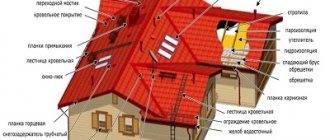
The choice of a specific roof and roofing must be made at the design stage of the building. Modern technologies and building materials allow architects to create a huge variety of solutions both in terms of design features and the coatings and technologies used. When choosing a specific solution, a large number of factors influencing the roof elements are taken into account. Despite such a variety of roof types and designs, they all have several common elements.
Roof elements. Titles
| Roof element name | Short description |
Rafter system | It can be flat, single-slope, gable, multi-slope hip, complex, domed, etc. The rafters themselves can be layered and hanging, whole or extendable. |
Lathing | Depending on the type of roofing materials, it can be solid or lattice. Some roofs have a special ventilation counter-lattice. |
Roofing pie | Used during the installation of warm roofs, it consists of a vapor barrier layer, insulation and wind protection. |
Roof covering | It can be rolled or pieced, made from natural or artificial materials. Roofing materials have a significant impact on its cost and complexity of roofing work. |
The table shows only general names; each type of roof has its own additional elements. Roofs may have windows and gables, gutters and other engineering structures.
The design of a gable roof and its elements
Today, gable roofs with a residential attic (attic) are very popular. Often these rooms are equipped as summer rooms. But you can also find reliably insulated roofs.
Elements of a warm gable roof:
- rafter system - includes rafter legs resting on each other (in pairs). Location: on the walls; one level;
- two pediments or sewn walls - they are formed when the rafters intersect (read: “How to make a pediment with your own hands”);
- roofing pie - consists of sheathing, waterproofing layer, roofing material, vapor barrier membrane, insulation and interior finishing elements;
- drainage system;
- other elements, for example, a viewing window in the roof. Read more: “Gable roof construction: structural elements.”
Types of rafters
There are two designs:
- with layered rafters;
- with hanging rafters.
Installing a roof on a wooden house is only possible using the former. This is caused by two rules:
- hanging rafters must be firmly attached to the mauerlat;
- in a wooden house, the rafters must be hinged to the mauerlat.
These two statements contradict each other, so the rafter system of a wooden house can only contain layered elements.
Only layered rafters are installed in a wooden house
Layered beams are elements that rest on the mauerlat at the lowest point and on the ridge girder at the top. This allows you to reduce the horizontal thrust that acts on the walls when the rafters try to move apart and take a horizontal position. Elements can be reinforced with racks or struts. In this case, contractions can be placed through one pair of legs.
Hanging tanks rest only on the Mauerlat at the lowest point. At the top they just rest against each other. To prevent the system of wooden elements from moving apart, tightening must be done. It is better to install them on each pair of legs. This option is characterized by a strong thrust effect on the external walls, but it allows you to get more free space inside the attic.
Natural ceramic and concrete tiles
The widest range of additional elements is available for roofing made from natural ceramic or concrete tiles. This is due to the fragility of ceramics, although its strength and durability are high. It is not recommended to drill tiles, so separate elements are produced for all possible cases: for snow retainers, ladders, antennas. Ventilation outlets and gable elements are available.
There are special side tiles for gables, they come in left and right. As for the ridge, in addition to ordinary elements, they also produce ridge parts that complete the intersections of several ridges of complex roofs.
Different types of ridge elements, including for intersections
There are many types of tiles; each type has its own range of additional elements. For various types of ceramic tiles, additional elements unique to them are used.
The basis of the supporting structure of the roof
The basis of the supporting structure of a sloped roof is the rafters. They perform a very important function, supporting the sheathing and thereby bearing the weight of the roof, snow and wind pressure. In addition, the design contains additional elements of the truss roof (mauerlat, crossbars, spacers, etc.), which serve to fasten and impart rigidity to the truss frame.
The estimated snow load for the middle strip is 180 kg/m2 in the horizontal projection of the roof. With a slight roof slope, snow accumulation can increase this figure to 400-500 kg/m2. However, with a slope greater than 60°, the snow load can be ignored. At the same time, when the roof slope is more than 30°, rafter calculations must be carried out taking into account the wind load. For the middle zone it is equal to 35 kg/m2.
An important factor is the dead weight of the roof elements and sub-roof structures, which directly depend on the roofing materials used and the size of the entire roof. When using heavy materials (for example, natural or cement-sand tiles) in the rafter system, it is necessary to use large-section timber, installing rafters with a minimum pitch. If lightweight roofing material is used when constructing the roof of a house (for example, Euro slate, bitumen tiles), then even timber with a cross-section of 50 x 150 mm can be used, and the pitch of the rafters can be significantly increased - up to 1.5 m.
Requirements for the rafter system
Rigidity
First of all, each part of the system, as well as the joints, must be rigid, not deforming either under shear or thrust forces. The basis of the entire structure is a triangle. This is exactly the shape of the frames (trusses), which are fixed parallel to each other. Their rigid fixation provides the roof with the necessary stability. But if the farms turn out to be mobile, disaster is not far away. Such a defective roof can itself collapse and the walls collapse.
