Organization of a workplace for carpentry work
TO
category:
Carpentry work
Organization of a workplace for carpentry work
Next: Equipment and auxiliary tools
Proper organization of the workplace is of great importance for increasing labor productivity. Depending on the nature of the operations performed, the workplace is organized differently, but the basic requirements for its equipment remain unchanged.
The workplace of a carpenter engaged in wood processing, manufacturing of parts and assembling them is equipped with a workbench and the necessary equipment for this work. The height of the workbench is selected according to the height of the worker so that, standing at the workbench, he can, without bending over and at the same time without raising or bending his arms, put his palms on the workbench board.
If the workbench is low, the worker has to bend down more and expend additional energy. At a high workbench, the worker is forced to stretch out his arms and keep them suspended, and this is very tiring.
When performing work while standing, to release the muscles of the arms and torso from excessive tension, the spine should maintain a straight position, the torso should be bent at the hip joint, the leg should be very slightly bent at the ankle and not at all bent at the knee. If one leg is moved forward and the other is left behind, the torso will take an oblique position in relation to the workbench, and if the legs are placed so that the feet are parallel to each other, the torso will take a straight position. In each of these working positions, curvature of the spine is prevented, the chest and abdomen are not compressed, and free breathing and blood circulation occur.
Rice. 1. Selecting a workbench by height
Rice. 2. Body position when working: a - oblique position when sawing, b - straight position when sawing, c - oblique position when planing
To avoid fatigue, it is advisable to change your body position.
When performing work that requires greater stress - planing, sawing, chiseling - you should take an oblique position of the body.
When lifting heavy workpieces from the ground or the floor, do not load the weaker back muscles by bending the torso. The load should be transferred to the leg muscles, maintaining a straight spine. This type of lifting is less tiring.
For adolescents, compliance with these requirements is especially necessary, since violation of them can lead to abnormal changes in body shape, and sometimes to curvature of the spine.
The workplace should be illuminated with uniform light of constant intensity (natural or artificial). The illumination of the workplace and the visibility of surrounding objects largely depend on the color of production premises and equipment.
Rice. 3. Body position when lifting the board: a - correct, b - incorrect
Rational painting of premises and equipment increases visual efficiency and reduces worker fatigue, reduces injuries, reduces the number of defects and instills a love of order and cleanliness. When selecting colors, you should strive to create a contrast between the color of the material being processed, the equipment and the room.
For woodworking shops, we can roughly recommend the following colors for painting: light blue ceilings; walls: the lower part to a height of up to two meters is soft green, the upper part is cream (light ocher); the floors (asphalt) are light gray, the floors around the trash bins are white, the floor and ceiling against the fire extinguishers are red.
Painting of machines and equipment: the foundation and base are dark brown, the frame is green, the moving part is ivory, the levers and handles are bright yellow, the guards and stop buttons are red.
All electrical equipment must be in good working order and grounded.
The task is given the day before the work and, in accordance with its nature, the necessary materials and tools are prepared.
Before starting work, you need to check the tools, work orders, and drawings. They should be placed on the workbench so that they are visible and easy to use. In advance, according to the technology of making the product, it is also necessary to prepare the corresponding devices (braces, clamps, miter box, workbench stands).
Materials and semi-finished products should be conveniently located near the machine or workbench so that unnecessary movements are not required during work.
The workplace must be kept clean - systematically cleared of shavings, dust, wood chips, etc. After work, the workplace must be cleaned, and tools and devices must be checked, prepared for subsequent work and placed in the designated place. Semi-finished and processed products should also be put back in their place.
In order not to clutter up workplaces, it is necessary to timely deliver the necessary lumber to the workshop and systematically remove finished products from it and remove wood waste. For this purpose, intra-shop transport (rail and trackless) is used. Along a narrow-gauge rail track, lumber is delivered to the workshop on trolleys and finished products are removed from it. For intra-shop transportation, they use trackless transport - manual jacking trolleys, electric trolleys and forklifts.
