What do you need to know?
How to choose high-quality lumber whose properties meet current standards? This question is asked by most people who are starting construction work for the first time using edged boards or edged timber. A large number of varieties of softwood lumber can create difficulties when choosing and purchasing. If you want to understand this issue and purchase only those lumber that will meet your requirements, you should read this article and the GOSTs given in it.
- Firstly , you will need GOST 18288–87, which contains a list of technical terms used in the sawmill industry and definitions of lumber; this GOST also helps to understand the numerous names and existing variety of assortments.
- Secondly , it is advisable to know the basic characteristics and properties of lumber before choosing an edged board or edged beam for use in construction, since the quality of softwood lumber has a significant impact not only on the cost of construction or a product, but also on its durability and physical characteristics . For this purpose, you should additionally read the article Classification of wood defects. If the boards are selected correctly, the quality of the work performed significantly increases while optimizing the estimated cost, otherwise an unnecessary increase in cost or a significant decrease in quality is possible. You will find a detailed description of how wood defects affect quality in GOST 2140-81.
- Thirdly , you will need to estimate the dimensions of the lumber. How to measure an edged board or timber is described in detail in GOST 24454–80. This GOST defines the fields of permissible deviations depending on the linear dimensions and assortment. It should be noted that measurements of lumber must be carried out using a ruler and retreating from the end of the product by 5-10 centimeters. Detailed rules for measuring lumber are specified in GOST 6564–84.
- Fourth , based on previous State Standards, it is possible to determine the grade of softwood lumber (edged boards and edged timber). This information is contained in detail in GOST 8486–86. This GOST concerns defects in coniferous boards and timber; it regulates the types, quantity and specific placement of defects depending on the type of edged board. The standard contains a classification based on natural defects in the development of wood and specifies how to determine the grade of edged boards depending on the type, quantity and location of defects.
Types of coniferous boards
All details on current GOSTs today can be found here...
Thus, we found out that currently there are several state standards that regulate production technology, technical parameters and classification depending on natural growth factors, the presence of wood defects, cutting methods and linear dimensions of lumber. If you still have questions and you don’t understand how to choose boards and beams using regulations? We offer a detailed description of methods for determining the grades of edged timber and boards.
It is very difficult for ordinary consumers to study all the provisions of the current standards, and it is not necessary. It is enough to know the main provisions of the classification and pay attention to them. Another important factor. Some manufacturers use technical specifications (technical conditions) instead of GOST standards. What are the differences between these concepts? State standards establish criteria for grading wood, taking into account generally accepted standards, for general consumption and are strictly regulated. Technical conditions, first of all, take into account the specific technical capabilities of the manufacturer and the raw materials it procures. In other words, TU * is lumber manufactured with deviations from GOST, both in quality and size. This means that the quality of lumber according to specifications in the vast majority of cases is lower than the quality of boards according to state standards.
Determining the grade of lumber (edged boards and edged timber)
In total, there are five grades of lumber, depending on developmental defects, cutting methods and linear deviations from specified parameters: selected, first, second, third and fourth grades. Most often, the first and second grades are used in wooden house construction and the furniture industry. They should be discussed in more detail.
- First grade softwood
The first grade board has characteristics that are quite acceptable for most architectural building structures, both temporary and permanent. The boards must have a relative humidity in the range of 20-22%, the cut edges are smooth, the planes are parallel, the tolerance limits cannot go beyond the margins established by GOST 24454–80. The main differences between grade 1 boards are the complete absence of visible damage to the wood by putrefactive bacteria, the number of end cracks cannot exceed 25%, all knots must be healthy. The heel makes up no more than 20% of the total area; core mushroom spots cannot exceed 10% of the surface area of the lumber.
Before determining the type of board, you should carefully inspect the surfaces of the lumber for the presence of any type of rot and unhealthy knots. Even the slightest traces of these defects serve as evidence of a lower grade of lumber. First grade boards are used to create rafter systems, interior partitions, subfloors, etc. After processing on milling machines, they can be used to make furniture.
- Second grade softwood
Grade 2 boards have “softer” characteristics, large resin pockets are allowed, may have slight coloring from fungi, and significant wane is allowed. The use of second grade boards is much wider, due to their lower price and quite satisfactory operational and physical characteristics. Grade 2 edged boards are perfect for making formwork; you can also use it to make scaffolding yourself. Grade 2 boards are indispensable for temporary buildings, cabins and sheds.
