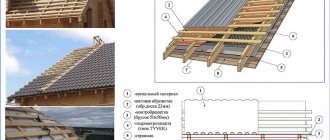
The roof rafter frame is only part of the necessary lumber that is needed to build your own home.
In addition to this, you still need to use quite a lot of material in order to make high-quality and correct sheathing for the roofing material.
This roof element is very important , therefore, when constructing it, you must adhere to established building rules and regulations, depending on the materials chosen.
In this article you will learn what the sheathing is and how to install it correctly.
Roof sheathing - what is it and why is it needed?
Roof sheathing is a special frame structure consisting of beams or boards that are laid at an angle of 90 degrees on the rafters.
NOTE!
The sheathing transfers to the rafters the load that it will experience in the future from the weight of the roofing material and precipitation (snow, ice and rain). The sheathing is also designed to fully hold the roof on the building.
The construction of sheathing requires some of the following materials, depending on the roofing material:
- beam;
- regular or tongue and groove boards;
- tes;
- plywood.
The installation of roof sheathing must be carried out in accordance with established construction rules. This is important because if it is not installed correctly or the instructions are not followed, the entire roof could end up on the ground due to gusts of wind or adverse weather conditions.
Roof sheathing
Therefore, before starting work on the construction of the sheathing, you must first fully understand the structure of the roofing pie, the types of materials and the possibility of their use in specific cases.
Definition, purpose, requirements
This design is presented in the form of a system of discharged slats or continuous flooring, packed perpendicularly on top of the rafters for the purpose of:
Redistribution of weight loads from the roofing pie on the rafters or frame.- Retains the counter-lattice (an important but optional element of ventilated structures) and the roofing itself.
- Improving the tightness of slopes with a small slope.
- Additional fixation of rolled insulating materials.
Reference. The design requirements are relatively simple, but clear - the lathing is designed to withstand weight, snow, wind and other loads for the longest possible service life. The pitch of its installation must be uniform and sufficient to securely hold the roofing materials.
Installation of a roof pie
Regardless of whether the roof of the building was planned - flat or pitched, the roof must be constructed in a certain way.
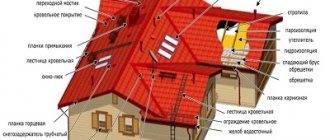
This element of the structure consists of several layers, which builders have come to call a roofing pie.
It allows you to protect the interior of the building from the adverse effects of any external environmental factors.
The following layers of the pie allow this to be achieved:
- interior decoration;
- sheathing;
- vapor barrier layer;
- counter-lattice;
- layer of insulating material;
- roofing film under the sheathing - waterproofing layer;
- ventilated space;
- directly the roofing material itself.
Roofing pie
Each of the above layers, if installed correctly, performs its specific function. If you skip one part of the roof, the remaining elements will be more susceptible to various external factors . In addition, the interior of the building will become less secure and comfortable for living and use.
Interior finishing is most often a layer of plasterboard and a finishing coating, which can be plaster, wallpaper or paint. This part of the pie has only an aesthetic function , covering the inner layers of the roof.
- The sheathing is a special frame on which the roofing material will be held in the future. A special vapor barrier film is laid on the inside of the roof rafters, which prevents the penetration of fumes from the room into the pie.
- Most often, insulation material is laid between the roof rafters . Its most popular types are mineral wool and polystyrene foam. The first type of insulation is fire-resistant and more expensive. It requires large human resources for installation. Polystyrene foam is subject to rapid combustion in a fire and releases toxic substances when melting, but at the same time it is more affordable and easier to install.
- Waterproofing is a film that is placed on top of the rafter legs. It prevents precipitation from penetrating into the room, and also prevents condensation that can form in the ventilated space from flowing into the roofing pie.
- Ventilation in the roof is designed to make the rooms directly below it more comfortable for people to live and stay in. also protects the roofing pie from water vapor .
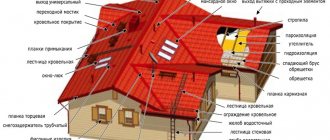
Pie under metal tiles
Roofing material can be completely different - both piece and roll. Depending on which of the presented options is chosen, the installation of the sheathing also depends, since it is she who must hold it on the roof.
Is it worth doing it yourself?