Light weight
The roof should not be heavy, so the rafter system is usually made of wood. If the weight of the roof is substantial, then the supporting base is made of metal. Or they take coniferous wood, not lower than first grade, with a moisture content below 18 percent. The use of antiseptic treatment and the use of fire retardants for fire protection are two mandatory conditions. Then the fastening points of the roof truss system will be strong and strong.
High quality material
The tree for the rafters should be as follows:
- Wood is taken from grades 1 - 3. There should be a minimum of cracks and knots. There can be 3 knots per meter with a height of no more than 3 cm. Cracks are not allowed along the entire depth, up to half the length of the board.
- Load-bearing elements are made from wooden parts with a thickness of 5 cm and an area of 40 cm2.
- Coniferous boards can be up to 6.5 m long, and deciduous boards - up to 4.5 m.
- Purlins, pillows and mauerlat are made from hardwood. They are treated with an antiseptic.
Soft types of roofing
Roll materials. They can be used on slopes with a slope of up to 50 degrees. The thickness of this type of roof is 1-6 mm, the specific weight of the carpet does not exceed 10-12 kg. The advantages include the relatively low cost and the ability to provide waterproofing even on a zero slope. The main problem is the large number of joints. Previously, paper-based roll materials (tar paper, roofing felt) were used. Today they are gradually being replaced by more advanced bitumen-polymer products.
Roof shapes: A - pitched; B - gable gable; B - tent; G - semi-hip hipped; D - four-slope hip; E - gable half-hip; F - multi-pincer; Z - half-hip attic; I - Attic hip; K - conical forceps; L - hip with a broken slope; M - pyramidal forceps; 1 - slope; 2 — gable (pediment); 3 - hip; 4 - half-hip; 5 skate; 6 - broken slope.
Membranes. This is a polymer that has the most optimal performance characteristics among other rolled materials used for soft roofing. The main disadvantage of this type of coating is the high cost and the need to attract qualified specialists. Among the main advantages:
- durability: service life can reach up to 50 years;
- frost resistance;
- resistance to precipitation;
- immunity to ultraviolet radiation.
Bitumen shingles (shingles). This is a coating that has a wide variety of shapes, color shades and has no “contraindications” associated with the required angle of inclination of the slopes. Therefore, shingles are well used on roofs with complex configurations. Such tiles do not conduct sound well and resist the effects of precipitation and sun well.
Copper tiles
Copper is used in roofing work not only in sheets, but also in the form of finished tiles. This type of roof finishing is durable, highly aesthetic, but very expensive. There are a number of manufacturers of copper tiles and each of them has its own range and design of tiles and additional elements.
There are many types of copper roofing. In the photo - tiles, the basis of which is sheets of fiberglass impregnated with a bitumen-polymer composition
On top of this roof is a fairly thin layer of copper. This type of copper tile is quite flexible, so the additional elements are similar to those used for bitumen shingles.
Additional roofing elements are an integral part of modern roofing systems, without which the roof will not fully perform its functions. When designing a house, it is necessary to take into account that the more complex the roof, the higher its cost per square meter will be. The more complex the roof, the more “additions” will be needed, and this costs money, sometimes a lot. Additional elements for metal tiles have the lowest cost relative to the base material, and the highest cost for natural tiles. Companies supplying roofing materials help buyers calculate the consumption and cost of materials. Having a roof plan, it is worth seeking advice in advance.
Main parts of the roof
The roof is the main final covering of the roof and consists of many components. The main elements that make up the roof:
- Slopes are inclined planes that ensure the removal of precipitation from the roof. The slopes are 95% of the roof. There is only one requirement for them - the angle of the slope must be chosen in such a way as to withstand maximum loads.
- Slanted ribs are obtained at the junction of the slopes and look like protruding corners.
- Skates are horizontal ribs. These elements are designed to cover the gap at the junction of two slopes.
- Valleys, or valleys, are internal angles that are formed at the intersection of two slopes. These elements must be collected in such a way that precipitation does not leak inside.
- Drip cap is the lower part of the slope that protects the walls from water ingress. It is a strip that covers the overhangs from moisture and gives the overhang a clear edge and a complete shape.
- The horizontal part of the slope extends beyond the walls of the building and is called the “eaves overhang.”
- Front overhang is the inclined part of the slope extending beyond the walls.
- A gutter for collecting and discharging precipitation is located along the edge of the slope. The collected liquid is carried away from the house by drainpipes. A drain funnel is installed at the junction of the gutter and drainpipe.
Features of creating a gable roof
For competent construction, they use drawings of a gable roof and design documentation, which indicates all its dimensions (for more details: “Drawings of house roofs - design stages”).
When the walls of a house are built of logs or timber, the function of the mauerlat is performed by the upper beam. But, if the walls of the building are made of brick, to attach the mauerlat to the load-bearing base before installing a gable or hipped roof, metal threaded rods of at least 10 mm are mounted into the masonry and bolts with washers are used. When installing the Mauerlat, an interval of 1-1.5 meters is maintained between adjacent fasteners. To avoid getting the walls wet, waterproofing is laid from two layers of roofing material.
