Regardless of whether there is a screed under the floor or just a filling of expanded clay, or maybe there is even damp earth under the floor, in order for the floorboards of a wooden floor to be warm, the space under the top flooring will need to be insulated.
For this, the well-known and most common method is used: insulating the floor along the joists. What logs are and what insulation is best suited for thermal insulation of wooden floors, as well as what schemes are best to implement this will be discussed in our material.
Floor insulation with polystyrene foam
If you chose the first method, then you should lay wooden blocks - logs - on the leveled and cleaned concrete screed, maintaining an interval between them equal to the width of the selected insulation.
The lags are fastened with anchors or self-tapping screws on steel corners; their leveling is done using wooden spacers. Calculation of the height of the upper plane of the block above the floor looks like this: insulation thickness + 50 mm clearance for ventilation. Advice. When concrete floors are insulated with mineral or basalt materials, it is better to make the distance between the joists less than the width of the insulation by 1 cm so that the insulation fits there as tightly as possible. For expanded polystyrene boards, the interval should be made smaller by a couple of millimeters for the same purpose.
Now let’s talk about how to properly install the insulation. First, waterproofing is laid from a dense polyethylene film with an overlap of 100 mm between the sheets and the joints are taped. Then the thermal insulation slabs are laid. On top they are again covered with a vapor barrier film so that moisture from the premises does not penetrate into the insulation.
Advice. Contrary to popular belief, polystyrene foam absorbs moisture, although in very small proportions. Therefore, protective films on both sides of the insulation are always needed when using any materials, especially cotton wool and polystyrene foam. This will significantly extend their service life.
Penofol is often used instead of film; it allows you to reduce the layer of the main insulator and protect it from moisture. The joints are also taped, only with foil tape. This completes the insulation of the concrete floor; you can lay the coating and laminate or linoleum.
For reference. The thickness of the cement screed should be in the range from 50 to 80 mm. The optimal option, taking into account different loads on the floors of a living space, is 70 mm.
When it comes to a wooden house, it should be taken into account that such structures can be slightly deformed because the wood “breathes”. This is almost unnoticeable in an old house, but in a newly built one, concrete floor coverings can crack if damping is not provided. To do this, a thin layer of polystyrene (up to 15 mm) is laid along the entire perimeter along the walls, even before work begins, as shown in the photo:
Materials
There are many ways to protect the interior of a house from the cold, but first of all you need to insulate the floor and roof, since it is through these structural elements that the main heat loss occurs. Only when these structures are well protected from the cold does it make sense to insulate a wooden house from the inside or outside.
It is advisable to insulate the floors of the second and subsequent floors if they are installed on concrete floors.
For insulation, various materials with a low thermal conductivity coefficient are used:
- polystyrene foam or penoplex;
- polyurethane foam;
- mineral or glass wool;
- penofol;
- wood sawdust.
Each of them has its own advantages, and in most cases the choice depends on the availability of a particular material and the personal preferences of the homeowner. The thickness of the heat insulator depends on the climate in which the wooden house is located, on its location in relation to the ground level, as well as on the manufacturer’s recommendations.
Thermoplastics
Polystyrene foam and penoplex are very similar materials. They are produced by foaming plastic masses, sometimes introducing additional additives that prevent decomposition and make them unattractive to rodents. Both of these materials have a very low thermal conductivity.
Note! For comparison: in terms of thermal efficiency, 5 cm thick foam is equivalent to 75 cm thick brickwork.
It is convenient to use such materials, as they are produced in the form of sheets of various thicknesses. Transporting them to the construction site is not a hassle. They are very light and durable. You can cut polystyrene foam or penoplex with a regular stationery knife. When insulating the surface, they can be used to seal the resulting gaps at the joints with ordinary polyurethane foam. Adhesion with insulation is very good.
Polyurethane foam is a material that is more commonly seen in everyday life as foam mats. Such mats are not used in construction, and polyurethane foam is applied to the surface by spraying. Later, during the process of hardening and polymerization, it foams and hardens. As a result, polyurethane foam forms a durable, waterproof, airtight, warm coat for building structures.
Mineral wool
Various construction wools have been used as insulation for a very long time. Currently, glass wool, mineral or basalt wool are most often used.
In appearance and production technology, they are very similar to each other, differing from each other only in the raw materials used. To obtain them, raw materials are heated, melted using special equipment, and then drawn into threads. Later, when these fibers harden, looms that vaguely resemble weaving machines knit a bulky mass of low density from them.
Such insulation is produced in the form of rectangular mats of various thicknesses or in the form of rolls.
Penofol
Penofol refers to thin plates or sheets of polyethylene foam. Their thickness can be from 3 mm to 10 mm. In terms of thermal insulation qualities, this material is comparable to foam plastic or penoplex, but it is more convenient to work with due to the fact that it is flexible. Penofol is produced and supplied for sale and to construction sites in rolls 0.5 meters and 1 meter wide.
