In order not to fall for their marketing ploy, you need to understand what the term “Canadian frame house” includes.
Many developers will be very surprised to learn that in Canada they actually build frame residential buildings not from SIP panels, but with mineral wool insulation.
Local authorities in Canada are interested in having as many such energy-efficient houses on their territory as possible, helping developers in every possible way, for example, connecting these facilities to central utility networks for free.
What does the concept mean?
By this term, experts understand a prefabricated structure with a completion period of 2 to 5 months .
The basis of the house is a wooden frame formed from solid wall structures. Houses can be produced both for permanent residence and for seasonal residence in the form of summer country houses.
The difference between them is in the thickness of the insulation; in the first case, a reinforced layer is installed in the wall - from 200 mm, in the second - no higher than 150 mm.
In addition, permanent residential buildings for permanent residence are characterized by a significantly high level of life support . Such a household must have reliable autonomous or centralized sources: electricity, water supply, sewerage and heating.
The issue of mandatory gasification in the regulatory plan for houses with permanent and seasonal residence is not fixed; everything will depend on the availability of main gas pipelines in the development area.
to erect such buildings in any place, on any soil, without fear of subsidence of load-bearing structures. Such buildings do not need a reinforced foundation, since the weight of wall structures and roofs is small compared to stone structures.
Frame houses in Canada are built only by certified teams; the work of each stage of construction is checked by state supervision; without its visa, the house cannot be put into operation. This ensures high quality houses and long standard service life - more than 100 years.
There are two options for constructing Canadian buildings using frame technology - on site, on site and in a factory using modern CNC machining equipment. Canadian developers, according to statistics, build frame houses on the construction site in 89% of cases, and only in 11% of cases are they prefabricated. This is due to the significant difference in cost of these construction options.
Canadian prices for the construction of frame housing construction: assembly of factory-made elements on the construction site - $1,800 per 1 m2; modular frame-panel buildings, houses 18x4.9 m - $2,500 per 1 m2; ready-made factory house with utilities - $3,500 or more per 1 m2.
Typical wall pie, insulation used
Canadian technology for the construction of frame houses implies low cost per square meter and at the same time very low thermal conductivity of the walls. Such a balance of price-strength-high thermal insulation is possible when high-quality structural materials and modern insulation are used in construction. A typical frame house wall pie is as follows: external cladding, OSB panel cladding, hydro-windproofing membrane, insulation, vapor barrier layer, internal OSB panel cladding, interior finishing. A very important element in this whole scheme is the insulation; it is its quality and thickness of the layer that determines how long the house can retain heat inside itself and how much energy is needed for heating. In classic frame construction, stone wool based on basalt fiber or ecowool is used.
frame house pie
- Stone wool made from basalt fiber. Very low thermal conductivity coefficient, relatively cheap, easy to install, breathable. But it has one drawback - if the insulation technology is not followed or if it is exposed to moisture for a long time, it gets wet and completely loses its original thermal insulation properties.
- The insulation is based on cellulose, ecowool, light gray in color, 80% made from recycled cellulose (paper), 12% from antiseptic (boric acid), 8% from fire retardants (borax). All components of this material are non-toxic to the body. Ecowool perfectly retains heat in the house, does not rot, allows steam to pass through, can withstand open fire for a long time, and is cheaper than basalt fiber. It is poured into the cavity or applied by spraying.
Differences in design
Despite the external similarity of frame structures, Canadian ones differ in the installation of reinforced headers in the openings when the board is installed on the edge, as well as the use of double racks in the openings and on the top trim. This significantly strengthens the structure of the frame, so they are mostly built two-, three-story and with an attic living space.
The main structural differences of Canadian frame buildings:
Power post-beam frame: dry planed board 150x50 mm.- The strapping for the top and bottom is a double and sometimes triple board, in the case of using LVL beams made of ply veneer.
- In this house design, the floors are never covered after the walls.
- The walls are assembled on the floor and must be installed exclusively on a ready-made platform.
- The frame is covered with OSB of 12 mm and higher; in this case, the jibs are not installed.
- In the case where OSB cladding is not provided, and the box is sheathed immediately with facade cladding, for its strength, jibs are installed, they are cut into racks at 45 degrees, resting on the upper and lower trim.
- Mineral wool in slabs is used as insulation and sound absorber, since it is easier to install it between racks by surprise.
- The key to durability and energy efficiency is the presence of a vapor barrier layer with a thickness of at least 200 microns.
- The foundation can be erected columnar with a grillage or on screw piles. Often Canadian houses are built on an insulated Swedish slab.
- An opening in a non-load-bearing wall does not bear large loads, so a regular box is installed and finished with plasterboard, natural panels or imitation natural material, OSB boards.
- The lintel over the opening in the load-bearing wall is reinforced with several boards.
- Boards in interfloor ceilings are installed on edge on the top frame.
- For rooms where the length is greater than the length of the boards, an intermediate beam support is installed to prevent sagging.
