Today, for many developers, building a log house is not just a continuation of the age-old traditions of their ancestors, but a desire to obtain environmentally friendly and energy-efficient home ownership.
In order for the tree to work as fully as possible to create favorable conditions for living in the house, you need to correctly select the sizes of logs for the structural elements of the house: external and internal load-bearing walls, floors, ceilings and roofing.
The dimensions of the logs influence many indicators of the finished house building, but most of all its heat-insulating characteristics, the final price of construction and the external appearance of the building. Having chosen the diameter of the round timber, you need to be prepared for the fact that in fact the supplier may supply the cross-section of the products by 2-3 cm smaller.
Material
A rounded or calibrated log is a tree trunk that has been completely cleared of the loosest top layer and has undergone milling processing, ensuring the same geometry and size along the entire length, as well as a flat, smooth surface.
Advantages and disadvantages
As a result of special processing, the following advantages are achieved:
- The log is dried at a temperature of 130-180 degrees, which makes it possible to obtain material with a certain humidity.
- The treatment provides structural changes to the wood, increasing strength and reducing thermal conductivity by 15-25%, as well as the hygroscopicity of the top layer.
- Improved appearance due to a smooth surface, stability of color shade (ennobling), exclusion of blue, and manifestation of texture.
- Geometric stability along the entire length, equal size of logs throughout the entire batch, which simplifies the preparation of material for construction and reduces the amount of waste.
The main disadvantage of such logs is their increased cost. In addition, during processing the layer with maximum resin content is removed, which reduces the natural protection of the wood from rotting. To increase durability, they must be impregnated with an antiseptic.
Manufacturing
The technology for the production of rounded logs includes the following processes:
- selection of the highest quality logs as raw materials;
- processing in a special machine, on which the top layer is removed by milling to a given diameter (diameter deviation along the length should not exceed 4 mm);
- natural or forced drying;
- compensation cut (at the discretion of the manufacturer or by order of the buyer);
- cutting logs to length (logs in one batch have the same length).
For ease of construction, a ready-made kit for the house is assembled from rounded logs. In this case, additional operations are performed:
- Formation of seats (bowls) for the assembly of the log house. Typically, longitudinal and transverse (diagonal) bowls are made.
- Formation of longitudinal grooves for laying insulation.
- Processing the ends of logs.
- Antiseptic impregnation. The most commonly used antiseptic composition is water-based.
Ready-made kits are more expensive, but they allow you to assemble log houses like a construction set, without resorting to additional processing.
What kind of wood is best used to assemble a wooden frame to keep it warm?
Rounded logs are mainly made from softwood.
Their increased resin content ensures durability and warmth in the home. Pine is considered the best option. It combines quality and price well. Pine logs have increased thermal insulation properties and sufficient resistance to atmospheric influences.
The material is available in many regions of the Russian Federation. Arkhangelsk pine is particularly resistant to cracking.
Spruce is slightly inferior in properties, but spruce logs are easier to process. Cedar and fir do not have superior characteristics to pine or spruce, but they are noticeably more expensive, which limits their use. The choice of these breeds is explained by their attractive appearance.
Larch is characterized by the greatest strength and water resistance . It is most resistant to temperature changes. However, logs from this species cost 2 times more than pine.
This circumstance leads to the fact that larch is most often used for laying lower (basement) crowns, which are subject to maximum load and high humidity.
What is needed to design a one- (two-) storey building made of calibrated material?
When designing a log house, it is necessary to take into account the following log parameters:
- Diameter. The thickness of the walls and, accordingly, the strength characteristics, thermal resistance and other parameters of the entire structure depend on it. The diameter of the finished rounded logs ranges from 16-32 cm. The most in demand is a log with a diameter of 24 cm.
- Real (working) height of the log . It is defined as the difference between the diameter and height of the groove. Depending on the diameter and type of groove, the height ranges from 14 to 27.2 cm.
- Log length . The standard log length is 2-6.5 m with a multiplicity of 0.5 m. Products up to 12 m are manufactured upon request.
