The most common question that arises during the process of building a house is how to make a roof gable canopy so that it fits organically into the overall design of the building, protects from precipitation and saves energy during the installation process. Finishing the roof gable is quite important and necessary work, since the appearance of the house (or building) largely depends on it.
The canopy on the pediment allows you to protect the ends of the load-bearing walls from precipitation.
Carrying out such work is quite difficult, this is due not only to the dangerous work under the roof, but also to the need to carefully think through and implement a design that will correspond to the design of the building. Often a person who has done similar work knows how important it is to think through the design of the pediment in advance: it is this that determines the shape of the canopy. How to make a roof gable canopy is described in this material.
Design Features
It is better to use wooden beams as a load-bearing structure.
The canopy on the pediment is a necessary element, since it allows you to protect the ends of the load-bearing walls from precipitation, just as the pediment is protected by the roof. This significantly reduces the risk of wall destruction and also increases service life. When installing it, it is necessary to remember about the aesthetic appearance of the building. After all, if it is done untidy or does not match the design of the house, it will be very noticeable. Everyone probably understands that it will be necessary to make at least 2 canopies for the pediment. After all, houses are often built with a gable roof. Accordingly, the building has 2 pediments.
At the moment, a visor can be made from a variety of materials, the main ones of which will be discussed below. An important point in the construction process is that the load-bearing structures under the canopy should be installed before the gable cladding begins. Otherwise, it will have to be attached to the walls and gable cladding, which significantly reduces the reliability of the structure of both the gable and the canopy. Competent craftsmen plan the construction of the canopy long before the roof is designed. In this case, the design must provide the following functions:
- Protection of load-bearing walls and structures from water ingress.
- Stability and strength of the structure under the influence of precipitation and wind.
- Building decoration. The visor will look like a “skirt” that should be organically integrated into the design.
- The covering materials of the canopy and supporting structures must be durable, provide the necessary protection and have a pleasant shape and color.
Hardware is used for fastening both load-bearing structures and roofing.
Almost always the canopy is made with a single slope (less often - flat). At the same time, they try to provide the design for mounting the visor in advance. If the canopy is installed after the work on the gable is completed, the canopy will have less strength. There is a possibility that it will be blown away by the wind or will not withstand precipitation.
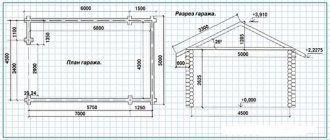
As a load-bearing structure, you can use wooden beams or wide boards, which are installed either parallel to the ground (flat pediment) or at a certain angle. It is recommended to choose the width of the visor so that a person can stand under it during rain (so that the rain does not wet it). For buildings with a wall height of about 3 meters, the width of the canopy should be approximately 0.8 meters. The minimum permissible width is 0.5-0.6 meters. This will protect the wall from flooding. To ensure the required width of the canopy, the length of the beams of the supporting structure should be calculated in advance so that the canopy lies completely on them. In this case, the length of the supporting beams must ensure their reliable fastening.
Once you have an idea of what kind of structure the canopy should have, you can begin to create it.
Finishing the gable wall
Every pitched roof has a pediment, except the hipped roof, so the question of how to inexpensively and accurately decorate this part of the wall worries many. Don’t think that this is just an aesthetic issue, because a properly constructed pediment serves practical purposes:
- Rationalizes the distribution and conservation of heat inside the house. This function of finishing the pediment is especially relevant for the roof of the attic, which is used year-round as a living space. Without adequate cladding and insulation, the pediment will become a black hole into which the money spent on heating the room in winter flies away .
- Protection from adverse weather conditions. In order to preserve the interior decoration, and even the structure of the roof of the house itself, you should take care of a reliable pediment, which will become a protective barrier between you and the external environment, which tests the strength of the piercing wind, lines, and snow.
- Stingray support. Subject to correct calculations and professional work, the gable wall will become an additional point of support, helping to distribute the load from the slopes. Experienced roofers can use gable repairs to fix roofs that have sagged as a result of design errors or from time to time.
- Creation of a unified architectural image of the structure. A pediment, designed competently, in harmony with the roof and decoration of the main walls, without serious expenses makes the image of the house complete, holistic, emphasizing its style and the designer’s idea.
Please note that the material from which the pediment is made does not always match the finish of the main walls. Experienced builders strive to minimize the weight of a home by using lighter materials. This allows you to save money spent on laying the foundation.
Sheathing methods
When starting to build the roof of a house, you should decide in advance in what order to carry out the work. There are two options:
- First the pediment. If you decide to build the gable first, and then install the rafter system and roof, then you will need to install a mast, the length of which corresponds to the height of the ridge, in the middle of the gable hay and pull a cord from it to the corners of the house. The cord will outline the space that needs to be stitched. This option is good because the rafters and beams do not impede access, and the finished pediment will provide additional support for the slopes of the future roof, which is necessary if it has a large weight or area. It is important to strictly follow the project, check, align the corners so as not to warp the rafter structure.
If construction is carried out in winter or in regions with frequent squally winds, it is better to first build the gable and then move on to constructing the roof . This will protect the slopes from tipping over, and the wood of the rafter frame from the penetration of excess moisture.
Insulation
Experienced builders consider insulation to be a key operation in finishing a gable wall. If you plan to heat the attic, then this procedure is mandatory, and for non-residential attics it is highly recommended. Most often, the thermal insulation of the pediment is performed using fibrous materials based on minerals. There are two ways to “seal” heat inside the attic:
- From the inside. According to research and the experience of professional craftsmen, this is a more rational solution, which is more effective. When insulating from the inside, work is carried out from the attic side, setting up a frame, between the beams of which mineral wool is compacted, covered with a vapor barrier and sheathed with plasterboard.
When purchasing insulation for a gable, please note that if it is to be used indoors, you need to choose from options that are safe for human health. Hypoallergenic and non-toxic insulation based on flax fiber has proven itself to be excellent. The so-called ecowool is not inferior to mineral wool in terms of thermal conductivity, hygroscopicity, and noise insulation, but is better suited for use inside residential premises.
