Production and use of lumber
Lumber is made from hardwood or softwood. To obtain high-quality products, during manufacturing the wood is thoroughly dried and treated with protective agents. This prevents rotting and drying out, the appearance of mold and rot, and the formation of cracks.
Based on the degree of humidity, dry products with a humidity of 8-10% are distinguished, which are used for the manufacture of parquet boards and panels. Wood with a moisture content of 12-15% is considered universal and is suitable for the manufacture of floor boards, skirting boards and trim, fillets and interior doors. Materials with 18% humidity are used for lathing and rafter structures, and exterior finishing.
The result is a high-quality and reliable dry material that is resistant to the negative effects of moisture and steam, insects and ultraviolet radiation. It is lightweight. Such products are easy to cut and saw, lay, coat with paint, varnish and oils. Lumber is characterized by easy and quick installation, simple processing and availability, environmental friendliness and naturalness.
Notes on the topic: “Lumber” 6th grade.
Lesson topic:
Lumber: types (beams, boards, whetstones, sleepers, slats, planks, planks), purpose and characteristics of the main types.
Goals
: to familiarize students with wood as a structural material, with the types of lumber and wood materials; teach to identify tree species by the appearance of samples; cultivate a caring attitude towards wood and timber.
Tools and equipment:
table “Structure of wood”; collection of samples of wood species; set of wood lumber, veneer, plywood, fiberboard, chipboard;
During the classes
Wood is a natural construction material. It is obtained from the trunks of felled trees of various species. The following tree species are distinguished: deciduous (oak, birch, linden, aspen, beech, etc.), and coniferous (spruce, pine, cedar)
Let's look at the structure of wood:
When longitudinally sawing tree trunks on sawmill frames, various lumber
(see figure):
beams, whetstones, boards, plates, quarters and slabs
.
timber
— lumber with a thickness and width of more than 100 mm. If the beam is sawn on both sides, then it is called two-edged, and if on four sides, then four-edged.
Bruschi
- lumber having a thickness of 50-100 mm and a width of no more than double the thickness, i.e. 100-200 mm.
Boards
- these are lumber 13-100 mm thick and 80-250 mm wide, i.e. more than double thickness.
Plates
obtained by longitudinally sawing logs in half, and quarters - into four parts.
A board differs from a block in that its width is more than 2 times the thickness
.
A slab
, or
an obapole
, is the sawn side part of a log
. Lumber:
a – four-edged beam;
b – double-edged beam; c – bars; g – edged boards; d – unedged boards; e - plate; g - quarter; h – slab (1 – face; 2 – edge; 3 – end; 4 – rib). Obapol
- the side parts of a log, cut off during longitudinal sawing.
Planks and planks
are thin and short lumber of rectangular cross-section, and
slats
are flat bars and thin narrow boards.
According to the nature of processing, lumber is divided into unedged and edged
.
For edged materials,
all four sides are sawn, and the dimensions of the wane do not exceed the permissible limits;
In unedged ones
, the sides are sawn, and the edges are not sawn at all or partially sawn.
Blanks
.
These are boards and bars, cut to the overall dimensions of the parts with appropriate allowances for shrinkage and subsequent processing. Blanks used in the construction of joinery and furniture products can be either solid or glued, and have various cross-sectional shapes. Lumber
has the following elements:
faces, edges, ribs and ends
.
The face
is the wide plane of the lumber, and
the edge
is the narrow plane.
An edge
is the line of intersection of these two planes.
End
- transverse (end) plane of lumber.
Lumber can be obtained from a log by sawing it into beams and boards, turning it over and changing the distances between saws. Several cutting options are shown below.
Plywood is widely used as a construction material.
.
veneer
- onto each other .
“Veneer” translated from German means “sliver” (shavings) Veneer.
It has been known since ancient times, and the mechanical method of producing veneer (on a machine) was invented at the beginning of the 16th century.
Currently, peeled and sliced veneers
.
Peeled veneer
is single-layer sheets of wood obtained by peeling birch, alder, maple, beech, pine, spruce, and larch wood on machines.