- Groove size . To tightly lay the logs in the log house, a longitudinal groove is cut on one side of them. The dimensions of a standard groove are shown in Fig. 1. This element can be of several types - Finnish, lunar, extended. They vary in width. So, with a log diameter of 22 mm, these grooves have a width of 14, 11 and 16 cm, respectively.
- Availability of compensation cut . It is formed to relieve internal stresses in the material to reduce cracking. The cutting depth can be 1-2 cm depending on the diameter of the log.
When designing a house, it is important to take into account the physical and technical characteristics of the building material:
- Thermal conductivity. For pine and spruce, the thermal conductivity coefficient is 0.14-0.19 W/mhdeg.
- Residual moisture . It significantly affects the shrinkage of the log house and depends on the method of drying the logs. The parameter can fluctuate in the range of 15-25%.
- Strength. The most important are resistance to bending and compression.
For high-quality construction, stable length dimensions of lumber are required. Finished rounded logs are highly stable, but it is advisable to purchase material of the 1st grade and one batch.
Calculation of a log house
You can go the other way and calculate a log house by first counting the number of logs, then the volume of each log, as a result we will find the total volume of the log house by multiplying the number of logs by the volume of one log.
This is a longer path, because with different widths of the sides of the log house, the assortment for cutting the log house must include logs of different lengths.
This arrangement of log material is called sub-log.
This method of calculating the volume of a log house is good for cutting a log house yourself, when you buy only logs and assemble them into a log house yourself.
As we previously determined, for a log house measuring 3 x 4 m, you will need two standard sizes of logs when cutting into a bowl:
- logs 4.5m long
- logs 3.5m long
In height you need 12 pieces of logs, therefore for this log house you will need logs 4.5 m long and 3.5 m long - 24 pieces of each length.
The volume of an individual log of a specific standard size (in our example, the formula is for logs with a length of 3.5 m and 4.5 m, respectively) MUST be calculated manually using the formula for calculating the volume of a cylinder through the product of the area of the circle and the length:
3.14*0.12*0.12*3.5=0.158256 m3
3.14*0.12*0.12*4.5=0.203472 m3
What's the catch at this level of calculation? The fact is that companies use ready-made tables for calculating volumes in accordance with GOST 2708-75 “Round timber. Volume tables.”
That’s why these tables are used because the volumes in them are significantly overestimated. So, for example, the volume of a log D = 24 cm with a length of 3.5 m is equal to 0.184 m3, and with a length of 4.5 m - 0.24 m3. This is more than the numbers we calculated above: 0.158256 m3 and 0.203472 m3
It seems that the overestimation of the volume of a single log is small. But, for our example of a log house in monetary terms, “reserves” result in the figure of 1,495 m3, which corresponds to almost 13 thousand.
Country house and cottage for permanent residence in winter
Depending on the purpose of the building, there are 2 main types of houses:
- Cold buildings . These include houses with periodic, seasonal residence and various outbuildings. Insulation is not particularly important in them, and therefore the thickness of the walls is calculated based only on the strength characteristics.
- Year-round houses . They are designed for permanent residence, incl. in the winter season. The most important requirement for them is to retain heat indoors.
Based on the requirements, the following log sizes are selected during design:
- Houses for seasonal residence, cottages, outbuildings for the southern regions of the country - the diameter of the rounded log is 16-18 mm.
- Summer houses, outbuildings in the European part of the Russian Federation - 20 cm.
- Houses for seasonal residence and cottages for areas with a temperate climate - 22 cm.
- Year-round, one-story and two-story houses with an area of no more than 250 sq.m. for regions with cold climates - 24-26 cm.
- The same with an area of more than 250 sq.m - 28-32 cm.
A more accurate selection of logs is made based on the results of calculations taking into account mechanical loads, foundation strength and thermal resistance.
Which ones are suitable for building a house and other buildings?
For the construction of buildings, the size of logs is selected from:
- purpose of the object,
- type of use - seasonal or permanent,
- climatic operating conditions,
- design dimensions in plan and height.