Facing
Facing is the finishing line in the design of the pediment. It covers the unsightly appearance of the insulation and protects the wall material from moisture. Whatever material you use, the principle of installing the cladding is the same - first, a frame is set up, onto which decorative boards or panels are then attached. The leading materials for finishing the pediment are:
- Siding. Decorative panels made of polyvinyl chloride, metal or asbestos cement. They are durable, do not suffer from temperature changes, do not fade, do not rot, and do not deform. A variety of colors and textures provides interesting architectural solutions that decorate the exterior of the house. The siding is attached to a metal profile using a locking system.
Important! A metal frame is not suitable for wooden cladding, since wood changes its shape depending on humidity, but metal does not. This difference in properties is detrimental to wood, which is rigidly fixed to a metal frame; it warps and cracks.
Now that you have an idea of how to make a pediment, we remind you that after construction it requires seasonal inspection and preventive repairs (coating with protective compounds) every 5-8 years.
Stage 1: Necessary tools and materials
To build the canopy, we will need the following materials:
Tools for building a canopy.
- Beam 50x100. Necessary for the construction of load-bearing structures. The amount of timber is determined by the width of the house, the selected width of the canopy, and the roofing material for the canopy.
- Roofing material. This can be slate, metal tiles, corrugated sheets, etc. It is important that the material has a color and texture similar to the finish of the walls or roof.
- Hardware. They are used for fastening both load-bearing structures and roofing. Most often they are screws or anchors.
- Corners. For attaching timber to the roof structure (rafters or other load-bearing elements).
- Material for ebb tides.
- Measuring instruments. You should get a tape measure, a ruler and a pencil, plumb lines, and a level.
- Screwdriver with a set of bits.
- Glue.
- Ladder.
After all the materials have been collected, we begin to install the canopy.
Specifics of the construction of frame gables
Pediments are the vertical walls of a pitched roof, bounded above by its inclined planes and below by a horizontal ceiling. In the construction of gables, all types of building materials used for the construction of standard walls are used: brick, foam concrete blocks, similar flat panels with a locking mounting connection, logs with beams.
If the gables are built as extensions of walls made of stone or wood, then structurally they become gables, and the roofs resting on them are called gables.
However, frame gable structures are rightfully considered the most common option. These are triangular or pentagonal end walls with a frame made of timber or paired boards, covered with natural or artificial facing material.
The list of advantages of constructing pediments using frame technology includes:
- Minimum weight . Frame gables weigh significantly less than their counterparts made of stone and lumber. Lightness allows you to save on the construction of the foundation of the house by choosing an inexpensive pile type of foundation.
- Simplicity of the device . An inexperienced contractor can handle the construction of the frame and sealing the ends of the roof without any problems. Cutting, installing and fastening parts does not require in-depth knowledge and skills.
- Economic effect . Using the frame method in the construction of gable walls will provide a significant reduction in costs. In addition, to deliver building materials to the construction site, you will not need to rent special equipment.
Frame technology is ideal for the construction of gables of both insulated mansard roofs and cold structures erected above seasonal country houses and change houses. This is the easiest way to achieve the necessary heating engineering parameters and protect the structure from rain and wind.
True, the lightness of the end walls of gable structures does not always benefit the structure as a whole. The disadvantages of lightness are especially evident in regions with increased wind activity: in the steppe, mountain and coastal regions.
The walls, which do not have sufficient mass to resist gusty winds, are subject to an impressive horizontal force. On the windward side, it strives to overturn a vertical obstacle that stands in the way. Downwind, i.e. on the opposite side, during the period of exposure to wind, a suction is formed due to a significant vacuum, due to which this part of the roof is given the opportunity to take off.
Roofs with low gable walls, but wide eaves overhangs in areas with a similar climate also do not behave well. Therefore, it is not customary there to get carried away with the width of the gable and eaves roof extensions. Usually no more than 30 cm of the slope along the perimeter of the roof protrudes beyond the perimeter of the house.
In addition to the horizontally directed force, the gable walls are subject to a vertical load, consisting of the sum of permanent and temporary loads. Constant loads include the weight of the truss resting directly on the pediment, the weight of insulation, sheathing and the roofing itself. They are determined during calculations for selecting the cross-section of the rafters.
Temporary loads are represented by snow deposits and the effects of winds. They are found using maps - graphic appendices to SP 20.13330.2011 and used in calculations according to the recommendations of the specified reference book.
It is not necessary to use accurate calculations in calculating the cross-section of racks for the frame of gable walls. There are simplified formulas focused on lumber produced in the country, and software products that allow you to select material for constructing a pediment and calculate consumption in a matter of minutes. Only without knowledge of the principles of calculations is it difficult not to get confused in their algorithm, which we will now thoroughly analyze.
Calculation of the cross-section of frame supports
The principle of frame construction is to install vertical supports that determine the configuration of the wall and then attach the facing material to the same posts. Craftsmen who want to install and sew up gables with their own hands need only adhere to generally accepted rules for constructing frame walls.
Suppose that we calculate the dimensions of the racks for the gables of a private residential building up to 9 m wide, two floors or one with an attic. The maximum ceiling height should not exceed 2.4 m. For the attic floor, the ceiling height is considered to be the distance from the subfloor to the ceiling beam, which can serve as a truss crossbar.
In most cases, in low-rise construction there is no point in performing highly complex calculations. It is better to take advantage of the existing experience of builders who have been designing and constructing frame houses for many years. For example, there is a table from Norwegian engineers with recommended timber sizes for constructing frame walls.
If the width of the building is more than 10 m, and the height of the central pillar of the frame gable is more than 3 m, then Norwegian builders do not have the right to independently determine the cross-section of building materials for frame structures. This work must be carried out by a design engineer, taking into account the number of floors of the building and local conditions.
We do not have equally strict requirements for the design and calculation procedure. The cross-section of the support for a high and wide pediment can be calculated independently. They are calculated as compressed structural elements, i.e. They check only for compression resistance.
The minimum rack size is 100×100 mm. If a support of this size does not meet the technical requirements, enlarge one of the faces of the block and again check for resistance to bending. If necessary, the calculation process is carried out again until a cross-section of lumber that can easily withstand the load is obtained. Do not forget that a paired board can be used instead of a block.
Rack installation step
It should be remembered that with an increase in the number of frame supports, it becomes possible to reduce the cross-section of lumber used for their construction. This does not mean that instead of a frame you can build a “picket fence” from a thin block, because in the majority of situations, the pediment frame must resist vertical compressive force and support the door and window frames.