You can do the installation of the sheathing yourself, but it is not easy, especially for a beginner in the field of construction. You need to have certain tools, plan and prepare everything correctly. It is important to have theoretical knowledge and skills in carrying out repair and construction work. It is advisable to have an assistant. Self-manufacturing and installation of such a design will save money. But, if you lack self-confidence and tools, then it is better to turn to professionals. After all, there is a risk of making gross mistakes, as a result of which the roof will soon have to be redone.
Features of solid and sparse lathing
What determines the sheathing pitch in a roof structure? Depending on what roofing material was chosen for the roof, there are two different types of sheathing for it:
- Continuous roof sheathing - installation of boards of this design is carried out in increments that do not exceed one centimeter. The option of using plywood sheets is also allowed. Most often, such sheathing is made for such types of roofing materials as soft tiles and flat slate. Also, all types of soft roofing coverings are laid on this type of sheathing.
- Sparse - installation of planks of this design can vary depending on the material, reaching several tens of centimeters. Most often, this type of lathing is used under metal tiles, slate and ceramic tiles.
IMPORTANT!
In some cases, continuous lathing may be applicable for other types of materials if heavy loads will be placed on the roof . Sometimes boards or plywood in such cases are mounted in two layers.
Most often, the thickness of this type of lathing is 25 millimeters . One of the ideal types of lumber for such a structure is a tongue and groove board.
Continuous sheathing
The frame of the sparse sheathing consists of rows of boards or slats parallel to the ridge of the roof and to each other with a certain spacing between them. It can be completely different - from 10 to 800 millimeters.
Most often, for such a design, a wider board is used for sheathing the roof. The minimum size of its cross-section is within 40 millimeters. The heavier the roofing material, the more reliable the frame needs to be made. Therefore, in some cases, the thickness of the boards is increased, and the pitch of their arrangement is reduced.
Video description
About the intricacies of roof installation in the following video:
Metal for sheathing
Sheathing made of metal profiles is recommended for buildings with a slope length exceeding 6 m, as well as for buildings with a high level of fire hazard. The metal structure can only be sparse; it is assembled from pipes of a suitable cross-section, channels and I-beams; made of steel (stainless or galvanized). The elements are fastened with self-tapping screws or welding (the latter is possible if the rafter structure also consists of metal elements). Metal roof sheathing has many advantages:
- Dimensional accuracy . The use of a metal frame minimizes mistakes that even professional builders make when installing a complex structure (for example, an attic floor).
- Expanded application possibilities . The design is suitable for arranging roofs of a large area (with long slopes), including for buildings for industrial purposes.
Using a hat profile Source prostanki.com
- Increased strength . The characteristic affects not only the service life, but also the resistance of the system to wind and snow loads.
- Resistance to deformation when changing temperature and humidity.
- Corrosion resistance . The structural parts are coated with modern polymer compounds that reliably protect the metal from moisture.
- Installation of the structure is permitted in any weather conditions .
The obvious disadvantage is the cost of metal sheathing and the complexity of installation work - its installation will require the involvement of specialists with skills in working with metal and welding.
Characteristics of the material used for lathing
In order to understand what material can be laid on the sheathing, you should first understand the characteristics of its most popular types. These include:
- tiles (ceramic, cement-sand, polymer-cement);
- slate (asbestos cement sheets), euro slate (ondulin);
- seam roofing;
- metal tiles;
- soft roof.
Various types of tiles (except metal) are small-sized piece roofing elements . This material is considered one of the best due to its properties and long service life.
At the same time, tile roofing is the heaviest , which is why it requires a good foundation in the truss frame and appropriate sheathing. It is best to use bars with a cross-section of 50 to 60 millimeters.
The sheathing pitch must be calculated depending on the covering length of each shard , which may vary depending on the manufacturer.
Roof tiles
Slate is one of the most common roofing materials throughout the country for various reasons. Small sheet sizes can be placed on bars whose size does not exceed 50 millimeters.
If you are installing slate units that are large in size and weight, it is best to use bars about 80 millimeters thick . The step must be selected depending on the size.
They can be either 120*68 centimeters or 175*112.5 centimeters. It is worth remembering that one sheet must be supported by at least three bars so that it does not bend under its own weight and the pressure of atmospheric precipitation.