- The typical ceiling height in a Canadian house is traditionally about 3 meters for the first floor, and no higher than 2.6 m for the subsequent ones.
- Wood, calibrated, dry with a moisture content not exceeding 15%. The quality of drying is so high that these units are not impregnated with anything, only those areas that are in direct contact with the concrete. They are impregnated with antiseptic at the factory under pressure. The Canadian technology of using dry wood without treatment has proven its reliability in practice; such houses have been in use for more than 100 years without impregnation.
- As a roofing covering, bituminous shingles are most often used with a guarantee of at least 35 years.
- For Canadian frame houses, it is allowed to use only open electrical wiring made from insulated wires, which are secured with special brackets that have limited depth so that the wire remains free and not pinched.
- The most common intra-house heating system is a water heated floor, since it provides the lowest cost of heat per 1 m2 of heated area.
- Energy-efficient ventilation with heat recovery is used.
What materials are used
When the frame of the future house is ready, it’s time to make the walls. OSB boards and moisture-resistant plywood are used as wall materials. OSB boards consist of wood chips glued together under a press; they are very dense and perfectly repel moisture. Moisture-resistant plywood is not inferior in strength characteristics to oriented strand board, but it tolerates moisture less well; with prolonged exposure, its surface begins to warp. Plywood is a little more expensive than OSB board, so pressed boards are most often used.
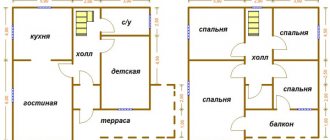
Options for layouts and projects
All such households, starting from the middle of the last century, have been built with complex architecture :
- multi-storey;
- with warm attics and a warm garage;
- verandas;
- terraces and balconies.
Premises on the 1st floor, as a rule, have high ceilings up to 3 m, large square, rectangular or arched windows. The first floor is a guest floor, there is a spacious hall, living room and dining room. The second floor is used for living rooms, there is also a nursery and an office.
Furnaces are usually located in basements, and air heating is provided throughout the house through a duct system. A general air conditioning and ventilation system is also installed. There is a separate laundry area in the basement or utility room on the first floor.
Exterior finishes in most parts of Canada are imitation brick, a material bonded to the outside of the wood frame. Roofs are often covered with asphalt or cedar shingles; recently, metal tiles have become more popular.
The most common roofing materials
Since the walls, roof frame and interfloor partitions of a frame house are quite light in weight compared to cottages built using classical technologies, and the strength of the frame building is very high - at the request of the owner of the house, the roof can be built from any material: ceramic or polymer sand tiles, corrugated sheet, asbestos-cement sheet (slate), ondulin (corrugated bitumen sheet). The only requirement when choosing a roofing covering is that the slope of the roof slope according to the construction project corresponds to the permissible angle of inclination of the roof made of the material of interest. The cheapest option would be a roof made of corrugated sheets, but metal does not have good sound insulation. Roofing made of bitumen-based materials, such as ondulin (aka Euroslate) or polymer-sand tiles, perfectly protects the upper floor from the sounds of rain, falling hail and wind. In frame house construction using Canadian technology, a soft roof based on bitumen is more often used. If you plan to make an attic or attic living space in your house, you need to think about good insulation; the material could be wall insulation that was used on the lower floor - stone wool or ecowool.
Video with the full cycle of building a frame house in Canada:
Features of construction technology
Despite the fact that this group of houses belongs to the frame type, they have their own characteristics :
When constructing a frame, a platform is first assembled to cover the 1st floor, which will become the base of the frame skeleton.- The walls are assembled on a platform in a horizontal position, they are then raised and installed strictly vertically on the lower frame along the foundation.
The maximum inter-column distance along the axes is 600 mm, which further allows for reliable and tight installation of insulation mats. - Set of multi-layer wall.
- Making the top lining of the walls with boards.
- Making a multi-layer floor, the boards are laid on the top frame on the edge.
- For long rooms it is possible to install an intermediate support beam.
- Arrangement of warm corners.
- Construction of a technological opening for windows and doors; a lintel made of double or triple boards is installed in the load-bearing walls.
- To stabilize wall structures, 25x100mm jibs are installed at an angle of 45 degrees with respect to the vertical support posts.
Bevels or braces
These elements are necessary if the frame of the house walls is being assembled on site. The slopes can be temporary - on the inside of the walls, if it is intended to cover the frame with any slab material. These elements are needed in order to set the racks in a strictly vertical position and fix them until the sheathing is completed. After this, the cuttings are removed.
When using stacked cladding, for example, lining, you need to install permanent braces. They are installed on each pair of racks, 4 pieces - 2 on top and 2 on bottom. You should not neglect this rule, since during the sheathing process the racks may “float” and the geometry will be disrupted.
Advice! To reduce construction costs, you can use the technology of prefabricated racks, which are assembled from two boards. To do this, they need to be knocked down with nails in a checkerboard pattern in 20 cm increments. Of course, construction will take more time, since each rack will have to be assembled separately, but the load-bearing capacity of these elements is several times higher.