How to properly insulate a roof in a wooden house made of timber
How to properly insulate a roof in a wooden house
Before insulating the roof, the homeowner must understand from which side this work will be carried out. The roof can be insulated both from the outside and from the inside. Based on this, it will be possible to decide which insulation is best for the roof.
But it is necessary to understand that internal insulation is associated with a number of difficulties. External insulation is simpler, but you need to stock up on equipment to perform work at height.
After choosing the insulation method, you need to prepare everything you need:
Make sectors that look like sheathing, its width should be of such dimensions that it will allow you to lay insulation, hydro and vapor barriers. In addition, you need to have tape and a stapler on hand. That is, we can say that with appropriate preparation, roof insulation is not such a difficult operation.
The insulation procedure looks something like this.
After the rafter system is built, its sheathing must be covered with boards. The result should be a structure consisting of many cells that are intended for laying insulation.
Before installation, the resulting structure must be treated with impregnation. Then, at the bottom of the boxes it is necessary to install a vapor barrier for the roof; you can use, for example, a diffusion membrane. And only then the insulation is injected. Its dimensions should be slightly larger than the size of the cell in which it will be placed.
If bulk insulation is used instead of mineral wool or polystyrene foam, it must first be prepared. Sawdust can be used as a base, to which cement can be added. The installation order looks like this. The box for the heater, in which the vapor barrier is already placed, is covered with boards and thus a cavity will be formed into which the mixture is poured.
When performing insulation work from the inside, all work is performed in the reverse order.
Roof elements
Different designs have their advantages and disadvantages, so before erecting a building, the feasibility of using any type of roof should be clearly determined. All elements can be divided into two types: geometric and structural. The former include all kinds of slopes, ridges, ends and valleys, and the latter include rafters, beams, supports, and mauerlats. Each element plays a specific role.
The main load-bearing component of any pitched model is the rafters. They can be classified depending on the type of support, for example, rafters are equipped with a support leg, vertical or diagonal support. One end of the rafters rests against the wall of the house, and the other against the base of the roof. The upper support is often called the ridge, which performs the stabilizing functions of the entire configuration. They can be made from logs, bars or boards. In order to, are often used. They must be made of the same material as the main part.
Types of roof truss systems.
The rafter leg rests on the mauerlat, which can be made of timber or other material. In wooden houses, this is the top point of the wall or an additional wooden element that is placed on its surface.
Ties are L-shaped structures that connect the rafters at the highest points. To increase reliability, transverse beams can be used, which will significantly increase rigidity. Thus, the puffs can be made in an A-shape. The wall that comes into contact with the ridge must be equipped with a special ridge beam placed at the very top. They are made from the same material as the rafters. End beams are used only if the second floor of the building is equipped with walls.
End beams serve to connect the ridge and the wall, but, as a rule, they are placed diagonally rather than at right angles. Like rafters, they can be reinforced with various beams and posts. After the waterproofing measures have been completed, the rafter structure is supplemented with a counter-lattice - a system that acts as a gap between the surface and the waterproofing material. If this issue is not resolved in a timely manner, the moisture that forms from condensation will take a long time to dry out and thereby damage the coating and the structure as a whole.
But do not confuse the counter-lattice with the sheathing - these are different things. Sheathing is the base for the roof, which, in most cases, is made of wood. It is the wooden lathing that allows you to quickly and reliably fasten tiles, slate, ondulin and other types of roofing materials to its surface. The thickness of such boards should vary depending on the type of roofing and can range from 15 to 30 mm. If soft tiles are used for the roof, the surface of the sheathing should not have gaps and should be continuous. Then, instead of boards, plywood or boards made of wood materials can be used, since a continuous arrangement of boards is, at a minimum, uneconomical.
Rafters can form certain planes called slopes. and will be called a slope, hence the division of roofs into single-pitched, gable, hipped and so on. If the slopes have combined surface edges, then such a model will be called a tent model, the description of which was presented above. - this is an indicator that determines how much the roof will extend beyond the walls of the house.
The walls that border the slopes and extend up to the ridge are called external gables. To hide the entire system of rafter elements, a special binder is used. It allows you to improve roof ventilation, which will prevent the formation of moisture. The plane on which two fixed slopes touch is called a ridge. In some types of roofs there may be several ridges, for example, hip or hip roofs. At the bottom, the slopes are attached to the valley, but this element is used exclusively in single-pitch structures.
Roofing
All roofing work can be divided into 3 main groups:
- Procurement. This stage includes selection, sorting or cleaning, cutting of rolled materials. Roofing elements are made from sheet steel, slate is cut, and mastics are prepared.
- Preparatory. The base for the roof is completely prepared.
- Basic. Roofing materials are laid, secured to the base, and cared for after installation is completed.