Peeled veneer
is cut (peeled) with a sharp knife of a special peeling machine while rotating a log, previously steamed in hot water, about 2.0 m long (see figure).
In this case, the log, like a roll, is rolled out into a veneer strip. The veneer strip is cut into square sheets, which are dried in dryers, coated with glue and laid on top of each other so that the direction of the fibers in them is perpendicular to each other. The sheets are glued together under a press. This is how plywood with a thickness of 2 to 20 mm is obtained. Veneer is used for veneering wood products and making plywood, glued and bent-glued products, as well as furniture, sports equipment and other products from plywood. Veneer dimensions at a humidity of 8±2% should have a length of 800–2500 mm (with gradations of 100 mm), a width of 150–2500 mm and a thickness of 0.35–4.0 mm. Sliced veneer
is thin sheets obtained by planing beams from wood species with a beautiful texture (oak, beech, walnut, maple, ash, mahogany) on veneer planing machines.
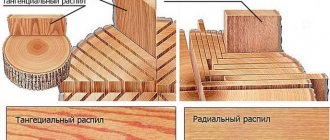
When planing, the log is stationary, and the knife moves back and forth and cuts the wood layer by layer (sliced veneer). Depending on the texture of the wood, sliced veneer is divided into tangential, radial, semi-radial and tangential-end
. Sliced veneer can have a length of over 300 mm with a gradation of 100 mm and a thickness of 0.4-1.0 mm. The width of the veneer, depending on the type and texture of the wood, must be at least 60 mm. The moisture content of veneer varies between 8 + 2% Veneer sheets are placed in bundles in the order in which the sheets were released when planing wood. Sliced veneer is used for lining wood products and semi-finished wood products in the manufacture of furniture. From it you can type various geometric and other ornaments.
Veneer is obtained in several ways: planing, peeling or sawing
Sliced veneer
used for cladding furniture,
peeled
- for making multilayer plywood. Veneer can cover not only flat surfaces, but also complex curved shapes. To cover such surfaces with veneer, special “beds” are most often used, which cover sheets of veneer or in which they lay it, pressing it with clamps or a press.
Plywood
.
It is obtained by gluing three or more sheets of peeled veneer
.
The joined sheets are positioned so that the direction of the fibers in them is mutually perpendicular. The type of plywood is determined by the type of wood from which its outer layers are made. The dimensions of plywood sheets are as follows: length (width) 1220–2440 mm, width (length) 725–1525 mm, thickness 1.5–18 mm. Plywood
differs from other sheet materials in the comparative uniformity of physical and mechanical properties due to the cross direction of wood fibers in adjacent layers, less warping and cracking under various conditions of use.
Plywood
is stronger than wood, almost does not dry out or crack, and bends and processes well.
In housing construction, it is used for cladding panel doors and panels, making attic floors, etc.; in car and shipbuilding it is used as a front finish; In the furniture industry, plywood is used to make the back walls of cabinets, bookshelves, chairs, table tops and other products. Plywood is made mainly from birch wood. Particle boards (chipboards)
are produced by pressing and gluing crushed wood in the form of shavings, sawdust, and wood dust.
For the production of particle boards, mainly wood waste and even bark are used. , flat pressing
slabs are distinguished (with the arrangement of wood particles parallel to the surface);
continuous pressing
(with the arrangement of wood particles perpendicular to the surface. Depending on the design, chipboards are divided into single-, three- and multi-layer. The boards are produced
uncoated
(unsanded and sanded),
lined with peeled or planed veneer, paper
. In addition, lined boards can be
finished and unfinished
(with or without paint coating). Chipboards have the following dimensions: length 2400-5500 mm, width 1220-2440 mm, thickness 10-26 mm. Flat pressing boards are used for the manufacture of furniture and critical parts in construction, and continuous pressing boards - for the production of non-essential building parts. They are durable, almost do not warp, can be processed well with cutting tools. Furniture, doors, partitions, walls, floors are made from them. However, over time they emit substances harmful to health, so they are undesirable for use in residential premises .
