People love to live and work in warmth and space, and modern house construction technologies take these needs into account without fail. In this regard, Finnish technology is close to ideal and our compatriots are happy to order such houses, especially since our countries have the same northern wind rose, soil properties and air humidity. This means that construction can be carried out without adaptation to the climate. Additional advantages of Finnish houses that attract buyers are their efficiency, speed of construction and aesthetic appearance. Read more about the Finnish technology of building frame houses and a description of the construction sequence in this article.
Classic Finnish house Source tula.stroimdom.com
Peculiarities
What is a Finnish frame house? Its technology is distinguished by its simplicity and structural reliability. The frame is erected from wooden boards or beams, the distance between which is from 20 centimeters to a meter. When installation and interior finishing begin, the space between them is covered with transverse boards and sheets that do not bear load. It is safe and free to change the internal layout of rooms and the material of walls and ceilings using Finnish technology: install new doors, cut windows, change electrical wiring lines and combine rooms.
At the core, every part of a Finnish house is made of wood, a material that is economical and pleasant to the touch and smell. Wood does not evaporate harmful substances, breathes easily, slowly corrodes and deforms by 0.5-1%. This is an environmentally friendly material that does not cause allergic reactions.
Pie wall device
A classic Scandinavian frame house pie consists of the following elements:
- Interior finishing - a good option for the base layer is plasterboard; OSB boards are also used for this. Drywall is used in narrow or regular thickness - from 9.5 to 1 9 mm. A good solution is to use 9.5 mm thick vapor barrier plasterboard. If we talk about OSB, then most often OSB-3 is used for finishing inside a frame house.
- An additional layer of insulation is mineral wool 50 mm thick, but this layer is not mandatory, since it is mainly used for sound insulation.
- Vapor barrier - it is better to use a vapor barrier membrane.
- Insulation - it is better to use mineral wool 150 mm thick, which fills the entire space between the racks.
- The frame elements are load-bearing posts with a cross-section of 100x150 mm, and if the wall is not load-bearing, you can use timber with a cross-section of 50x150 mm.
- OSB board - OSB-3 and OSB-4 boards have sufficient strength required for external cladding of the facade.
- Waterproofing, and the best solution would be to use a diffusion membrane.
- Exterior finishing - if desired, this can be: siding with an air gap, block house, facade brick, tiles, vertical board cladding, decorative plaster and other materials.
It remains to learn about the features of the Scandinavian construction option, evaluate its advantages and talk about its disadvantages.
Advantages and disadvantages of technology
Today, every fifth standing house in Russia is frame. The rest is occupied by obsolete brick houses of Soviet construction or block cottages.
Frame technology is a universal solution that is used for the construction of both an ultra-modern cottage and a cozy country house.
An example of a Finnish country house project Source kitchencafe.tk
The cost-effectiveness of the technology also makes it attractive for the construction of industrial premises and simple small domestic buildings.
In general, the following advantages of Finnish houses are distinguished:
- Price . To build a house with an area of 130 square meters will cost 960-990 thousand rubles. This is 120 thousand rubles less than the market value of wooden country houses of comparable size, which will be left for decor and amenities. At the same time, the house will remain without the stamp of an already designed one, with a strict internal layout.
- Comfortable microclimate . The house using Finnish technology is not afraid of sudden changes in temperature, humidity above 50% and wind. Wooden beams are durable, not subject to cracks, moisture-proof and heat-resistant. Warmth and dryness are maintained around the clock, and the installation of ventilation and air conditioning creates an internal microclimate.
- Ease of construction . Construction will not require a separate entrance for heavy construction equipment, installation of special lifting tools and installation of materials.
- No seasonal restrictions . Construction concrete is not used in the construction of the foundation for the house. Instead, solid bricks or rubble concrete are laid, which are not limited by cold frosts and floods.
Construction can only be changed by a strong storm or rain; the rest of the time, in winter and summer, work goes on as usual Source proftula.ru
- Safety and reliability . The frame materials are not afraid of open fire, resistant to seismic activity and strong winds. Flexibility and a large cross-section of materials save when brick and ordinary non-Finnish wooden frame structures are deformed and destroyed.
The technology also has disadvantages, but they are quite easy to deal with:
- Noise insulation . Thin and natural wooden partitions allow sound from neighboring rooms and outdoor areas to pass through, which is inconvenient in large settlements and communities. The solution is to double the insulation layer between the layers of the wall and build a separate soundproofing sheet.