Valleys and drainage system
The most vulnerable elements on the roof are the valleys, which form the recessed angle; precipitation accumulates in them at any time of the year. That is why the construction of this roofing element must be approached with all responsibility. The valley is a tray with a width of at least 300 mm, made of boards 25 mm thick. It is covered with galvanized, roofing or black painted steel so that its ends extend 200 mm under the roof on all sides.
The chimney is also surrounded by a roofing steel collar. From the ridge side, a sheet of steel needs to be placed under the roof, and from the eaves on top of the roof, the result is a kind of apron. Next to the pipe, the sheet must be placed under the brickwork. According to fire safety requirements, the roofing and sheathing must be no less than 140 mm from the pipe, and all wooden elements must be no less than 400-500 mm.
When choosing drainpipes, you should give preference to a diameter of 100-140 mm; they are located at least 120 mm from the wall. If the roof is covered with tiles or asbestos-cement sheets, then drain pipes will be needed to drain the water. Their basis is roofing steel; they are hung with a slope of 2-3 degrees relative to the corners of the structure.
Dormer windows are also covered with the same roofing material. Carefully separate the junctions between the windows and the roof slope.
Types and purpose of additional elements
The roof of a house today is not only an enclosing protective structure. New technologies and materials make it possible to implement the most seemingly crazy ideas both in roof architecture and in their use. And all thanks to additional elements, of which there are quite a lot. Let's look at the main, most common extras:
- upper and lower valley - strips to protect the junction of two adjacent surfaces;
- eaves slats - to protect roof eaves from precipitation;
- a ridge plate, sharp or flat, bent at a certain angle, protects the junction of the slopes;
- snow barrier - keeps snow and ice from falling;
- end strip - preserves the under-roof space at the ends from moisture, dirt, dust;
- window sill - protects the building from moisture penetration through window openings;
- umbrella for ventilation and stove shafts - a dome over the pipes to prevent moisture from entering the house through chimneys, ventilation ducts and pipes;
- junction strips are an important element that protects the junction of the roofing decking with pipes, chimneys, parapets;
- gutters - designed to drain water from the roof;
- parapets - protect the side flat surfaces of the roof from the penetration of water during precipitation and melting snow.
When installing the roof, you will also need plugs for gutters and ridges, gaskets and seals. All this is purchased in stores or made individually.
Additional elements allow you to implement many interesting architectural solutions
Calculation of the number of additional elements
The calculation of additions is based on the roof or facade design. You can calculate the quantity yourself, taking into account the main point - the necessary additional elements are always purchased with a reserve.
- The cornice strip runs along the entire perimeter of the cornices, so their footage will be the required size of this extension.
- Valleys (lower and upper) are calculated based on the length of all converging edges of the slopes + 10% for overlaps.
- The length of the end strip is equal to the length of all ends of the roof.
- The dimensions of the seal are calculated based on the number of additional panels under which it will be placed.
- Drainage extensions are purchased based on the perimeter of the building plus 10–15% for overlap at joints and for trimming. In addition to the gutters, you need to select funnels, brackets and drainpipes from a material similar to the ebb.
- Additional elements for covering the ridges at the junction of the ribs or longitudinal edges of the slopes are purchased taking into account the total length of the ribs and ridge plus 7–10% for overlap.
Selection of additional elements
When purchasing extras, you need to follow certain rules:
- It is advisable to purchase goods (roofing and accessories) from one seller - if you purchase large volumes, you can get a good discount. In addition, a guarantee is provided on all elements and in case of defects it is easier to replace defective products in one place. When shopping at different retail outlets, it is not always possible to guess the color scheme and texture of the roofing coverings, so purchasing the entire roofing kit at once can save time.
- Additional elements must be installed according to the rules established by the manufacturer. In case of their violation with subsequent damage to the accessories or improper transportation, the warranty does not apply.
- Don't forget to buy fasteners for the extensions. Here you will need a manager's consultation, since each accessory has its own fastening system, and sometimes even several - hardened nails with wide heads, plugs, special bolts with nuts, self-tapping screws with drill-shaped legs and silicone gaskets. You can, of course, get by with ordinary roofing nails, but a beautiful roof needs a decent frame, so today few people use nails the old fashioned way.
Types of wooden roofing coverings
The name “wooden roofing” combines quite a few varieties. They differ:
- by quality and type of wood;
- by installation methods;
- according to the shape and type of plates.
Let's look at the types of plates, since they determine everything else.
Shingle
The word “shingle”, along with the principles of application, came from Poland. Formally, this term combines shingles, wood chips, and shindel.
Shingles (from the Polish word gont) are thin and short wooden plates or planks used to cover roofs - “shingles”.
Encyclopedic Dictionary of Brockhaus and Efron
https://ru.wikisource.org/wiki/%D0%AD%D0%A1%D0%91%D0%95/%D0%93%D0%BE%D0%BD%D1%82
Shingles are made in two ways.
