Introduction
Plywood is a multi-layer material made from veneer. The number of veneer layers is always odd, that is, there are three-layer, five-layer and multi-layer. There is plywood that can have 23 layers. To maximize strength, the layers are always arranged perpendicularly, although, of course, there may be options with a parallel arrangement, but this is a very rare case and should not be taken into account. Plywood differs in its strength from other wood panels, such as chipboard.
Plywood is processed and sawed without the use of any special industrial tools; you can even use an ordinary household jigsaw and simple wood saws.
Areas of application
Due to its excellent technical characteristics, this type of material is widely in demand in several areas:
- construction;
- packaging;
- industrial;
- carriage building;
- radio engineering;
- shipbuilding;
- furniture, etc.
It is used in concrete and roofing processes, is used in automobile and carriage construction, and serves as the basis for large and small packaging containers. Suitable for outdoor use, because it not only resists moisture well, but also nails, drills, and saws well.
Plywood classification
Despite its apparent simplicity, plywood has a number of different classifications, among which the following main criteria can be distinguished:
- By quality (grade). This classification distinguishes different groups according to the type of quality of the top layer;
- By type of adhesive. This classification defines different degrees of moisture resistance of plywood depending on the adhesive composition used in manufacturing;
- By processing the top layer. This classification determines the type of processing of the top layer.
Veneer for making plywood
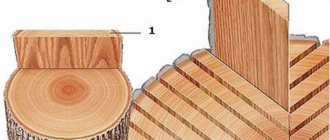
Veneer is the main element of plywood, which is thin sheets of wood with a thickness of 0.1 mm to 8 mm. To understand the features of plywood, you need to talk in more detail about the veneer from which it is made.
Normative base
Veneer production is regulated by the following regulations:
- GOST 99-96 “Rolled veneer”
- GOST 2977-82. "Sliced veneer"
- GOST 99-89. “Rolled veneer” (obsolete)
Type of production
There are three main methods for producing veneer:
- Peeling;
- Planing;
- Sawing.
Peeled veneer
For the peeling operation, special peeling machines are used. The principle is as follows: a log (a sawn tree trunk, cleared of bark) rotates around its own axis, and a special knife of a peeling machine, located parallel to the log, cuts off a thin layer of wood of a given thickness. As the block rotates, the knife moves towards its center, thereby ensuring an even thickness of the veneer. Both coniferous and deciduous wood species can be used for peeling:
- pine;
- birch;
- Linden;
- beech;
- oak;
- maple;
- ash;
- fir;
- cedar;
- alder;
- aspen;
- spruce
etc.
Sliced veneer
To obtain sliced veneer, the surface of the wood is cut (planed) on special machines. In this case, the width of the resulting veneer does not exceed the width of the planed timber.
By varying different angles of the knife relative to the longitudinal axis of the timber, you can get different patterns and textures. Both coniferous and deciduous wood species can be used for planing:
- pine;
- birch
- beech;
- oak;
- pear;
- elm;
- chestnut;
- Red tree;
- Linden;
- ash;
- alder;
- maple;
- velvet tree;
- nut
etc.
Sawn veneer
This is the simplest and oldest method, in which a plate 0.5 - 5 mm thick is simply sawed off from the workpiece. For the production of sawn veneer, both coniferous and deciduous wood species are mainly used:
- pine;
- birch
- beech;
- oak;
- Linden
etc.
"Fine-line" veneer
If the result of the types of veneer production discussed above is a thin sheet of wood, then “fine-line” veneer is an artificial veneer. It is based on wood, but also contains glue and dyes (about 8%). To make it, natural veneer is taken from soft wood, soaked in special solutions and dye, after which it is glued and pressed under high pressure into special bundles. These pressed bundles are then cut into ultra-thin sheets called “fine-line” veneer.