- Natural pests . Small insects and other living creatures can inhabit the space between the upholstery slabs of houses that are filled with sealant. Mice and ants often take advantage of this chance to settle, but it is enough for them to simply block the road if you ensure that there are no microcracks and that construction technology is followed. This problem is mostly far-fetched, since we heard about mice in the house long before the advent of new construction technologies.
Any tree can be attacked by insects.
To avoid these troubles, all wooden components of the house are processed at the factory. Source kostromaterem.ru See also: Catalog of frame house projects presented at the “Low-Rise Country” exhibition.
Frame
Unlike America, in Scandinavia there are no uniform rules (building code) governing how the frame itself should be implemented. Therefore, for a particular company, the frame can be very specific. But the main elements are performed in the same way as in American frame construction. The basis of the frame, of course, is the same as in any other civilized country - dry planed board. Wooden beams are used extremely rarely, only to solve some highly specific specific problems. And then, most likely, it will not be just timber, but the same laminated timber or LVL.
One of the interesting features of the Finnish frame is the so-called “Finnish crossbar”. A board (and most often LVL timber) embedded “on edge” into the racks under the top trim. This solution allows you to do without double top trim and window “headers”, which are mandatory for use in American frame house construction.
Another feature from the Americans. Double and especially triple racks are not always used in the area of window openings. This is probably due to the fact that in the American frame these boards are mainly used to support the same “header”, which in the Scandinavian version is replaced by crossbars embedded in the racks.
Companies that make large panels such as omatalo (finndomo), yukkatalo use something like I-beams for racks to combat “cold bridges.” Or combined composite racks, with a “thermal break” made of material with low thermal conductivity. It is already difficult to repeat such options in artisanal conditions. This is a solution for industrial production.
Typical Finnish frame - planed boards, embedded crossbar along the top of the wall, single posts at the window openings
Construction materials
The simplicity of the cottage design using Finnish technology lies in established and similar materials. The frame is constructed from glued beams, the service life of which reaches several centuries. Their cross-section is 2.5 centimeters larger than the standard, which gives a margin of safety, the cost is low, and flammability and tendency to rot and loss of strength over the years are excluded.
After the construction of the frame, the supporting structure, the stage of creating walls and horizontal floors begins. The subfloor is laid out with sheets of OSB or plywood on the ceilings, after which it becomes the first layer of flooring on the second floor. The cross frame is designed to support the load and maintain a ventilation gap, which prevents the finished floorboards from rotting in high humidity conditions.
For thermal insulation, sheets of plasterboard and mineral wool are installed between the wooden wall slabs. In this case, the cracks and gaps are covered with mounting foam to avoid backlash and drafts.
Insulating walls with mineral wool Source pilasebastovce.sk
The roof is mounted on a rafter system, the elements of which are fixed with nails. For strength, the structure is fastened with boards. After this, the rafter legs are laid on the base of the wall, they are fixed and the roof is installed. Most often this is metal tiles.
Interior decoration: step-by-step instructions
The walls and ceiling in a frame house are usually finished with gypsum board (plasterboard), and then it is painted or wallpaper is glued to it. GCR is good because it does not burn well. In Canada, it is generally prohibited to build frames without gypsum boards due to fire safety requirements. And more and more often we have lining or imitation timber nailed onto the ceiling and painted (I especially like the white color in this place).
After finishing the walls and ceiling, you can pour a concrete screed, finish the floor with tiles or laminate, and then install interior doors. Finnish interior doors are especially good; many people praise them, but their prices are now exorbitant.
Foundation
The main dilemma is choosing the right foundation for the right building. Houses built using Finnish technology are structurally light - but people are free to make the structure heavier as needed.
An area of less than 200 square meters and the absence of additional massive structures in the house (stone stove) will most likely lead to the choice of a pile-grillage foundation . In this case, holes for piles are drilled in the ground, and formwork is installed above them for a shallow strip foundation. Everything is poured with concrete and as a result the piles stand at the level of soil freezing, and the grillage transfers the load from the house to them.
Due to the relative lightness of the entire structure, the foundation can be chosen based not only on the quality of the soil Source remontik.org
Weight, multi-story structure, constant air flow and soil susceptibility to erosion are all prerequisites for installing a strip foundation . This is a massive and reliable reinforced concrete strip laid in a monolithic layer under each load-bearing wall of the house. This is more expensive than the previous option, but stronger and suitable for houses of all sizes.