The choice of distance between racks is influenced by:
- Width of the insulation mat. The insulation must be firmly fixed in the cell between the rafters.
- Sheathing sheet width. For example, OSB or plywood or plasterboard panels must be supported by at least three vertical bars. This means that the installation step will be equal to half the width of the panel minus 5 - 7 cm to fix the edge of the slab.
- The width of the window or door frame. It is desirable that in order to arrange the openings it is not necessary to cut the frame supports, because the resistance of the structure to compressive and horizontal loads will decrease.
When constructing the pediment of a frame house, the supports of the end walls of the attic are installed directly above the racks of the frame walls of the first floor.
In principle, cutting supports to install boxes after constructing the frame is practiced among craftsmen. However, such methods require strengthening the structure with additional racks on the side of the installed box and horizontal lintels placed above the opening.
Insulation from steam and winds with rain
A barrier from the wind from outside the structure and from the effects of household fumes from the inside is constructed if the use of the attic space is planned. Such gable frames are insulated in accordance with the rules for thermal insulation of frame walls.
The thickness of thermal insulation is taken in accordance with the instructions of the collection of standards for building climatology. Mineral wool mats are used as insulation, the width of which is 1–2 cm greater than the distance between adjacent rafters. Thermal insulation is installed by surprise into a cell limited by the rafters, straightens out in it, and then tightly fills the entire space.
If the calculated thickness of the thermal insulation layer for the attic gable is greater than the adjacent size of the support, then the missing distance is increased by lathing. In addition to compensating for the missing thickness of lumber, the slats are designed to perform another important function - they form a ventilation gap between the insulation layer and the wind protection located on the outside.
Two schemes for organizing ventilation of insulated gables are used:
- Two-level. This type involves the formation of two ventilation channels 2–3 cm wide. The first of them is arranged between thermal insulation and wind protection, if it is made of reinforced polyethylene film. A second channel is created between the windbreak and the external cladding of the gable.
- Single-level. It is assumed that only one ventilation duct will be installed between the façade finishing and the wind protection. The scheme is applicable if a diffusion membrane is used as a wind barrier, which can be in contact with thermal insulation without a ventilation device between them.
The laths are attached to the posts of the pediment frame along their direction if it is necessary to increase the thickness of the bar for laying insulation in one layer. The same method is used to form vertical ventilation ducts. If thermal insulation is constructed in two layers, then the laths and the outer layer of insulation are installed in a cross to the racks.
A vapor barrier layer is attached in the same way to the inside of the attic gables. A ventilation gap is also required between it and the inner lining of the attic.
The gables of cold roofs are insulated according to a different scheme. Because Living within uninsulated attics is not planned, then the need for a vapor barrier automatically disappears, but wind protection is installed. Ventilation of cold attics is constructed according to a single-level scheme, regardless of the type of insulating material used.
Attaching frame supports
The method of fixing the frame supports depends on the type of base to which the fastening is made. They are placed on floors made of reinforced concrete slabs or beams made of timber, logs, sewn boards, or pressed wood. In all cases, the racks are in direct contact only with wooden parts. When installed on a reinforced concrete base, brick or concrete walls, the supports are attached to the mauerlat bars.
When fixing to horizontally laid structural elements, a T-shaped frontal fastening scheme is used. A perfectly trimmed rack is installed perpendicular to the mauerlat or ceiling beam, its position is reinforced by side plank overlays. Instead of overlays, metal toothed corners and plates can be used.
Installing gable wall supports on a log is somewhat more complicated. To implement it, you must first select nests in the end logs of the upper crown for installing racks. Marking of nests and subsequent installation of frame elements is carried out using a control cord. Then, lower teeth are selected on the support blanks, complementary in size and shape to the sockets arranged.
After forming the elements of the locking connection on the log and blanks of the racks, the line of the upper gash is determined. The search for it is carried out during the fitting of each workpiece to the installation site. The gash line is outlined by placing the tooth in its intended socket. According to the markings, they are filed down, returned to place and fixed at the top with one wooden overlay to the rafters from the attic side.
Anchoring the gable wall
Low-rise buildings are not very resistant to wind loads, especially if they are fully or partially made using frame technology. A gusty wind can easily not only overturn light structures, but also carry them away. For gable roofs with framed gables, aerodynamic rules apply by analogy with airplane wings.
Often news reports about hurricanes that have occurred somewhere indicate the number of roofs that were torn off. To prevent such situations from happening, the rafter structure is attached to the walls of the building with wire twists to metal ribbed pins hammered into them - ruffs.
The supports of the gable frame also need to be strengthened and connections to the foundation through the walls be formed. Those. the pediment posts must be connected to the walls, which in turn are fixed to the base of the house, because a lightweight frame structure requires not only spatial rigidity, but also reliable fixation to stable structures.
To ensure spatial rigidity, it is recommended to take the following measures:
- It is advisable to sheathe the gable on the windward side with rigid slabs.
- In regions that require increased structural rigidity, it is better to construct the subfloor over the attic beams from tongue-and-groove boards rather than from sheet material.
- If the gable is installed for an uninsulated roof, then spacers should be installed to increase the rigidity of the gable frame.
In order for the load to be redistributed to the walls and foundation, all structural elements must be firmly connected to each other. Connections are made by anchoring, the need for which increases acutely during the construction period, when the walls and roof of the house have already been built, but the door and window openings have not yet been equipped. It is needed to withstand both horizontal and vertical influences.
The size of the anchor bolts and the distance between the fastening points are determined based on their slope of the structure, the size of the covered span and the width of the overhangs. In order not to get involved in mind-numbing calculations, you can use the tables of Norwegian engineers, compiled on the basis of many years of practice in low-rise frame construction.
Anchoring of gable walls is carried out:
- To concrete floors. Anchor bolts for resistance to horizontal loads. Anchor bolts paired with metal corners to resist vertically directed forces.
- To wooden floors. Metal perforated tape and slats nailed to the post and the upper ceiling to resist vertically acting force - winds.
Strengthening the fastening of gables to wooden floors against horizontal load is carried out during the installation of supports; it is believed that the fasteners installed during the assembly of the frame are quite sufficient.
Before installing gable overhangs, if they are included in the project, and performing cladding, door and window openings are arranged, boxes are constructed in which frames with opening sashes will be mounted. If you plan to install only dormer windows in a non-residential attic, then you can cut holes for their installation after installing the board cladding.