- Split shingles are dies that break off from a block using a cleaver, but due to inaccurate manufacturing, they do not connect well and warp more. In addition, split shingles require more wood and labor, so they cost more.
- Sawn shingles are produced using special machines. It has a lower cost, but when sawing, the structure of the fibers is disrupted and moisture penetrates better into the rough surface after sawing, so the service life of sawn shingles is shorter.
Based on the type of section, shingles are divided into two types.
- Tongue - wedge-shaped in cross-section, with a trapezoidal groove in cross-section (or tongue, flange) cut into the thick longitudinal edge of the “shard”. Its length is 65-70 centimeters, width - 11-13 centimeters. The thin longitudinal edge (edge, ridge or feather) is sharp; when laid, it fits tightly into the groove of the previous shingle. Such shingles can be mounted not strictly parallel to the slope, but with an inclination, which looks unusual and beautiful. It is this variety that is called shingles in everyday life.
The tongue-and-groove shingles are tightly connected to each other, forming an airtight coating - Non-grooved. It is manufactured in the form of ordinary plates up to 10 cm thick without special connecting locks.
Non-grooved shingles are also called shingles.
Due to the complex design of the plates, a tongue-and-groove shingle roof is very durable, but it is almost impossible to make it yourself.
Shingles and wood chips
Non-grooved shingles come in lenticular or rectangular sections and are then called shingles.
Special shingles more than a centimeter thick made from Canadian cedar will last for decades
Shingles got their name from the verb “to tear” - plates 35-100 centimeters long, 15-20 centimeters wide, and a centimeter thick are cut or chipped from a log or lump along the fibers.
If coniferous species are used, then the shingles are split manually using a cleaver (special ax) and a “dryna” - a beater.
The shingles are plucked off using a cleaver and a drill
If soft linden or aspen are used, a shingle machine works better. The historical machine for “drawing” was called a mahal. The master “waves” a log with a knife attached to it, which splits off the shingles from the attached block.
Mahalo - a machine for pinching shingles - requires great physical effort
It is quite possible to make such a machine yourself. You need to movably fasten the end of a heavy log about three meters long with a pin to a heavy long base. Attach a latch for the block on the base a meter from the kingpin, and on the log - a knife-clip with a length of at least 50 centimeters. A handle is attached to the second end of the log for convenience. True, only a physically strong person can work on such a machine.
Video: homemade machine for tearing
Properly made shingles are plastic, do not flake, on the one hand it is smooth and even (and is laid with this side down), on the other it is splintered, which is precisely why it does not crack when driving a nail. It bends only towards the smooth surface. The finished roof is very beautiful and looks like wrinkled scales.
Thin (up to 10 millimeters, and usually 2-3 millimeters) non-grooved shingles of rectangular cross-section are called chips or shavings. It is planed from blocks of equal length and width either by machine or by hand. On the upper side of the chips there are always “spins” that are noticeable when bent. The wood chips must be laid with the smooth surface down, and the “pins” must be directed towards the eaves of the roof so that water flows down them. Chips make it easy to create a coating with a large number of layers, which increases the protective properties of the roof in all respects.
Video: features of roofing chips
Producing the required amount of wood chips or shingles and laying them is within the capabilities of any meticulous non-professional.
Chips lying on the roof often acquire beautiful shades
Video: installation of shingles
Shindel (wooden tiles)
Shindel is often confused with shingles. This, of course, is one of its options, but more labor-intensive to manufacture. The name "wood shingles" is more accurate. Its form and name came to us from Europe: scindula from the Latin verb scindere - to split. Wood preparation is similar to that used in the production of non-grooved shingles and shingles. But then each plate is individually planed on all sides - the thickness is removed from one end, where it will be attached. For a better fit, the plates are butted on the sides, and a transverse chamfer is removed from the bottom edge to facilitate water drainage, or its entire geometry is changed - the edge is rounded or takes on a different shape.
On the side where the shindle will be attached to the roof, its thickness is less
Making a spindle yourself is almost impossible due to the incredible labor intensity.
Depending on the shape of the shingle, you can get a variety of patterns of roofing material
Video: serial production of schindel
ploughshare
The ploughshare is the most beautiful of all types of wooden roofing; it resembles a concave blade with carvings along the edge. The already mentioned churches of the 17th-18th centuries are covered with a ploughshare. And also - boyar mansions and wooden palaces. The ploughshare is made only from soft aspen, cut down in late spring, with the maximum amount of sap. Each petal is a unique piece of art. It takes a lot of wood and a huge amount of manual labor. Therefore, the ploughshare is now used only for the restoration of old and, rarely, for the construction of new churches. When covering a dome, each row has its own “patterns” that differ in curvature. Due to humidity and time, the ploughshare bends even more and creates an impeccable dome shape.
A dome made of ploughshare is very expensive, so this material is most often used for the restoration of ancient temples
The ploughshare represents true ancient art. I saw temples whose heads were covered with ploughshares. It looks incredible. They are covered with a noble silver patina and shine in the sun. It's as if the heads are covered with pure silver.