The insulation is produced in three versions - foil on one side, on both sides, or foil on one side and with an adhesive layer applied on the other. The latter option is most preferable to use, since installation of such insulation takes very little time. It is enough to cut out the required blank from the sheet and, having separated the protective film from the adhesive layer, apply it to the wooden surface and press briefly.
Sawdust
Sawdust has traditionally been used as insulation, since it was a by-product of any sawmill production, and its origin has always accompanied the production of lumber. For a very long time, sawdust was used to insulate wooden floors, falling asleep in layers between the joists.
A mass of sawdust, if it is not subject to getting wet, can lie in a closed space for years without caking. At the same time, the low density of such insulation is maintained, which provides excellent thermal insulation properties. The disadvantage of such insulation is that the sawdust cakes very quickly and even begins to rot, as soon as you wet them a little. To prevent rotting of sawdust and damage by various wood borers, they are treated with a solution of potassium permanganate or the sawdust is mixed with lime.
Water heated floor system
Such a system is performed in the following sequence:
The base of the floor is poured (cement screed) or concrete slabs are laid. Any insulation can be installed; its thickness can be from two to ten centimeters.
Reinforcement mesh is laid. The pipeline system is being installed. It is attached with plastic clamps to the reinforcing mesh.
The floor is filled with suitable materials (flooded floor system). A substrate is used if necessary. Finish floor coverings are being laid.
Electric “warm floors” in a wooden house
It is much easier to make electric heated floors. You can use cable structures or film heating elements. In this case, the cable can be stretched on a metal mesh attached to the joists.
If infrared film materials are used, they can be laid directly on the screed protected by thermal insulation materials.
The variety of thermal insulation materials on the modern construction market often leads buyers to a dead end. To choose the right material, you need to know its features and possibilities of use.
Insulate.
This is a thermal insulation material in rolls made in China. The quality of the material is quite high at a low price. The insulation is suitable for thermal insulation of any structures.
Ursa
One of the most popular thermal insulation materials. This material is more often used for horizontal surfaces. It has a low price, excellent thermal insulation and sound insulation qualities.
Thermolife
Used for light loads on thermal insulation. It is most often used for insulating walls, roofs, ceilings, and interfloor spaces. Can be used on horizontal, vertical and inclined surfaces.
No less popular are thermal insulation materials such as:
Rockwool, Isolite, Isovent, Teplex, Penoplex and many other types of thermal insulation
It is important to make the right choice for your wooden house
Insulating the house from the inside
Insulating a house that does not yet have any interior decoration is much easier than doing it in a house that is already fully furnished and landscaped.
There is no need to rush into any interior work until every room in the house is properly insulated. Thanks to modern materials, you can do this yourself. Any room will be cozy and comfortable if you approach the matter competently and carefully read the technology for insulating the ceiling, walls and floor.
As a rule, ceiling insulation is not treated responsibly.
Many people believe that there is no need to insulate it, but this is far from true. The air that people try so hard to heat in winter rises up and goes through the ceiling to the street. Making a serious mistake - leaving the ceiling uninsulated, many people unknowingly lose half the heat, they senselessly spend money on heat that goes into the unknown.
Ceiling insulation material:
For the construction and covering of the frame you will need:
Tools for ceiling insulation:
Stages of ceiling insulation:
We make a frame from an edged board; you need to be prepared for the fact that this will reduce the height of the room. The distance between the frame boards should be no more than 1 meter. Glassine must be glued between the frame boards, leaving no empty spaces, so that the material holds well, it needs to be coated a little with tile adhesive. We lay insulation on top of the glassine - mineral wool.
Do not leave holes between the insulation. If the material does not hold, use tile adhesive in small quantities. The last step is covering the ceiling with plasterboard. Using a screwdriver, screw the sheets of drywall to the wooden frame.
Calculation of average insulation thickness
Many homeowners don't fully appreciate the importance of insulation. Meanwhile, properly selected insulation can save up to 30% on heating costs.
Particularly high savings can be achieved through the use of a heated floor system. It must be insulated from below so that it does not transfer heat to the floors or the ground.
Choosing the insulation that is best suited for your home is only half the battle. The main thing is that its thickness provides the maximum possible thermal insulation. The fact is that even the best insulation will not be able to provide effective thermal insulation if it is not laid in a sufficiently warm layer. But an excessively thick layer will reduce the volume of the room.
When choosing a thermal insulation material and the required thickness, it is necessary to be guided by the climatic indicators of the place where the house is being built. These data can be found in the following regulatory documentation.