Construction of a gable overhang
If it is planned to install a gable overhang to protect the wall from the harmful effects of slanting rains, it is constructed from shortened rafters. Naturally, no insulation or special calculations are needed for this. It is only desirable that the width of the gable extension be approximately equal to the width of the cornice.
The outer rafters are nailed to the vertical supports and the upper crown, trim or mauerlat, between which the lace is pulled. These mini-rafters are first only attached, and after determining their optimal position they are finally fixed. To ensure rigidity, each element of a kind of canopy is equipped with a rafter leg of the appropriate size.
Ordinary mini-rafters are installed according to indications with laces and fastened in the same way. It is not necessary to mount them near each frame post. The distance can be approximately 1 m, because there is no serious snow load on the gable overhangs.
After installing the rafter system, a sheathing is installed under the gable overhang along the shortened legs with a pitch corresponding to the material chosen for installation. Then you can safely begin the finishing and cladding work: make the gable cladding as presented in one of the methods described on our website, lay the roofing material on the overhang and place a tin flashing along the line where the gable wall and overhang meet.
Stage 2: Preparatory work
Before purchasing materials, you need to draw up a drawing of the future canopy, in which you indicate the exact location of the load-bearing elements. The pitch for fastening the sheathing for the canopy should be taken depending on the amount of precipitation in a particular region and windiness. On average, the step should be 0.5-0.6 meters. After this, the required amount of materials is calculated and purchased.
Visor attachment diagram.
Next, after drawing up the diagram and purchasing materials, all wooden and metal parts should be processed. The wood is treated with antifungal liquids in 2 layers, a primer and aquastop. Metal materials (if they do not have a factory protective coating) are primed in 2 layers and painted. All materials must be given time to dry, and the boards must be kept for several days so that they straighten and do not have internal stresses after transportation. After which they are cut into parts of the required size.
Selection of material for casting
Metal tiles, roofing tiles, slate, roofing iron, etc. are used in the manufacture of drip linings.
Experts recommend making flashings for the pediment from the same material that was used as roofing. This will create a common style throughout the house, but the use of dissimilar materials can introduce dissonance into the overall composition.
The main materials for making castings are the following:
- metal tiles;
- tiles;
- slate;
- roofing iron;
- tree;
- plastic;
- bitumen shingles.
Each of these materials has its own advantages and disadvantages. Products such as metal tiles or slate have high reliability and a long service life, but they are heavy, and special supporting structures need to be made for them. And the craftsman will also need to perform a number of additional works at the joint between the ebb and the wall of the house. After all, the structure of these materials does not allow them to fit tightly so that there are no gaps where rainwater or melted snow can get in.
Stage 3: Installation of the visor
The sealant is needed to fix leaks on the roof canopy.
The canopy begins to be sheathed with roofing material only after the pediment has been sewn up. To do this, the material, pre-cut to the required dimensions, is lifted up, placed on the sheathing and secured with self-tapping screws to the sheathing. It is important that there are several attachment points per beam.
The material itself is laid so that there are no leaks at the joints. To do this, sheets of slate, metal tiles, corrugated sheets and a number of other materials are overlapped. Other materials such as roofing felt or bitumen shingles are laid continuously, and the joints are reinforced with an additional layer of material.
If metal roofing materials are used for the coating, they are fastened using self-tapping screws with a special rubber gasket. If slate is used, it is secured with slate nails. Soft tiles and roofing felt are laid on glue.
The last job that needs to be done is installing the flashings. For them, a stainless steel sheet is often used, which is cut into strips about 20-25 cm wide. Next, the sheet is bent along the length by about ¼ of the width (5-6 cm). Then it is attached to the junction of the canopy and the pediment. The attachment points should be on both the gable and the canopy. The gaps that will be between the ebb and flow, as well as between the ebb and the canopy, should be sealed with sealant or silica gel. After the first rain, check the tightness of the cracks. If a leak is detected, it should be repaired with sealants.
After this, the visor is ready. It is worth noting that if slate is used as the material for the canopy, it can be painted in any color.
—>
| Google Ads |
| Site search |
Pediment cladding
There are many options to add decorative value to the pediment with your own hands, these include: cladding, wooden and other sidings, plastic and corrugated sheeting, and others. But regardless of the material, you should proceed in the following order:
- Calculating the area is important for choosing materials according to cost estimates. Formulas from a school textbook will be useful for this; knowing the edges of the desired figure, the area is calculated using formulas from the school textbook. It is necessary to subtract the area of windows and doors from the total area, and also take a reserve for damaged material.
- Installation of the sheathing - the sheathing is installed in a classic manner, without any special features; this stage is notable for the need to lay waterproofing and thermal insulation materials, especially if the room is residential.
- Installation of a drain - it is necessary to lay the panels carefully and overlap.
- Facing is carried out according to the instructions supplied with the material.
Installation of gable canopies.
Canopy, pediment, ebb.
To prevent precipitation from falling on the end walls (under the gables), canopies are installed at the bottom of the gables . Since there are two pediments, there will also be two pediment canopies.
The canopy is made before the pediment is mounted.
The overhang of the canopy (the distance from the wall to the edge of the canopy) is selected so that rain does not fall on the walls. My visor overhang is 60cm, but this is not enough. If I were making a canopy now, the overhang would be about 80cm so that during rain you could stand under the canopy and breathe fresh air (i.e., smoke).
Frame for the pediment.
First, we mount the window frame from a bar with a cross-section of 50mm by 100mm. We adjust the intersection of the bars so that the window frame fits into it. Window sizes depend on your needs. If there is a full room in the attic, then the dimensions may be larger. The internal dimensions of my attic window frame are: height - 50cm, width - 85cm. It was just that such a window was available.
Installed mini canopy rafters.
Next, a base is made from a 50mm by 100mm block - mini-rafters for the canopy with supports (green in the picture). In my case, the length of the mini rafters is 80cm. The length of the support is 50cm. These dimensions allow you to make the overhang of the visor about 60cm. However, as I already said, it is advisable to make the overhang of the visor larger, 75 - 80 cm. Then the length of the mini rafters will be approximately 100cm.
Mini - rafter and support.
Nails for fastening mini rafters and supports.
Photo of mini rafters.