Fiberboards (Fiberboard).
This is a sheet material made from wood fibers compressed into a homogeneous material under high pressure and high temperature.
Based on their bending strength, slabs are divided into super-hard, hard, semi-hard and soft. The length of the slabs is in the range of 1200–6100 mm, width 1000–2140 mm, and thickness 10–25 mm. Fiberboard
is used along with plywood in the manufacture of joinery and furniture and joinery and construction products, for interior decoration: cladding walls, ceilings, floors, in the production of furniture and doors. They have a pleasant gray or brown color, smooth surfaces, and bend, like plywood. The disadvantage of plywood, particle boards and fibreboards is that they are susceptible to dampness. Under the influence of water and moisture, plywood delaminates, and the boards swell, lose strength and crumble.
Practical part
Studying samples of lumber and wood materials a) determining the type of lumber b) finding face, edge, edge, end in lumber samples c) consider plywood, chipboard, fiberboard. Count the layers in plywood d) check for processing with a file or hacksaw. 5. The final part - cleaning workplaces, class - - summing up the lesson - - assessments - - homework - § 3
Types of lumber
According to the processing method, edged and unedged materials are distinguished. The first option is the most popular, since the sides of the product are cut and processed. The result is smooth and even sides, an attractive and aesthetic appearance. The trimming method of processing expands the scope of application of products and extends the service life.
The following assortment is produced:
- The beam has a rectangular or square cross-section with a side of over 100 mm. Used in construction and finishing. They produce profiled and laminated timber;
- Bar - a beam with smaller dimensions, which is used for rough work and arranging sheathing;
- Board is a finishing and building material with a thickness of up to 100 mm and a width greater than twice the length. They make floor boards, edged and unedged, planed and unplaned;
- Sleepers are beams that support the rails;
- Obapol has an outer unsawed side and an inner sawn side. Used to create formwork for foundations and sheathing, for collecting firewood, making scaffolding and fasteners;
- A slab is a side part of a log with one sawn and one unsawed surface. Represents a board convex on one side. Suitable for making firewood and flooring, formwork, constructing outbuildings (shed, greenhouse) and building fences;
- Lining is a wooden finishing material with smooth, even sides and high-quality processing. We present narrow slats with convenient tongue-and-groove fastening. Used for covering floors, walls inside and outside. A block house is also distinguished. This is a type of lining that is flat on one side and imitates a log on the other.
For construction and finishing, it is important to choose products without rot, knots, wormholes and other defects. Choose the highest (selected) or first grade lumber with the required moisture content from a reliable manufacturer. Good products are made in compliance with GOST and must have quality certificates. In addition, the rules for transporting and storing wood must be observed.
Technology lesson notes
6th grade
Module:
Technology of processing of structural materials and elements of mechanical engineering.
Chapter:
Wood processing technology and elements of mechanical engineering.
Subject:
Production and use of lumber.
Lesson objective:
Study of the production process and methods of using lumber.
Goals:
Educational:
- To familiarize students with the process of production and use of lumber.
- Learn to distinguish types of lumber.
- Developmental:
- To develop curiosity among schoolchildren.
- Ability to analyze.
- Apply the acquired knowledge in practice.
- Educational:
- Improve environmental education of students.
- Instill an active life position.
- Foster initiative and independence.
- Career guidance:
- To create students' interest in professions
Forester, forester, carpenter.
Methodological equipment of the lesson:
- Material and technical base:
- School workshop
- Computer and media projector
- Didactic support:
- student workbook
- posters: “Wood processing products”,
“What can be obtained from one cubic meter of wood”, “Defects of wood”, “Practical work”.
Film "Sawmill Frame"
- Materials for monitoring students' knowledge:
Game “Is the statement true?”
- Cards: “Defects of wood.”
- Literature:
Textbook "Technology" 6th grade.
Magazine “Holiday at School” – 2005
Vocabulary work:
sawmill frame, saw set, cut, falling rollers, trolley.