The purpose of the object determines its size and dimensions, so a house for permanent residence will have a large area of up to 250 m2, can be two or three floors, and therefore will require the installation of massive load-bearing walls with good thermal insulation; on the contrary, auxiliary utility rooms: garages, sheds and summer cottages built from much smaller timber.
GOST requirements for the use of logs for the construction of buildings for their intended purpose:
- Summer kitchen no less than 180 mm.
- Non-residential extensions from 150 to 180 mm.
- Residential one-story houses for seasonal residence, from 150 to 200 mm.
- Residential one-story houses with permanent residence from 220 to 250 mm.
- Two-storey houses with permanent residence from 250 to 300 mm.
- Houses in the northern regions of the country from 300 mm.
- Saunas for year-round use from 250 mm.
For developers who are building a house “to last forever,” the best option is logs from 300 to 400 mm. It will last for many years and will always be warm and strong. Such logs change the appearance of house construction, the house looks more solid and attractive. Of these, a wild-style log house with Canadian timber looks beautiful, adding individuality and providing high thermal resistance of wall structures.
The use of logs larger than 400 mm only affects the appearance; its positive characteristics do not increase in reliability and heat resistance, but the price increases significantly.
For such logs, pine is practically not used, mainly larch or spruce , the purchase price of which is much higher.
As a rule, timber with a diameter above 400 mm refers to “overripe” wood, whose age is from 100 to 150 years, and by this period the tree loses its own biological strength.
The larger the cross-section of the log, the higher the cost of materials and assembly work. It is known from practice that the coefficient of increase in the cost of constructing log cabins when switching from different diameters is:
200 to 220 mm - 1.18;- 220 to 240 mm - 1.15;
- 260 to 280 mm - 1.14;
- 280 to 300 mm - 1.14;
- 300 to 320 mm - 1.12;
- 320 to 340 mm - 1.11;
- 340 to 360 mm - 1.11;
- 360 to 380 mm - 1.105;
- 380 to 400 mm - 1.105;
- 400 to 420 mm - 1.10.
When choosing the diameter of a log, you need to take into account the percentage of shrinkage; it is better to buy winter-harvested wood, in which case its humidity will not exceed 12%. Such a log house will have the least shrinkage, so you can choose smaller sizes.
Load-bearing external and internal walls
External load-bearing walls are the most important structural element of a house ; they must ensure the transfer of the total load from their own weight and the structures above to the foundation and have high thermal resistance.
For houses with permanent residence up to 2 floors, according to reliability conditions, a log with a cross-section of 280-300 mm will be sufficient, but according to energy efficiency conditions, this size should be about 400 mm for the central and northern regions.
Therefore, it will be correct if the choice of thickness is made by technical and economic comparison of two options with a thick single-layer wall or a thinner multi-layer structure. For example, from a log with a diameter of 300 mm and an additional heat protection system of 100 mm.
For internal load-bearing wall structures, thermal protection no longer has the same effect as for external ones, since they operate under conditions of a relatively constant internal air temperature from 16 to 25 C. The choice of their thickness will be influenced by two parameters:
- Strength characteristics of the wall and endurance of its structure . According to the current calculation, for a two-story log country house, the thickness for internal load-bearing walls is 160 mm.
- Noise protection . The log has good noise insulation properties compared to stone walls, provided that the caulking of the crown joints is carefully carried out; a diameter of 160 mm will be enough to keep the interior of the house quiet.
The ideal option for a developer is to build a house with a single-layer log wall without installing additional thermal insulation. To do this, you will need to correctly calculate its parameters and carry out the caulking process most carefully.
At the same time, it is necessary to take into account that the effective width of log wall structures will be determined by the size of the inter-crown connection. This figure is almost 2 times smaller than the cross-section of the logs used to assemble the log house. For example, for logs with a thickness of 24 cm and 28 cm, the inter-crown joint will be 12 cm and 14 cm, respectively.
This indicator is normalized for a specific climatic region:
- from 14 to 16 cm at -40C;
- from 12 to 13 cm at -30C;
- from 10 to 12 cm at -40C.