The resulting veneer has a number of advantages:
- like natural veneer, it is environmentally friendly;
- has no defects on the surface, unlike traditional 100% veneer;
- it can have any pattern, texture or just a solid color applied on it;
- high – elasticity and flexibility;
- Inexpensive types of wood are used for its manufacture, which makes it less expensive than traditional 100% veneer;
- moisture resistant, that is, can be used in rooms with high humidity.
However, there are also disadvantages, namely:
- Low strength (fragility). Due to the use of soft wood, it is susceptible to deformation under mechanical stress;
- Possible appearance of cracks. To increase strength, the material is coated with varnish, which under certain influences can form cracks.
- The presence of artificial components (8% glue and dyes) does not allow this material to be classified as 100% environmentally friendly.
Fine-line veneer has a wide range of applications. For example, it is widely used in the production of furniture, doors, flooring, as well as various decorative materials to create interior design solutions.
Additional points
FSF plywood, made from softwood, is much more suitable for construction than the same birch plywood. It is used as a frame in the construction of buildings; it is an alternative to OSB. FSF plywood is mainly coniferous and is considered a direct competitor to OSB. Builders, when it is necessary to lay subfloors, mainly use FSF coniferous plywood. Fasteners can be easily screwed into this material. It has high elasticity and is not subject to deformation. The properties listed above are the main advantages of coniferous plywood in comparison with birch grade.
Another positive property of coniferous plywood is its excellent wear resistance and enormous strength when chipped.
When such coniferous plywood is made, due to the high porosity of the pine needles, the glue is immersed much deeper into the veneer layers, resulting in increased flexibility and increased strength of the material. This type of plywood is endowed with excellent thermal insulation properties. Builders use coniferous slabs for especially critical structures.
Plywood grade
The quality of the top layer is the most important parameter, which largely determines the quality of the plywood itself and its scope of application. The number and nature of defects allowed on its surface determines the grade of plywood. Thus, there are five main types of plywood.
| GOST99-96 | GOST 99-89 (outdated) | GOST 10.55-71 (outdated) | Nature of acceptable defects | Application |
| Grade E(Elite) | A | — | This is the highest grade, in which visible flaws and damage are not allowed. At the same time, a very small amount of defects is still acceptable. The presence of falling knots and holes made by them is strictly prohibited. | This type of plywood is used in the production of laminated plywood, and can also be varnished. |
| Grade I | AB | IN | This class also has almost no defects and flaws, however, the presence of knots (falling out, partially fused, not fused) or holes from them is acceptable. Small wormholes are acceptable, which should have a diameter of no more than 6 mm, and no more than three pieces per square meter of area. | This grade of plywood is used in the production of laminated plywood. |
| Grade II | IN | BB | The presence of falling knots and holes from them is allowed, and there may also be wormholes, no more than six pieces per square meter of area. In addition, the presence of fused knots (diameter no more than 25 mm), no more than ten pieces per square meter of area, is permissible. We will allow surface repair by decorating with veneer inserts. | Coating with varnish and paint is allowed. |
| Grade III | BB | SR | The presence of falling knots and holes from them is allowed, and there may also be wormholes, no more than ten pieces per square meter of area. The number of healthy fused knots is not limited. | It is used for the production of containers and packaging, and it is also possible to create structures without external visibility. |
| Grade IV | WITH | WITH | The presence of falling knots and holes from them, manufacturing defects may also be present, and there may also be wormholes with a diameter of up to 40 mm in an unlimited quantity. | It has increased strength and is used for the production of containers and packaging. |
Southern part of Moscow
The FaneraMonolit company delivers plywood to all central administrative districts of the Russian capital, namely:
- SEAD (Kapotnya, Lefortovo, Nekrasovka, Kuzminki, Yuzhny Port, Pechatniki, Tekstilshchiki and Lyublino, Maryinsky Nizhny Novgorod and Ryazan districts, as well as in Vykhino-Zhulebino).