External slab cladding, wind protection and frame stiffening elements.
Another striking difference from the Americans.
In the American frame, in 99% of cases, continuous cladding with OSB3 boards is used on the outside + a wind-hydroprotective membrane on top. OSB plays a structural role - giving the frame spatial rigidity. And the membrane protects the OSB from excess moisture in case of any leaks along the facade.
In Scandinavian frames, this is an extremely rare, almost never seen option. Basically, three types of implementation of sheathing, wind protection and stiffening elements can be distinguished.
- External use of soft fiberboards (MDF). In our market, such slabs are known under the brands Isoplaat and Steico. These plates perform 4 roles at once. They give spatial rigidity to the frame, perform the function of wind protection, additional insulation and sound insulation.
- Facade plasterboard. This is a very common solution. The most typical option is Gyproc GTS9. Unfortunately, this type of material is not available for free sale on the Russian market at all. Knauf tried to release a trial batch, but the product did not find widespread consumer demand and production was discontinued. I hope with the development of frame housing construction the situation will change. Since this is an excellent solution for spatial rigidity of the frame and wind protection for minimal money.
The house is covered with façade gypsum plasterboardInstallation of façade gypsum boards, secured to brackets
- Giving rigidity to the frame with embedded jibs or rigid board materials (plywood) installed only at the corners of the building. There is no slab covering on the outside of the frame, only a windproof film.
Recently, options have begun to appear using OSB in the wall, but unlike the American version, in the Scandinavian version OSB is usually installed on the inside of the room.
In addition, sometimes (but not always) in the first two options a windproof film is also placed on top.
I am impressed by this approach to wall construction, because the Scandinavians never use material with relatively low vapor transmission (for example, OSB) on the outside - due to which, from the point of view of vapor permeability, the design turns out to be more correct and “foolproof”.
On the Russian “Internet” you can often come across the opinion that if you use fairly soft materials such as gypsum plasterboard or MDVP for cladding, then you must definitely use jibs. Because compared to American OSB, these materials are flimsy. I don't agree with this opinion. Firstly, you need to understand in which direction these materials work in the wall. And in this direction, soft materials are very durable. In addition, what I call the “bundle of arrows principle” operates here. Perhaps slab cladding alone with these materials will not be enough, but in combination with internal and external facade cladding - it is quite enough. That is, each “layer of the wall cake” makes a small contribution to the structural rigidity and the result is quite sufficient.
Calculations and project
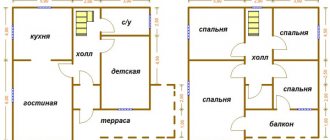
When a person plans his own home, he describes the necessary qualities of the house. To work, you need a personal office, a family with several children will need (number of children + 1-2) rooms, the head of the family will get a room on the second floor with a private window and a balcony. Design in our case is determining the location of the rooms, how they will connect and correlate with each other, what materials will be needed.
The layout of a house for a family with more than one child might look something like this Source elbrus-house.ru
Pay attention to what will surround the house and how to prepare for it:
- Climatic features of the region.
The amount of rainfall will affect the quality and type of roof surface. Composite tiles, a steel sheet with an aluminum-zinc coating, will be needed in case of constant rainfall, so that water reaches the drainage paths and does not wash out the blocks. Cheap and cheerful corrugated sheets will be better in calm environments.
The thermal insulation material depends on the wind rose. Cellulose wool, foam glass for the chilly Nordic winds, polystyrene foam and chipboard for warmth and comfort.
- Terrain
Uneven surfaces will be a prerequisite for the installation of a pile-grillage foundation, which varies in depth of penetration and angle of entry into the ground rocks. The inclination and flatness of the surface will affect the type of frame assembled, the amount of materials required and methods of fastening.
- Composition and type of soil, number of floors of the house
It will affect the type of foundation used and the location of the vertical beams from each other.
If the terrain and soil characteristics allow, a Finnish house may also have a basement. Source krovmart.ru
Life time
Who doesn’t want a house built with their own hands to be passed down from generation to generation? Unfortunately, not every technology can boast of durability, which cannot be said about Scandinavian houses.