A manual jacking trolley with a rising platform is shown in Fig. 4. Such carts require special racks that are installed on racks. The trolley platform is brought under the platform of the rack between its racks. By moving the drawbar, the platform rises and the container racks are above the floor level. The loaded trolley is taken to the unloading point, where the platform with the container is lowered by moving the drawbar. Thanks to the racks, workspaces are not cluttered and parts do not spill out or fall on the floor.
Rice. 4. Trolley with lifting table
A trolley table is also used, on which the material is not only transported, but also raw and processed parts are stored at the machines. The trolley table consists of a steel frame 1.6 m long and 0.8 m wide, to which two swivels with wheels are attached. The top of the frame is covered with 40 mm thick boards, forming a platform. The height of the platform from the floor is 385 mm.
Rice. 5. Permanent shelving with racks
Thanks to swivels and one free wheel rotating on an axis, the trolley table has good maneuverability and can easily be turned in one place.
The electric trolley has electric and hand brakes. It is equipped with a lock that prevents workers who are not authorized to ride the trolley from using it.
When starting a new job, you need to think through the technological process of its implementation in advance. Technological process
is a series of sequential operations necessary to produce the desired joinery product from a material, such as boards. Any technological process is divided into work processes - main and auxiliary. As a result of the main processes, finished products are created; auxiliary processes ensure only the normal course of the main process.
Rice. 6. Electric trolley EK-2P
In the carpentry and construction business, the technological process of manufacturing and installing products (window frames, doors) consists of preparing parts, assembling them and installing them in place. In turn, each work process is divided into a number of operations performed by workers of various qualifications. Due to the close relationship of individual operations within the same work process, the workers performing these operations are united into links. The correct composition of the team should ensure the division of labor between workers and create conditions for the productive work of all members of the team.
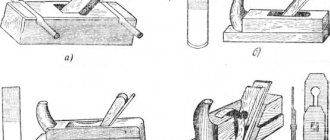
Carpenter's workplace when processing wood manuallyThe main equipment of the workplace for manual wood processing is a carpentry workbench (Fig. 35, a).
The workbench consists of a bench 1 and a lid 3. The bench is usually made of pine, and the lid is made of solid, well-dried wood of oak, beech, birch, less often hornbeam or elm. The workbench cover consists of a board 60-80 mm thick, tied with bars, a front clamping screw 2 and a rear clamping box 6.
In the cover of the workbench, including the rear clamping box, through sockets 4 are arranged parallel to the front edge, into which wooden or metal workbench blades (Fig. 35.6) or combs (Fig. 35, c) are inserted. Thanks to the presence of flat springs, they can be installed in the nest at any height. Blades and combs are used to clamp the material being processed on a workbench in a horizontal position.
Rice. 35. Carpentry workbench: a - general view, b - workbench blade, c - comb
When processing material in a vertical position, it can be clamped with a front clamping screw or a rear clamping box. When processing boards in a horizontal position <on edge> they are clamped with a front screw.
In the lid of the workbench on the non-working side there is a tray 5, or, as it is often called, a tool board, in which small tools are held during work.
When processing long boards, a special stand is used to support the free end of the board. The stand has a height of 90 cm and consists of a vertical block of rectangular cross-section, on one side of which there are cuts (notches) with an adjustable saddle.
At the workplace, in close proximity to the workbench, there should be a locker for storing tools, auxiliary materials, and drawings. The tool should be stored in a strictly defined order.
The workplace must be properly organized. This will help achieve high labor productivity. The basic requirements for organizing a workplace are as follows. The workplace should only have everything necessary for work.
2. The area of the workplace must be such that the worker does not make unnecessary movements during the normal process, but is not constrained in the necessary production movements.