- Southern Administrative District (Biryulyovo (both Eastern and Western), in all parts of Chertanovo, in Tsaritsyno, in the South and North, Orekhovo-Borisovo, Zyablikovo, Donskoy, Brateevsky, Nagorny and Danilovsky districts, as well as in Nagatinsky Zaton, Moskvorechye Saburovo and NagatinoSadovniki).
- SWAD (Butovo (both Northern and Southern), Zyuzino, Kotlovka, Konkovo, Teply Stan, Cheryomushki, Gagarinsky, Obruchevsky, Academic and Lomonosovsky districts, as well as Yasenevo).
Also in the southern part of the capital are Novomoskovsky and Troitsky districts. We also deliver plywood to all settlements, from Voskresensky, Vnukovsky and Kokoshkino to Kievsky, Troitsky, Pervomaisky.
Plywood marking
Plywood, like any other building material, has markings based on its various properties.
The following parameters used for marking are distinguished:
- by type of adhesive
- for processing the top layer
- by formaldehyde content
- decorative plywood marking
Let us examine these notations in more detail.
By type of adhesive
The moisture resistance of plywood is determined primarily by the composition of the adhesive. Depending on it, the following grades of plywood are distinguished.
| Designation | Adhesive composition | Moisture resistance | Application |
| FC | Urea adhesive with the addition of formaldehyde resins | Yes | It can be used both indoors and outdoors. belongs to a high class of environmental cleanliness. |
| FSF | Phenol-formaldehyde glue | Yes | It can only be used outdoors, as the binding components are hazardous to health. It is used for the manufacture of laminated plywood, which is used in the construction of external structures. |
| FBA | Albumocasein glue | No | It can be used indoors. |
| FB | Bakelite varnish | Yes | It can be used in any climatic conditions and at maximum humidity. Withstands exposure to sea water. |
| BS | Alcohol-containing bakelite glue | Yes | The characteristics are even better than those of FB. It is often used in aircraft and shipbuilding, which is why it is also called “aviation”. |
| BV | Bakelite composition | No | Since water-soluble bakelite is used in production, plywood is not moisture resistant. However, plywood is quite durable. |
By processing the top layer
An important parameter of plywood is the quality of the top layer of plywood and its processing. A special marking for this parameter has been defined.
| Designation | Description |
| Ш1 | The veneer is sanded on only one side of the plywood |
| Ш2 | The veneer is sanded on both sides of the plywood |
| NS | The veneer of the top layers of plywood is not sanded |
According to formaldehyde content
Since formaldehyde is very harmful to human health, the amount contained in plywood is important and affects the environmental friendliness of the material.
| Designation | Formaldehyde content per 100 g of material |
| E1 | does not reach 10 mg |
| E2 | from 10 to 30 mg |
| E3 | from 30 to 60 mg |
Marking of decorative plywood
Decorative plywood (DP) can be covered with various film coatings and paper, which give it a unique appearance and additional enhanced characteristics. The following brands are distinguished.
| Designation | Facing coatings | Resins |
| DF-1 | Transparent, does not hide the texture of natural wood | Urea-melaminephore-maldehyde |
| DF-2 | Opaque with decorative paper to imitate the texture of precious wood. Any design is possible. | |
| DF-3 | Increased water resistance. Transparent, does not hide the texture of natural wood | Melaminephore-maldehyde |
| DF-4 | Increased water resistance. Opaque with decorative paper that imitates the texture of precious wood. Any design is possible. |
Properties and characteristics
FSF plywood has many advantages that are important for working with it. The most important thing is that it is moisture resistant and retains its strength. The density of the material determines its strength; the better the bonding of the layers and the more of them, the better these qualities. Moisture resistance is explained by the fact that FSF plywood is laminated, while it does not lose its technical characteristics.
Many manufacturers test the finished building material for delamination by prolonged soaking or boiling in water. After such manipulations and drying, the layers do not come apart and retain their original shape.