It is impossible not to take into account the design features of the house. For example, in areas with a cold climate, especially if the base of the house is not insulated, then it makes sense to lay insulation with a thickness of 150 - 200 mm. In areas with a temperate climate, a layer of insulation 100 mm thick is sufficient.
In fact, the thickness of the insulation in a house located in Crimea will be significantly less than that built in the Krasnoyarsk region.
Briefly about the main thing
If you don’t know how to install a vapor barrier on the floor of a wooden house correctly, you can find out within a couple of years that it has begun to rot, and the insulation has gotten wet and stopped working. The main rule is not to use impenetrable films that are prone to condensation accumulation for vapor barrier of wooden structures. The material must retain excess moisture and gradually evaporate it. Special films and membranes have these properties, some of which are intended for indoor use, others for outdoor use.
During installation, it is important to take into account that such materials are double-sided and to lay them correctly
Source
Ecowool thermal insulation
This material basically contains waste paper and other paper waste. To preserve it from fire, rodents and insects, it is treated with special compounds.
This cotton wool is a loose material and the higher its density, the lower its thermal conductivity.
Ecowool thermal insulation
In addition to high thermal conductivity parameters, it, of course, after treatment with special compounds, firmly resists strong heat and open flame. This material contains boron. When heated strongly, it provokes the appearance of water contained in the material, that is, self-extinguishing occurs.
It can be poured dry; this is the method used for thermal insulation of the floor. It is simply poured between the joists (see Figure 4.)
Among all the properties inherent in insulation, this one has several disadvantages: after a certain period of time, it can cake and become denser. In addition, it absorbs moisture well and begins to rot. Of course, this happens if it is not protected from moisture.
Note to builders
- Penoplex and teplex are products of progressive techniques created on the basis of extruded polystyrene. The base for the teplex was a foamy “cocktail” of ozone and freons. Innovative materials are highly effective as a heat insulator and have no disadvantages.
- Isoven and isolight confirm the best quality properties of rocks.
- Ursa is a type of mineral wool.
- Insulation - this option is similar in properties to the previous type. The basis is staple fabric, and the cost is half the price of the above-mentioned heat insulators.
- Thermolife is a processed stone wool based on basalt rocks.
The incoming cold air from the underground affects the blackness of the walls and the dampness of the air. There are two ways to get rid of such problems: carry out work on insulating the subfloor directly on the ground or install logs. But the problem should be solved, starting with the first action, which requires making the necessary thermal calculations.
Floor insulation technology
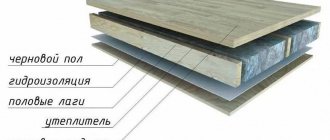
It is important to lay the insulation correctly, observing the correct order of all layers. The floor pie when insulating the attic floor, the floor of the second floor or the first has not always noticeable, but significant differences
Insulation of the floor of the first floor from below
In this case, when carrying out work with your own hands, the materials should be correctly laid in the following order:
- waterproofing;
- insulation;
- vapor barrier;
- ceiling design.
When building a house from timber or frame, the material is secured along the beams. After which the filing is performed. As a protection against moisture and steam, you can use ordinary polyethylene film. As a second option for waterproofing, moisture-proof membranes are used. If all layers are laid correctly, the structure will be reliably and competently protected from the cold from the point of view of heating engineering.
Also, for insulation from below, the method of insulating the ceiling with foam is perfect.
- vapor barrier;
- insulation;
- waterproofing;
- beam-based floor structure.
Insulating the attic floor
- ease of installation;
- the possibility of using inexpensive bulk materials;
- competent thermal protection;
- insulation of not only the room, but also the ceiling along the beams of a house made of timber or frame;
- prevention of condensation in the thickness of the ceiling.
To ensure proper protection, the layers are laid in the following order from bottom to top:
- floor design;
- vapor barrier;
- thermal insulation material;
- waterproofing.
For waterproofing, a plastic film will be sufficient, but as a second, more serious option, you can use roofing felt. When building a house from timber or during frame construction, you can also read the article “Insulating the attic floor using wooden beams.”
Insulation of the ground floor floor from the inside
Carrying out work under the ceiling is quite inconvenient, therefore, when constructing a frame house or a building made of timber, insulation of the first floor ceiling is often carried out using beams from above. In this case, in addition to the previously mentioned materials, you can use bulk materials such as sawdust and expanded clay. When carrying out insulation with your own hands, correctly lay all layers in the following sequence:
- floor design;
- waterproofing;
- insulation;
- vapor barrier;
- clean floor.
Insulation of interfloor ceilings
In the first case, the insulation dampens airborne noise: human speech, music, etc. In the second case, the structure is also perfectly insulated from impact noise - steps, jumps, etc.
