- Image of splines on a rod
- Threaded connections
- Riveted connections
Detachable and permanent connections:
Connections of parts in devices and machines are very diverse in their purpose, design, and manufacturing technology.
Connections are divided into detachable and permanent.
Main types of connections
All connections are usually divided into the following two main types:
- motionless. In this case, the parts are connected so that their relative spatial arrangement does not change during operation. The most obvious example is welded joints;
- movable. This type of connection provides for the possibility of moving parts relative to each other during operation. You don’t have to look far for examples either - a gear connection best fits this definition.
Compounds of these types are in turn divided into two large groups:
- detachable. They provide the ability to carry out multiple assembly and disassembly of the structure without compromising the integrity of its components. For example, threaded connections, etc.;
- one-piece. In this case, disassembling the connection is accompanied by the destruction of its constituent parts.
Fixed permanent connections are made:
Mechanical method:
- press pressure – pressing;
- flattening the tip of the fastener - riveting;
- deviation of the edge of the connecting element - bending;
- the formation of point depressions - corening;
- by pressing the heads of rivets and the edges of metal plates - embossing;
Using adhesion manifested at the physico-chemical level:
- fusing workpieces by heating them - welding;
- introduction of a metal melt between the parts being fastened - soldering;
- connection by means of an adhesive composition - gluing;
Immersion of workpieces in the melt:
molding into:
- chilli;
- a special mold for injection molding - a compression mold.
The assembly of movable detachable connections is carried out:
- metallurgical operation, as a result of which the length of the workpiece increases and the cross-sectional area decreases - free crimping;
- giving the workpiece a certain profile by passing it through rollers - flaring.
The formation of such connections is intended to replace an entire structural element if its production from a single workpiece is not economically profitable or is associated with insoluble technological difficulties.
Rivet fixation
This coupling method is mainly used for joining sheet metal and shaped profiles. The technological hole in the surfaces is made by drilling, then a rivet is inserted.
Due to mechanical action, the rod and head are deformed, fill and fix the hole. This operation is performed manually and mechanized. Rivets are used to fix material that is not amenable to welding, soldering, gluing, and to parts where it is necessary to delay the destructive process.
Detachable connections
Connections of this type are widely used where there is a need to periodically replace parts. The reasons for carrying out this operation are completely different, from routine maintenance to the replacement of a worn-out working component of the unit.
Threaded connections
Detachable connections of this type are most widespread. This is due to the relatively low cost indicators of the manufacturing process of a unit of threaded fasteners, as well as the simplicity and convenience of installation/disassembly. The concept of “thread” means a sequence of protrusions equidistant from one another, located along a helical line on the surface of a rod or hole. They may have different shapes, but in each specific case the cross-section of the protrusions on the entire threaded thread is unchanged.
Threads can be metric (most often used in fasteners) and inch (used when making pipe connections). According to other criteria, it is divided into:
- cylindrical. The place of its formation is the lateral surface of a regular circular cylinder;
- conical A threaded thread is applied to a steel rod or pipe, characterized by a cone-shaped configuration;
- trapezoidal A subtype of metric thread. It is distinguished by a coil profile in the form of an isosceles trapezoid;
- round. The profile is formed by arcs united by straight sections. The sides form an angle of 30°;
- persistent. The cross-section of the turns looks like an unequal trapezoid. The slope of one side to the vertical is the same 30°, and the other - working - 3°.
Depending on the number of threads, threads can be single- or multi-start.
Pin connections
The formation of this connection is carried out by jointly drilling the fastened structural elements and then installing special parts called pins into the created holes. The last operation must be carried out with an interference fit.
The production of cylindrical pins is regulated by the provisions of four State standards. Drawings of the versions of these clamps they installed are presented below.
Execution of pins in accordance with GOST 10774-80
Execution of pins in accordance with GOST 12207-79
Dimensional characteristics
To get an idea of the order of numbers reflecting the range of changes in the sizes of cylindrical pins, we present the data prescribed by the standards of GOST 3128-70.
- External diameter (designation “d”): from 0.6 mm to 50.0 mm;
- Height of the larger chamfer (parameter “c”): minimum 0.12 mm; maximum 8.0 mm.
- Height of the smaller chamfer (designation “a”): min 0.08 mm; max 6.3 mm.
- Total length of the pin (parameter “l”): 2.0 mm...280.0 mm.
Today, tapered pins are also produced. Compared to the cylindrical ones described above, they provide fixation with greater accuracy. At the same time, the value of this characteristic remains practically unchanged after numerous bulkheads. It is also not affected by pin wear. This part is simply immersed to a greater depth, so its seating density is restored.
The production of conical pins is regulated by the provisions of three State standards. Below are the design drawings of this type of clamps approved by them.
Dimensional characteristics
Below, for specifics, the limits for changing the dimensions of conical pins approved by GOST 9465-79 are presented. A special feature of these hardware is the presence of threaded knurling on one of the parts of the rod.