The end of the mini rafter on the back side of the pediment.
Mini rafters are nailed to the top log, to the window frame and to the front truss posts. The support is inserted with a spike into a recess hollowed out in the log and secured with a nail driven diagonally into the side.
Sheathing bars are nailed to the top of the mini rafters in two rows using 100mm nails. It is advisable to choose a section of the bars that is no less than 80 by 50 mm, since we will walk on these bars when installing the pediment. The distance between the bars is 30 - 40cm.
Fastening the ends of the sheathing.
For strength, the ends of the sheathing can be screwed to the gable overhang.
We complete the installation of the canopies after installing the gables.
Covering the canopy with slate.
We nail sheets of slate (ondulin) cut to the size of the canopy.
In order to prevent moisture from slanting rain or snow from flowing under the canopy from the gable, we make ebbs from galvanized iron. The ebb is bent as shown in the photo.
We screw the ebbs to the pediment and to the sheathing (through slate) with screws of the appropriate length (pediment - 4mm by 25mm, sheathing - 4mm by 120mm). For tightness, under each screw we place an M5 washer and a rubber gasket with a diameter of 10 - 15 mm.
Materials used
The following describes how a horizontal gable overhang can be arranged:
For these purposes, lining is sometimes used. This option is considered one of the most convenient. Before installing it, you need to carry out processing. It is not necessary to use a finishing tongue and groove board here.
Lining is considered one of the most comfortable materials
Instead, you can use pine or spruce boards. A beam is nailed to the wall along the edge of the rafters. A board is attached to it from below. And only after that the lining is attached. It is believed that there should be a distance of 2 cm between the boards. In addition, it is recommended that a ventilation hole be installed instead of every third plank. These measures are necessary to ensure ventilation for the roof.
Corrugated sheet
You can also use a gable roof overhang made of corrugated sheets. Since it is made of metal, during installation it must be taken into account that it can change its size depending on the temperature. Therefore, you need to attach the strips, providing a small gap between them.
It is recommended to attach corrugated sheets using self-tapping screws. It is not recommended to use nails for this purpose.
Gable roof overhang made of corrugated sheets
Blank PVC panels
Such an overhang will be easily damaged, however, this option is the cheapest. The installation is similar. How to install a clapboard overhang.
On our website you can get acquainted with the most popular plots in the Moscow region for the construction of a country house. In the filters you can set the desired direction, the presence of gas, water, electricity and other communications.
Steel sheets
The thickness of the sheets usually ranges from 0.6 mm to 10 mm. Steel must be galvanized to protect the metal from rust. Sheets of other materials can also be used: copper or aluminum. When installing them, actions similar to those previously discussed occur.
Since during the work you will need to cut sheets of galvanized steel, you need to take into account that the edges are not protected from rust. To fix this, you need to paint them in this place.
It is not recommended to use sheets longer than 5 m. This is due to the fact that otherwise they will sag.
Wall siding
This option is advantageous to use in cases where the house was lined with it. If the same material is used for the gable overhang, it will look stylish.
Use of metal soffits
This option is considered reliable and durable.
Such an overhang will be quite expensive
It is made from galvanized iron, copper or aluminum. Not only is it of good quality, but it also looks beautiful.
Content:
The pediment is a section of the wall that is located between the roof slopes, at the bottom of which a cornice is installed. The pediment, one way or another, is present in any roof, with the exception of a hip or hip roof. The gables of houses built from logs can be divided into several types:
- triangular - classic;
- trapezoidal;
- pentagonal.
In fact, in construction there are generally more varieties of this element, for example, semicircular.
Quite often this element of the roof is called the face of the house. But, meanwhile, it also has a certain function, namely, protecting the roof, and the house as a whole, from the effects of wind and precipitation. In other words, its design and construction must be approached with the utmost care.
Features of a gable roof
Structurally, such a roof consists of several elements:
There are several types of gable roofs:
broken line - the traditional version, which is based on an isosceles triangle;
symmetrical - it is chosen if the room under the roof will be used as an attic; it is the roof with equal sides that allows you to create the most extensive living space;
the asymmetrical design of the roof makes it extravagant; in this design, the ridge is slightly offset from the center, which is why the attic space is reduced.
There is also a multi-level gable roof that will decorate any home, but its implementation is complex, so it is not common.
Pediment structure
Formally, the pediment is a wall mounted on a mauerlat, but this element can include a cornice and overhang, which are built together with it.
The overhang is a part of the roof slopes that frame the gable on the sides and smoothly transition into the cornice. The size of the overhang beyond the pediment is not standardized anywhere, but practice shows that it is usually built at 0.4 - 0.7 meters. Here it should be noted that the more it protrudes, the better the protection of this element from precipitation on its surface. When forming the roof slope, one must be guided by the fact that it is in harmony with the overall architectural design.
Front overhang structures
Let's start with the concept of a front overhang - this is a continuation of the elements of the roof slope, framing the end gable on the sides and in the final stage turning into a cornice.
Building codes do not regulate the width of the overhang; it usually ranges from 40 cm to 70 cm.
Design solutions can be made as follows:
The overhang is formed by roof sheathing . This is the most economical way. Simply when installing the sheathing, the rafters are extended by 30-50 cm above the end wall.
This constructive method is used for light roofing coverings (soft roofing, European slate, metal tiles). There are also restrictions on the width of the overhang, no more than 50 cm. If you make the width larger, the roof will warp and bend due to the heavy load on the rafters.
- A method in which there is no gable overhang . This is when the gable is located at the same height as the roof. Inherent in buildings in the style of minimalism.
The overhang is made parallel to the rafter structure. Rafters are installed both inside the roof and outside the roof gable. The rafter leg plays the role of a foundation for the sheathing and roof.
To strengthen the overhang, intermediate beams and support ridges are taken out, which are classified as load-bearing elements of the roof. This scheme allows for a large overhang.
Used on roofs with heavy roofing (concrete tiles, slate, ceramic tiles).
Pediment canopy
Construct a canopy on the pediment of a wooden house using sheathing during its installation on the rafters. They simply make it longer so that a canopy (overhang) is formed to a given length. This method is used for roofing that will be covered with lightweight materials, for example, bitumen shingles. For heavy materials, this method of forming a canopy (overhang) is not entirely suitable; the sheathing boards may not withstand the load.