The ploughshare-covered dome of the chapel of St. John the Evangelist in the village of Zekhnovo, Arkhangelsk region, gives the impression of being made of pure silver
Video: how a ploughshare is made today in one of the monasteries
Only a very few professional woodworkers can use the plowshare.
Tes (plank roof)
Tes are simply boards, often equal in length to the size of the slope or half of it. Initially, they were split from a long log with an ax, and then hewn to a more or less flat surface - hence the name. From that time, only grooves remained on the upper side of the boards for quick drainage of water.
The roof is made of planks using old Russian technologies.
The boards are laid perpendicular to the ridge in three ways:
- in two rows, fitted close to each other. The top row is placed so as to evenly overlap the seams of the bottom row;
The roof is made of planks in two rows: the upper row overlaps the seams of the lower - the bottom row is placed with a small gap of about half the width of the board, then the empty space is covered with the top board - this is a more economical, but also riskier method: there is a danger that when drying, the roof will begin to leak;
Roofing from planks in two rows with a gap saves wood, but it is risky - the cracks of a single row of boards are covered with narrower boards - flashings with an overlap of at least 5 centimeters.
Roofing made of planks in one row with flashing also provides savings
In all cases, the boards of the bottom row are laid with the core down, and the top row - out. Then, when the boards of both rows are deformed, they will create an airtight structure.
If the principle of laying planks is followed, the roof will never leak
You can lay the democratic plank yourself.
Roof classification
Depending on the slope of the roof slopes, there are pitched (more than 10%) and flat (up to 2.5%). In individual housing construction, as a rule, pitched and flat roofs are used. In flat roofs, stagnant water may form on the roof and, as a result, leaks may appear in these places. The advantage of flat roofs is the ability to use them for various purposes. According to the design, roofs can be attic (separate) or without attic (combined). Attic roofs can be insulated or cold. In atticless (combined) roofs, load-bearing elements serve as the ceiling of the upper floor of the building. Attic roofs can be ventilated, partially ventilated and unventilated. Depending on operating conditions, roofs can be used or not. The type of roof is mainly determined by its geometric shape and roofing material. Depending on the shape, roofs can be single-slope, gable, three-, four-slope, multi-slope.
A pitched roof with its plane (slope) rests on load-bearing walls of different heights. This roof is most suitable for the construction of outbuildings.
A gable roof consists of two sloped planes resting on load-bearing walls of the same height. The space between the slopes, which has a triangular shape, is called gables or gables. A type of gable roof is the attic. If the roof consists of four triangular slopes converging at one upper point, then it is called a hip roof.
A roof formed by two trapezoidal slopes and two triangular end slopes is called a hip hipped roof. There are also gable hip (half-hip) ones, when the gables are cut off.
The gable roof of an industrial building with a longitudinal lantern differs from the gable roof of a residential building in the smaller slope of the slopes and greater width and length.
A vaulted roof in cross section can be outlined by a circular arc or other geometric curve.
A folded roof is formed from the connection of individual trapezoidal elements - folds.
The dome-shaped roof is half a sphere in outline, supported entirely by a cylindrical wall.
A multi-gable roof is formed by connecting the slopes of the planes. It is used on houses with a complex polygonal plan shape. Such roofs have a larger number of valleys (internal corners) and ribs (protruding corners that form the intersections of the roof slopes), which requires high qualifications when performing roofing work.
The cross vault consists of four closed arched vaults.
The outline of the spherical shell is a vault resting at several points on the base. The space between the supports is usually used to install translucent lanterns.
The spire-shaped roof consists of several steep triangles-slopes, connecting at the apex.
The roof of oblique surfaces consists of several flat planes supported by load-bearing walls standing at different levels.
A flat roof rests on load-bearing walls of the same height. Flat roofs are most widely used in both civil and industrial construction. Unlike pitched roofs, flat roofs do not use piece or sheet materials as roofing materials. Here, materials are needed that allow the construction of a continuous carpet (bitumen, bitumen-polymer and polymer materials, as well as mastics). This carpet must be elastic enough to withstand temperature and mechanical deformations of the roof base. The thermal insulation surface, load-bearing slabs, and screeds are used as the base.
Classification of wood roofs
The assembly of a wooden roof is always made from piece elements. The laying technology and the principle of construction depend on the shape and size of these elements, which include:
- Schindel. Planks obtained by “splitting” or chopping logs along the grain. Produced both manually and mechanically. For handmade products, differences in shape and thickness are acceptable within the same batch. It was used on the territory of the German principalities.
- Shingles. According to the manufacturing method, it is similar to a shindel, but thinner. By analogy, the geometric dimensions of piece elements may differ. It was used in Rus' in the arrangement of peasant huts.
- Shingle. Figuratively sawn planks with a swallowtail shape in the cut. The narrow side edge, which plays the role of a tenon, is inserted into the edge of the adjacent element with a characteristic groove, thereby creating an almost airtight connection. Used in Western European countries.