Lesson type:
A lesson in acquiring new knowledge and skills and applying them in practice.
Methods:
Verbal, visual, practical.
During the classes.
- Organizing time.
- greetings
- checking student attendance
- teacher filling out a class register
- checking students' readiness for the lesson (notebooks, pens)
- getting students in the mood for work.
Teacher - Hello guys.
Uch. Guys, please tell me, do any of you like the autumn forest?
Scientist Yes!!!
Uch. Why do you love him?
Scientist Because in autumn the leaves of the trees turn different colors and it becomes very beautiful; you can collect mushrooms, nuts, etc.
Uch. What else does the forest give us?
Scientist Wood!
Teacher. How do trees turn into boards and beams?
Learned!!!???
Teaches: It’s okay, today we will learn everything, and so the topic of our lesson is “Production and use of lumber.”
- Updating students' knowledge:
First, let's remember what we talked about in previous classes.
Game “Is the statement true?”
The class is divided into 2 groups. The teacher asks questions to the groups. If the student gives the correct answer, the teacher hands over the sheet. (Guys must collect as many leaves as possible, i.e. points)
- Cracks are defects in wood. (Yes).
- Larch does not shed its needles in winter. (No)
- Cedar is a hardwood (no)
- Plywood is made from sawdust (no).
- All materials made from wood that have preserved its natural state are called timber (yes).
- The ripeness of wood is determined by taxators (yes).
- The work of foresters is supervised by forest rangers (yes).
- Wood moisture content is characterized by its moisture content (yes)
- Fiberboard stands for particle board (no)
- Sticks, logs, ridges and logs are timber (yes).
Guys. Please name the wood processing products, i.e. what is obtained from wood?
(FIG. 1.)Wood processing products.
Fine. In the last lesson we studied the topic “Defects of wood”. Now I will give you cards where you need to show with arrows the defects of the wood. Time for task 1-2 minutes.
Presentation by the teacher of new material:
Teacher. And so “Production and use of lumber.” In grade 5, we already became acquainted with the main types of lumber. Who will help me remember them?
- Student. Beams, whetstones, edged and unshaped boards.
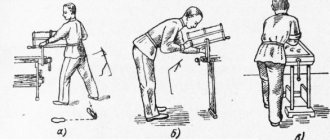
Teacher - correct. We know that lumber comes from sawmill frames. Has anyone seen how a saw frame works?
(Teacher shows a drawing of a sawmill frame)
Logs are transported to sawmill frames using chain log transporters
.
The sawmill frame consists of a saw frame with a set of vertically mounted strip saws. A set of saws in a saw frame, installed at a certain distance from one another to cut boards of a given thickness, is called a set.
The saw frame is mounted on guides. It can make vertical movements up and down using a crank-slider mechanism driven by an electric motor.
At the front and rear of the sawmill frame there are driven, rotating grooved double rollers that drop the log forward.
In front of and behind the frame, carts are installed on rails to accommodate logs and boards.
Principle of operation. The log is thrown from the log hauler onto a cart installed in front of the frame and falls between two falling, rotating grooved rollers. The rollers grab the log and push it onto a saw frame with saw blades moving up and down. The saws cut the log into lumber, which is grabbed by grooved rollers located behind the frame and fed to a cart installed behind the frame.
This is how boards and beams are obtained.
Edged boards are obtained by sawing logs in 2 steps.
To better consolidate the knowledge gained, let’s watch a video clip of how a sawmill frame works.
Vocabulary work
.
Sawmill frame, saw set, log hauler, cut, falling rollers, cart.
- Practical work.
- Induction training. The children are given circles of different diameters (ø20-ø30) - this is the cross-section of the logs.
- Teacher - Guys, there are circles in front of you. Imagine that this is a cross section of logs. Your task is to determine what kind of lumber can be obtained from these “logs”. To do this you need to have a ruler and a pencil. We know that our floorboards are from 40mm to 60mm thick, planks are from 20mm to 30mm, timber is 200mm on sides, timber is 100mm on sides.
