New sanctions against Russia from the EU and the United States have already affected many areas of industry, including, of course, the timber industry, the work of which largely depends on the situation on world markets and the supply of high-tech equipment.
Thus, specialists from the international consulting firm Wood Resources International (WRI), specializing in assessments of global forest resources, markets for wood raw materials and trade in forest products, presented a report according to which new EU sanctions could negatively affect not only the export and import of forest products from Russia, but and on the supply of timber industry products throughout the world. According to their forecasts, financial transactions will also suffer—Russia’s trade with the West will decrease significantly.
It is worth remembering that today the Russian Federation is the largest exporter of lumber in the world and ranks seventh in the ranking of countries for timber exports. And over the past five years, the export of forest products from the Russian Federation has grown rapidly, including due to the assistance of the Russian government, which encouraged the modernization and expansion of existing production facilities and the creation of new ones.
During this time, new solid biofuel plants appeared in the country, investment projects appeared aimed at creating forest processing facilities in the Far East and Siberia, including several projects for the construction of new pulp and paper mills, etc. Analysts at Wood Resources International believe that many investment projects in the forestry sector industries may be “frozen” or completely stopped due to the abundance of sanctions from the West.
EU sanctions against Russia have also limited transactions on correspondent accounts between European and Russian banks. Even Sberbank decided to leave the European market, as its subsidiary banks faced an abnormal outflow of funds.
Main industries
Thus, the main features of the forest industry of our country include, first of all, the widespread and very complex structure of the organization. Conventionally, the branches of this sphere of the national economy are classified into four large main groups:
- actual logging;
- woodworking (production of lumber and furniture);
- pulp and paper (chemical processing);
- forest chemicals (production of turpentine, rosin, etc.).
Enterprises related to the logging industry
- Ind Timber LLC;
- Rimbunan Hijau MDF LLC;
- LLC "Priangarsky Timber Processing Complex";
- OJSC Terneyles;
- GBU SO "Samarales";
- Russian Forest Alliance LLC;
- OJSC "Lakhdenpokhsky Timber Industry Enterprise";
- LLC Industrial and commercial enterprise "Titan";
- LLC "Group of Companies ULK";
- LLC "Lesprom-yug"
Other companies operating in this industry are presented in the Woodworking Plants section.
Useful functions of the forest
The most significant product supplied to our market by such an industry as the forestry industry is, of course, logs. They build houses from it, and also produce materials used to make furniture, paper, cellulose, ethyl alcohol, matches, etc. Among other things, forest is:
- One of the largest sources of feed and food resources.
- Habitat for valuable game animals.
- A source of various kinds of medicinal plants.
- A means of protecting fields from wind and soil erosion.
- A source of oxygen and a place to relax.
Plywood production
This material is widely used in furniture manufacturing, construction, and transport engineering. More than 50% of products produced in Russia are exported. In 2016, the volume of plywood production in the Russian Federation amounted to 3.65 million m3. Of these, 2.55 million were sold abroad.
The industry is actively updating equipment. The main production resources are concentrated in the mixed forest zone and in the south of the taiga. The largest manufacturers were also located there. The leaders in plywood production are the Komi Republic and the Kostroma region. Large production facilities are also located in: Irkutsk, Novgorod, Vologda, Leningrad regions and Perm region.
As statistics show, from 2010 to 2016. plywood production volumes increased 2.5 times. Production is divided approximately equally between three groups of enterprises: second-tier factories, small manufacturers. In terms of plywood export volumes, the Russian Federation remains firmly in fourth place, behind only China, Indonesia and Malaysia.
Resource Allocation
The total amount of forests suitable for felling in Russia is about 1.4 billion m3 with an annual increase of 830 million m3. Approximately half of these reserves are concentrated in the East Siberian and West Siberian regions of the country. About 1/5 is in the Far East. In the European part of Russia, the largest reserves of forest resources are located in the Northern and Ural regions. The highest quality wood is harvested in the Komi Republic, Arkhangelsk and Vologda regions, as well as in Karelia. These areas are home to pine and spruce forests, the cutting of which is the main focus of the country's timber industry. Important suppliers of valuable hardwood species are Sakhalin Island and the south of Primorsky Krai.
Lumber production
Russian-made lumber is in great demand on the world market. The main reason for this is the high quality of the products. Lumber from Siberia and the North-Western region, which has high strength during processing and a dense structure, is especially valued. Small and large timber industry complexes in the Russian Federation had to take advantage of this trump card when the government imposed large duties on the export of round timber. Thus, from the beginning of 2010, the volume of supplies of softwood lumber abroad began to grow. The main sales are in China, Uzbekistan, Egypt, Iran and Japan.
Among the federal districts, the largest volume of production occurs in Siberia, which produces up to 40% of the total volume in the country. In second place is the Northwestern District (28.4%), and in third place is the Volga District (11%). The established distribution of shares in the total production volume reflects the geographical location of timber processing enterprises.
