In buildings made of wood, the problem of indoor microclimate is especially acute. Due to the drying out of the floor boards and the appearance of cracks through which drafts wander, the rate of heat loss can reach 30%.
Timely insulation of the floor in a wooden house will help reduce thermal costs, especially since it is quite possible to perform thermal insulation without the involvement of specialists. Agree, this approach to solving the issue will save a decent amount and significantly increase the thermal efficiency of the house. Do you doubt your own abilities?
We will help you navigate the variety of insulation methods and provide practical recommendations for choosing a thermal insulation material. In addition, we will describe the technology for performing work using the most popular materials: sawdust, expanded clay and penoplex.
Methods for carrying out thermal insulation work
Work on laying insulation can be carried out directly in the living room or from the basement. In the first case, it is customary to talk about thermal insulation from above, in the second - about thermal insulation from below. In addition, you can use other methods of floor insulation, which will be discussed in more detail below.
Method No. 1 - installing insulation from above
In this case, the insulation is installed directly in the room. Such work is quite easy to perform, but a number of problems may arise.
Disadvantages of “surface” installation of insulation:
- the height of the walls decreases;
- the lower layers of the structure are not warmed up enough;
- The thermal insulation layer experiences increased load, which is why it is necessary to select a material of increased rigidity.
Due to the difficulties listed above, experts, answering the question of how to properly and easily insulate floors in cottages and wooden houses, recommend using this technology only in special cases.
It is necessary, for example, if there is a shallow underground under the building or the building stands on a monolithic slab.
It is advisable to leave a small gap between the layer of thermal insulation material laid on the joists and the finishing coating to ensure the free passage of air flow
Work on laying thermal insulation begins with dismantling the baseboards and finished floor, which is necessary to gain access to the joists. After this, the support beams are inspected.
Detected rotten areas must be removed, replacing them with suitable sized fragments of new beams, which are fixed using galvanized metal corners or channels.
A cranial beam is strengthened along the lower edge of each joist. Boards or wooden panels approximately 30 mm thick are laid on the prepared structure without fastenings. The created structure must be treated with an antiseptic.
The length of each fragment should be less than the installation step of the logs by 10-20 mm.
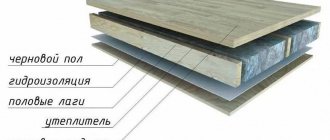
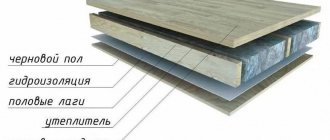
Waterproofing, insulation, a vapor barrier, a counter batten creating a ventilation gap, and finally a finishing floor covering are laid on the assembled subfloor.
If the finished floor is made from tongue and groove boards and is in good condition, it can be reused. To facilitate the subsequent assembly process, it is advisable to number the boards when dismantling
Method No. 2 - insulation from the basement
When insulating floors in a private wooden house from below, the installation of a protective coating is carried out between the frame elements and the top finishing layer.
Carrying out work in this case requires more labor than laying insulation on top, but the result provides a number of advantages.
The main advantages include:
- the height of the room remains unchanged;
- the insulation layer is not affected by loads from heavy furniture standing on the floor, which allows the use of any types of materials, regardless of their hardness;
- The heat insulator laid underneath provides protection from freezing not only of the top layer, but also of the entire floor frame - this reduces the risk of moisture penetration, which increases the life of the structure.
This option is well suited for frame buildings installed on pile and pile-screw foundations.
A necessary condition for the use of such technology is the presence of a cellar, basement or other auxiliary room under the house.
Bottom insulation is usually carried out using joists. Boards are laid on these beams with parameters of 5 * 10 centimeters, and then other insulating layers indicated in the diagram
The following work order is recommended:
- First of all, it is necessary to dismantle the old rough floor to gain access to the joists.
- Beams should be cleared of debris and their condition inspected, replacing damaged fragments as described above.
- A vapor barrier, such as a membrane, needs to be laid around the perimeter of the ceiling. If materials are used in rolls, the width of the strips overlapping each other should exceed 10 cm.
- A 30*30 mm cranial beam must be nailed to the side walls of each joist. It will serve as a support for the heat-insulating material and create a ventilation gap between it and the finished floor.