Another method of forming a canopy is done using a rafter system. Before making the canopy on the pediment, the mauerlat beam is made slightly longer. In this case, the first pair of rafters and the ridge beam will form it. The distance to which the timber will be carried determines the size of the overhang. It should be said that the second method of forming an overhang is more expensive and more difficult to implement, but this design allows it to withstand any weight of the roofing.
How to make a roof gable
Today in the construction of low-rise buildings there are three main approaches to how to properly build the gable of a house. The main difference is in the method of erecting and tying the vertical gable walls to the frame and roof rafters:
- For small one-story buildings, gable parts are often made simultaneously with rafter assemblies, using one template, which ensures high accuracy of the entire structure. In this case, a gable roof is installed, starting with the installation of gables and ridge beams, and only then the rafter pairs, struts, and sheathing are installed. Thus, it is easier to assemble a gable roof for a bathhouse or a country house;
- For buildings with increased roof slopes, the roof gables are arranged and covered with boards after the rafters, sheathing and all the load-bearing elements of the frame are installed. The more complex the roof structure, the later the gable parts are made;
- Brick buildings can be built according to a combined scheme. If the plane of the roof gable is supposed to be covered with brick or aerated concrete masonry, it is erected before the rafter system is installed.
For your information! Pre-built gables greatly facilitate the construction of the rafter frame during strong gusts of wind, but require very careful adjustment of the dimensions so that gaps do not form between the overhangs and the masonry due to mismatches in the sizes of the beams.
The easiest way to assemble a gable structure is to make a frame sheathing structure from wooden planks or timber, lay insulation, a layer of waterproofing and cover the surface with plastic siding or clapboard. The scheme for laying insulation on the gable of a house is in many ways similar to roof insulation.
Finishing gable siding
The use of these modular panels, which are made from PVC or sheet metal, will not require annual processing. In addition, manufacturers offer the consumer a wide range of color solutions, which allows you to choose the color that best suits the roof or finished wall of the house.
By the way, when covering the front wall, you need to think about how to make a flashing on the pediment. Although there is nothing special to think about, it is installed using approximately the same technology as those that stand in window openings.
Subtleties of the rafter system
You need to understand that the front walls erected after the installation of the rafters can be built using bricks or blocks. But, at the same time, you need to understand that the walls located underneath them must have sufficient load-bearing capacity. The width of the supporting wall should be wider than the pediment itself, at least 5 cm.
Why should you sheathe the gable of a house?
One of the tasks that the pediment must solve is protecting the under-roof space from bad weather. That is, it prevents heat loss from the ceiling, and protects the attic from wind, rain and snow. In addition, if it is planned to arrange a living room in the attic, then it is even more necessary to thoroughly insulate it. The sheathing in this case will be part of the thermal insulation.
In addition, a sheathed front wall, after finishing, for example painting the pediment of a wooden house, gives the house a finished look.
Cladding of the pediment
After this wall is built, the homeowner is faced with the question - how to sew up the pediment of a wooden house? The answer lies on the surface - it is sheathed with the same material that is used for the external decoration of the walls of the building, for example, clapboard.
This method of cladding can be safely called classic; it will never lose its relevance. The thing is, the wood from which the lining is made perfectly protects the building from low temperatures and wind. But when using lining, you must remember that it will have to be treated with protective compounds and coated with paint or varnish at least once a season. If these measures are not carried out, then in 10 - 15 years a major repair of the pediment of a wooden house or its complete replacement will be required.
Types of pediments
In addition to classification by appearance, as discussed at the beginning, these roof elements are divided according to the method of construction. That is, those that are built before the roof is erected, and those that are equipped after all the roofing work is completed, and one must understand that there are serious differences between them in the method of arrangement.
The first ones, as a rule, are made of the same material as load-bearing walls, that is, brick, logs, etc. When making such a structure for this element, it is necessary to build temporary and permanent support, which must be installed from the attic side.
The construction of such a structure will require the future homeowner to carry out careful calculations of the structure and, of course, extreme precision during its construction. There are known cases when, at the stage of arranging the roof, cases arose with the connection of the pediment and the rafter system. By the way, violations during the construction of this structure can lead to it simply falling to the ground.
If the gables erected at different ends of the roof have different shapes, then the rafter system will be skewed. Moreover, if the pediment is built from logs or beams, it is much easier to eliminate this problem than on those structures that are raised from blocks or bricks.
This method will require additional costs and time from the homeowner, especially if errors made during its construction are identified.
Sometimes this approach is used, that is, the construction of the front wall is carried out simultaneously with the roofing system. This approach is necessary when, according to the requirements of the working documentation, some parts have to be built into this wall.
The second approach, that is, the construction of the front wall after the construction of the rafter system is completed, is much simpler. The work starts after the last rafters are installed, and the boundaries of the front wall are immediately drawn in front of the builders.
This method of constructing a pediment is used quite often, especially when constructing country houses. To build the front wall, they use a frame, which is insulated, and then they decide how to cover the pediment of a wooden house with boards or siding.
The frame for the construction of this wall can have a different design, when choosing which, the future homeowner should be guided by the following criteria:
- roof height at ridge;
- how many windows or doors will be installed in the gable.
What is a pediment
The pediment of a building is the front part of the facade, located on top of the building, limited on the sides by the roof slopes, and below by the eaves of the house. From a design point of view, the pediment is the “face” of the house, since it is on it that the gaze of passers-by and family guests falls. That is why it is so important to properly decorate this part of the house. From a construction point of view, the pediment is also not fun, but a very functional part of the house. The main tasks of the pediment include:
- fixing the roof position, as well as imparting rigidity to the building frame in general and the roof in particular;
- acting as a protective barrier for the attic (attic) space, the pediment prevents precipitation, birds, and insects from entering the attic;
- thermal insulation of the attic, helping to maintain a favorable microclimate in all rooms of the house;
- improvement of the attic space from the outside and the possibility of creating a separate living or other functional attic room inside.
Materials for building a pediment
To build a pediment, you can use different materials. When choosing a material, you must be guided by what the load-bearing walls of the house were built from.
If the walls are built from bricks or blocks, then the pediment is often constructed from the same material. That is, it becomes a kind of continuation of the wall.
Wooden houses mean that this part of the structure should not be overly massive and therefore the pediment is made according to the following scheme - first they build a frame, and then it is sheathed with some kind of material.