Geography of logging
Three regions are currently considered leading in this area of the Russian national economy:
- Ural (Perm and Sverdlovsk regions);
- Northern (Arkhangelsk region);
- East Siberian (Irkutsk region and Krasnoyarsk region).
Recently, there has been an increase in logging in the Far East. Until recently, a lot of wood was supplied to the market in the Central and Volga-Vyatka regions. However, unfortunately, the pace of procurement in these regions has currently decreased.
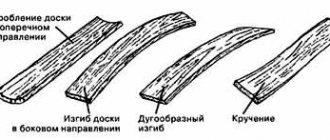
Technological process
The first thing that specialists do after choosing a site for logging is felling trees. Next stages:
- trimming the crown and branches;
- removing bark from the trunk;
- skidding (transportation to the loading dock), sawing or bucking (transverse division of trunks) of wood;
- measuring and sorting.
The final stage is stacking, loading and transportation.
Note: almost the entire process is mechanized.
Geography of the forest industry: processing
The most labor-intensive sub-sector of this sector of the national economy is the woodworking industry. The types of products it produces are incredibly diverse. Forest processing includes the following main groups of production:
- Plywood. Enterprises of this group are the largest consumers of birch wood. Plywood is mostly made from it. Therefore, factories specializing in the production of this building material are located mostly in the Northern, Northwestern and Ural regions.
- Sawmill production. This is the initial stage of log processing. Among other things, the Russian forestry industry supplies the market with materials such as timber, boards, slabs, picket fences, etc. Historically, sawmill production is concentrated in our country in the European part.
- Production of chipboard and fibreboard. These materials are made mainly from wood waste. Therefore, enterprises of this group are located mostly in areas of logging and sawmilling.
- Furniture industry. This industry requires qualified personnel. And furniture factories and workshops are built mainly in cities.
- Match production. This product is made from aspen. As a result, match factories are located mainly in regions with large reserves of this type of wood.
Is the operation of foreign assets on the territory of the Russian Federation stopping?
The “first shock” is gradually passing, and European partners who, in one way or another, cooperate with Russian companies or work in our country, are beginning to make their first decisions.
For example, the Finnish chemical company Kemira Oyj, from March 1, 2022, stopped supplying its products not only to Russia, but also to Belarus “until further notice.” At the same time, our country last year accounted for about 3% of the company’s total revenue, whose supplies were important for consumers in the pulp and paper segment.
Finnish Stora Enso made a similar decision. The company's press service reported that management decided to temporarily “freeze” all production and supplies in Russia. There are three Stora Enso cardboard packaging plants in the Russian Federation - in the Nizhny Novgorod, Kaluga and Moscow regions, as well as two sawmills in Karelia and the Novgorod region. Today, they employ a total of 1.1 thousand employees.
“Most likely, the overall drop in production volumes at the end of the year will be from 40 to 70 percent, investments in the development of high-tech enterprises may cease almost completely. The severance of relations with European, American and Japanese companies and consumers could make the Russian timber complex absolutely dependent on the Chinese timber market and Chinese investors (despite the fact that for China itself, Russian timber is not of fundamental importance, so its conditions may turn out to be completely enslaving).” ,” Alexey Yaroshenko, head of the forestry department of Greenpeace Russia and editor of the Forest Forum, commented on the situation.
The misfortune has not spared pellet producers either: the largest Danish energy company, Orsted AS, which is engaged in the conversion of old coal-fired thermal power plants into modern ones operating on the basis of biomass, refused to supply Russian fuel pellets. The company's management refuses to enter into new contracts with our biofuel and coal producers.
However, Orsted AS is not refusing Russian gas supplies. The company's CEO Mads Nipper believes that such a measure could have serious social consequences for European residents.
The Swedish furniture concern IKEA recently announced a suspension of work in Russia and the Republic of Belarus. The company's management decided to suspend all exports and imports in the region, and from March 4, 2022, to completely stop production of Inter IKEA in Russia. Consequently, supplies from Russian subcontractors to IKEA Industry facilities were also stopped.
The company's press service also noted that the Ingka Group management decided to close all of the group's stores in the Russian Federation, but MEGA shopping centers will continue to operate. Sales will also be discontinued in the online store. The company's management guaranteed the employees continued income and employment in the future.
To be fair, it is worth noting that some foreign companies have suspended the operation of their assets not only in Russia and Belarus, but also in Ukraine. Thus, the international group for the production of packaging materials and paper Mondi, in an official press release, announced the suspension of the work of its plant for the production of paper bags in Lviv. At the same time, Mondi’s Russian enterprises continued to operate as before.
Geography of the pulp and paper sub-industry
Forest industry enterprises in this group produce materials using high-tech equipment using various complex chemical raw materials and are extremely energy-intensive. Paper, cardboard and pulp are made mainly from softwood. Therefore, the leading regions for the production of these materials are Karelia, as well as the Ural and Volga-Vyatka regions.
general characteristics
A quarter of the world's timber reserves are located on the territory of the Russian Federation. Forests occupy about 45% of the state's area. The main share of forest-forming species is formed from conifers: spruce, pine, larch and cedar.