- After this, the insulation is installed, the thickness of which should not be greater than the height of the logs. Depending on the type of thermal insulation, it is strengthened using mounting adhesive, foam or cross-bar.
- A layer of waterproofing is applied on top of the heat insulator layer, which can be roofing felt or ordinary polyethylene film.
The final stage is applying the finishing coating: boards, waterproof plywood or other materials.
Method No. 3 - double floor arrangement
To qualitatively reduce heat loss in wooden buildings, double floors are often applied. In this case, the first step is to install the logs. Uncut boards are fixed on them, which form the so-called subfloor.
When making double floors, it is important to ensure that the subfloor boards fit tightly to each other, while the cracks are filled with polyurethane foam. To fill gaps in the final coating, you can use putty compounds intended for wood
Next, logs made of thinner timber are installed. The space between them is filled with thermal insulation material. Then a finishing floor made of tongue and groove or edged boards is applied.
If desired, a finishing decorative coating is also used. Between two wooden layers it is convenient to place service communications: corrugated pipes with cables, water supply network.
Instead of laying a subfloor, you can use various types of smooth or embossed floor coverings that have a high degree of thermal insulation. These materials are even preferable because they do not accumulate debris.
This layer is attached with bustylate glue, which is applied to the material in the form of strips with mandatory gluing of all joints.
Read more about the technology of floor insulation using joists in this article.
Method No. 4 - heated floor system
The “warm floor” technology, which also uses traditional insulation, is very popular, which is quite natural. It ensures uniform heating of the entire coating, thereby effectively achieving a comfortable room temperature and reducing its humidity.
When choosing a heated floor design, it is best to choose an option that allows you to adjust the heating temperature. This will not only maintain a comfortable temperature in the room, but will also ensure economical energy consumption
There are two options for such systems, in which heating is carried out using water or electric current.
The water floor is constructed following the following sequence of actions:
- Prepare the foundation, for which concrete slabs are installed or a cement screed is performed.
- The surface is covered with the selected insulation, the thickness of which can vary from 2 to 10 cm.
- A reinforcing mesh is laid on top, along which a pipeline system is mounted, secured with plastic clamps.
- Next, the surface is filled with a special material, and, if necessary, a substrate is installed.
- The final stage of arranging a water floor can be considered the installation of the finishing coating.
An electric “warm floor” is made in a similar way to the option described above, but a cable stretched on a metal mesh is used as a heating element, which is firmly connected to the joists.
The installation technology and connection diagrams for the electric heating system are described in detail here.
An alternative heating source is infrared film materials, which are laid directly on the thermal insulation layer covering the screed.
Insulation with isolon
When insulating a floor, the material that is used plays a key role. In recent years, material such as isolon (foamed polyethylene) has been particularly popular. Its use provides the following advantages:
Insulation with isolon
The use of this material allows you to achieve high results with minimal expense.
Foil-coated isolon avoids the use of hydraulic vapor barrier materials. It itself has low vapor conductivity.
Low hygroscopicity allows it to be used in rooms with high humidity without any special preparation.
The thickness of this material ranges from 1 to 5 mm. It is often used as a substrate for laminate or parquet. Its use significantly insulates the floor. In addition, as already noted, its installation avoids the use of vapor barrier films.
Foil-coated isolon is used together with heated floor systems. Heat cables laid on top of foil-coated isolon emit only into the room.
The importance of hydro- and thermal insulation
It should be especially emphasized that for proper insulation of floors in wooden houses, one must not forget about laying hydro/thermal insulation layers.
The waterproofing coating is designed to protect the structure from moisture that falls on a warm surface when cold air flows in. Water particles penetrating into wooden elements lead to the development of fungi, mold, and, ultimately, to the destruction of the structure.
For hydro- and vapor barrier, you can use moisture-and-windproof membranes, which allow air masses to circulate, trapping moisture inside. Polyethylene film can be a budget replacement for specialized materials
The vapor barrier layer is no less important. Electrical equipment operating in the house, as well as people in the rooms, constantly generate heat. Warmed air flows from rooms that pass through the ceilings of structures come into contact with cold air masses.