The building material is resistant to mechanical damage. Having a special structure, plywood is resistant to tears, bends and other deformations. FSF plywood is fireproof, as it is treated with special substances. Plywood sheets are impregnated with antiperine; in terms of strength and fire resistance, it is compared to steel. In order to cause the material to burn, a temperature above 400º C is required, and the combustion process will proceed slowly.
The material is convenient to use, easy and quick to assemble, process and install. To secure it, you can use self-tapping screws, screws and nails. FSF plywood can be easily combined with other materials of natural or synthetic origin. Plywood can be sawed, cut, sanded and coated with finishing agents.
Among the technical characteristics, it should be noted the light weight of the material and attractive texture pattern, environmental safety and thermal conductivity. The material becomes environmentally friendly after special treatment; without it, the material is toxic and can only be used for exterior decoration. To increase the safety and environmental friendliness of the material, at the stage of gluing the layers, a substance is added that absorbs harmful formaldehyde vapors.
Classification of plywood by purpose
General purpose plywood
Plywood is a very unique and versatile material. It is used in a wide variety of areas: construction of structures, interior design, furniture manufacturing, in the aviation industry, shipbuilding, spacecraft, in the manufacture of children's toys, homemade tools, structures for playgrounds, house construction, etc.
The range is very wide due to the high mechanical characteristics of the material, environmental friendliness and affordability.
Plywood for construction
For example, it is widely used for the construction of internal partitions in apartments and offices; Formwork is made from plywood for pouring concrete structures. In addition, this material is often used to form the surface of the ceiling, floor, and walls.
There are no special quality requirements for plywood used for such work. As a rule, grades 3 and 4 are used in construction. The thickness is selected depending on the tasks that it is designed to solve. For example, for the construction of formwork, sheets with a thickness of 18 millimeters or more are used. To prepare the surface of the walls for further processing, it is permissible to use sheets with a thickness of 10 - 12 mm.
In construction, coniferous or combined sheets are used. This allows you to reduce costs for materials and thereby reduce the cost of work.
Furniture plywood
Plywood is widely used in the manufacture of furniture due to the fact that it has the following properties:
- Environmental friendliness;
- Durability;
- Strength
- Possibility to give the desired color and texture (laminated plywood)
- Not high cost.
Not all types of plywood can be used in furniture production. The important characteristics of such plywood are:
- high quality surface, there should be no obvious visible defects;
- high resistance to loads, including bending.
- plywood used for the manufacture of front parts must have a sanded surface.
Type of FSF
Its outer layer is covered with a laminate, resulting in laminated plywood. A characteristic feature of this brand is its long service life and excellent practicality. In order for this type of plywood to acquire increased moisture-resistant characteristics and fire safety, it is covered with a thin metal sheet and plastic, and sometimes tarred paper is used. This type has found application in:
- shipbuilding;
- monolithic construction;
- furniture production;
- decoration;
- production of prefabricated houses;
- installation work;
- production of advertising posters, etc.;
- installation of exhibition equipment.
Many positive properties characterize moisture-resistant plywood of the FSF brand:
Table of indicators of calculated resistances of various types of plywood.
- high strength;
- increased moisture resistance;
- after grinding, an absolutely smooth surface is obtained;
- excellent texture;
- easy high-speed installation;
- free processing;
- any sheet dimensions;
- compatibility with other materials.
Such properties have allowed this material to gain great popularity and demand in industrial and construction work.
Special types of plywood
Bakelite (bakelized) plywood
Description
This is a very durable plywood, which is made, as a rule, from birch veneer, impregnated with bakelite glue at high temperature and under pressure (4 MPa), then cooled under pressure. Pressing allows you to close all the pores with an adhesive composition, make the plywood thinner and therefore denser, and also increases its strength.