Formation of products
An integral characteristic of high-quality insulation of a wooden house is ventilation of the lower point of the “pie”, a ventilation system for the underground space. The better the ventilation scheme is thought out, the better the insulation and logs are protected from waterlogging as a result of condensation (dew point)
Ventilation also prevents radon gas, which is harmful to human health, from accumulating under the house.
The area of the underground vents is 1/400 of the total underground area. For example, to make proper insulation with your own hands for a house of 100 square meters. m., you will need 14 ventilation pipes with a diameter of 150 mm.
It is advisable to make a foundation at least 40 cm high for better ventilation. Additional moisture insulation is achieved by laying a vapor barrier on the open ground under the house and sprinkling it with a 100 mm layer of sand.
Technology and features of floor insulation from below in a wooden house
For each type of insulation, there are some specific features of use.
Mineral wool
The sizes of rolls and slabs are usually multiples of 60 cm, which makes this distance the optimal step between the logs. Mineral wool is cut to size with a cutter and placed in the space between the joists. For a tight fit, the size should be 1–2 cm larger than the distance between the joists. Cotton wool should not be pressed down forcefully as this may affect its characteristics.
The best option would be to lay two layers of insulation. The second layer is laid so that the joint of the lower layer falls on the center of the upper piece. This method of installation will prevent cold air from entering the room.
Video description
You can see the stages of floor insulation with mineral wool along joists in the video:
Penoplex and foam plastic
If foam plastic is used when insulating a wooden floor from below in a private house, you must take into account several rules for working with it:
- Foam absorbs water, so waterproofing is required. Many experts do not take this property into account during installation, which leads to a decrease in thermal insulation characteristics.
- It is recommended to cut the sheets not exactly to the size of the gap between the joists, but 1–2 cm smaller. This will allow you to fill the gaps between the sheet and the joist with polyurethane foam, which will increase the thermal insulation properties. The joints between the sheets also need to be foamed.
Sheets can be fastened using slats, spacer wedges or special adhesives.
Floor insulation with foam plastic in a wooden houseSource sk-amigo.ru
The principle of working with penoplex is no different. But due to the smaller thickness of the material, it can be laid with overlapping sheet joints to avoid the formation of cold islands (similar to mineral wool).
But this method significantly increases material consumption, which means additional financial costs.
Penofol
Due to its property of not allowing moisture to pass through, penofol does not require additional installation of vapor and waterproofing. But to prevent the water vapor that forms in the room from settling on the insulation layer, an air gap is needed between it and the flooring for air circulation.
Laying is done with the foil side up only. This will allow heat to be reflected, which will increase the temperature in the house. Penofol can be used as waterproofing when laying mineral wool or polystyrene foam. This can increase thermal insulation several times, but this method is quite expensive.
Penofol joints are sealed with adhesive tapeSource build.4-u.info
The material is sold in rolls and can be easily cut into pieces of the desired size. Fastening is carried out with a construction stapler on staples or with thin slats that are nailed. To improve the result, it is recommended to lay penofol in several layers.
One of the main problems of wooden houses is cold floors, which interfere with a comfortable life and increase heating costs. Proper insulation will solve this problem. Regardless of the material that is chosen for insulating the finished floor in a wooden house from below, it is necessary to strictly follow the general technology and procedure for insulation, as well as take into account the features of a particular insulation. The cost of installing insulation pays off within one season.
Types and application of insulation
When choosing insulation, they are guided by cost, thermal insulation properties, and durability. The latter indicator must be comparable to the planned service life of the building before major repairs or demolition.
Recently, environmental safety has been seriously assessed. This is not all right with modern materials. If used incorrectly, there is a chance of developing chronic diseases in the new home.
Detailed thermal characteristics of almost all materials are given in Appendix 3 of SNiP II-3-79 “Construction Heat Engineering”.
Let us briefly describe the main ones.
Mineral wool and fiberglass
Here are mats, slabs made of mineral, glass, glass-staple fiber on an organic, synthetic binder or pierced. Soft, semi-rigid or hard with a density from 50 to 350 kg/m3. The specific heat capacity of all materials in this group is 0.84 kJ/(kg x °C). The thermal conductivity coefficient depends on the density. Within the range of 0.048 – 0.091 W/(m×°C).
The big advantage of mineral wool insulation is that it is a waste-free material. All trimmings and scraps go into use.
Non-flammable (NG), fire-resistant materials (up to 1000° C). Suitable for floor insulation without restrictions.
Toxicity: modern cotton wool does not contain phenols and formaldehyde, there are practically no emissions. It receives a minus in terms of environmental friendliness for the formation of dust from fibers during installation. During the operation of floors with such insulation, a vapor barrier protects the living space from microparticles.
The disadvantage of fiber materials is considered to be high moisture absorption. This is actually not a mineral wool problem. This is the problem of those who lay it down. Without creating an insulation system, part of which is cotton wool, the expected result will not be achieved.