This leads to condensation, which can result in wood swelling and rotting.
Requirements for thermal insulation materials
There are many types of insulation, ranging from simple natural materials to complex synthetic compounds.
In order to make the right choice, you need to take into account a number of factors, namely:
- The degree of thermal conductivity . The higher this indicator, the lower the heat loss will be.
- Term of use . This determines how long it will take to repair and replace the material.
- Insulation weight . Too heavy options are not recommended for use in frame houses.
- Moisture resistance . This factor is especially important if the building is located in a low-lying or swampy area, as well as when constructing houses in a humid climate.
- The presence of an unheated room under the floor. In a cold basement, it is better to give preference to denser thermal insulation.
- Level of difficulty in work . Ease of installation can be considered an undeniable advantage.
- Fire resistance . The insulation should not burn or support combustion, and also emit gases hazardous to health when heated.
It is also necessary to take into account the ability of the material to resist mold, fungi and other destructive biofactors.
When choosing a thermal insulation material, it is useful to compare the most important indicators. However, we should not forget about the features of various types of insulation.
Finally, an important criterion is the cost of the thermal insulation material. You shouldn’t chase cheapness: expensive products are usually easy to install and have a long service life, which allows you to save on labor costs and repairs.
Popular materials for insulation
Among the most commonly used insulation materials are:
- sawdust;
- expanded clay;
- mineral wool;
- Styrofoam;
- penoplex.
Sawdust is still quite popular for thermal insulation work. This is an environmentally friendly, accessible and inexpensive product, moreover, it is convenient to use in hard-to-reach places.
However, it also has disadvantages: over time, sawdust cakes, which leads to loss of quality; they are also susceptible to microorganisms, fungi, and insects.
Expanded clay is a bulk material formed by firing clay or shale. This completely environmentally friendly material, shaped like balls, has high thermal insulation properties.
It is resistant to freezing and has good fire resistance. The disadvantages of expanded clay include its relatively large weight; in addition, this material cakes, which leads to shrinkage of the house and a drop in thermal conductivity.
Mineral wool is considered one of the best insulation materials, since it does not burn and is not destroyed under the influence of biofactors. In addition to good thermal insulation, it also has sound insulation properties.
Among the negative qualities are low mechanical strength and deterioration of insulating qualities when exposed to water or steam, which requires special attention to vapor/waterproofing.
Penofol is foamed plastic covered with foil on one or both sides. Due to its flexibility, the material is convenient to use for insulating rooms of complex configuration; it can also be combined with other insulation materials
Polystyrene foam has become widespread. It easily retains heat, effectively retains heat loss, has sufficient mechanical strength, and a long service life.
It is necessary to remember, however, about the negative qualities of this material: when burning, foam releases toxic substances, in addition, it is able to absorb water, which leads to a decrease in performance.
Penoplex . A relatively recently appeared material that quickly gained popularity. This type of insulation consists of foamed polystyrene boards, which have excellent thermal insulation characteristics. The easy-to-install slabs do not burn and are not susceptible to bioorganisms.
Other synthetic and natural materials are also used as insulation, including isolon, penofol, ecowool, cork, and fibrovit.
How can you insulate the floor?
When choosing a material, you need to understand that all types of insulation have different thermal conductivity coefficients. Of course, the lower it is, the better. This means that the insulation has a good ability to retain heat inside the room. The lower this indicator is for the material, the thinner the coating layer will be needed to protect the building.
Table. Thermal conductivity coefficients of different types of insulation.
| Material | Thermal conductivity coefficient, W/(m*C) |
| Expanded clay | 0,1 |
| Stone wool | 0,038…0.047 |
| Glass wool | 0,035…0,05 |
| Extruded polystyrene foam | 0,028…0,04 |
| Polyurethane foam | 0,02…0,04 |
| Ecowool | 0,04 |
| Linen insulation | 0,038 |
| Penoizol | 0,03…0,4 |
| Styrofoam | 0, 0033…0,038 |
| Sawdust | 0,07…0,1 |
In addition, it is necessary to pay attention to the density of the product, its moisture, fire resistance and other characteristics. An important aspect for owners of country houses is the interest of insulation for rodents. After all, for example, the fire resistance of a material is unlikely to help if a wooden house catches fire. And the places where mice live and their passages, which they make in thermal insulation, can seriously deteriorate the characteristics of the laid coating.