Non-load bearing partitions
Before choosing the design and thickness of partitions in the house, you need to understand how they differ from internal load-bearing walls.
Partitions are not really important to a house structure. All of them are installed on ceilings and perform only a zoning role.
Therefore, they may not even be solid, but made, for example, in the form of shelves , which is important for kitchens and offices. They have a very important difference from main walls - the ability to be easily mounted and dismantled.
Speaking about partitions in a log house, they can be made from any building material except brick. It is also prohibited to make partitions for shrinkage. That is, first the box is raised, then the process of shrinkage takes place over 12-18 months, only after that they begin to install the partitions. If the opposite is done, they will be very seriously deformed when the house shrinks.
When choosing the thickness of log partitions, you need to take into account the characteristics that partitions in a wooden house should have:
Low weight.- Strength sufficient to secure household equipment and furniture on it.
- Noise insulation qualities not lower than 43 dB.
- Environmental Safety.
- Moisture resistance and fire resistance when using environmentally friendly impregnations.
Thus, in order to ensure all the above characteristics, it is enough to install partition walls made of logs with a thickness of 100 to 120 mm.
DIY work stages
The construction of a house from rounded logs is subject to the general rules for the construction of log cabins . This material facilitates preparation and reduces labor intensity, especially when purchasing ready-made kits.
It does not require additional drying, and construction can begin immediately.
Preparation
At the stage of preparation for the construction of a log house, it is necessary to carry out the following operations:
- Design. The project is developed independently, entrusted to specialists or selected from ready-made options. On the Internet you can find projects for every taste.
- Purchase of materials . First of all, it is necessary to calculate the need for logs with a reserve. It should be remembered that dimensional stability is guaranteed in one batch. Repurchasing the missing material may cause differences in the diameter and shape of the grooves and bowls.
- Site preparation . The construction site must be carefully leveled. Garbage is removed and disposed of. All vegetation should be removed by uprooting the roots of trees and shrubs. It is advisable to cut off the fertile soil layer.
- House marking . The corners are marked with pegs, and the dimensions are marked with a cord. The location of the internal partitions should also be noted.
- Making the foundation . A strip foundation is most suitable for a log house. Its depth depends on the composition of the soil, the depth of freezing and the occurrence of groundwater. The foundation is raised 40-50 cm above the ground surface to prevent contact of the lower crowns of the frame with sedimentary and flood moisture. The top of the concrete strip is carefully leveled, and the horizontalness is controlled by the building level.
Waterproofing plays an important role in preparation . The lower crowns of the log house must be protected as much as possible from moisture. To do this, a bitumen layer is applied on top of the concrete and 2-3 layers of roofing material are laid.
An installation board with a thickness of at least 5 cm and a width of at least 20 cm is laid on the waterproofing along the entire perimeter of the house.
Another layer of roofing material is applied on top of the board. Its edges must extend beyond the edges of the foundation to a length of at least 25 cm.
Assembly of crowns
A log house consists of rows (crowns) of logs, which can be divided into the following categories, taking into account the specifics of operation and load distribution:
- Bottom or frame crown. It is laid on the foundation.
- Second or lag crown (bottom trim). The floor joists crash into it.
- Ordinary or wall crowns.
- Window crowns. Made from shortened logs to form openings.
- Window sills. Rows located under the window opening.
- Above-window crowns. They are located above the window opening.
- Top harness. This is the upper crown on which the ceiling beams and rafter system are fixed.
For the lower crown, it is advisable to use logs made of dense wood (larch). The log is cut in half lengthwise. The flat part is installed on the foundation. Most often, the casing crown is not attached to the foundation.
If the project provides for fastening, then vertical metal pins are pre-embedded in the foundation . In this case, holes are drilled in the lower log into which these pins are passed.
One of the most critical steps is laying the second crown to form the bottom trim. It is also advisable to make this row from high-strength wood (larch or oak).
