5a0 fdb 302 e42 8c7 609 bb8 0a1 4bb 6d2 61c 390 06a f56 1dc eb1 0d6 583 e84 673 92b b35 956 38e 7da f12 93a e09 dd4 b41 3d0 70a 23e c6d 5 31 d6c 928 249 e8c e09 95a f9c c1e 8e1 66b d1f 572 695 78d 4c7 435 f3d 7cb 59a 35f ec6 cd2 a6f 9d1 5eb 62c df9 c17 0b5 b77 4a6 35a 98a 5b3 8e2 f8b 16d f80 e1d 1b5 bfa a5d 6c7 830 e29 87c a31 607 f0c 68e 5ff 5c7 152 a10 3c9 752 ece 728 513 f40 4e6 8b0 45b 13f 681
The main disadvantages of floors with wooden beams include:
Hello everybody. The essence of the question is this: We bought an apartment on the top floor in a new building. I decided to go to the attic to look at the insulation and saw mineral wool slabs there with a density of at most 30 kg/m3, there were no walking bridges. The laid layer of thermal insulation with a thickness of 200 mm in the places of passages along it turned into a layer of thermal insulation with a thickness of 30-50 mm (the insulation did not regain its shape after walking on it). We asked the developer for documentation - the developer completed everything in accordance with the project (insulation sq. 30-40 kg/m3, no walkways). Accordingly, the questions that are urgent: 1. Is there a document that specifies standards for the construction of walkways when laying insulation in the attic? low density? 2. Are there standards for the density of attic insulation coatings?
The transition bridge can be installed on any type of roof.
What is an attic
The attic space is limited by the roof slopes and the ceiling of the residential floor. This place is often used to create additional living space.
There are two types of attics in private households:
- Residential . It is called an attic. It can be equipped with a living room, study, bedroom, library, etc. The height of the room in this case should be at least 220 centimeters. In addition, it is necessary to provide ventilation, natural lighting, and insulate the slopes.
- Non-residential . Such attic space is usually used to house technical equipment and store old or unnecessary things. In this case, a 2-meter height will be sufficient, and there is no need to provide natural lighting. Instead of insulating the slopes, they insulate the attic floor.
When making a decision to repair or rebuild a house, you need to decide in advance for what purpose the attic will be used in order to make calculations and a design for the floor. The list of necessary materials and the gap between the beams depend on this. They must provide the required strength and load-bearing capacity.
Functional purpose of floors
The design of the attic floor depends on the parameters of the structure and the purposes for which it is planned to use the under-roof space. The attic functions as a kind of air gap that separates the cold roof from the heated floors.
The floor in the attic performs a number of tasks:
- carrier _ The floor, located between the upper residential floor and the attic space, is assigned a load-bearing function, so it is made reliable and durable, since people will move on it, they plan to place equipment on it and arrange storage areas;
- insulating _ In a cold attic, the temperature differs little from that outside the house. In this case, the floors in the attic have a thermal insulating function, thereby preventing the air from cooling on the residential floors. To retain heat, the attic floor needs to be insulated. It is advisable to entrust such work to professionals.
Features of the device and design of floors
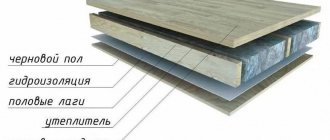
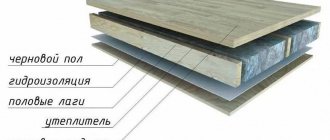
Since attic floors perform two functions - load-bearing and insulating, they have a multi-layer structure. Each of the elements of the “pie” complements each other, which ensures the created structure has a long service life, strength and the ability to withstand heavy loads.
The construction of the floor in the attic requires the presence of the following layers:
- Finish floor . This name is given to the floor covering, which is laid on a rough base. If it is an attic, then when installing the finished floor, linoleum, laminate, parquet, etc. are laid. In non-residential premises there may be no finishing floor covering.
- Rough base . It is a boardwalk that is mounted on logs. The subfloor is lined with edged boards 4–5 centimeters thick or, to save money, with unedged boards.
- Lags . These are strong, level pieces of wood that are laid perpendicular to the floor joists to create a floor covering. When installing an attic floor on wooden beams, insulation is placed between the joists, which is protected from below with a layer of vapor barrier, and covered with waterproofing material on top. If you do not use insulating layers, then repairs will be required in a few years.
- Beams . The frame of the floors is built from thick and strong beams, which are either mounted on the projections of the walls or built into them. They must support the entire weight of the structure. A flat roof can also be made on wooden beams, which is quite practical.
- Ceiling trim . On the side of the rooms, the floors are decorated with finishing materials, for example, natural wood or plasterboard.
Roof waterproofing
Micro-perforated film is best suited for waterproofing cold roofs. This is one of the cheapest and easiest to install materials that completely solves the problem of condensation. During installation, the roll of film is rolled out across the slope of the slope, starting from the bottom. Each subsequent canvas should be laid with an overlap on the bottom one with a width of about 70 mm.