The country's forest fund is divided into three main groups:
- Field-protective, water-protective, protected and recreational forests. In such areas, logging is carried out only for sanitary reasons.
- Territories where deforestation is carried out selectively and does not exceed the volume of annual growth.
- Operational areas in which clear cutting of commercial timber is carried out.
Wood chemical industry
This sub-industry includes only two main groups of production. Firstly, this is the hydrolysis industry. Factories in this group produce products such as alcohol, glycerin, turpentine, rosin, etc. The main raw materials for their production are wood processing industry waste. The second large group of enterprises produces plastics, cellophane, artificial fiber, varnishes, esters, and linoleum. The raw materials for these materials and compositions are products of the pulp and paper industry.
Woodworking industry of the Russian Federation
This industrial branch performs mechanical, chemical and mechanical processing of wood.
It includes several productions:
- sawmill (creation of sleepers and lumber);
- production of houses from wood;
- production of wooden parts for construction;
- production of wood-based boards (blocks for doors and windows, parquet boards, wood fiber boards, wood chip boards, carpentry products);
- production of containers from wood;
- production of plywood, including parts that are glued and bent, as well as veneer;
- making matches;
- furniture manufacturing;
- production of other wood products (wood flour, skis, frames for greenhouses).
Main problems
Unfortunately, the Russian forest industry is currently not as profitable as it could be. Enterprises in this industry, unfortunately, process no more than 11% of the supplied raw materials. Such wastefulness can be called the main problem of the complex. Currently, more than 0.5 billion tons of biological mass are harvested per year. Only about 25% of raw materials are recycled. Bark, branches and most of the needles go to waste.
Irrational use of resources, therefore, is the most serious problem in such a sector of the national economy as the forestry industry. The branches and sub-sectors of this traditional production for the country cannot develop quite successfully also because of:
- Constant and uncontrolled increase in fuel prices.
- Commercialization of the transport industry. In terms of volume of transportation, timber cargo in our country is second only to coal and oil.
- Lack of a regulatory framework regulating economic relations with foreign enterprises. This problem is actually very serious, since most of the harvested wood is currently exported. Every year, timber worth 1.5-3.1 billion dollars is exported from Russia.
- Lack of control and orderliness in terms of investment.
All forest industry areas without exception are experiencing similar problems. Quite significant limiting factors are also:
- Lack of labor resources.
- Weak degree of development of forest-rich areas.
- Harsh climatic conditions.
As you can see, the timber industry in Russia is experiencing many difficulties. However, this branch of production still remains traditional and extremely important for our country.
Impact of the global crisis
At the end of 2008, due to the global economic crisis, construction volumes in Western Europe, China and Japan fell sharply. Along with them, the volume of output of the timber industry in industries that consume wood has decreased. In 2008, the volume of timber harvesting in the Russian Federation was reduced by 14.4% compared to the previous year. At the same time, even a small increase was observed in wood processing and pulp and paper production: 1.4 and 0.8%, respectively.
The net profit ratio of Russian timber industry enterprises in 2008 also fell sharply, which is confirmed by the annual rating of the Forest Industry magazine. According to the publication, the total revenue of the companies included in the top 50 amounted to just over 216 billion rubles. 70% of this amount came from the top ten rankings. The share of enterprises specializing exclusively in wood processing amounted to 27% of total revenue.
World development trends
Depending on the places of concentration of forests on our planet, the following zones are distinguished:
- Northern. This is the territory of taiga forests on the Eurasian and North American continents, where coniferous timber is harvested. A number of developed countries of the Eurasian and North American continents (USA, Russia, Finland, Canada, Sweden) specialize in the supply of wood raw materials on an international scale.
- Southern. Hardwood timber is harvested in three main regions of the globe - the forests of Brazil, tropical Africa and southeast Asia. Huge reserves of wood raw materials are concentrated on the South American continent, from where it is exported to Europe and Japan for further processing, or used as fuel for heating homes. In countries located in the southern hemisphere, alternative raw materials (not wood) are widely used for the production of paper products: bamboo branches are processed in India, sisal in Brazil and Tanzania, jute in Bangladesh, and sugar cane pulp in Peru.
The uneven distribution of forest resources, which are classified as renewable, poses the threat of their excessive use, which can lead to total deforestation of territories. For example, uncontrolled deforestation of equatorial rainforests has already led to large-scale environmental problems in Brazil and Mexico.
The developing countries of Asia, Africa and South America are increasing the procurement of wood raw materials every year, and China and India have already appeared among the traditional developed countries (USA, Canada, Finland, etc.), which were previously among the top ten procurement countries , Brazil and Indonesia, Nigeria and Congo. However, in developed countries, the percentage of industrial (high-quality) wood exceeds the share of firewood (used for fuel) several times, and in the countries of Latin America and Asia this picture is completely opposite. In the USA, Sweden, Finland, Canada, etc. In the structure of fuel consumption, firewood takes up from 3 to 12%, while in African countries - up to 78%, in China - up to 65%, in South America, about 57% of all harvested wood raw materials is used for firewood.