Edged board 1st grade
Edged board 2nd grade
What is the difference between 1st and 2nd grade boards
Despite the abundance of building materials, the popularity of using wooden boards has not fallen to this day. Edged wood is suitable for use in the interior and exterior decoration of buildings, premises, subflooring, roofing work, the creation of decorative elements, outbuildings, design objects when organizing landscape design, at industrial facilities, for the construction of barriers.
How to distinguish the type of board
Most often, buyers choose between two options - first and second grade boards.
A first-class edged board has a fairly high quality - smooth edges, parallel planes, absence of putrefactive lesions of the wood, diseased knots, pockets, wormholes, end cracks - small, no more than 25% of the area, material moisture content in the range of 20-22%. If such lumber is processed on a milling machine, its quality will reach the level of furniture boards.
For boards of the second grade, the presence of wormholes (up to 2 per square meter), fungal infections, pockets, tilted fibers, rotten areas (up to 0.4 cm), various kinds of knots, unfinished edges, and stains is acceptable. In terms of quality, this grade is slightly inferior to the first, but purely externally the board looks unattractive, so it is used only as a rough material.
Price per cube of board 2nd grade
| 1 | 2nd grade board 25x100x6000 More details | m3 | 4200 |
| 2 | 2nd grade board 25x150x6000 More details | m3 | 4200 |
- Easy to store (you just need to protect from moisture and provide ventilation)
- Ease of work (this material will behave perfectly both in the hands of a specialist and a novice builder)
- Availability of transportation (there will be no problems during transportation - the board does not leave debris, weighs little, is easy to load and unload)
- Low price (compared to other materials, the low cost is an additional incentive to purchase this particular material)
- An assortment of wood types (the difference in quality and cost makes it possible to choose exactly the board that is needed for your specific tasks).
The difference between second-grade timber and first-class timber and application
According to the description of the appearance, 2nd grade timber looks less presentable in comparison with first-class timber; the presence of small fallen knots, pockets of resin, darkening and fungal stains, and deep cracks is allowed.
As for the sizes of second-grade timber, there is a very wide variation in length. GOST 24454-80 sets from 1 to 6.5 m with a gradation of 25 cm. Most often you can find a six-meter one on sale. The thickness of the edged timber can be from 100 to 200 mm in increments of 25 mm. The timber is also sold with a thickness of 250 mm. The width varies from 100 to 250 mm with gradations of 25 mm. In any case, it should be greater than the thickness or equal to it, but not less.
Temporary and auxiliary building structures are often made from second-grade edged timber. It is too expensive to use the highest grades of timber for them, and due to the small differences in characteristics from the 2nd grade timber, it does not make sense. The rough load-bearing subsystems, which are covered with sheathing, are also made from second-grade timber. The fact is that, in addition to the not particularly aesthetic appearance, such timber has somewhat weakened load-bearing capabilities. This disadvantage is mainly due to the defects mentioned above. You can find fences, canopies, and cabins made from the specified material. They serve no less than if they were made from first-class timber, but the cost is much lower.
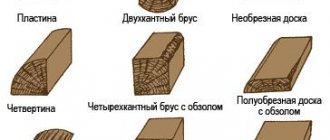
Types of lumber
The entire variety of lumber according to current standards consists of:
- timber (3 versions);
- boards (3 versions);
- plates;
- quarters;
- croaker.
In the volume of material presented, the main attention is paid to the board. So, 3 options for their execution:
- unedged;
- semi-edged;
- edged
An unedged board has trimmed longitudinal sides and uncut end sides. However, it is quite durable. It has an affordable price and is used where the appearance of the structure is unimportant, for example for sheathing.
The semi-edged board has, in addition to the longitudinal ones, one cut end. This is a higher quality material than unedged material, but is practically unsuitable for exterior decoration due to its rather low requirements.
Content:
- Features and distinctive features of second grade lumber
- Difference between second grade boards and first grade boards and application
- The difference between second-grade timber and first-class timber and application
- Advantages
- Minuses
- Tips for choosing
Second-grade lumber refers to lumber of good, but not superior quality. They do not have such an impeccable appearance as first-class ones, they are not much inferior to them in terms of hardness and strength, nevertheless they are suitable for the vast majority of construction work in which wood is used, mainly two types of goods are purchased for them.
What to consider before purchasing
1. Dimensions established by the standard: 2, 3 and 6 m – length; width – 100, 150, 200 mm; thickness – 25, 40, 50 mm. Everything else is classified as “substandard” and should be sold at a lower price (with the exception of special orders).