It is necessary to secure the floor joists in it. The logs are placed on the lower crown and fastened with dowels. The longitudinal groove must clearly coincide with the first log. To insert a log into a log, a transverse groove is cut to the size of the log using a chainsaw. Installation step – 60-80 cm.
Ordinary crowns are laid from logs of the same diameter . In each crown, a longitudinal groove is located at the bottom and is directed exactly along the lower element of the frame. The connection of the crowns with each other is ensured by dowels.
When laying each row, a sealant (usually jute) is placed in the groove. As construction progresses, it is important to control the horizontality of the crowns with a level and the verticality of the wall using a plumb line (verticality should be checked from the inside of the wall).
The following elements of the crown assembly stand out:
- Connecting the crowns with dowels . The mounting diagram is shown in Fig. 1. Wooden rods with a diameter of 2-3 cm are used as dowels. To install them, a hole is drilled, starting in the center of the lowest log, passing through the next crown and ending in the center of the 3rd log, i.e. 3 rows are fastened at once. The wall mounts are staggered.
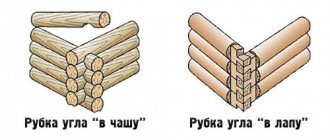
- Corner connection . In the corner, the logs in each crown can be connected without a remainder, forming a right angle, or with a remainder when the ends extend beyond the surface of the wall. In the first case, the ligament is provided by 2 main methods: “in the paw” or “dovetail” (Fig. 2). The second option can be implemented in the following ways: “half a tree”, “filled comb” and “tail tail” (Fig. 3). The most popular method is “half a tree”.
- Longitudinal connection of logs . The ends of logs are usually connected using the dovetail method.
The connection between the internal partitions and the log house should also be highlighted. To do this, a T-shaped connection is formed. It can be carried out without a residue using the “dovetail” method or with a residue, using the “half-tree” method (Fig. 4).
Picture 1
Figure 2
Figure 3
Figure 4
Floors
The floor beams cut into the corresponding crown of the frame . The floor joists are laid in the second crown. They are usually made from 50x(150-200) mm timber. The connection itself is carried out using the dovetail method.
A groove is cut in the log with a chainsaw, and a corresponding tenon is formed at the end of the beam. The log is driven tightly into the log, and metal pins are sometimes used to strengthen the joint.
The ceiling is inserted in the same way. The beams are tightly inserted into the penultimate crown of the log house and secured in it.
Installation of window and door blocks
When installing window and door units, it is important to eliminate distortions and deformations, strengthen openings and ensure insulation of joints.
At the level of window openings, so-called window crowns are installed.
Shortened logs are laid in the space between the windows . To securely fasten them near the opening, the crowns should be secured with a double dowel.
The final formation of the openings is carried out after the completion of shrinkage of the entire log house. This will require at least 6 months. After leveling the walls, vertical spikes are cut out from the sides. Then, a casing box is inserted into the opening.
A groove is pre-cut on its side posts. Gaps are left at the bottom and top by installing tabs. After shrinkage is completed, these gaps are filled with polyurethane foam and insulation.
It is important to remember that the box cannot be nailed or secured with screws . Door and window blocks are then fixed in it.
Grinding
An important advantage of rounded logs is the elimination of such a labor-intensive operation as grinding the frame. Their surface is quite smooth and does not require additional processing.
Only the joint areas where the corresponding profiles were formed, as well as accidentally damaged areas, are subjected to grinding.
Caulk
To insulate a wooden frame, all joints and inter-crown seams are caulked.
The main caulking materials: flax, tow, felt, moss and hemp . Recently, ready-made sealants based on rubbers and plastics have been increasingly used.
Caulking materials are driven tightly and as deeply as possible into all cracks and gaps. For this, a special tool is used - a caulk and a wooden hammer.
The work begins from the outside of the wall, and then is carried out from the inside, and from the lower crowns.
The first caulking of a log house is carried out 10-12 months after its construction , when the most intense shrinkage is completed. Repeated procedures are carried out during operation, as necessary.
We must remember that you should not “clog” an excessive amount of material, because... this can lift the crowns. Particular care should be taken to caulk the connecting bowls.