Slate
Seam roofing is less popular, but it is still sometimes used . If the roof slope is up to 14 degrees, or its configuration itself is quite complex, manufacturers recommend installing the material on a continuous sheathing .
What kind of board is needed for roof sheathing? The cross-section of the timber should be within 50*50 millimeters. with a cross section of 32*100 millimeters instead .
You need to start installing the sheathing under the seam roof from the eaves. The protruding parts of the roof should be finished with a solid board over a distance of 60 centimeters in increments of no more than 1 centimeter.
Seam roofing
Soft roofing is quite simple to install, but requires one- or two-layer continuous sheathing . The weight of such material is quite small.
The cost, unlike some other types of roofing, is also quite reasonable. However, the service life of soft materials may not be very long. In addition, they are quite toxic when burned and are not very fire resistant.
Flexible tiles
Edged board 2nd grade
| Product name | Thickness, mm | Width, mm | Wood type | Variety | The price of the product |
| Edged board 25 x 100 second grade | 25 | 100 | needles (spruce, pine) | 2nd grade | RUB 14,000.00 |
| Edged board 25 x 150 second grade | 25 | 150 | needles (spruce, pine) | 2nd grade | RUB 14,000.00 |
| Edged board 40 x 100 second grade | 40 | 100 | needles (spruce, pine) | 2nd grade | RUB 17,499.62 |
| Edged board 40 x 150 second grade | 40 | 150 | needles (spruce, pine) | 2nd grade | RUB 17,499.78 |
| Edged board 50 x 100 second grade | 50 | 100 | needles (spruce, pine) | 2nd grade | RUB 17,499.90 |
| Edged board 50 x 150 second grade | 50 | 150 | needles (spruce, pine) | 2nd grade | RUB 17,499.90 |
Selecting the sheathing pitch depending on the roofing material
Each type of material used for roofing buildings must be mounted on the lathing with a certain individual pitch.
This value often needs to be determined independently, depending on the dimensions of the sheets of material, while adhering to strict construction rules. The following patterns can be distinguished for different types of roofing:
- soft rolled materials - you need to use a continuous sheathing with a minimum pitch between its elements of up to 10 millimeters;
- slate - it is necessary to individually select the pitch depending on the thickness of the sheets - from 50 to 75 centimeters;
- metal tiles - the instructions of the material manufacturer should be taken into account, but in general it can be indicated that the total pitch is in the range from 300 to 400 millimeters, and the distance between the last two slats should be half as large;
- tiles (ceramic, polymer and sand) - you need to follow the manufacturer’s instructions, taking into account the angle of inclination of the blood; most often, boards are laid at intervals of 320 to 380 millimeters;
- seam roofing - the most common lathing pitch is 200 millimeters, although there are others.
NOTE!
It is worth remembering that the correct calculation ( calculator for calculating roof sheathing here) and the choice of sheathing pitch determine how tightly the roofing material will adhere to the roof.
Edged boards 1st grade GOST
| Product name | Thickness, mm | Width, mm | Wood type | Variety | The price of the product |
| Edged board 25 x 100 GOST | 25 | 100 | needles (spruce, pine) | 1st grade | RUB 20,899.56 |
| Edged board 25 x 150 GOST | 25 | 150 | needles (spruce, pine) | 1st grade | RUB 20,900.00 |
| Edged board 40 x 100 GOST | 40 | 100 | needles (spruce, pine) | 1st grade | RUB 20,899.75 |
| Edged board 40 x 150 GOST | 40 | 150 | needles (spruce, pine) | 1st grade | RUB 20,899.89 |
| Edged board 50 x 100 GOST | 50 | 100 | needles (spruce, pine) | 1st grade | RUB 20,899.89 |
| Edged board 50 x 150 GOST | 50 | 150 | needles (spruce, pine) | 1st grade | RUB 20,900.00 |
| Edged board 50 x 200 GOST | 50 | 200 | needles (spruce, pine) | 1st grade | RUB 20,900.00 |
Do-it-yourself roof sheathing installation
After purchasing the material, you need to order wood for the roof.
The calculation of its dimensions must be made taking into account the dimensions of the roof that was purchased, as well as depending on the size of the roof.
It is worth remembering that the more complex the design, the more waste and substandard elements there will be.
Therefore, it is best to order material with a 10% reserve.
