- Business: Agribusiness; investments from 20,000 rubles;
- Business area: production
Woodworking business
The timber and woodworking business is one of the most profitable, both in terms of the turnover of invested funds and in terms of increased profitability with the consolidation of production.
Timber is a renewable raw material, the demand for wood products is steadily growing and the market is constantly expanding, and there seem to be enough forest resources in Russia...
Anticipating your objections, dear gentlemen, entrepreneurs, I agree with them:
- Yes, we haven’t regenerated the forest for 25 years, but we can’t get to quality round timber - there are no roads, and it’s expensive to transport from abroad - prices are rising by leaps and bounds;
- Yes, it is very difficult to enter an already established timber market; greater administrative and financial capabilities are needed;
- Yes, the needs of this very market are steadily growing, but the competition is also very tough.
And yet there are open doors and a gigantic free niche in the timber trade and woodworking. The Finns were the first to enter it, followed by the Germans, Dutch, and French, promoting the production of thermally modified wood (TMW).
The essence of the technology: removal of some moisture-loving chemicals from wood by thermal decomposition and - we obtain hydrophobic wood with new color properties.
The largest companies with huge turnovers appeared, such as Platho (Holland), Mohlbeck (Austria), Finnforest and Stora Enso Timber (Finland), Thermoholz (Germany). The capacity of the Russian market alone is estimated by experts at 100-125 thousand cubic meters per year.
The disadvantages of TMD also appeared: the color range quickly fades in sunlight, to obtain high-quality products, high-quality source species are also needed (beech, ash, oak, tropical wood), production is energy-intensive, and hence the prices are considerable.
And is it necessary to decompose the natural chemical components already present in wood in order to ensure hydrophobicity? After all, the density and strength decreases, fire and bioresistance remain the same, that is, TMD burns in the same way as the original wood, and rots and molds.
It was then that the European Union lifted the ban on chemical modification of wood and began its research and production in earnest.
So far, only the production of chemically modified wood (CMW) has been announced: “Accoya” in Holland by acetylation and “Kebony” in Norway by furfilling the original wood. Unique bridges and multi-story buildings have already been built there (photo on the Internet), since the specific strength of wood exceeds many grades of steel.
Europeans, Americans and Japanese realized that they could eliminate the shortcomings, as well as impart new useful properties to such an old and seemingly familiar material as wood, simply by introducing certain modifier substances into the solid wood, which, under favorable conditions, react with the natural components of wood , make it possible to obtain a new biocomposite with predetermined performance properties. The Japanese are even planning to use modified wood in space.
By the way, it’s interesting: did you understand it yourself or did they spy on us? After all, wood modification was actively developed, GOSTed and used in the Soviet Union: “Destam” for the production of bearings, “Lignamon” for parquet and furniture (still produced in Slovakia).
Well, yes, as they say - “new is old, only forgotten by everyone.” After all, in the vastness of the Union there was production of its own TMD (Minsk), acetylated modified wood (Perm), furfulized wood (Barnaul), and most importantly, all these developments led to the creation of a new technology, which, having absorbed all the experience, can finally really create new modified wood from any original wood whose properties are specified during its production, according to customer requirements.
This is a mechanochemical modification of wood, in which an inexpensive main modifier-synergist, introduced into the intercellular level of the wood substance, carries, while repeatedly enhancing its properties, a small amount of specific functional additives, which give the new material the desired properties.
The chemical reaction between the modifier and natural wood components occurs in solid wood under the influence of pressure, temperature and mechanical forces. The preliminary name of the new biocomposite is mechanochemically modified wood (MCW).
It is MHMD that is the very door that allows you to find so far (the Germans have already given it the name HSG or Holz Super Gut - superwood) that unoccupied space in the woodworking products market. I'll explain how.
Raw materials
In the production of MHMD, any wood raw material can be used: solid wood of any species, burnt wood, driftwood, thin wood, wood waste, even straw. When using solid wood (logs, beams, boards) as the initial wood, it is more economically profitable to use fast-growing “non-commercial” wood species: aspen, poplar, willow, alder, sedge, birch, etc.
That is, everything that modern timber harvesters in your area do not yet need, because it is not in demand, and they will give it to you cheaply. If you believe the experts, there are more than 16 million cubic meters of such goodness in the European part of Russia alone!
The reserves of driftwood in the European part of Russia (according to the Central Research Institute of Lesosplav) only on active timber rivers exceed 9.0 million cubic meters! The cost of one raised cube of driftwood starts from 500 rubles. These are the resources!
It is also necessary to take into account that cleaning rivers is a matter of great importance for Russia - here even the native administration can finance it, and the people will say thank you. And the entrepreneur has not only first-class timber assortment, but also a stained one, which, using MHMD technology, can be turned into pure gold abroad, where it is especially in demand.
Of course, a specialist in matters of driftwood will object to me that 50% of the entire raised driftwood will be of excellent assortment, and the rest will be spoiled and rotten wood, roots, snags... For the MHMD technology, this is also the raw material.