– Teacher – Safety briefing:
- Instructing the teacher on completing homework.
- Teacher - Guys, I present to your attention a simple storage device - a product that is mounted on the wall, where you can hang keys, brushes, and anything else needed in the household. Your task is to develop your own individual drive based on this drive. Those. For the next lesson you bring me a sketch of the drive where you can already put down the approximate dimensions.
- Summing up the lesson.
- Teacher - And so today, guys, we studied the topic “Production and use of lumber.”
What new things have you learned about yourself?
- Teacher - Well done. Lesson grades.
- Message from the teacher about the achievement of the lesson goal.
- Message about the topic of the next lesson “Drawing of a part. Assembly drawing".
Wooden house from the manufacturer
The MariSrub company independently produces construction and finishing materials from durable, selected pine. This wood is distinguished by its high density, resistance to wear and moisture, long service life, aesthetics and original textured pattern. We carefully monitor the selection of raw materials and product quality, comply with GOST requirements, standards for storage and transportation of lumber.
When harvesting wood, we use condensation drying, which thoroughly, carefully and evenly dries the material inside and out. As a result, the products do not crack and last longer. In addition, condensation drying prevents the formation of manufacturing defects. Read more about this drying method here.
Each material is treated with protective compounds. We offer timber and logs of various sizes, we select suitable products for the construction and finishing of the house. We carry out a full range of work, including developing a project, manufacturing and installing a log house, building a foundation and covering the roof.
We build wooden houses from timber and logs according to individual and standard designs. We carry out utility networks, install windows and doors, stairs and interior partitions. We do the finishing, hydro- and sound insulation, insulate the structure and treat it with protective agents. We guarantee high quality and efficiency of construction!
General concepts
Materials that are obtained through the transverse and longitudinal cutting of fallen trunks and parts of trees are called timber.
The upper end of round timber cannot be less than 12 cm, thin logs up to 11 cm in diameter, and poles up to 7 cm. The logs are cleared of branches to the surface level, the bark is removed from them, and the bast layer is completely removed.
Round timber can be used for construction or sawing purposes.
Construction logs are mainly made from coniferous trees, less often from oak. Thanks to construction logs, load-bearing structures such as piles, various supports for the construction of bridges, tunnels, etc. are created. construction logs range in length from 3 to 6.5 meters. Wood is divided into 4 grades according to quality characteristics, but only grades 2 and 3 are used in construction.
Bucking is the process of dividing fallen trunks into different sections. A tree whip is a fallen trunk that has been completely cleared of bark, branches and leaves. Commercial and firewood is obtained by bucking logs. This division is carried out solely due to size and the presence or absence of defects.
Lumber is obtained from saw logs, and plywood is created from scraps. Logs are stored in stacks, laid out in accordance with the type of wood, category, length. Lumber is distinguished by wood species and geometric shape, and can be considered one of the most important types of wood products.
Assortment and assortment of wood - division of lumber into edged and unedged parts. For the assortment there is a regulatory GOST 24454-80.
Types of timber
Timber products differ greatly from each other; they may have their own purpose, their own GOST standards, and manufacturing method. Round timber is pieces of tree trunks of various trees that are completely cleared of twigs, branches, and leaves. The cross-section is round, obtained by cross-cutting a whip. Logs can be either with or without bark.
The range of timber differs in the nature of processing: they can be edged or unedged. Some lumber can only be cut on one side.
- Edged lumber - materials with parallel front or back sides, edges that were sawn perpendicular to the face, with a sawing defect not exceeding acceptable values.
- Unedged lumber – materials with parallel front and back sides, with fully or partially sawn longitudinal narrow sides, with sawing defects exceeding the permissible values.
Types of lumber
Lumber is divided into:
- Plates representing a half log that has been sawn along the stem axis.
- Wood quarters obtained by sawing a log along two diameters, which are mutually perpendicular to each other, into 4 parts.
- The bars are more than 10 cm thick and wide.
- Wooden sleepers - look like timber with a large cross-section. Designed mainly for laying under railway rails.