2. Humidity is natural. But it should be borne in mind that according to the current SNiP, use in construction with an indicator of more than 25% is not allowed.
3. One working surface must be processed (finished).
4. The highest grade billets have a regular rectangle in cross-section. Grade II edged boards allow the presence of wane (irregularities on the sides). This is reflected in GOST 24454-80. This takes into account the dimensions of the board itself, as well as the type of wood. Wane can occur both along the entire surface and in individual areas
5. Cracks. Measured in fractions of the total length of the product. For reservoirs (deep and shallow) the norm is no more than 1/3. The length of the through ones cannot exceed 20 cm. However, this is true for materials with a humidity of up to 22%. If it is larger, then the size of permissible cracks is reduced by 2 times.
6. Damage to wood. Mushroom stripes (cores) in area - no more than 1/5 of the entire surface. The presence of any signs of rot is not allowed. Wormhole - 2 for every meter of length.
7. There should be no mechanical damage to surfaces, as well as the presence of foreign bodies (nails, metal shavings, etc.).
Prices
As a rule, this material is made from coniferous wood. The most common are products made from spruce and pine. You can buy second-grade edged boards at the following prices (approximately):
- Length 2 m, 25 x (100 – 200) mm – from 2,700 rubles/m3
- Length 3 m, 25 x (100 – 200) mm – from 2,800 rubles/m3
- Length 6 m, 25 x (100 – 200) mm – from 2,900 rubles/m3
Thicker boards cost more. For example, 50 x (150, 200) mm - from 4,500 rubles/m3. Larch can be purchased for 940 rubles/m2 – 45 x (100, 150) x (3,000, 6,000) mm.
When choosing, you need to pay attention to the end parts. It is there that markings should be applied (with chalk, paint) indicating the grade of wood
For grade 2, the designations can be 2 dots or 2 diagonal strokes. In some cases, 2 transverse lines are applied to one of the wide surfaces. Just by appearance alone, it is quite difficult for a non-professional to distinguish boards of 2nd grade from 3rd or even 4th.
If the seller has his own production, then the blanks can be cut according to the customer’s dimensions. This option is more economical. Having made a specific order, the buyer will receive exactly what he needs. Consequently, the amount of waste will be significantly reduced, which will significantly reduce the cost of purchasing material.
Tips for choosing
When choosing, it is not enough to know about timber and boards of the 2nd grade, what they are, you also need to take into account a number of other factors.
- Understand exactly for which structures you intend to use second-grade lumber products. Check out the acceptable values for them. In particular, strength is extremely important for load-bearing elements, and for those products that are intended to be used for insulation, a minimum number of through cracks and holes from fallen knots, etc.;
- Find out the average price and base your choice on it. Under no circumstances should you buy sawn timber that is too cheap. Surely there is a serious flaw in them that forced the seller to reduce the price;
- Pay attention to the wane. Less is better. You will have to delete it anyway. Otherwise, insects will appear under the bark, which will seriously damage the wood and significantly reduce its service life;
- Try to find out as much as possible about the storage conditions of the batch of material. Further warping of the wood, its moisture content and changes in linear dimensions depend on them.
Quality and regulatory documents
The main criterion for determining product quality is the presence of defects on the front and back sides, moisture and strength. GOST 8486-86 allows for violations of the integrity of the board material depending on the grade. For example, if for grade 4 even the presence of rot in rare places is allowed, then for grade 2 minor flaws are also unacceptable. Types of defects are classified by GOST and determined by manufacturers in accordance with regulatory documents.
Here are some defects and standards for grade 2 edged boards:
- the presence of rot is unacceptable;
- knots (partially fused and unfused) - no more than two per 1 linear line. m;
- pockets - no more than 4;
- end cracks are allowed only on one side within 1/6 of the board width.
And more than 10 points.
Manufacturers
- Lindexport LLC is a company that began to develop back in 2004. Now the lumber market is developing dynamically and conquering it. The company is located in Belarus, in the Minsk region, or rather 50 km from the highway. They are engaged in logging, woodworking and the production of various lumber. Of course, they also produce edged boards.
- PUE "Khompil" is a private enterprise in the woodworking industry. They have been working on the market for about 15 years. They supply their products to Belarusian markets and Western partners. The company produces lumber and assembles wooden containers. The company also engages in carpentry and timber cutting. The enterprise is located 30 km from the city of Brest.
- Lestorg LLC has been producing lumber for about 14 years. The company works directly with customers. Delivery is carried out anywhere in the world.