Here we come to the main thing: the material does not forgive mistakes. It serves effectively for quite a long time, provided that it is installed correctly and has proper vapor barrier. This work can only be entrusted to a responsible, qualified builder.
A significant drawback is shrinkage. The higher the density, the lower this value. Wool with a density of 35 kg/m3 over 10 years in floors can decrease in volume by up to 10%. Therefore, they lay it tightly, with compression. This compensates for future shrinkage.
If the decision is made, you should only use material from a well-known brand, in original packaging.
Polymer
For thermal insulation, foamed (polyfoam) or extruded polystyrene (penoplex, EPS), penofol (thin foil polystyrene), PIR, polyurethane foam are used. Density from 20 to 200 kg/m3, specific heat capacity 1.26 – 1.68 kJ/(kg x °C), thermal conductivity coefficient 1.26 – 1.47 W/(m×°C).
Polystyrene is the most famous material: inexpensive, lightweight, easy to install. According to the new GOST 15588-2014 this is PPS, in the old 15588-86 it is PSB.
It is not recommended to insulate a wooden floor with an open surface inside a living space. For the following reasons: it emits styrene; it burns well in wooden structures, producing extremely toxic smoke.
PIR boards (polyisocyanurate) thermal conductivity 0.023 W/(m K), not used for floors for the same reason. Foil has a flammability rating of G 1, low flammability. Covered with paper - G 2, moderately flammable (GOST 30244-94). This material is considered a new product, but in 2022 it was used to burn down the Grenfell Tower of London.
PUR (polyurethane foam) thermal conductivity 0.029 - 0.041 W/(m K) moderately flammable. Rigid in slabs or sprayed directly on the surface by combining two components (spray foam - the same polyurethane foam). The use of open floors for insulation of residential premises is not provided for by regulatory documents.
The penoplex manufacturer recommends a cement-sand screed (for floor tiles) or a prefabricated sheet screed made of 2 layers of gypsum fiber board or other sheet materials with overlapping joints (for linoleum, laminate, parquet) on top of the material.
However, open polymers are used to insulate floors in homes. Those specifically built for sale use only polystyrene. The arguments are clear: cheap and fast.
Insulating the floor with penoplex or extruded polystyrene or other polymer boards and then pouring concrete is a completely safe method. This is the technology used to make a popular foundation: an insulated Swedish slab.
Organic
Quite a large group of materials. A perfectionist developer will give preference only to them.
Expanded clay
The brands are specified in GOST 9757-90. Expanded clay sand, gravel and crushed stone have different thermal conductivity coefficients, from 0.12 to 0.19 W/(m K). It depends on the size of the fraction. The gravel used is light oval elements with closed pores.
Insulating a floor with expanded clay is not labor-intensive and can be done by one person.
Weight from 450 to 600 kg/m3. This is a lot, so more brick columns need to be placed under the logs. Or sew two fifty boards together. Of the required total amount, 10-20% is purchased in smaller fractions to fill hard-to-reach places.
A layer of 200 mm is usually sufficient for the middle strip. And inexpensive. If you need to make a calculation, it is said above how to do it. The technology is similar to laying any insulation. Below there is a wind and water barrier, above the expanded clay there is a vapor barrier flooring.
The use of films is mandatory, since expanded clay is very hygroscopic.
Perlite
Volcanic aluminosilicate rock, expanded by heating.
Both sand (backfill insulation) and a slab with organic or polymer filler are used. Thermal conductivity due to fillers is not very high: 0.118 W/(m °C).
Thermal insulating molded material is used in residential and commercial buildings. Eternal material: does not burn, does not rot, is not interesting to rodents. It is hygroscopic and must be protected from moisture penetration.
Vermiculite
A natural mineral, after heating it turns into worm-like scales. Used as backfill or in slab form (with a reduced thermal conductivity coefficient).
Perlite-like material. Does not cake, does not emit harmful substances, and is not damaged by rodents. Strong, does not wear off into sand like perlite. The country has good reserves of vermiculite, but the high price hinders mass use.
Ecowool
The result of recycling waste paper, cellulose. The addition of 12% boric acid makes it non-flammable, 7% borax is added as an antiseptic.
The disadvantage is the second group of flammability. Apply by fluffing or spraying. Floor insulation in a frame house is carried out according to this scheme.
In terms of heat-saving properties, it is similar to mineral wool and polystyrene foam, but does not generate dust and does not emit harmful substances.
Cork
Modified bark of the tree of the same name. Treated with fire retardant. Flammability G 1. Thermal conductivity - 0.04 ± 0.1 W/mK.
The slabs are produced with a thickness of up to 50 mm. For floors, it is correct to use black agglomerate - the bark of tree branches. The high cost makes such insulation practically inaccessible.