- Boards – up to 10 cm thick, no more than 20 cm wide.
- Bars - lumber less than 10 cm thick, up to 20 cm thick.
- Croakers are waste obtained from sawing the side of logs.
- Planks are lumber having a thickness of 6 to 8 cm and a width of 10 to 16 cm.
- Flat slats - thin wooden boards, bars.
Lumber range
The assortment is useful to know for people who currently want to engage in private construction of permanent buildings and independent outbuildings.
Each cutting parameter and the main size of the material are prescribed in state standards, independent study and analysis of which will not take much time.
Products manufactured by any sawmill must fully comply with generally accepted state standards.
There are basic assortments for deciduous and coniferous trees. Deciduous wood is usually divided into 4 grades, and coniferous wood into 5.
Selected timber is considered an additional type of coniferous wood. Specific materials are judged by the worst of the cut parts, the edges.
Wood grades are determined by the presence or absence of defects, defects, moisture and the presence of mold or rot.
The grade of sawn wood can be determined by its filigree processing.
- First-class ones are used in the construction of permanent and temporary buildings. They can also be used to decorate walls and floors of standard thicknesses.
- Second-class raw materials are used for flooring and sheathing.
- Third-grade load-bearing structures are constructed from third-grade wood.
- The fourth is used to make containers and small preparations.
Requirements for lumber
Lumber must comply with generally accepted standards. The main GOST for lumber under the number 8486-86 determines the basic dimensions for coniferous timber.
For deciduous trees, GOST 2695-83 is considered the main one. For example, there is a GOST that specifies the dimensions of wooden beams: from 10 cm in width and thickness.
Assumptions for deviations in lumber dimensional parameters
The dimensions of wood are regulated by GOST and have their own limitations depending on the scope of use of the timber:
- for the construction area, dimensions can vary from 100 to 650 cm;
- container boards – starting from 50 cm;
- bars and special boards – 325 cm;
- for export – from 90 to 630 cm.
GOST timber provides for the following deviations:
- width – no more than 2.5%;
- width – no more than 2%;
- length – -2.5, +5 cm.
If the timber is less than 1.5 m in size, then all restrictions are lifted for them.
Wood defects associated with structural features
Wood defects are deviations from established standards associated with the structure of the trunk of a fallen tree. Most often these are knots, warping, various cracks, and defects associated with the formation of the trunk. The tree could also be susceptible to fungal infections. Often, material with defects cannot be used in construction, but it is useful for design.
Marking
For labeling timber, it is important to take into account and record in production such indicators as:
- Type of lumber or timber.
- Types of wood.
- Wood species.
- Basic standards of parameters, while width is not specified for unedged lumber.
- State standards (mainly for timber indicate No. 8486-86).
Production technology
The lumber production process begins with the purchase of round timber. At the same time, it is important to choose the right wood - the subsequent quality and price of the finished product depends on this.
It is important to pay special attention to safety precautions during production. Accidents happen very often. Before starting work, the wood is well processed, completely cleared of branches and bark.
There are special forestry machines that can clear wood immediately in the forest.
After cleaning, the wood is sawn, the main indicators of the beams are determined, sorted, and sent for further processing.
The production of round timber is carried out from coniferous and deciduous trees. To obtain the highest quality products, the wood is completely dried and treated with special compounds during production. Thus, the resulting product is completely ready for use, it does not rot or dry out.
Products are divided according to humidity indicators:
- Dry, the humidity of which does not exceed 10%. Parquet and panels are made from such lumber.
- Universal with humidity from 12% to 15%. Such lumber becomes the basis for the production of floor boards, baseboards, trim for windows and doors, and is used to create interior doors.
- Wet lumber with 18% moisture content is used for arranging rafter structures, as well as for exterior finishing of structures.
Thanks to high-quality processing, you can obtain good material for home improvement, as well as for construction. Such lumber will be lightweight, easy to saw, install, and paint. Before purchasing timber or lumber, it is important to know the exact purpose of the purchase.