Thus, the result is a wear-resistant, waterproof, durable, elastic material, which in its physical properties is not inferior to some types of low-alloy steel. In addition, it is not exposed to high and low temperatures (+ / - 50°C) and water, including sea water, does not become covered with fungus, does not rot, and can be used in countries with tropical climates, which is why such plywood is often called "nautical". Its service life exceeds 15 years.
Regulatory requirements for bakelite (bakelized) plywood are formalized in GOST 11539-2014.
Marking
There are two main types of bakelite plywood: FBV and FBS. The difference lies in the composition of bakelite. In the production of bakelite (bakelized) plywood marked FBV, resins are used that can dissolve in water, and in the production of plywood marked FBS, resins are used that are soluble only in alcohol compounds. Since the moisture resistance of the FBV variant is significantly lower than that of FBS, it is obvious that the most common is the FBS variant. FBV plywood can only be used in places where there is no direct exposure to moisture on the material.
The marking table for bakelite plywood is presented below.
| Designation | Description |
| FBS | This is the most expensive production option, which involves complete immersion of all layers of plywood into a bakelite screen with full impregnation. Accordingly, this production method produces the most expensive material. This type of plywood has maximum mechanical characteristics, as well as resistance to aggressive environments and temperature changes. |
| FBS-1 | To produce this type of plywood, complete immersion is not used, but rather the veneer layers are coated (applied) with a bakelite raster. The result is a material that is inferior in strength properties to the FBS type. However, such plywood is also very durable and resistant to mechanical stress, aggressive environments and temperature changes. |
| FBS-A | This is a variation of the FBS-1 production option. The difference is that in this case, a material (veneer) of poorer quality is used, which allows this plywood to be used in places where there are no high quality requirements. |
| FBS-1A | This is the cheapest option for bakelite (bakelized plywood). During its production, impregnation of the inner layers of plywood is not provided; only the outer ones are processed. This, of course, affects the quality of the material, reducing its mechanical and other characteristics, however, its cost is not high and, accordingly, there is a certain scope of its application. |
| FBV | The production technology involves complete immersion of all layers of plywood with complete impregnation in a water-based bakelite solution. |
| FBV-1 | The production technology of this type of plywood differs from FBV in that the outer layers are completely impregnated with the solution by immersion, and the inner layers are only coated. This worsens the characteristics of plywood, but at the same time reduces the cost of its production. |
Laminated (veneered) plywood
The process of laminating (veneering) plywood is coating the outer layers of plywood with some kind of coating. This coating can vary from paper impregnated with a resin solution to plastic.
Description
The cladding process improves both the mechanical characteristics of plywood, its moisture resistance, and also makes it possible to reuse the plywood. In addition, when laminating, it is possible to give it a unique appearance, from the formation of the desired texture or monotonous color to arbitrary ornaments and patterns. Non-deliveries include high price and toxicity, since the material now contains formaldehyde.
The production of laminated (veneered) plywood begins at the stage of creating a type-setting mass and differs from the production of non-laminated plywood. In particular, each layer is processed separately and prepared for lamination; in addition, technology is used only with perpendicular layers of veneer.
Marking
The above GOST defines the designation of this laminated plywood with the abbreviation “FL”. Thus, we distinguish:
- FL is standard;
- FL construction.
In addition, there is marking of the laminating layer:
| Designation | Description |
| SP | Paper |
| W | Reticulate |
| F | Smooth |
Material for production
Waterproof plywood can be different, because the basis for it is several types of wood, which is pre-peeled into veneer. So, it could be:
- coniferous (from fir, pine, spruce, larch - more often used in the construction industry as a variety of bases);
- deciduous (birch or beech, as well as aspen, maple, alder, hornbeam - used for decorative purposes, for finishing).
But, in essence, other tree species that are widespread in a particular geographic area cannot be excluded. That is, whatever there is more of, FSF is produced from. There is even a pear one.
FSF plywood pack
Suitable lumber is peeled and glued with phenol-formaldehyde resins, which make the plywood able to withstand moisture, as well as mechanical pressure and fracture stress.