It is better to install the hydrobarrier in calm weather. Temporary fastening is carried out with staples to the upper edge of the rafter legs; in this case, it is necessary to adjust the force of the stapler spring so that the staple does not press close to the film, pushing it, but creates a gap of about 0.5 mm. The film must be attached in such a way that there is a sag of about 20–25 mm between the rafters. This way, water will not soak the counter-lattice, collecting at the lowest point.
When the entire slope is covered with a hydraulic barrier, you need to nail the counter-lattice - slats of the same thickness as the rafter legs. Before nailing the batten, the side on which it is adjacent to the rafters can be coated with any alkyd enamel. Lumber for counter-lattice and sheathing should be pre-treated with fire-bioprotective impregnation. It is recommended to fasten the counter-lattice either with straight nails or anodized screws. Black hardened screws are not suitable for this purpose.
The counter grille performs several functions at once. Firstly, it reliably presses the hydraulic barrier, while covering the punctures at the attachment points. Secondly, due to the increased distance between the coating and the waterproofing, a path appears for the ascending air flow, due to which the formed moisture quickly evaporates.
Types of attic floors
To construct the ceiling of a cold attic, materials differing in weight, durability, cost and load-bearing capacity are used.
There are several types of floors depending on what they are made of:
- Wooden elements . For their manufacture, you can use beams with a cross-section of 150x150 or 200x200 millimeters. The advantage of this option is that wood is quite durable and at the same time relatively light material, so wooden elements do not put additional load on the foundation of the house. In addition, their big advantage is their low price and availability. But such an attic floor is used when the size of the building does not exceed 6-10 meters, since this is the maximum length of lumber.
- Metal products . Metal I-beams are distinguished by their strength and ability to withstand heavy weight without deformation. But they weigh a fair amount, so they are rarely used in wooden houses, but for brick and aerated concrete buildings they are the best option.
- Reinforced concrete products. Molded floor beams, made from reinforced heavy-duty concrete, are used for multi-story buildings, since they are heavier and the same length.
Of all the above types of floors, in private low-rise housing construction, in most cases, preference is given to wooden beams. They have the optimal balance between price and quality. If the calculations are carried out correctly and the technology is followed, repairs to the ceiling will not be required in the coming years. Ventilation is also necessary in the attic of a private house, the arrangement of which will require additional knowledge.
Preparation
The lumber used in the construction of the roof frame is constantly exposed to moisture, and therefore can rot and deform over time. Therefore, it is important not only to choose correctly, but also to properly prepare materials for installation. The following requirements apply to wooden sheathing:
- Boards and lumber used for installation must be brought to a standard moisture content of 19-20% so that they do not deform or rot during operation.
- To prevent rotting of the sheathing, the wood must be treated with an antiseptic composition. Deep impregnation with an antiseptic allows you to double the service life of the frame.
- Sheathing elements for soft roofing coverings (bitumen shingles, membranes, roofing felt) must be sharpened so that the uneven surface does not damage the material during installation or operation.
Remember that nails or other fasteners to secure the sheathing must also be moisture-resistant and have a length equal to twice the thickness of the board or plywood from which it is made. In addition, you cannot drive the nails all the way in; you need to leave a small gap necessary to compensate for thermal expansion.
Requirements for the device of the pie
Since the safety of staying in the house depends on the quality of installation and repair of attic floors, a number of requirements are imposed on their arrangement.
In order to know the maximum permissible load that the structure can withstand, it is necessary to perform the appropriate calculations, and then, based on their results, they begin to develop a project from which it will be clear how to properly insulate the attic floor in the house.
- Load-bearing capacity . It directly depends on the material used to make the beams and the gap between them.
- Distances between load-bearing elements . The maximum permissible value for this parameter in accordance with building codes is 4 meters.
- Resistance to temperature changes . It is necessary that the beams can withstand such changes without problems. The fact is that the difference between the air temperature in the residential floors and in the attic always exceeds 4 degrees.
- Isolation . The attic floor covering of a cold attic should protect the premises of the household from the penetration of cold and moisture from the under-roof space.
During the design process, you should take into account the requirements for the beams used to arrange the floor in the attic so that the result is reliable and durable. The distance between them must be calculated based on the loads exerted on them.
What responsibilities does the management company have for maintaining the roofs of houses?
Often, residents of an apartment building are faced with the fact that the management company (MC) violates their rights. Moreover, the residents themselves usually do not even suspect that their rights are being violated. Therefore, you should understand what is the direct responsibilities of a management company in the housing and communal services sector for the maintenance and repair of houses, in particular, for maintaining the roof of an apartment building.