Sawdust
Traditional cheap insulation. It is not used in its pure form. When adding 10% slaked lime, 5% gypsum, the flowability decreases and the material sets. Prepare in small portions. The technology looks like this.
Notation. 1. Laga. 2. Cranial block. 3. Subfloor. 4. Lutrasil, glassine. 5. Sawdust. 6. Milk of lime. 7. Finish wood floors.
Sawdust or shavings are mixed with clay and cement.
Reed mats
Natural material. Flammable Used in the following system.
When the material is inaccessible to fire, moisture, and rodents, it successfully copes with insulation.
Slag
Old, accessible material, but its use has nuances. Fresh slag has a lot of impurities. They are washed out by rain and weathered. This process lasts for months. It is difficult to determine how “fresh” the material was brought.
Boiler slag has a thermal conductivity of 0.29 W/m K. This is a low figure, but if free material is available, it is worth considering this option.
Insulation of floors installed on tiled floors
Scheme of floor insulation on floor slabs.
Before starting work, waterproofing material is laid on the concrete foundations. At the top, after about 1 m, wooden logs are attached. The boards should be about 2 m long, 20 to 30 mm thick and 80 to 100 mm wide. If there is a need for joining, grooves are cut out in the joists to ensure the strength of the connection. The joints of the joists of adjacent rows must be shifted relative to each other by at least 50 cm.
The material is recessed between the joists and is not subject to stress. Since compressive strength is not taken into account in this regard, you can purchase basalt insulation or fiberglass for the job.
A vapor barrier material with overlaps is laid on top of the insulation and taped with special tape.
If thermal insulation is carried out using foil material, an air gap should be provided between it and the base of the flooring and the shiny surface should be directed towards the warm side of the ceilings or walls.
When insulation is required from below
There are several main reasons why a wooden house is thermally insulated from below. These include:
When is floor insulation required in a home?
- the need to reduce the height of the room;
- protection of the floor and the entire covering from freezing;
- moving the dew point, thereby avoiding the process of rotting.
Insulation of floors protects the house from freezing
During renovation work in a private house, some difficulties often arise that are directly related to the insulation of the bottom. Let's look at the most common of them:
- more reliable fixation of the heat-insulating material is required;
- the presence of a low subfloor greatly complicates the work;
- insulation of the floor from below contributes to rapid fatigue of workers, which greatly delays the process;
- The variety of types of insulation is not very large.
How and with what you can insulate the floor in a private house
Floor insulation is a rather complex process that requires preparation. First of all, before starting repair work, you need to decide on the choice of insulation.
How can you insulate the floor in a private house and what materials should you use?
Vapor barrier of the floor in a wooden house
Underfloor ventilation
In the space under the floor, air exchange occurs due to the natural movement of air masses. This can be done by installing vents - holes located diagonally from each other in the floor through which ventilation will take place. But the required level of air exchange still cannot be achieved with the help of holes alone. Vents will need to be made along the entire perimeter of the base, one or two in each of the walls. If there are solid partitions inside the basement, they will also be equipped with holes. Each of them should be slightly offset relative to the one opposite. The recommended vent diameter is ten centimeters.
It is better to insulate the underground space located under the building. Modern types of heat insulators make it possible to minimize the level of heat loss in a building associated with heat leakage in the basement. In winter, it is better to leave the vents open, and only cover some of them in severe frosts.
Optimal insulation for wooden floors
There is no point in discussing the best material for thermal insulation of a wooden floor. Almost everything is applicable, from grandfather’s dry leaves to expensive vermiculite. Floors in wooden houses are insulated using loose thermal insulation options, mats and slabs.
Since the list of requirements for any insulation consistently includes lightness, minimal water permeability, durability, and operational safety, all these qualities are quite satisfactory for builders and owners of wooden houses.
The choice mainly depends on the financial capabilities of the owner, the type of base and the method of installation. Owners who are not limited in funds will be able to purchase progressive, easy-to-install materials with detailed instructions on how to insulate the floor in a private house without the involvement of builders and with an accurate indication of the thermal properties of the factory product on the packaging. If you want to save money, you will have to tinker a lot with traditional insulation schemes.
Insulation for thrifty owners
Independent home craftsmen who do not want or do not have the opportunity to invest significant sums in insulation can use the following as a heat insulator:
- dry sawdust, which pleases with a minimal price, but requires reliable waterproofing on both sides of the insulating layer due to the tendency of the material to actively absorb moisture;
- sawdust granules, which are a more practical option, treated with an antiseptic and fire retardant;
- slag, which attracts cost, but is used primarily in floor insulation schemes on the ground;
- expanded clay, used to create a heat-insulating layer of considerable thickness, since its optimal thickness for our latitudes is considered to be 30 cm;
- simple mineral wool without foil and corrugated shells that increase thermal performance;
- roll insulation, created on the basis of glass fibers, slag wool;
- polystyrene foam, which requires measures to protect it from the encroachment of rodents and from fires.