It is necessary to process it into sawdust and make chipboard, again using MCMD technology, without the use of expensive resins. According to my calculations, the cost per square meter of such chipboard in a woodworking industry that processes only 160 tons of its waste is about 100 rubles.
Auxiliary raw materials – an aqueous solution of the modifier. The current water consumption for the technical process is insignificant for a small manufacturer (200-300 cubic meters of MHMD per month) and can not be taken into account when calculating the cost. It is more important at what price to purchase the main modifier.
In my case, it is urea (preferably grade A, also food grade) and prices for it range from 11 thousand rubles per ton at Salavatnefteorgsintez LLC and up to 38 rubles per kilogram at a nearby store. So - how much it will cost you in the cost of MHMD (and sometimes you need up to 200 kg per cubic meter) - the work of your supplier. The share of functional additives to the main modifier is insignificant. Although they are expensive, they require several kilograms per ton of solution.
Modern wood processing technologies
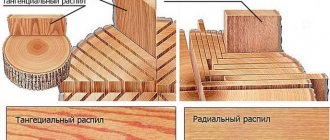
Wood is an organic, porous material of plant origin that can be subject to biological, mechanical or chemical influences.
- Biological wood processing is the processing of low-quality wood and millions of tons of various wood and agricultural waste into the most important product - feed protein yeast, as well as producing ethyl alcohol, furfural, xylitol. Biological processing of wood designed to provide agricultural production with valuable products of microbiological synthesis.
- Mechanical processing of wood is a process in which the shape and volume of wood is changed without changing the substance itself. This type of wood treatment differs sharply from chemical treatment, which changes the substance of the wood. The vast majority of wood materials are processed in a way that disrupts the bond between the fibers. This processing of wood is based on the property of divisibility and is carried out mainly by cutting: sawing, planing, milling, etc. Processing without breaking the connection between fibers (pressing, bending) is much less commonly used, which uses the plastic properties of wood, i.e. the ability to maintain the given its deformation after the cessation of external forces. However, the ductility of wood is very small compared to the ductility of materials such as metal, and therefore this property is used to a lesser extent in wood.
- Chemical wood treatment is a process in which wood is exposed to various chemical compounds. Chemical processing of wood combines several industries: Pulp and paper production - production of paper and cardboard; Hydrolysis production; Pyrolysis (dry distillation) of wood produces charcoal, methyl alcohol, acetic acid, phenolic resins, and various organic solvents; Rosin and turpentine production makes it possible to obtain rosin and turpentine. Which are used in the paint, perfume and pharmaceutical industries.
In this regard, in any woodworking, sawmill or chemical industry, wood processing occurs in stages, during which the final wood product is given certain properties that must meet certain market requirements. Only if these requirements are met, it is possible to guarantee the stability of the product during its operation, mechanical resistance, and invariance of linear dimensions in an environment where changes in humidity and temperature often occur.
Let's look into the past and see that with the development of mankind at all stages of its history, the use of wood in construction, everyday life, technology, and art expanded. At the same time, wood processing methods developed and improved. At all times, craftsmen who skillfully wield an ax, saw, and chisel have earned universal respect and honor.
With the advent of crafts, wood became one of the first construction materials for the manufacture of spinning, weaving, mill, pottery and other machines. It was widely used in the carriage, ship, automobile and aircraft industries.
The development of the production of high-strength alloy steels and light metals, as well as advances in polymer chemistry, have led to the gradual displacement of wood from the main branches of transport engineering. However, the enormous importance of wood products today has not diminished and will undoubtedly remain in the future. This is explained by many reasons and, above all, by a number of the most valuable properties of wood as a structural material.
Currently, thousands of items are made from it. This is primarily furniture of all kinds and purposes, parts of buildings and structures, numerous household and sports equipment, and musical instruments.
Despite the wide variety of wood products and their designs, wood processing technologies are based on the same principles: sawing, planing, drilling, turning and grinding. The only thing that has changed is the methods and methods of wood processing: mechanical means of production have replaced manual ones. Powered by electricity, they significantly reduce the processing time of wood, significantly increase labor productivity and the quality of manufactured products. Therefore, woodworking machines today are used not only in industrial production, but also in the workshops of private users. These are mainly small-sized, sometimes multifunctional stationary or portable machines that allow you to perform all the necessary types of mechanical processing of wood . Many of these universal machines are already on sale, but they are quite expensive. Therefore, you can make a woodworking machine of a simple design yourself.
In addition, the reader of this online reference book will help to obtain the necessary level of knowledge about the main types and properties of wood species, tolerances and fits, the theoretical basis for optimizing the cutting of wood materials and allowances for their processing, as well as about such topics as modern woodworking technologies.
Separate sections of the site are devoted to various technological processes of mechanical processing of wood. In particular, wood cutting, milling, drilling, turning and grinding on machines are covered in detail.
This site is intended for both large woodworking enterprises and home craftsmen who already have small-sized woodworking machines at their disposal and are planning to purchase them or make them themselves. The site will be interesting and useful not only to those who have begun to study and master the basics of mechanization of carpentry, but also to more experienced craftsmen who have certain experience and skills in working with wood and woodworking mechanisms.