There is another variant of the design of this architectural element, it is called chopped. As a rule, they are used in the construction of log houses. In this case, the pediment is also a continuation of the wall.
But the frame method is considered the simplest and least expensive. It can be constructed on a building erected using any building materials. If the homeowner plans to make the attic habitable, then, of course, it is necessary to insulate the gable
Roof design options with gables
There are many ways to arrange and decorate the pediment plane. It is clear that the specific design solution largely depends on how the owners intend to use the under-roof or attic space, but at the same time it is necessary to take into account what materials the building frame and roof are planned to be constructed from. Most often, the gable wall is finished in the form of:
- Prefabricated frame made of wooden slats, DSP or OSB boards with laying a layer of thermal insulation and external finishing with siding or lining, edged boards;
- Masonry made of red brick or aerated concrete followed by surface finishing with cement-sand plaster;
- Laying timber or logs in the form of a continuation of the vertical part of the load-bearing walls of a log house.
The building with a roof of 4 gable sections looks very impressive. In this case, the four triangles or trapezoids of the pediments of the roof of a wooden house become an integral part of the facade, therefore, for a brick and wooden house, the structure is adjusted so that the masonry is visually perceived as one whole.
Calculation of the quantity of materials
The calculation is performed at the design stage of the house.
Usually the pediment is shaped like a triangle. Its top is the ridge of the roof, the two sides are its slopes. Usually this triangle is isosceles - the ridge is in the center. But sometimes the geometry of the pediment can shift. In any case, the sides of the pediment and the end of the rafter system coincide and represent the same figure.
Typically, craftsmen begin calculating the required amount of material by determining the height of the ridge - this figure will be the height of the entire pediment. It depends on what functions the attic space will perform. If a full-fledged floor of a residential building is planned here, then the height of the ridge is usually made from 270 cm to 350 cm. If a simple attic is meant, then a height of 200-250 cm will be sufficient. However, it is worth considering that if the height of the pediment is small, the entire house will will look squat.
If the pediment has the shape of an isosceles triangle, simple geometric formulas can be used to calculate its area:
H = ½ × L × tg a – determination of the height of the pediment by the angle of the slope (where a is the angle of the slope);
tg a = 2 × H / L – determination of the angle of the triangle at the base or the steepness of the roof (where H is the height of the ridge).
S = H × L / 2 – calculation of the pediment area based on the base and height;
However, if the pediment triangle is not isosceles, then these formulas need to be adjusted. So, each side will have its own slope angle (a1 and a2). And instead of (½ × L), in the first formula it will be necessary to substitute the distance from the point of the vertical projection of the skate on the base of this triangle to the angle (L1 and L2).
If you do not have a mathematical background to calculate tangents, various construction sites have special calculators for calculating the area of the gable.
Stages of work
First, the craftsmen mark the walls and find the middle - in order to understand where the ridge will be located. If the roof is asymmetrical, the projection of the ridge is shifted to the required distance. After this, a rail is attached to the supporting wall - it is also called a mast - which should reach the height of the future ridge. The master will be guided by this mast in his work. At the end of this rail, nylon cords are attached, which are then stretched to the sides and secured to the corners of the wall. This design will be a kind of projection of the future boundaries of the pediment. At the same stage, they plan at what height the windows will be located, if they are included in the project. Their level is marked on the rod.
A) Construction of a pediment from brick or block. After this, they begin to lay out the pediment. After several lower rows, the order of installation changes - work begins not from the edge, but from the middle of the future pediment. In this case, you need to leave openings for the windows and focus on the stretched cord. As a result, the upper edges of the pediment should be stepped. A groove is left at the top of the triangle - it is needed for laying the so-called ridge girder. Sometimes, to strengthen the structure, the lower rows are reinforced with steel rods. In general, laying a brick pediment requires special care. Each row must be measured with a plumb line and level.
The standard mortar for masonry is mixed - cement and sand in a ratio of one to three.
After installation, the “fresh” pediment is supported from the inside by something durable, for example, thick boards. So that during drying it does not lead.
After the solution has completely dried, you can begin installing the rafter system. First of all, the ridge purlin is laid - the central board at the top of the roof slope. Then the so-called rafter legs and racks that will hold the ridge are attached to it.
B) Construction of a pediment from a log or timber. The blanks for a chopped pediment have different lengths - they should decrease towards the ridge, forming something like a pyramid. Logs or beams are attached to each other using dowels. In the case of building a chopped gable, it is usually possible to avoid skewing of the roof, since both gables are laid at the same time. This is due to the fact that during construction, they are connected to each other by slings, which are laid along the edges of the triangles being erected. The topmost slab is called princely - it serves as a support for the ridge of the roof. The rafter legs will rest on the remaining legs. The distance between the legs can be different - 80-150 centimeters.
It is believed that working with logs requires special carpentry skills, so without experience, it is better to invite specialists to build a log house.
Usually, even at the roof design stage, provision is made for attaching an overhang to it above the gable. Which will partially protect it from precipitation. After installation, the overhang is sheathed with plywood, clapboard or siding. In this case, special openings are provided - ventilation ducts - to ventilate the under-roof space.
Covering the gable opening
The construction of gable walls is carried out using different materials, the main thing is that they exert as little pressure as possible on the load-bearing walls. Typically, hollow bricks, foam blocks, boards or any sheet material are used. In order for the cladding to blend harmoniously with the house, as shown in the photo, it is better to make it from the same material that was used for cladding the facade.
Covering the pediment of a wooden house
The front opening of a wooden house is covered with siding, corrugated board, wooden boards or any other similar material. Calculate material consumption using the following formulas:
- for a triangular shape, the calculation is made by multiplying the height by half the width of the base;
- a complex shape is divided into regular geometric shapes, for example, a square or a triangle, and their area is calculated.
The boards are nailed to the end wall. If the sheathing is made with siding or other similar material, a sheathing is made for them, taking into account the installation of insulation.
Brick lining
In houses with brick walls, the gable opening is filled with similar material, only the masonry is not made in two rows, but in one row. At the junction of each row with the roof slope, the corners of the brick are cut off to reduce the gap. If the wall is erected before the rafters are installed, then a contour is made from a cord under it, which is gradually laid with brick.