- Diameter of the smooth section of the rod (parameter “d”): from 5.0 mm to 50.0 mm.
- Metric thread diameter (designation “d1”): minimum M5; maximum M36.
- Length of the threaded segment (parameter “b”): not less than 14.0 mm; no more than 78.0 mm.
- The width of the transition from the smooth cone-shaped section of the rod to the threaded section (designation “a”): min 2.4 mm; max 12.0 mm.
- Total length of the conical pin (parameter “l”): 40.0 mm...400.0 mm.
- The height of the trapezoidal end (designation “c”): from 0.8 mm to 6.3 mm.
Keyed connections
The purpose of these connections is to transmit torque. They are used to secure fans, couplings, gears, pulleys, etc. to the shafts. As a rule, medium-carbon steels are used as raw materials for the manufacture of keys. The creation of keyways on the shaft is carried out using end or disk mills, and on the hubs - using broaching or chiselling technologies.
Varieties
There are two types of keyed connections.
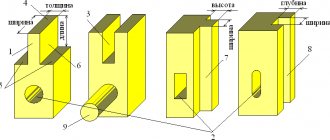
Unstressed. Provide a high degree of alignment of mating structural elements. Unstressed connections are formed using prismatic keys (item “a” in the figure below) and segment keys (item “b”).
The height and width of the keys (designation “h” and “b”, respectively) are characteristics derived from the diameter of the shaft and are established by the provisions of State Standards. For example, the requirements of GOST 23360-78 apply to prismatic hardware. The length of the keys (parameter “l”) is calculated in each specific case.
Tense. To create these connections, two types of keys are used: wedge keys. These are self-braking wedges with a slope of 1:100. (pos. “a” in the figure below); tangential. When work is carried out in reverse mode, fixation is carried out by installing two pairs of keys of this type, maintaining an angle of 120° between them (item “b”).
The degree of coaxiality provided by stressed connections is not as high as compared to unstressed ones. When using the former while driving wedges, the hub may become skewed. Therefore, restrictions are imposed on the use of stressed keyed connections.
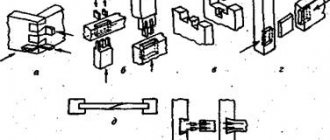
Spline connections
These connections are used to transmit significant moments. Compared to keyed ones, they weaken the shaft less. Splines are made using rolling, chiselling or milling technologies. As for the grooves in the hubs, in large-scale production they are obtained by broaching, and in small-scale production - by chiselling.
The splines differ in profile shape.
They are:
- straight-sided (position “a” in the above figure). Used for shafts whose diameter does not exceed 125.0 mm;
- involute (position “b”). They are used for shafts with a diameter (designation d) varying in the range of 4.0 mm≤d≤500.0 mm. Compared to the previous version, the involute connection is characterized by a lower stress concentration and greater manufacturability;
- triangular (position “c”). They are used when it is necessary to transmit small torque using hollow shafts and thin-walled hubs. Another widespread option is the use of torsion shafts in interfaces or in control drives. Motorists are familiar with the connection with triangular splines to drive windshield wiper blades.
Regulations
Technical characteristics of spline connections are established by State standards under the numbers:
- 1139-58 – straight-sided splines;
- 6033-80 – involute splines.
The performance parameters of triangular spline joints are specified in Industry Standard 1.00092, adopted in 1973.
Keyed
The keys secure the shaft with parts that transmit rotation and vibration. The design of such elements can be prismatic, wedge, segmental, tangential. Such fasteners form the following types of connections:
- Unstressed ones are carried out using prismatic segment keys. There is no pre-stress during assembly.
- Stressed ones are produced by tangential and segmental keys. Mounting stress appears during assembly. Used for complex mechanisms.
Permanent connections
In modern industrial production, mainly three types of permanent connections are used. Let's look at them briefly.
Pressed connections
Press fittings are the most widely used for the implementation of connections of this type. These shaped parts are used to connect radiators, boilers, water mixers and other plumbing equipment. Installation of press fittings is carried out using special crimping tools - manual or electric press pliers. The sequence of actions is presented below in the pictures.
The use of a press fitting ensures the tightness of the permanent connection. The most widely used parts are those made of copper (Cu element) and copper-containing alloys. The technical requirements for them are approved by GOST 32591-2013. The nominal diameter of press fittings (designation d) varies in the range 6.0 mm≤d≤267.0 mm. They connect pipes with a minimum wall thickness of 0.6 mm to 3.0 mm.
Welded joints
Of the permanent type connections, welded ones are the most advanced. Forces operate here at the interatomic level. The edges of the fastened structural elements melt, and a strong weld is formed after they cool. This operation is most often performed using electric arc or gas welding.