To install the base you may need the following tools:
- hammer and nails;
- screwdriver and screws;
- hacksaw or grinder;
- pliers;
- pencil or chalk for marking;
- roulette;
- building level.
Installation of waterproofing
When installing, you should adhere to the following instructions:
- First, depending on the selected material, you should mark the location of the boards or bars on the rafters . Depending on the type of roof, the markings may not be uniform. Most often, smaller steps should be taken at the edges .
- After the marking has been carried out, using a hammer and nails, or a screwdriver and screws, you need to carry out a step-by-step installation of boards or bars on the rafter legs .
- After each nailing of the next element, it is necessary to check its location relative to the previous one, as well as the correct installation using a level .
- The roofing material should be installed directly on the base itself.
Installation of sheathing
Calculation of lumber for sheathing under metal tiles
To avoid unnecessary expenses, the required lumber is calculated in advance. To do this, using a tape measure, measure the length and height of the slopes, the total length of all eaves overhangs, the total length of the valleys (if any) and ridge lines.
Calculation of continuous sheathing
The initial data for the example is a roof area of 50 m², 25x100 mm boards used, 6 m long.
- We determine the area of 1 board - 0.1 (board width, m) x 6 (board length, m) = 0.6 m².
- We calculate the number of boards - 50 (total area, m²): 0.6 = 83.33 ≈ 84 pcs.
- We calculate the required volume - 0.1 x 0.025 x 6 x 84 = 1.26 m³.
- We add a margin of 10% for trimming, trimming and random errors. As a result, we get 1.26 x 1.1 = 1.386 m³ ≈ 1.4 m³.
Calculation of sparse sheathing
The initial data is the same, the sheathing pitch is 350 mm, the length of the eaves overhangs is 30 m, the length of the ridge line is 8 m, there are no valleys, a simple gable roof.
- We count the number of boards for sheathing the main roof area - 50 (total area, m²): 0.35 (pitch, m) = 142.8 linear. m: 6 (board length, m) = 23.8 pcs. ≈ 24 pcs.
- We determine the required volume 24 x 0.025 (board thickness, m) = 0.6 m³.
- We calculate the number of cubes for the arrangement of the ridge and cornices - 30 + 8 = 38 linear meters. m: 6 = 6.3 pcs. x 0.025 (board thickness) = 0.16 m³.
- We calculate the total number of cubes of lumber - 0.6 + 0.16 = 0.77 m³.
- We add a margin of 10% - 0.77 x 1.1 ≈ 0.85 m³.
A more accurate calculation of the sheathing can be made using an online calculator on online construction resources or on the website of the manufacturer of the selected metal tile.
Wood species
Roof boards are usually made from three types of wood:
- Pine is the most common option. Cheap, durable wood that holds bending loads well. Disadvantages include resin, a large number of knots, and a tendency to crack.
- is similar to pine in many ways, but it is less resinous, less knotty and weighs less. However, spruce roof boards are much more prone to deformation under load, especially when it comes to long runs.
- Larch is an extremely strong and durable type of wood: houses made from it have been standing for centuries. But it is very expensive, and therefore rare.
Which board is best to use for roofing? Oddly enough, from pine. Most programs for calculating a rafter system are made for pine lumber and often do not take into account the characteristics of spruce, even if such a tree species can be selected in the initial data.
This is not relevant for larch - it is stronger than pine. But she has another problem - grades. Due to the high price and much lower prevalence of the material, long larch boards of suitable quality for the roof are difficult to find. Usually, sellers offer unmarketable lumber for rafters, claiming that the high strength of larch more than compensates for “small defects.” Naturally, this is not so.
Let's sum it up
Which boards are best to use for the roof:
- humidity not more than 12% for load-bearing structures and not more than 20% for enclosing structures;
- without serious wood defects;
- cut or calibrated;
- from pine;
- long enough to span the entire span without splicing.
In addition, before choosing boards for the roof, you must make a calculation of the rafter system. Especially if we are talking about a residential building or building where valuables will be stored.
Try to choose the boards personally and monitor their loading - do not trust the seller with this.
Content
- Material requirements
- Lathing design
- Video
Wood is an expensive material, so mistakes in its selection can lead to significant costs. You should pay attention to the type and quality of the wood from which the board is made. And also on the recommendations of specialists on the arrangement of the sheathing and frame as a whole.