Equipment
I’ll make a reservation right away - equipment using TMD technology can only be used for drying and heat treating MCMD, but impregnation will have to be done by diffusion in baths or purchased a special autoclave for it.
The technical process of mechanochemical modification of wood itself consists of impregnating the original wood (therefore it is better to use raw, freshly cut wood) with an aqueous solution of the modifier, drying the impregnated wood, heat treating it and compacting it (if the customer requires low-density MCMD, we will also resolve the issue).
All these processes can be combined in one autoclave of the AVTRM type (these were previously used in sand-lime brick factories) or in a specially ordered one (in which case “Scholz” Germany would be better).
No one yet produces special equipment; one Nizhny Novgorod company took on the design and subsequent production, we wish them good luck!
Therefore, it is still difficult to name the price of MHMD equipment. For example: the autoclave AVTZM 2800-10000-12.5 (diameter 2.8 m, length 10 m), specially ordered for the production of MHMD at a Russian enterprise, allowing the production of up to 450 cubic meters per month, cost 8.5 million. rubles
Again, as an example, I provide a list of equipment for company X, which produces 250 m3 of unpressed moldings and 100 m3 of pressed products per month (parquet boards with a density of 1100 kg/m3):
Cost of equipment (thousand rubles):
- Loading and transport equipment (forklift, overhead crane) – 500
- Autoclave (chemical pump, modifier tank, vacuum pump with receiver, stack heating system, instrumentation) - 8500
- Aspiration system - 300
- Thermal chamber (2 pcs.) – 500
- Heated hydraulic press with a set of molds - 2500
- Circular saw cross-cutting machine (TSK-01)-120
- Four-sided four-spindle machine (S25-5A)-250
- Four-sided seven-spindle machine (Beaver 723 UP) - 1650
- Milling double-sided tenoning machine (Beaver 8025) - 800
- Equipment for recycling MHMD waste (hydraulic press, heat chamber, molds) - 2300
- Sharpening equipment - 500
- Packaging line (PM) - 400
Total: 18,320,000 rubles.
Production of products from MCMD
It is easy to talk about this if we are talking about the promoted mass production of some product that has been in production for a long time. There are statistics and a lot of economic calculations. Our conversation concerns a new promising production, “the green sprouts of which smiled at the sun for the first time.”
Therefore, I will again refer to the calculations of promising enterprise X, which produces massive parquet boards and facing slabs from waste from its own production.
Electricity costs for modifying one MHMD cube are 200-220 kW, for mechanical processing - traditionally for processing hardwood. A monthly supply of edged boards in the amount of 450 m3 is expected at a price of 5 thousand rubles. per cubic meter and urea at a price of 11 thousand rubles. per ton. The company operates around the clock, with an average workforce of 35 people.
The estimated cost per cubic meter of unpressed MCMD board for enterprise X is 11.25 thousand rubles. , and pressed - 22.5 thousand rubles. The calculation is based on the condition that the enterprise has one autoclave AVTZM 2800-10000-12.5, specially converted for the MHMD technical process.
Properties of manufactured products
If I haven’t tired you yet, then let’s remember that the main advantage of MHMD is that the properties of the product are set during the production process in accordance with the wishes of the customer or consumer.
I will note some individual properties of MHMD:
- it can be bent in the most unexpected planes;
- obtain images such as intarsia or holography, relief images with straight and sharp angles and a relief height of 10 mm by pressing;
- arbitrarily change the texture and color of the original wood;
- increase the density to more than 2000 kg/m3, which entails a direct proportional increase in strength, hardness and abrasion;
- produce pressed panels of theoretically unlimited sizes, spliced using the technology of reinforcement with a power grid, without using pressing equipment.
And how many properties of this 21st century material have we not yet discovered, how many technological possibilities have not yet been identified, how many new types of products from it will still be invented?
I’ll answer the skeptics right away: yes, products made from MHMD are not yet mass-produced (well, except perhaps the barometer housings of Utes OJSC), but what you see in the photo was made and photographed by the author of the article and you can, with his consent, touch it all and touch.
World innovations in the woodworking market
Biorefining is considered one of the most promising innovative projects in the field of wood processing today. This technology involves complex processing of wood, which results in new types of effective biofuels. One of the first companies to adopt innovative technology was UPM.
UPM uses biorefining technology in both the pulp and paper and wood processing complexes, using 98% of wood. The company produces biofuels for cars and chemical materials (bioplastics). Based on patented Biofore technology, UPM has proposed a concept for a car of the future that uses biological materials from wood, and the design of the concept car allows the use of biological substances as fuel.
Russian forestry complexes do not lag behind foreign ones and also use biorefining technology. Thus, the Ilim production group is promoting the Larch project, the essence of which is the synthesis of nanotechnology, biorefining and the creation of new products from wood species that contain a high amount of lignin. It provides strength to innovative wood building materials.
Wood pellets are also an innovative product - pressed wood pellets, biological and safe fuel. Pellets are used both to supply small power plants (furnaces, boiler houses) and to operate the largest power plants in the world.