- OJSC Sokolsky Woodworking Plant produces not only lumber, but also produces finished houses. In 2008, 35 thousand square meters were produced.
- AltaiForest LLC is an enterprise that produces lumber from coniferous trees in huge quantities. In the Altai Territory, he has the largest production facility.
Edged boards are used in a wide variety of applications. The base of the foundation, which rises 30 cm above the ground, may require formwork. But only if it is not a whole cast block. For subfloors, boards are also used, which are laid on pre-prepared joists. But edged boards can also be used for laying white floors. And hardboard or plywood sheets are laid on top. Class A lining is often used for lining interior rooms. The next layer involves laying laminate or linoleum. Partitions with further cladding are also built from edged boards, which are cheaper than dry profiled timber. Here you can make thick walls, which can later be insulated, but first leave a distance between the boards.
The material can be used in a variety of fields using its various forms
The most important thing is to know that raw materials made from natural ingredients require special care.
It is worth considering that the natural coating should be topcoated with fire-retardant varnishes and anti-bioaging agents.
Board 3 grade
Grade 3 board has limited use when used under a transparent coating. But it is widely used for all other purposes, incl. and in some structural elements during construction. Third grade board has large knots, incl. they can be tobacco and rotten. Cracks up to half the board, tilt up to 1/2 of the lumber area, and an abundance of resin pockets are also allowed. Mushroom spots are not limited, wormholes, large wane, deep gouges and waviness are allowed.
A third grade board does not necessarily have all the defects inherent in this grade. Therefore, in order to determine whether it is suitable for any specific needs, you must first look at it. For example, a pine board has healthy intergrown knots, but their size takes up half the width of the board - this is a good board, but its grade is reduced. A third grade board may not have many knots, but have large wane on one side. If part of the board with the wane can be hidden during installation, then you can significantly save on the cost of lumber.
The grading of grade 3 boards is determined according to STB 1713-2007 in the Republic of Belarus and GOST 8486-86 in the Russian Federation. The defects taken into account according to GOST 2140-81 in grade 3 boards are shown in the table.
Board defects 3 grades
| Wood defect | Location | Qty | Size |
| Healthy fused knots (any healthy ones in any quantity in timber) | Plasti, ribs | 4 | 50% width |
| Edge thickness up to 4 cm | 2 | 100% width | |
| Healthy knots, partially fused or not fused | Plasti, ribs | 3 | 33.3% width |
| Edge thickness up to 4 cm | 2 | 100% width | |
| The bitches are rotten and tobacco | Plates, ribs, edge | can be up to 50% of all knots | |
| Cracks, incl. with end exit | Face, edge | up to 50% length | |
| Plast through | up to 16.67% length | ||
| End, except for shrinkage cracks | up to 50% width | ||
| Inclination of wood grain | Everywhere | allowed | |
| Kren (thickening of annual layers on one side of the trunk) | Everywhere | up to 50% of the surface area | |
| Resin pockets | On the one side | 4 | length up to 300 mm |
| Core (including double) | allowed | ||
| Overgrowth (overgrown wound with a radial slit-like cavity and remnants of bark and dead tissue) | allowed on one side up to 25% of the width and 10% of the length | ||
| Cancer (a wound on the top of a tree trunk infected with parasitic fungi and bacteria) | possible up to 33.3% of the length, but not more than 1 m | ||
| Fungal core spots (streaks) | possible | ||
| Mushroom staining of sapwood, mold | on the surface in the form of spots and stripes are allowed, deep ones are possible up to 50% of the area | ||
| Worm-hole | 3 pieces per 1 meter | ||
| Processing defects, mechanical damage, foreign inclusions | not allowed | ||
| Obzol | Plasti | up to 20 mm from each edge up to 50% of edge length | |
| Edges | up to 20 mm edge width up to 50% edge length | ||
| Bevel cut | up to 5% from the perpendicular of the end to the face and edge | ||
| Risks, waviness, tearing | allowed up to 3 mm deep | ||
| Warping along the face and edge | 0.4% of lumber length | ||
| Transverse warpage | 2% of lumber width |
Everything that is not included in the parameters of the third grade board belongs to the fourth grade.
Grade 4 board is a board with unfused knots of more than half the width of the board. It may have cracks of more than half the length of the board, heeling of more than half the area of the lumber, through cracks on 1/4 of the board and other defects in accordance with GOST 2140. Grade 4 boards are used for low-critical parts in construction, the manufacture of containers, cutting into smaller pieces, increasing the grade .