- Ploughshare. Lens-shaped parts, reminiscent of the working part of a spoon. Convex elements are made with a smooth or patterned bottom edge, made in the form of peculiar steps. The ploughshare was placed on the domes of wooden churches, and covered towers and boyar mansions with it.
- Tes. Simply full-size boards, they are also gorges. They are laid along or across the rafter system or on logs - logs resting on males. In Rus' in the old days they were used to construct roofs over the huts of rich merchants and wealthy peasants.
The smaller the size of the element, the more often a sheathing is constructed under it. The spacing between the laths is calculated so that there are at least three supports under each longitudinal row of piece elements.
The size of the block for shingle or shingle covering is 50×50 or 40×40 mm. If the length of the roofing part is more than 800 mm, a thicker bar or pole will be required.
For laying gorges, the sheathing is made from a bar with a cross-section of 60×60 mm or poles with a diameter of approximately 70 mm. The poles are hewn into two edges. The laths are attached to the rafters in increments of 60 - 70 cm.
Rafters
As the base of any roof, rafters made of wooden boards or beams are used. This is a load-bearing structure that takes the weight of the roof upon itself, so it is always made of high-quality wood, without cracks or rot. The material for making rafters is softwood boards or beams. They must be perfectly dried and contain a minimum number of knots. It is acceptable to use logs, but they are much heavier.
The support for the rafters is the mauerlat. This is a beam with a cross-section of at least 10x10 cm or a log, necessarily hewn from the bottom side. This element is also designed to ensure that the load on the load-bearing walls is distributed evenly. The upper crown of a log house can be used as a mauerlat for the construction of cobblestone and log buildings.
Rafter diagram for a gable roof. Mauerlat as a support is required.
The cross-section of the rafters is calculated additionally, and it depends on several indicators: the load created by the weight of the roof and snow precipitation, the pitch of the rafters, the size of the span and the slope of the roof. According to the method of installation, rafters are divided into two types: layered and hanging. The first ones are installed obliquely on supports, which serve as external walls (for a single-pitched roof) or internal and external walls (for a gable roof). Hanging rafters rest only on the walls of the building. They are installed in those buildings where there are no additional supports and internal load-bearing walls.
Removal and replacement of the roof
When asked when a roof replacement is needed, the most convincing answer is a wet spot on the ceiling of the home. Especially when water drips from it with stubborn persistence.
It is not worth taking it to such extremes; it is better to regularly carry out an annual inspection of the roof and carry out preventive work in a timely manner. However, if the leak comes as an unfortunate surprise, you need to make a strategic decision. This requires an inspection of the roof and supporting structure.
Read about the prerequisites for roof repair in a private house in our article - When the roof needs repairs.
Roof restoration work involves three possible solutions.
- When the damage affected only the roof, cracks, chips, pockets of corrosion, violation of the tightness of joints, etc. formed on the roof surface; repairs are only needed for the roofing itself. The volume is determined by the area of the lesion. If 40% of the area or more is out of order, it is not advisable to patch such a roof. It is better and cheaper to replace the entire coating. For example, replace slate roofing with metal tiles.
Over time, cracks and through holes form on the slate, which require replacement of damaged sheets or the entire covering
- If the wooden elements of the sheathing are damaged, fungus or mold is found on the surface of the boards or panels, blackening or salt protrusion, you will have to replace the sheathing frame along with the roof. Otherwise, the renewed roof will not last long, and the money will be wasted.
- And the last, worst-case scenario - violations affected the rafter system, the geometry of the attic or attic space was changed. The rafter legs have rotted, and the load-bearing or auxiliary structural elements (crossbars, tie-rods) have sagged. In this case, rafter repairs are necessary, which means complete dismantling of the roof cannot be avoided.
If, as a result of leaks, the load-bearing elements of the roof have become wet and rotted, it is necessary to completely dismantle the roofing pie and repair the rafter system
Dismantling is carried out in the reverse order of installation. For example, dismantling slate is carried out using a hammer and a nail puller. It is more convenient to disassemble such a roof with two people - one knocks the nails from the attic side, and the other pulls them out from the outside. Next, the released sheet is lowered from a height to the ground and stored.
To remove the slate covering, it is necessary to remove all fasteners and carefully lower the released sheets to the ground.
When rebuilding the roof, for example, from slate to metal tile, it is necessary to adjust the shape of the sheathing, because slate is attached to one row, and metal tile to two. The second frame serves to enhance the natural ventilation of the under-roof space. If the covering is changed from soft tiles to corrugated sheets, there is no need to redo the sheathing. If it’s the other way around, you’ll have to cover the slopes with a continuous coating of OSB or plywood.
Under the bitumen shingles it is necessary to make a continuous sheathing on which the underlayment will be mounted
Dismantling must be carried out by a team or with an assistant. You cannot do this alone; safety precautions when performing high-altitude work prohibit being on the roof without a helmet and insurance.
If the roof was fastened with screws (corrugated sheeting, polycarbonate, etc.), then its disassembly is carried out using a screwdriver. The installer sequentially unscrews the fasteners and removes the sheets from the roof slopes.