Regulations
The creation of a welded joint is regulated by State standards numbered:
- 5264-80. Contains requirements for manual electric arc welding;
- 8713-79. The rules for carrying out automatic as well as semi-automatic welding with/without the use of a backing seam (prevents burn-through during subsequent welding operations), flux-holding devices and linings are prescribed here;
- 1533-75. Standardizes automatic and semi-automatic welding under a protective layer of flux. In both cases, manual welding is provided;
- 15878-79. Regulates the performance of contact welding of all types, starting with spot welding, including relief and roller welding, and ending with butt welding;
- 15164-78. Contains requirements for electroslag type welding using a wire electrode;
- 14771-76. Approves technical conditions for conducting electric arc welding in gases that prevent the penetration of harmful compounds from atmospheric air into the melt zone. In particular, in inert non-flammable gases, for example, helium (He) and argon (Ar); in a gas with the formula CO2, known as carbon dioxide.
In the first case, non-consumable electrodes should be used, and in the second, consumable ones;
- 14806-80. This GOST specifies the rules for conducting electric arc welding in inert shielding gases of parts made from aluminum (Al element) and alloys that contain it;
- 16310-80. The requirements for welded joints of such polymeric materials as polyethylene (formula (C2H4)n) are specified; polypropylene (formula (C3H6)n); Viniplast is a plastic mass created on the basis of perchlorovinyl resin (common abbreviation - CPVC) and polyvinyl chloride (formula (C2H3Cl)n).
Riveted joints
A riveted connection is a connection between structural elements created using rivets, and the junction itself is usually called a riveted seam. This technology is usually used in relation to industrial and civil facilities subject to high vibration loads. In particular, the process of constructing spans of bridge structures cannot be done without rivets.
Regulations
There is no single State standard establishing the types of riveted joints acceptable for sale on the territory of our country. However, when creating them, you must be guided by the provisions of OCT 1 00872-77, which describe methods for testing objects in which rivets were used:
- for a static cut of these hardware;
- fatigue when the connection operates under conditions that cause shearing of the rivets.
It’s a different matter with regulatory documents regulating the production of fasteners themselves of all types. We are talking about State standards numbered:
- 10299-80, 10300-80, 10301-80, 10302-80, 10303-80. They stipulate the technical conditions for rivets of normal and rough precision with hemispherical, countersunk, semi-countersunk, hemispherical low and flat embedded heads, respectively;
- 10304-80. Contains general technical conditions for the production of rivets of normal and rough accuracy;
- 12638-80, 12639-80, 12640-80, 12641-80, 12642-80, 12643-80. These standards establish the technical specifications for semi-hollow rivets having a rounded, flat, countersunk, hemispherical, flat and countersunk head, respectively;
- 12644-80. Here are the general technical conditions for the production of hollow and semi-hollow rivet fasteners;
- 14797-85, 14798-85, 14799-85, 14800-85, 14801-85. These standards specify the design and dimensional characteristics of precision-manufactured rivets with hemispherical, 90° countersunk, 120° countersunk, plano-convex and flat head rivets, respectively.
Welding
What makes them special? These types of joints are formed by heating and fusing the material at the attachment point to form a weld. This clutch is considered one of the most common.
There are several welding options. The most popular of them:
- Electric arc welding. Three main subtypes can be distinguished: automatic submerged welding (characterized by high productivity and quality, used in mass production), semi-automatic submerged arc welding (used for short intermittent welds), manual (lower productivity speed, quality depends directly on the experience of the welder).
- Contact welding. Used in mass production for thin sheet metal. The seam is made as an overlap.
One of the popular mounting options is shown in the photo.
Often used in suburban construction.
What is a fitting
Fitting
- This is a part of the pipeline connection. This name is “foreign”; they like everything shortened so that it is easy to pronounce while running with your chewing mouth. Here is our definition of a fitting from GOST 15763-2005:
“ Pipeline connection parts
: Body parts (fittings, elbows, tees, crosses, plugs, plugs), connecting parts (sleeve and installation nuts, lock nuts, bolts, flanges) and sealing parts (cutting ring, clamping ring, welded and soldered nipples, gaskets, etc.), providing an assembled connection of pipelines.”
An uninformative name, isn't it? Actually, this article was written in order to consider these very details in more detail.
The term “coupling” has a more specific meaning, however, it also has a fairly wide list of parts. coupling
(plumbing) - this is a part of connecting two pipes to each other. The connected pipes can be either the same or different types (and diameters).
Couplings are usually threaded (cast iron, brass or bronze); combined, for joining metal with polypropylene (separable and non-separable); for soldering (polypropylene or copper); compression, for connecting metal with various plastics (cross-linked polyethylene or metal-plastic), which are more often called collets.
In practice, couplings for metal-plastic pipes and cross-linked polyethylene pipes (PEX-AL and PEX) are more often called fittings, although the term “coupling” is also applicable to them.