Another important aspect is the design of the building; the type of thermal insulation largely depends on this. The climatic conditions of the region also cannot be discounted.
Expert opinion
Masalsky A.V.
Editor of the “floor screed” category on the Pol-exp.com portal. Engineering systems specialist.
In general, all types of insulation can be divided into three categories: bulk, slab (or roll) and sprayed. Everyone chooses for themselves which type is more convenient to install.
Important ! I would like to note that if piece products have to be joined, adjusting the products to the required size, then when spraying mixtures, seams and the formation of cold bridges can be avoided.
Specifics of working with popular insulation materials
The installation of different types of heat insulators has its own characteristics, which can be seen in the example of three popular materials.
Features of working with sawdust
Sawdust can be used directly by pouring it into the space between the joists, but it is more advisable to use it in the form of a solution. To do this, a mixture is made of five parts sawdust and one part cement or clay, which is diluted with half the amount of water.
It is advisable to add broken glass or special additives to the prepared mixture against the appearance of rodents.
The voids between the joists must be carefully and thoroughly filled with freshly prepared mixture. The layer must be very even, otherwise there will be “holes” in the protective coating, resulting in the floor remaining cold.
If ordinary sawdust is used for thermal insulation, before starting work they must be thoroughly dried and treated with an antiseptic; you can also add dry lime to them
Carrying out thermal insulation with expanded clay
An inexpensive type of insulation is expanded clay, working with which also has its own characteristics. In this case, sand is additionally laid. This material is carefully and evenly applied to the base, and then carefully compacted.
As waterproofing, liquid mastic is poured onto the sand layer, after which expanded clay is backfilled, while ensuring maximum evenness of the coating. Next, a vapor barrier is installed, on top of which the finishing is laid.
Expanded clay is a rather heavy material, so it is not recommended for use when insulating buildings on a frame foundation.
When thermal insulation using expanded clay, it is better to give preference to a multi-fraction material, the elements of which differ in size, weight and other characteristics. In this case, the granules adhere more tightly to each other, due to which there are no pronounced voids in the layer
Special techniques when working with penoplex
Penoplex is a common insulation option. When using it, precise adjustment of the slabs is required, which creates a barrier to the penetration of cold air. The sheets are laid between the joists, and for maximum adhesion they are attached with mounting adhesive to the floor and to each other.
Lightweight penoplex insulation is considered the best option for thermal protection of the floor in a frame house. It provides minimal load on the foundation, which avoids shrinkage of the structure.
Penoplex slabs are convenient to use for both top and bottom thermal insulation. Since this material does not allow water to pass through, the waterproofing can be skipped in this case.
Thermal insulation with sawdust
When building a private house made of wood or stone, the developer must solve many problems, and one of them is creating effective insulation of the building.
Thermal insulation with sawdust
There is a large selection of materials on the market for room insulation, in particular floors, but many believe that one of the best options is to use sawdust. At the same time, they are guided by the following criteria of cheapness and environmental friendliness of this material.
Sawdust is considered the lowest cost material that can be used for thermal insulation. This insulation represents waste that is obtained during wood processing. It should be noted that many houses built in the past, or even the century before last, that have survived to this day, are insulated with sawdust and have not lost their thermal insulation properties.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of this material?
The undoubted advantages include:
Cheapness. Many wood processing companies are willing to give this material away for free. In this case, there will be costs for their delivery to the construction site. Sawdust does not emit any harmful substances, they do not cause allergic reactions in residents. In addition, they have high thermal insulation rates; in this parameter they are comparable to mineral wool.
To adequately evaluate this insulation, one cannot fail to mention its shortcomings. These include:
This is a flammable material. They can become a place for small rodents and insects to live
To avoid these shortcomings, cement, gypsum and some other materials are added to sawdust. After obtaining the mixture, it is treated with copper sulfate. As a result of these operations, the sawdust will not burn, and rodents will not like such food.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
The video below demonstrates the process of insulating a house using joists using mineral wool:
Video review detailing modern types of heat insulators:
In order to perform high-quality thermal insulation of the floor, it is important to carefully select the material, taking into account its features and the specific design of the building. Equally important is compliance with the installation technology recommended for this type of insulation, as well as careful execution of all stages of work.