Types of products
As for the main types of products shown in the diagram above, the following can be said about each of them:
| Unedged board | This option is distinguished by the fact that only two sides are cut off and the ends are not processed. Such elements are most often used for lathing and other structures where appearance is not particularly important; the main advantage of this solution is its affordable price, which is why it is the most affordable |
| Semi-edged board | This type of product most often has two sides and one of the ends processed, but there may be bevels and bark residues on the edges. In general, this solution is of higher quality, but nevertheless it also cannot be used on visible structures where aesthetic appeal is important |
| Edged board | The highest quality type of product, in which all sides are processed, so the geometric parameters of the elements are the same, and the strength indicators are much higher. This group of products is used most often and is in demand among developers much more than other types |
Important! According to scientific definition, a board is a type of lumber, the thickness of which does not exceed 100 m, and the width is at least twice as thick as the thickness. Elements up to 32 mm thick in hardwood and up to 40 mm in coniferous wood are classified as thin boards, while other options are classified as thick boards.
Thin boards are most often used for cladding any structures, while thick ones can also perform a load-bearing function.
Dimensions of edged boards
The dimensions of edged boards are measured in millimeters. The width, length and height are determined. Examples of boards: 25 by 150 by 4000 mm, 50 by 200 by 3000 mm. If the height and thickness are the same, then it is already timber. The manufacturer is guided by the GOST application, which lists all acceptable values. But it is worth knowing that any manufacturer can deviate from the norms, making the sizes requested by the customer. To select the required size of wooden beams, you need to know the basic parameters of the product. Today, a length of 6 meters has become the standard. The width of the edged board can be 75, 100, 125, 150 to 275 mm. Material thickness 16, 19, 22.25, 32, 40, 44, 50, 60, 75 mm. Approximate prices are from 6,000 to 8,000 rubles per cubic meter.
GOST standards for softwood lumber
There are no GOST standards for edged boards made of coniferous wood, so other standards are used. GOST 8486 86 and GOST 24454 80 are used. They talk about the general characteristics of all lumber. According to standards, lumber from coniferous tree species is divided into:
- selected variety
- first
- second
- third
- fourth.
Selected variety
In products of this type, the presence of dry and rotten knots is not allowed. Fused but healthy knots, edge and rib knots are allowed. The standards tables indicate the quantities allowed for such lumber. Deep end cracks should be no more than 10%, and shallow end cracks should not be more than 16%. Any manifestations or signs of fungus should be absent. Minor warping or uneven edges should not exceed 1% of the entire area.
First grade
Such lumber must have the correct geometric shape. Compared to the previous variety, the indicators change slightly. The number of knots of healthy origin is 10% more. And the number of shallow cracks is 26%. Mold, fungal staining and heart stains should occupy no more than 10% of the total area.
Rotten places should be completely absent. Such defects are appropriate for breeds in the summer. Therefore, they do not carry any consequences; the structure of the wood will not be destroyed. Let's say a “pencil” wane. In length and edge it should be no more than 10% of the length. Grade 1 edged boards are used in the installation of roofing, construction of houses, beams and ceilings.
Second grade
The most important positive side is the low cost. The fiber inclination value is much greater than that of grade 1 boards. Resin pockets are also acceptable for such boards. Wane can be significant. Fungus staining and blue spots are typical for type 2 boards. The material is used for formwork and lathing.
Third grade
Resin pockets are allowed here in the amount of 4 pieces. per 1 meter of length. A double core and significant heel are characteristic of such boards. 20% core stains are acceptable. Through cracks that extend to the end and healthy and unhealthy knots are typical for such boards, but the number should not be more than half the area of the board. As a result, all the properties of coniferous boards are significantly reduced. Therefore, the material is not used everywhere.
All floorboard sizes can be found in this article.
Usually used if you need to build a temporary building, a change house, usually used for making pallets.
Fourth grade
The number of black spots increases to 6 per meter. Rot is allowed in an amount of 10% of the total area. The wane can be blunt or sharp, warping and winging are also allowed.
According to GOST, the external surface and linear parameters must have the following characteristics:
- the roughness of the ends should be no more than 250 microns, this also applies to the rough side;
- roughness of the front side, as well as longitudinal edges, no more than 40 microns;
- deviation in thickness of 1 linear meter is no more than 0.3 mm;
- in parallelism, the deviation of the edges from the side is no more than 0.3 mm;
- relative humidity or when selling from 12 to 15%.
How many edged boards 50x150x6000 are in one cube can be found out in this article.