If you follow the rules for installing thermal insulation using the listed materials, heat leakage through the lower ceiling will be eliminated. However, laying them will require impressive labor efforts.
Modernized, expensive insulation materials
If the owner of a country property does not have the main task of how to insulate the floor in a wooden house at low cost, then he has at his disposal:
- Vermiculite is a product of processing hydrated mica, which has excellent insulating qualities and long service life;
- Penoplex is extruded polystyrene foam produced in slab format with increased strength and excellent waterproofing properties;
- Various modifications of insulation with the brands Ursa, Thermolife, Isovent, Penofol, Izolyte, etc., which are mats and slabs with bases made of foamed polystyrene, glass wool and a basalt analogue, optimized by increasing wear resistance, minimizing water permeability, applying foil shells to reflect back heat rays and other methods.
In case of minor heat leaks, you can insulate a wooden floor with ecowool or polyurethane foam, but without special equipment it is impossible to blow in these materials.
This is a significant disadvantage, but the advantage is the creation of a dense water-repellent insulation layer that does not require a device to protect the insulation from steam.
The procedure for self-insulation by joists
Thermal insulation of the floor can be carried out both during the construction stage and some time after the housing is in use.
The procedure for self-insulation by joists
Thermal insulation of a wooden floor requires the performer to have appropriate knowledge and skills in working with construction tools. In practice, two methods are used to install thermal insulation on joists. The first method implies that the logs are laid directly on the ground, and the second, when the logs are laid on concrete slabs. But this method is often used in rooms located above the first floor.
In addition, it must be remembered that under the floor there can be empty space of different sizes. In addition, in permanent buildings, a cellar is often installed under the floor, intended for long-term storage of food, preparations, etc.
It should be understood that the presence of such a cellar requires taking additional measures to insulate the floor. The whole point is that cold air enters through the hatch that leads into the room. That is, this place can be called a bridge of cold.
Floor insulation on joists on the ground is carried out in several stages, which are given below.
It is necessary to build concrete or brick, or monolithic concrete pillars. The installation step of these posts should be 2 meters. Their height must correspond to the floor height specified in the project. When installing supports, it is necessary to use a measuring tool, in particular, a building level. The tops of the columns should be located in the same plane. Even a small difference will cause the floors to skew. Cement mortar can be used to level the tops. If the leveling layer is more than 30 mm, then it must be reinforced with reinforcement. To do this, you can use reinforced mesh or small rods.
Once the posts are built, floor joists can be installed on them. The optimal cross-section of floor joists is considered to be 100*50 or 150*50 mm. Of course, you can use more massive bars. The width of the insulation, as a rule, lies in the range of 600 mm. Accordingly, based on this value, it is necessary to select the step for laying the lag. To attach the logs to the posts, you need to use fasteners. As a rule, anchors, dowels, etc. are used for this. Before installing the logs, they must be impregnated with antiseptic and fire-retardant compounds. This will ensure long-term and safe operation of the structure. To the bottom of the logs, which are already laid on posts, it is necessary to install a mesh made of galvanized steel. It is allowed to install boards with a thickness of at least 20 mm, which are nailed with some clearance. Nails, staples, and other fasteners can be used to secure the mesh or boards. It is necessary to lay material such as isospan on top of the fixed mesh or boards. It resists wind and water. In addition, this material prevents heat from escaping from the soil. The film is laid on top of the joists, in a direction transverse to the joists. When laying the canvas, it is necessary to lower it so that it lies on the nailed boards or mesh. This film is sewn to the joists using a construction stapler. The purchased insulation can be placed in the cells that were formed after laying the film. It must be installed tightly, this is necessary to prevent the formation of cold bridges. If there is a need to lay a second layer of insulation, then on top of the installed joists, it is necessary to install an additional beam with a height of at least 50 mm. The step when installing them should be within the width of the heat-insulating material being laid. After the thermal insulation material is laid in place, it is necessary to lay another layer of water vapor barrier material on top of it. The joints of the strips must be taped with special tape. Cover the resulting structure with a base for the finishing coating.
Wall insulation with Izolon
It is important to lay the sheets end to end and seal the gaps. As we have already found out, ordinary polyethylene foam does not provide the expected reduction in heat loss, so insulation of walls with Izolon from the inside must be carried out with foil materials
The shiny surface will send heat rays back into the room. If the foil is glued to a polyethylene base, then the ability to absorb sounds and vibration, as well as retain water and steam, is added to the reflective properties. All this is necessary when you need to insulate a bathhouse, or rather a steam room
As we have already found out, ordinary polyethylene foam does not provide the expected reduction in heat loss, so insulating walls with Izolon from the inside must be done with foil materials. The shiny surface will send heat rays back into the room. If the foil is glued to a polyethylene base, then the ability to absorb sounds and vibration, as well as retain water and steam, is added to the reflective properties. All this is necessary when you need to insulate a bathhouse, or rather a steam room.