When sewing up an opening with any material, it is necessary to provide openings for windows, of course, if they are necessary. Large pediments are reinforced on the inside with pilasters.
Facing and insulation of the pediment
When calculating the facing material for the facade of the house, you need to make a certain reserve. But before its installation, the façade opening must be insulated. If the attic will be equipped as a living space, the thermal insulation must be separated by hydro- and vapor barrier. All this work is carried out simultaneously with laying the roofing pie. A brick wall can be insulated from the outside with polystyrene foam under the plaster, so as not to take away the internal usable space. After all the work is completed, all that remains is to arrange the overhang by making it with your own hands from the side of the gable. You can see how to sheathe a pediment in the following video.
What else to read on the topic?
Stages of work
A properly sheathed end of a building should represent a strong supporting structure. You can do this yourself, adhering to the exact execution of the following installation steps.
Preparation
The design of the pediment should begin by preparing the wall base. To do this, it is necessary to remove the old coating and cover the surface with a new leveling compound.
Laying waterproofing
A waterproofing material is first placed on the dried surface or it is coated with a special compound that repels water (mastic or sealant)
Particular attention should be paid to the boundaries of the pediment and the joints of surfaces. The waterproof material is attached with a slight overlap: approximately 10-16 cm
Frame installation
After laying the waterproofing, a box is mounted on the wall surface. To do this, the prepared slats are secured with dowels along the boundaries of the pediment. Then the frame bars are mounted on them with screws. All wooden elements are pre-treated with an antiseptic. The remaining bars are fastened at a distance of 50 cm. Using a building level and a metal ruler, align the bars parallel to each other.
Installation of insulation
Thermal insulation is a mandatory element of covering the end of the roof with corrugated sheeting. A layer of insulation placed under sheets of thin steel will ensure that heat is retained inside the house while suppressing noise coming from outside. Foam plastic or mineral wool is used as insulation, which is placed in the nests of the sheathing.
Laying vapor barrier
After laying the insulation, it is necessary to carry out vapor barrier work: lay the film with the rough side inside the room. It is laid with an overlap, and the sheets must overlap each other by no less than 10 cm. All seams must be sealed, leaving a hole for ventilation.
Cutting and laying corrugated sheets
Finishing the pediment with corrugated board is called sheathing or cladding. The purpose of this procedure is to protect the entire structure from heat loss and moisture penetration while simultaneously increasing rigidity.
The final procedure for laying profiled sheets also consists of several stages.
- The cutting of corrugated sheets is carried out on the ground according to the drawings prepared in advance and the results of gable measurements. Using hand tools (grinders), steel sheets are cut into blanks. The finished cutting is lifted up and carefully placed on the sheathing.
- The first fragment of corrugated sheeting must be fixed in the left corner of the gable sheathing. The right corner should complete the layout of the cut elements. Sheets located at the border of the sheathing should have a gap of about 5 mm. This is necessary to fix the material on the sheathing. The sheets are laid vertically with an overlap of approximately 15 cm.
- The sheets are fastened with self-tapping screws at intervals of no more than 30 cm. First, holes are marked with a drill on the bottom of the wave. Then use a screwdriver to insert self-tapping screws into the sheathing bars.
- The perimeter of the pediment is equipped with facing corners, fixing them with self-tapping screws. Mounting tape secures the connection of the corners with the gable wall.
- The finishing of the pediment should be completed by installing flashings.
DIY pediment
Work on arranging the roof of a house requires construction experience and skills in handling household tools.
In order to make a gable roof gable, you will need the following tools and devices:
- high and stable stepladder;
- roulette;
- square;
- level;
- perforator;
- screwdriver;
- Bulgarian;
- cutter;
- knife;
- hammer;
- wood hacksaw;
- mallet;
- mites;
- electric drill;
- pliers;
- welding machine;
- smooth, serrated and rubber spatulas.
Universal set of materials and components:
- electrodes;
- nails;
- screws;
- cutting discs;
- roofing screws;
- sandpaper;
- steel corners;
- adhesive mixture;
- varnish;
- dye;
- stain;
- antiseptic solution;
- grout for seams;
- mastic;
- assembly helmet;
- safety glasses, gloves and gauze bandage.
The lists can be shortened or expanded based on the chosen method and materials for finishing the roof of the building.
The work is performed according to the following algorithm:
- Carrying out measurements, drawing up drawings, calculating building materials.
- Arrangement of the supporting structure. This can be a wall made of bricks, boards, panels or supports between the floor slab and rafters.
- Create single or double sheathing depending on trim orientation.
- Installation of waterproofing and insulation.
- Fastening the facing material to the frame. The technology corresponding to the type of finish is used.
- Finish lining. Decorations, decorative elements, platbands for windows and doors are fixed to the surface.
Dimensions
The strength of the base for fixing the facing material depends on how large the area of the pediment is. The wide and high vertical surface experiences strong wind loads. The base must be strong enough to withstand any horizontal pressure from the outside. In addition, the load is transferred to the roof, which must be sufficiently stable.
Based on the factors listed above, the optimal height of the pediment should be no more than 200 cm with a width of up to 800 cm. This rule does not apply to masonry made of brick and aerated concrete blocks. Walls made of these materials have their own support on the walls of the building, which transfers the load to the foundation.
Size restrictions do not apply to window and door sizes. The main condition is that these structures do not weaken the strength of the supporting structure.
How to make?
To make a strong and beautiful pediment, you must adhere to the following recommendations:
- You need to choose a material that has a service life no less than that of the roofing, so as not to have to deal with repairs every 2-3 years.
- Installation is best done on stable, factory-made scaffolding.
- You need to cut the workpieces on the ground. This way the work will be done accurately and safely. Lifting should be carried out using slings after secure fixation.
- Laying of all types of cladding is carried out from the bottom up, after fixing the ebb.
- You only need to work with working tools with undamaged housings and power cables.
Gable trim
When choosing a finish for the end of the roof, you need to focus not only on its cost and ease of installation. The texture and color of the material plays an important role in the exterior of the house. These parameters should be organically combined with the coloring of the walls, roof of the building and nearby buildings.
You can change the color of the coating using paint, colored varnishes and stain. A good visual effect is achieved by using techniques such as: artistic carving, laying out stripes or mosaics, stencil painting and airbrushing. Several different types of finishes can be attached to one surface.