3. Each item must have a permanent place.
4. The workplace must be well-equipped: provided with good ventilation, sufficiently lit and heated.
The area required for work, in addition to the workbench, as well as the location of the necessary tools and devices at the workplace depend in each individual case on the nature of the work being performed.
Nowadays, when the procurement of parts in many carpentry industries is almost completely mechanized, and with increasing processing accuracy, fitting work is significantly reduced and most of the operations for assembling products (for example, in the production of carpentry and construction parts) are successfully performed mechanized, the workbench is used less and less.
When performing carpentry work, various tools are used. They are divided into main and auxiliary. Basic tools include saws, planes, drills, chisels, etc., auxiliary tools include hammers, mallets, pliers, wire cutters, screwdrivers, files, etc.
The carpenter's hammer (Fig. 36, a) must be prismatic in shape with a smooth striking surface of the striker. A carpenter should have two or three hammers of different weights: 200, 400 and 600 g. A hammer weighing 400 g has a length of 110 mm, and the cross-section of the striker is 20 X 20 mm.
Handles for hammers are made from tough wood of dogwood, birch, hornbeam, etc.
Mallet (Fig. 36, b) is a wooden hammer used to strike the handle of a chisel or chisel. The head of the mallet can be flat or round (barrel-shaped). The mallet is made from elm, elm, hornbeam or silver birch. The barrel-shaped mallet is made with a maximum diameter of 120 mm, a diameter of the ends of 80 mm, a height of 180 mm, and a handle 390 mm long.
The screwdriver (Fig. 36, c) is used for screwing in screws.
depending on the size of the screws it has different widths
pointed end. The screwdriver blade can be single-sided or double-sided (adjustable). In this case, the ends of the piece of iron have different widths. A screwdriver inserted into the brace greatly facilitates work and allows you to work more productively.
Files are used to clean parts in places that are inaccessible to other tools. There are rectangular, triangular, round and semicircular files. According to the size of the notch, files are divided into rasps (Fig. 36, d), personal (Fig. 36, e) and velvet. Rasps have the largest notch in the form of pyramidal, staggered teeth-incisors. Personal and velvet files have a fine linear single-row and double-row notch.
Rice. 36. Auxiliary carpentry tools: a - hammer, b - mallet, c - screwdriver, d - rasps, d - personal files, f - pliers, g - wire cutters
Before use, it is recommended to wipe files with chalk or charcoal. This protects the notch from contamination. If dirty, clean the rasps with a steel brush. The simplest and most harmless way to clean files is to immerse them in boiling water for a few moments.
Pliers (Fig. 36, e) are used when pulling out nails or pins. Their jaws should fit tightly and be strong.
Nippers (Fig. 36, g) are used to bite off the heads of nails in order to obtain a pin necessary for the hidden connection of various parts of the product.
Read more about carpentry work...
ps When copying materials and photographs, a link to the site is required.
Saratov 2007-2015
Electrical tools
Electric saw
For electric models, the source of energy that powers their operation is an electric motor, which in turn is powered by an electrical network or batteries.
Such models have certain advantages and disadvantages in comparison with manual analogues, these are:
Advantages:
- When using it, practically no human physical strength is used.
- High efficiency of use.
- The ability to withstand high loads that are beyond human strength.
- Multifunctionality.
Flaws:
- Dependence on the presence of electrical networks.
- Inconvenience of performing work due to the presence of an electrical wire.
- High cost compared to manual analogues.
- Availability of operating costs associated with paying bills for consumed electrical energy.
Electrical devices are used at all stages of working with wood.
The industry produces electric chain saws and circular saws, as well as jigsaws used for sawing various types of lumber. Electric planes and drills are used for planing and drilling.
For the convenience of working with electric hand tools, models powered by rechargeable batteries are available, which allows you to be more mobile when working with them. Such a tool is a screwdriver.
Sometimes wood milling and engraving machines are used for wood processing; these units are distinguished by high productivity and precision of mechanical processing of parts. Such machines are often used in production, since their cost is quite high, but depending on the model, they are also used at home.