Let's consider installation methods with additional insulation with mineral wool:
- We attach wooden blocks to the wall - in any order, the main thing is that later it will be convenient to stuff the counter-lattice;
- Mineral wool is placed randomly between the bars; you don’t even have to glue it to the wall;
- on top of the bars, Izolon insulation, foil-coated with the shiny side, is nailed into the middle of the room with a stapler;
- the rolls are spread end-to-end, and the cracks are sealed with aluminum-coated tape;
- the second tier of the lathing is nailed (counter-lattice);
- Any finish can be attached.
This is necessary so that the material can realize its 100% potential. After all, the foil reflects IR rays, and they are transmitted only through the air; if there is no gap, then radiation is impossible in this case. Temperature will transfer from one material to another, and aluminum conducts heat very well. Therefore, instead of insulation, you can get the opposite result.
Advice from professionals
When insulating the floor of a wooden house, it is recommended to follow the advice of professionals:
- It is good to treat wood with antiseptics.
- Insulate the heat insulator from moisture from the floor and from the room.
- Use a building level when installing wooden joists. The floor after insulation must be level, otherwise the work will be difficult to redo.
- There should be a small air gap between the surface of the clean floor and the insulation, which will help prevent the formation of mold. Therefore, the thickness of the installed logs should be higher than the insulation.
To visually familiarize yourself with the insulation process, you can watch the video instructions. All stages of the work are described.
To insulate a wooden floor you do not need a special set of tools. It is enough to purchase materials for insulation, as well as carry out the installation correctly. Insulating the floor from above is simpler, but from below will require more effort. But the latter option will not take away precious centimeters of room height.
New generation insulation materials
Penofol is a modern cool insulation material that has not become widely used exclusively in its “youth” years. The option is presented in the form of a layer with fused polished foil. The well-known reflective ability of foil is enhanced by its high thermal insulation properties.
Available in various modifications with other materials. The base is built on foamed polyethylene technology, which is responsible for water resistance and, thus, eliminates the need for a vapor barrier layer.
Polyurethane foam
- technological synthesis of isocyantic and polyol components, indicated by a cellular structure, with pores filled with gas and air. Therefore, it is lightweight and has a low degree of thermal conductivity, resists rotting and the development of mold spores, and also does not react to the effects of alkalis and acids.
Ecowool
- a type of insulation consisting of 80% waste paper and cellulose fibers. The binding link is boric acid, and lignin is used as an antiseptic. Despite the paper content, the material resists fire and is only capable of smoldering.
Features and Benefits
If a wooden house has an underground or basement room, the insulation process should begin from there: as a result of cold air coming up from the freezing ground, a large loss of heat occurs. Also, before insulation, it is necessary to ensure complete drying of the entire room where the work will be carried out, using special ventilation devices.
The installation of thermal insulation coatings itself is not particularly difficult. The main thing is that the materials are of proper quality and treated with special means: this will help reduce the impact on them of the weight of the boards, soil and low temperatures. Before purchasing insulating coatings, you should consider what the load on them will be, as well as the level of the lowest temperature indicator that a particular type of material can adequately withstand.
But in general, any insulation technology has several main stages:
- First, the logs are installed, then dense sheets of wood are fixed on them, and only after that the installation of the insulation itself begins.
- After the insulation is laid, the base is sheathed with a material that has the property of insulating from steam and moisture: this ensures that the material will retain its original properties longer.
- At the end of the work, the rough base is refined using finishing.
Thermal insulation with expanded clay
Thermal insulation with expanded clay
Expanded clay is a granular material, light in weight and obtained as a result of clay compression. This material is considered natural and environmentally friendly. It has a number of properties that allow it to be used as insulation. Among them are:
- sound insulation – muffles extraneous sounds; retains heat well;
- resistance to low temperatures and it should not be destroyed when exposed to them;
- resistance to high temperatures and open flames;
- strength - this material does not change its structure;
- strength – does not change its structure under the influence of cold/hot water; long service life, it does not change its characteristics under the influence of many factors, including time.
We must not forget about its cheapness. Compared to many modern materials, it is much more profitable to use.
Summing up
When choosing a suitable insulation for the floor, it is necessary to take into account not only the technical characteristics, but also the conditions of its future operation. This is the only way you can choose the best option.
Therefore, thermal insulation material is always selected individually. But if you have 2 insulation materials with similar characteristics, then always choose the one produced by a well-known manufacturer. Then the likelihood that the material will serve without problems for many years will increase significantly!