Opinions regarding the service life of frame houses are different - some say that after 30 years they become unsuitable for living, others, on the contrary, are sure that grandchildren and even great-grandchildren will live happily in a Finnish house.
Instead of guessing “from the tea leaves,” let’s turn to Russian state standards, and according to Gosstroy documents, frame buildings are given a service life of 75 years.
Stages of building a house using Finnish technology
- Personal Preposition and Design . Determination of the number and size of rooms, floors, type of materials used and expected load on the skeleton and frame.
- Construction of the foundation . Allow at least two days to build the foundation to gain the necessary strength and stabilize it on the soil cushion.
- Beginning of construction of the zero tier of the frame . Wooden beams must be treated with an antiseptic and laid on a waterproofing layer on top of the foundation. At the corners of the house and at the intersection of walls, the timber is joined groove to groove and reinforced with self-tapping screws and studs for increased reliability.
- Erection of frame walls on the ground and lifting them using a winch. Fastening using grooves and corners, installing beams between walls. Laying out the subfloor, installing joists along the surface and sealing the insulation between them. Wood cladding and tiles will be installed last, in the final part of construction.
What is the difference between housing for seasonal and permanent residence in winter?
The main difference between summer houses is a less serious approach to the issue of thermal insulation than in the case of houses intended for year-round use.
For example, it is quite enough to use 50 mm thick stone wool as insulation. The cross-section of the support beam used for wall installation is 90-140 mm.
As for interior partitions, they are made of the same materials, only without insulation. On the inside, insulation of the walls is not required - a layer of vapor barrier is sufficient. The total thickness of the walls of the summer house thus does not exceed 150 mm.
For the construction of high-quality buildings intended for permanent residence, timber with a cross-section of 140x140 mm or more is used as supports.
It is worth noting that the thickness of the timber must correspond to the thickness of the insulation .
If the insulation is thinner, a layer of air may form, which will lead to the formation of cold bridges; if the insulation is thicker, it may become deformed.
The average thickness of the frame pie in a permanent residence is therefore 250 mm, and this is without finishing.
Video description
We wanted to show you another inexpensive and very interesting project of a frame house with a sauna inside the house:
- Erection of the roof and installation of external wooden slabs, future external walls of the building. Installation of insulation and future electrical wiring cables. Elimination of cracks and holes with polyurethane foam.
Recommendations for choosing heat-insulating material. Mineral wool insulation is reliable, its service life is about 25 years - at a competitive cost of the material, it is durable and does not require constant updating.
Expanded polystyrene decomposes over time, and at the same time polymer compounds are formed that poison the environment and residents.
In construction using Finnish technology, sandwich panels with mineral wool are more often used; it is universal and simple.
- Finishing external and internal works . Wall covering, from budget drywall to the personal preferences of future residents.
What the finished house will look like will depend on the owner’s imagination Source skywebpro.ru
Natural supply ventilation
- It is best to carry out installation before finishing the premises, right during construction. If the valve is located behind the heating radiator, it must be temporarily removed and the location of future ventilation must be marked with a marker.
- A hole is made for the ventilation duct.
- A ventilation pipe with insulation is installed into the resulting channel.
- The valve body should not touch the pipe, so it can be attached using foam. The body, like the pipe, can be insulated or a sound absorber can be put on.
- A protective grille is placed on the outside of the ventilation pipe, and a special cover on the inside.
If, when choosing a project for your future home, you chose Finnish frame houses, the construction will be durable and reliable, and with the right choice of materials it will save a significant part of the budget.
Is it possible to build in winter?
When using traditional building materials and technologies, there is often no need to talk about construction work in winter.
Meanwhile, this does not apply to Finnish houses, for which there are no restrictions on air temperature.
Moreover, it is even cheaper to build frame houses in winter, since significant discounts on lumber are offered during this period .
It is also worth noting that during severe frosts there is no precipitation, which means minimal humidity, which harms lumber. If in summer the average monthly precipitation is 735 mm, then in winter it is usually no more than 200 mm.
Another advantage of building in winter is the absence of shrinkage, although this does not threaten frame houses, in principle.
As for the disadvantages of winter construction, they also exist . In particular, the construction process is difficult due to the fact that builders are simply freezing, so their physical activity is significantly reduced.
But the cost of work in the autumn-winter period is significantly reduced due to a shortage of orders, and this is also a significant saving.