Sheets of corrugated sheets connected to the sheathing with screws are unscrewed when dismantled with a screwdriver
The most labor-intensive is considered to be the dismantling of a flat roof covered with several layers of roofing felt (up to 5 or more) . When heated in the sun, roofing material eventually bakes into a monolithic carpet, which is very difficult to remove. In this case, a roofing ax is used, with which the roofing is cut out into small islands and disposed of. On large areas, specialized organizations use curtain cutters - a mechanized tool that cuts the roof into pieces. There are wall cutters with electric or gasoline drive. They can only be used if the layer depth is at least 30 mm.
The wall cutter is designed for flat roofs with a thickness of 30 mm or more
Replacing a roof involves carrying out certain calculations. If the weight of the new coating exceeds the weight of the old (removed) one, it is necessary to correctly assess the ability of the rafter system to withstand increased loads. Sometimes it is necessary to strengthen the rafters by adding additional supporting elements. In this matter, using old-fashioned methods is not recommended. It is advisable that the calculations be carried out by a competent engineer familiar with the specifics of the industry.
When replacing heavy types of roofing with lightweight ones, it is enough to calculate the weight of the roof per square meter. For example, when replacing slate with corrugated board, this can be done as follows.
- It is known that a sheet of eight-wave slate weighs about 30 kg and has an area of 1.5 m2. Thus, per 1 m2 there are 30/1.5 = 20 kg.
- The corrugated sheet has dimensions of 1.2x1.2 m. We calculate its area: 1.2 ∙ 1.2 = 1.44 m2.
- The weight of the sheet (depending on the thickness of the metal) is from 7 to 9 kg, so the relative load from it can vary from 4.9 (7/1.44) to 6.3 (9/1.44) kg/m2.
This means that replacement can be done without additional extension of the rafters, since the pressure will decrease by almost 4 times.
Video: dismantling and installation of the roof (slate - metal tiles)
Euroslate
Euro slate (trademarks Onduline, Gutanit, Nuline, etc.) is similar to domestic asbestos-cement sheets only in shape; it is a polymer-cellulose base impregnated with bitumen components. The release program contains all the necessary elements: ridges, valleys, wind parts (gable), elements connecting to walls, ventilation outlets and cornice filler. A cornice element is not needed for a roof made of large-sized sheets. Euro slate is quite flexible, so additional elements are made to fit an average roof with a slope angle of 20°, and during installation they are given the desired shape.
The Euroslate ridge is secured with special nails through the wave
Due to the wavy section of the sheets and the straight profile of the ridge, valley and abutment to the walls, these units are ventilated. If necessary, the gaps can be closed with cornice filler, which also contains small holes closed with “plugs”. Some European slate manufacturers produce additional elements that provide the roof with, if not airtightness, then certainly airtightness.
The valley for Euro slate is shaped like an inverted ridge and effectively drains water
Given the general cheapness of Euro slate, additional elements are not that little, so developers with a limited budget can use alternative options. A ridge, valley and junction made of galvanized, polymer-coated metal will cost less and will look good. On wind overhangs, you can do without a tong altogether by simply bending the outermost wave of a fairly soft roofing sheet and nailing it to a vertical board.
The wind additional element of the tong can be omitted by bending the outermost wave of the profiled sheet. True, it won’t work out so neatly. The fasteners need to be placed more often, every 20-25 centimeters.
Composite tiles
Composite tiles can be conditionally described as improved metal tiles. It has a more expressive profile, quite reliably imitating natural material (ceramic tiles, natural slate or shingles), and is covered with colored stone chips. The ridge elements have a high figured profile and are also covered with a layer of stone dressing. The remaining elements (valley, cornice and pediment strips, abutments) are made of ordinary galvanized metal with a polymer coating. Elements from ordinary metal tiles can be used. The main thing is to get into color.
The ridge of the composite tile is also covered with stone chips. The photograph shows that the valley, unlike conventional metal tiles, is single and is located only at the bottom of the sheets
Of the entire range of basic and additional elements of a composite roof, only the ridge is processed with crumbs. The remaining elements can be made to order from flat sheets of polymer-coated galvanized steel.
Soft bitumen shingles
Since this material is really soft and quite thin, rigid strips made of polymer-coated metal are used as cornice and wind elements. Moreover, they are not placed on top of the roof, but, on the contrary, from below. The plank defines a clear edge; flexible tiles are glued on top of it.
The eaves and wind strips and the lining of these planes are made of metal
From a material similar to the main sheets of bitumen shingles, only the starting (initial) strip, ridge and valley are made. Ventilation is very important for a sealed asphalt shingle roof; manufacturers offer a number of ventilation devices. They are made of plastic in the color of the roof.
Roofing made of bituminous shingles in the process of installation. The starting metal strips (poorly matched in color) are clearly visible; the ventilation aerators located closer to the ridge are covered with tiles. You don't have to do this, they are plastic.