bars with a thickness of at least 100 mm and a length of less than 200 mm;
- slabs - wood waste obtained by sawing the side edges of logs;
- planks with dimensions: thickness - 60-80 mm; width - 100-160 mm.
Lumber
What are lumber
Lumber is produced by cutting logs longitudinally into long components that have at least one flat side (face). Most lumber has two flat edges parallel to each other.
Two methods of sawing logs are used - radial and tangential. With a radial approach, the cutting directions are oriented towards the center of the growth rings. The resulting boards or beams have different sizes, and their width is limited by the diameter of the tree being opened.
Tangential sawing is designed to produce long boards and is directed tangentially to the growth rings. In this way, a large number of fragments are obtained that have the same dimensions and cross-sectional shape.
Further processing and appearance depend on the planned use of the lumber. The more work is carried out to refine the surface and protect it from external influences, the higher the cost of the final product will be.
It is very important to choose high-quality lumber; which ones you should not buy can be seen in the video:
Assortment
Information about the assortment is useful for people engaged in independent construction of a house or commercial buildings. All sawing sizes and standard sizes of construction products of wood origin are regulated by state standards in the industry - GOSTs. You can understand such information, carefully study it and learn to apply knowledge in practice without outside help. No professional education is needed. Everything is presented in an accessible form.
Important! Products produced at a sawmill must necessarily comply with generally accepted government standards. Permissible deviations are regulated.
The assortment is described separately for deciduous and coniferous wood. Deciduous products are divided into 4 grades, coniferous products - into 5. An additional fifth grade is presented in the form of selected timber. Specific building materials are assessed based on edges in the worst condition. Products are sorted depending on the presence or absence of defects, size deviations, and the presence of mold and rot.
Marking
The separation of sawn wood grades is carried out according to filigree processing:
- first-class. The highest quality material used for the construction of permanent and temporary wooden structures. It is allowed to cover the surface of walls and floors;
- second-rate. The main area of purpose is the implementation of lathing and flooring;
- third-rate. Provide construction of third-rate load-bearing structures;
- fourth grade. It is preferably used to create containers and small workpieces.
Creation of aesthetic and protective functions of the material
Facing the front plane is divided into:
- transparent;
- opaque;
- imitation;
- mosaic;
- carving
Protective functions against rotting and fire. The negative influence of external environmental factors leads to premature destruction and aging of the material. A growing tree actively fights against biological and other types of destruction. Whereas after the log house the protective mechanisms are reduced.
To protect wooden products from fire, special impregnations, paints, coatings and other substances are used.
Lumber and wood products are popular raw materials for construction. It is difficult to imagine works in which at least a tablet is not used. Wood is easy to process. It has strength, reliability and durability. The use of specialized material processing substances can significantly improve the quality of the finished product.
Technological production process
The technological process of manufacturing lumber begins with the purchase of round timber. It is required to carefully approach the choice of wood. The quality and durability of the finished product and its final cost will depend on this in the future.
During the work process, safety requirements must be observed. Use only safe work practices. The rate of accidents at work is high. Sometimes with fatal consequences.
Wood raw materials are first subjected to high-quality cleaning from knots and bark. It is assumed that specialized logging equipment will be used to carry out the task of clearing the forest. After cleaning, the process of sawing the wood is carried out. The main parameters of the timber are determined. The products are sorted. Sent for further processing.
Round timber is produced from coniferous and deciduous trees. Obtaining a high-quality product requires complete drying of the workpieces. Additionally, products are treated with specialized compounds. The finished product is considered fully suitable for subsequent use during construction. It does not rot and does not dry out.
The finished products are divided according to the degree of humidity:
- dry. The humidity indicator does not exceed 10%. The main raw materials for the manufacture of panels and parquet boards;
- universal. The humidity level is between 12-15%. This is the main raw material base for the manufacture of floor boards, skirting boards and platbands. Allowed to be used for the manufacture of interior door structures;
- wet. Humidity exceeds 18%. The products are used for the implementation of rafter structures and external cladding.
General information about wood
Wood is the most important material of natural origin, characterized by environmental friendliness, accessibility, prevalence and demand. Characterized by a high degree of resistance to static and dynamic loads, lightness and strength.
The porosity of the structure provides high acoustic characteristics and a low degree of thermal conductivity. The material is easily subjected to all types of mechanical processing and gluing, and is held in place by metal fasteners.
A characteristic feature is the “breathing” structure. Regular air exchange is observed in the cellular structure of the tree. The relative humidity indoors of wooden structures is in the range of 45-55%.
The material has a low temperature coefficient of linear expansion. Shows resistance to chemical compounds: acids and alkalis. The wood is frost-resistant, decorative, with a constantly renewable raw material base. Modern technological processing of wood makes it possible to produce high-quality and durable wood that is resistant to moisture, rot and mold.