Do you have experience insulating floors in a wooden house? Please tell readers what thermal insulation material you used and whether you were satisfied with the result. Comment on the post and participate in discussions - the feedback block is located below.
Penofol insulation
Insulation with penofol
Penofol is a multilayer material that consists of a base and polished foil. Polyethylene foam of different densities, sizes and internal structures is used as a base. The foil used in penofol is polished to a coefficient of 97%. Its thickness is only 20 microns. It can be applied to both sides of the material. By the way, this material came to us from the space industry. It was used in the production of space suits.
The peculiarity of this material is that it does not retain the heat coming from the room, it reflects it in the opposite direction.
Cork material
The main advantage of natural cork insulation is the extremely high sound insulation of the coating. The high price of the material is compensated by the fact that you simultaneously solve the problem of heat and sound insulation. In addition, cork insulation almost does not burn, is not afraid of moisture, is resistant to rotting and is extremely durable, which allows it to be used as insulation under self-leveling floors.
Cork insulation
Due to its rather beautiful texture, cork insulation is sometimes left even as a finishing coating. In this case, the top layer is covered with a special varnish, which protects it and at the same time emphasizes the design.
Cork insulation is available in rolls and sheets with thicknesses from 3 mm to 200 mm. Sheets of maximum thickness allow you to insulate floors above the ground in just one layer, but at the same time they are very expensive. The cost per square meter of thick cork insulation can reach up to 5,000 rubles. For this reason, cork insulation on the first floors of buildings is rarely used.
Cork thermocork insulation
The thickness of cork insulation on the ground floor of a private house with concrete floors should be at least 100 mm; in floors between floors with concrete floors, a layer of 50 mm is sufficient; if the floors are wooden, then the layer should be increased to 70 mm. In an apartment building, cork insulation is laid in a layer of 10 mm to 30 mm; this is quite enough for effective thermal insulation and complete sound insulation from neighbors below.
Video - Cork insulation
General information
Selecting the type of insulation that is best suited for your room is only 50% of the job, success. It is important that the thickness of the insulation in the floor of the house is sufficient, because even the best material does not provide sufficient thermal insulation if it is laid in a thin layer. On the other hand, a very thick insulating layer will reduce the height of the ceiling in the room and is an unjustified waste of money.
It is extremely important to understand that the required insulation thickness will depend on the climate conditions in your area. It becomes obvious that when using the same insulating material in typical houses in Norilsk and Sochi, completely different layer thicknesses are required. For this reason, it is important to take into account that all the advice, as well as recommendations from the article, are given for the normal climate of central Russia, where in winter the temperature rarely drops below -25 degrees. If you live in a harsher or milder climate, it is recommended to adjust it down or up. We invite you to consider the main types of insulation, as well as data on layer thickness when used in different types of floors.
| TP - heated floor (factors) | Thickness of insulation material |
| TP above a room that is heated and the temperature is at least +18 degrees | 3 cm |
| TP above a heated room with an air temperature of +10…+17 degrees | 5 cm |
| TP above a heated room, where the temperature is 0...+10 degrees | 7 cm |
| TP above a room that is not heated | 10 cm |
| TP on the ground in the basement/ground floor with a recess of at least 1.5 meters | 12 cm |
| TP on soil in the basement/ground floor, the depth of which is 1.5 meters or more | 6 cm |
Ecowool
Ecowool
This material is very similar in characteristics to mineral wool, but is made from cellulose fibers, therefore it is absolutely safe for health. Just like mineral wool, ecowool is afraid of water and is easily deformed. Therefore, in most cases it is used to insulate wooden floors between floors.
Ecowool insulation
The big advantage of ecowool is that it is installed by spraying under pressure from a special pipe. Thus, the insulation can be “blown out” under the already assembled floor; for this you only need to make several small technological holes.
Spraying ecowool
The required thickness of the ecowool layer corresponds to the thickness of the mineral wool layer, all other things being equal.
Characteristics of basalt and ecowool