Basic woodworking techniques
JOINER'S WORKPLACE
The carpenter's workplace is equipped with a workbench and a set of necessary tools and equipment. On the workbench, parts up to 3 m long are processed and individual elements or entire products are assembled.
The workbench consists of a lid and a base - a bench. The bench board is equipped with front and rear vices. Its front edge has a number of holes (sockets) intended for installing wooden or metal stops. Along the workbench board (on the back side) there is a tray in which small tools are placed.
The base consists of posts connected to each other by bars. In some workbenches, a cabinet is installed in the underbench for storing tools and materials.
Front and rear vices are designed for clamping workpieces. The front vise has a clamping screw and a backing board, the rear vise moves with a screw. Stops are inserted into the sockets, between which the material being processed is placed in a horizontal position. By rotating the screw of the rear vise, the material is clamped. The stops are placed below the plane of the wood being processed so that the tool does not touch them. To hold the material being processed on the workbench, a notch is made in the stop adjacent to the wood. The stop is held in the socket by a spring.
When processing material in a vertical position, it is clamped in either a front or rear vice. Window sashes, door panels, and vents are placed between two combs (stops) and clamped with a rear vice.
The base of the workbench is made of coniferous wood, and the workbench board is made of birch, oak, ash, and beech. The thickness of the bench board is 60-70 mm, width 400-500 mm.
The height of the workbench is selected as follows: the carpenter should stand near the workbench and rest his palms on it. If, in a straightened state, it rests on the workbench without difficulty, then the height is selected correctly. With a low workbench, the worker has to bend down, with a high one, he has to stretch out his arms, which quickly tires.
The bench board must be level, without distortions, since it is impossible to perform precise work on a skewed board. The vice must firmly clamp the material being processed, and the bolts holding the workbench together must ensure its stability. The wedges should fit snugly into the sockets, but not too tight so as not to poke out their edges.
Screws are made of metal, less often - of wood. For smooth movement, the screws and running parts of the workbench are periodically lubricated. When not in use, it is recommended to keep the screws slightly tightened.
The workbench is covered with drying oil. Do not install it near heating appliances, place hot objects on it, or expose it to moisture.
When performing some work (sawing, chiselling, drilling, cutting with a chisel), a backing board is placed under the elements being processed in order to protect the workbench from possible damage.
The carpenter's workplace should be well lit and kept clean.
Small parts are clamped with clamps. A clamp is a bracket through one end of which a screw with a diameter of 20-25 mm passes with a handle with a diameter of 25-30 mm. Clamps can be wooden or metal. Metal clamps are used to glue small plots into panels.
Hand tools
Ax
A hand tool assumes that the energy that ensures its operation is the strength of the person using this tool; it is used in all wood processing operations.
- Hacksaws equipped with various types of blades are used for sawing boards in various planes. Round timber is harvested with two-handed saws, and with their help and with the use of bow saws, the harvested timber is cut. Jigsaws are used to make decorative design elements, as well as crafts and furniture of various designs.
- An ax is a construction tool and military weapon known from time immemorial. Axes are used by joiners and carpenters when performing various operations using wood (building houses, manufacturing structures and individual elements - windows, doors, etc.). Cleavers are used when preparing firewood.
- In the manufacture of wooden structures (windows, doors, stairs, etc.), various types of planes (sherkhebels, jointers, tongue and groove piles, etc.) are used to process the raw materials.
- When making grooves and tenons, and making holes, chisels and chisels of various sections are used.
- For drilling, hand drills and rotary hammers with drills of various designs (center, twisted, spoon) are used, as well as drills used for deep drilling.
- In the manufacture of furniture and various carpentry, clamps are used to tighten and fix the assembled elements into a single structure.
- Nail puller and pliers are indispensable types of tools when removing foreign objects from solid wood.