But like any building material, wood has disadvantages:
- heterogeneous structure;
- increased degree of hygroscopicity, leading to cracking, swelling and other types of damage to the material;
- anisotropy - the ability of a plant to take different positions under the same environmental factors;
- prone to fire;
- the appearance of rot in a humid environment.
But most of the negative aspects are removed through the use of specialized processing tools.
What is the difference between timber and sawn timber?
Sometimes the terms lumber and timber are used interchangeably. But in fact the difference is significant. Lumber - finished wood products. Timber products are semi-finished products that require further deep processing. These are blanks that are often used as consumable raw materials for the manufacture of lumber.
Lumber and timber are actively used in construction. But in order to get a reliable and high-quality structure, you need to choose the right material. When purchasing, it is recommended to require quality certificates.
Requirements for lumber
To use lumber in industry, it is necessary to take into account the presence of defects that may make it difficult or completely unsuitable for certain purposes. Wood defects may be associated with structural features of the tree trunk. Such defects include irregular shape, knots and branches. Damage as a result of exposure to pests, cracks, etc. is also possible. In addition, defects may arise due to violations in the processing of timber and improper storage - warping, etc. In this case, they are not used for construction. Technical requirements are determined by GOST lumber 8486-86 and GOST 24454-80.
GOST 8486-86 Softwood lumber. Specifications
1 file 440.08 KB
Vices and defects of lumber
Wane in lumber is a defect that is the presence of an unsawed area on the side of a log on which a piece of bark may remain. The cause of such defects is the uneven thickness of the tree trunk. Such logs require additional processing and their use is limited. They are not suitable for building a residential building, but can be used for various outbuildings.
Warping of wood raw materials is various changes in their shape caused by uneven shrinkage or swelling. As a result of warping, the appearance of lumber deteriorates and their use in industry becomes difficult.
Assumptions for deviations in lumber dimensional parameters
All possible deviations in parameters - length, width, thickness - must comply with the requirements. The dimensions of wood according to GOST 26002-83 and GOST 9302-83 are determined in a limited range. So, the run-up of the length size is:
- industrial wood for construction from – 1 to 6.5 m;
- container board – 0.5 m;
- wooden beam dimensions GOST 8486-86 – 3.25 m.
GOST 26002-83 Northern graded softwood lumber supplied for export. Specifications
1 file 570.47 KB
GOST 9302-83 Black Sea sorted softwood lumber supplied for export. Specifications
1 file 329.34 KB
GOST 8486-86 Softwood lumber. Specifications
1 file 440.08 KB
GOST timber 9463-88 allows deviations in the dimensions of lumber: width - 2%, thickness - 2.5%, length - 50-25 mm.
GOST 9463-88 Round softwood timber. Specifications
1 file 386.52 KB
Wood defects associated with structural features
One of the disadvantages is the presence of knots. They can be weakened or loose, as well as tobacco, which simply crumble when touched. Knots can spoil the appearance of lumber or fall out, leaving holes. Knotiness of lumber can significantly limit the possibility of their use.
Cracks occur when fibers break longitudinally. They appear for various reasons. This may be due to improper drying, frost, etc. Cracks reduce the quality of materials: if there are cracks, logs and boards are unsuitable for the construction of residential premises. Shrinkage of logs can cause deformation.
Parasitic insects and wood fungi not only spoil the appearance of lumber, but can also destroy the wood, leaving noticeable holes on its surface. Therefore, before using lumber, it is necessary to evaluate its quality. If defects are detected, decide whether the selected materials are suitable for use for certain purposes.
Heeling of timber and lumber is a defect that is characterized by thickening of the trunk and branches in the lower part. Appears as a result of compression or stretching of the lower area. This defect is typical for trees growing obliquely or twisted. On the end parts, dark areas are clearly visible, often in the form of a semiring. Such lumber is less easy to process. Dried lurch wood has high hardness, but lacks strength and is less resistant to mechanical shock, quickly absorbs moisture and swells. Logs with heel are not suitable for building houses and baths.
Marking
According to the requirements of the current GOST 6564-84, all lumber longer than 1 m must contain markings. It is applied to the face of the lumber with a special mark, chalk or paint. It must indicate the group, quality and grade of lumber. It consists of letters, numbers and symbols.
GOST 6564-84 Lumber and blanks. Acceptance rules, control methods, marking and transportation
1 file 278.52 KB
Marking features depend on the purpose of the lumber: those used in shipbuilding are marked with the letter C, for resonant ones - the letter P, for skis - L. If lumber is intended to be sold in a package, then the package is marked, and not all materials individually. The trademark of the enterprise or its name, package number, wood species, grade, cubic meters, cross-section of cuts, standard are indicated.