General pros and cons
Canadian houses, together with German modifications, are among the most durable residential frame buildings.
The main advantages of Canadian frame buildings:
- Low cost per 1 m2 of area, from 100 dollars.
- High speed of construction from one to two months, depending on the configuration and level of factory assembly.
- High heat, noise and moisture protection characteristics.
- Environmental Safety.
- Low unit costs for maintaining and repairing such a house.
- High strength and wear resistance of the structure; the service life of most of these projects is more than 100 years.
- All-season construction.
- Not demanding on complex and expensive construction tools and mechanisms.
- Biological and fire safety, thanks to special impregnation with antiseptics and fire retardants.
- Allows you to build an object according to any design decision.
The disadvantages of such houses include the need to attract highly paid specialists for construction.
Video description
Larry Hohn's film:
The Work of a Master shows that the construction of a durable building requires not only experience and skill, but also the selection of materials with the necessary technical characteristics. Unfortunately, when creating a home, “there are no small details.” For example, an incorrectly created foundation or a violation of roof insulation technology leads to premature destruction of the house.
The process of constructing a frame house Source 1asku.ru
Average prices for installation work
After the project has been selected and the basic components of the home have been cut out, the developer must select a contractor for construction and installation work.
The ideal option in this case is the “turnkey” option, when the customer works with one contractor from project development to putting the house into operation. In this case, the manufacturer gives the customer the most serious warranty period of 10 years or more.
The cost of construction work is almost individual, depending on the project, number of storeys, basic equipment, level of engineering support and type of finishing work.
Average prices for installation of Canadian houses depending on the number of floors and area:
summer house, 1st floor, 8.3x9.2 m, 76 m2, kit production price: 750,350 rubles, installation of frame and roof - 690,000 rubles, installation with utilities and finishing, from 1,050,350 rubles;- summer house, 1st floor, 11.2x12.4 m, 125 m2, kit production price: 1,099,200 rubles, installation of frame and roof - 790,000 rubles, installation with utilities and finishing, from 1,002,000 rubles;
- summer house, 2 floors, 8x8.3 m, 130 m2, kit production price: 1,399,200 rubles, installation of frame and roof - 870,000 rubles, installation with utilities and finishing, from 1,210,000 rubles;
- warm house, 1st floor, 11.2x12.4 m, 125 m2, kit production price: 2,300,000 rubles, installation of frame and roof - 890,000 rubles, installation with utilities and finishing, from 1,102,000 rubles;
- winter house, 2 floors, 8x8.3 m, 130 m2, kit production price: 2,600,100 rubles, installation of frame and roof - 1,050,000 rubles, installation with utilities and finishing, from 1,470,000 rubles.
Advantages of Canadian frame houses
This type of construction has gained enormous popularity due to its advantages:
- Cheapness of building materials and the type of fasteners used.
- Short construction time. The construction of the entire house from the foundation to the roof can take from a week to a month, after which it will be necessary to install utilities, perform finishing and bring furniture.
- Frame construction can be done at any time of the year, regardless of the season and weather conditions.
- There is no need to use heavy equipment or special vehicles when constructing a structure.
- Frame technology allows you to build complex geometric structures; you can easily bring to life any design solutions and original ideas.
- The wall pie turns out very warm. The thermal insulation of the entire house is excellent, without having to overpay for the outer layer of insulation.
- High level of sound insulation. Noise does not enter the rooms through the external walls of the house from the street and through the interfloor ceilings.
- Lightness of the entire structure of the house. There is no need for a massive foundation with great depth.
- A great flight of fancy for external and internal decoration; the technology allows the use of any cladding options and types of finishing materials.
- Electrical wiring and other communications can be hidden inside the walls.
Video with an overview of a typical American frame house (house 110 years old):
Insulation
To insulate a frame structure, you can use any of the known insulators that meet the characteristics and requirements for thermal insulation:
- Mineral wool - meets all the requirements, but it is worth remembering that this material is not moisture resistant and, when wet, can lose its insulating properties by 30-50%. To prevent such consequences, you need to install high-quality vapor barrier.
- Polystyrene foam is the most inexpensive and popular insulation material that does not absorb moisture, does not sag, and retains heat well.
- Basalt wool is a natural insulator that can be purchased both in rolls and in mats.
- Expanded polystyrene is almost the same foam, but its fraction is much finer. The material meets all sanitary standards, does not absorb moisture, and retains heat well. The only drawback is that direct sunlight destroys the material.
Important! When choosing the size of the insulating material, it is worth remembering that the slabs should be 2-4 cm larger than the gaps between the posts, so that when installing the insulator there are no unwanted cold bridges.
The choice of insulation material depends on financial capabilities and the region of construction, but it is better not to skimp on insulation, since this determines how much money you will spend on heating the room.