You need to know that, according to Article 161 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation, the management of an apartment building must ensure favorable and safe living conditions for citizens, as well as proper maintenance of the common property in it. The Government of the Russian Federation, in turn, has established standards and rules for the management of apartment buildings, according to which the roof enclosing the load-bearing structures of the house is the common property of the owners, but its maintenance is the responsibility of the management company.
Technology for creating an attic floor using wooden beams
If you have experience in construction work, you can install the ceiling of a cold attic using wooden beams yourself. This process is performed at the final stage of roofing work.
The sequence of actions will be as follows:
- Installation of load-bearing beams. For a small private house, wooden floors made from timber with a cross-section of 150x150 or 200x200 millimeters are suitable. They are laid on concrete or brick walls.
- Installation of lag. They are placed on the edge perpendicular to the beams in increments of 60 centimeters. The logs are made from boards with a cross section of 150x50 millimeters.
- Laying thermal insulation. The insulation is placed between the joists - it will protect against the penetration of cold from the attic.
- Installation of rough and finished floors.
- Covering load-bearing beams on the side of the room to decorate the ceiling surface.
Mistakes when arranging the attic
The insulation is laid directly on the suspended ceiling
Water vapor will inevitably seep into the thickness of the insulation, which will negatively affect its properties. In addition, there are inevitable gaps in the ceiling through which particles of insulation and/or chemicals released by it will penetrate into the rooms. Before installing the insulation, plank ceilings or rough rolls on beams must be covered with a continuous carpet of thin-layer rolled vapor barrier with an overlap of strips of at least 10 cm.
General scheme of attic floor insulation. Photo: Rockwool
The insulation layer is too thin
The attic floor has the same thermal insulation requirements as the attic roof. Accordingly, the thickness of mineral wool slabs or sprayed cellulose wool or polyurethane foam should be at least 200 mm (if you focus on Northern European standards, then 300 mm), low-density polystyrene slabs - at least 150 mm. By the way, when insulating with polystyrene foam, the joints of the sheets and their junctions with wooden beams must be sealed with polyurethane foam.
The insulation is not protected from weathering
This paragraph concerns fibrous materials, the structure of which is destroyed over time by air currents. Mineral or cellulose wool must be covered with a roll of vapor-permeable waterproofing on top.
Icicles on the eaves are a sure sign of insufficient insulation of the attic floor. Photo: Vladimir Grigoriev
Ventilation of the attic space is not provided
Water vapor somehow penetrates into the attic, and in cold weather it condenses on the sheathing, causing it to rot. And in the summer heat, the air under the roof becomes very hot and through the smallest cracks and leaks in the ceiling “flows” into the rooms on the second floor, where it also becomes hot. To avoid these troubles, you need to organize intensive ventilation of the attic. Today, most experts believe that the attic roof, like the attic roof, should be equipped with perforated eaves soffits and a ventilation ridge.
Gable dormers are often not sufficient for attic ventilation. Photo: MidAmerica
Movement is possible only on beams and boards placed here and there
The attic space can be used for laying communications, installing engineering equipment (both sometimes need revision) and storing things, such as seasonal sports equipment. But for this you need to make movement around the attic comfortable and safe, which means you cannot do without a floor, for which edged and unedged boards with a thickness of 35 mm or more or durable sheet materials (plywood, OSB, etc.) are suitable.
Perforated soffits provide intense and uniform air flow. Photo: FineBer
Comfortable lifting, loft and lighting are not provided
Even if you don’t use the attic as a storage room, you still sometimes have to go up there to inspect roof structures, chimneys or ventilation pipes. Moreover, the need to get into the attic may arise urgently (suppose you smelled burning and overheated metal near the chimney). Going to the barn in search of a stepladder will waste precious minutes. Therefore, it makes sense to acquire a stationary ladder or a special folding “invisible” ladder. And of course, we must not forget about the lighting - ideally it should turn on automatically (circuits with a motion sensor or a reed switch on the hatch).
The ventilation ridge, originally developed for attic roofs, is now often used in houses with a cold attic. Photo: Klober
Installation of sheathing
The type and method of installation of the transverse lathing depends on the roofing used. Slate, profiled sheets, metal and bitumen tiles are well suited for cold roofing. It all depends on aesthetic preferences and the slope of the slopes.
In total, there are two types of sheathing for cold roofs: solid and plank. Solid sheathing is well suited for soft tiles, as well as materials like corrugated sheets that make a lot of noise when it rains. Tightly pressing the covering onto a solid solid base eliminates the unwanted acoustic effect and greatly facilitates the installation of the roof.
The continuous sheathing is made either from OSB of classes 3 and 4, or from moisture-resistant plywood with phenol-formaldehyde resins. The minimum thickness of plywood is 8 mm with a pitch of rafter legs of 60 cm. OSB has a looser structure; for reliable fixation of fasteners in it, the thickness must be at least 12 mm.
It is recommended to install continuous sheathing starting from the front gable, laying solid sheets and moving the extensions to the least visible part of the slope. It is imperative to leave a deformation gap of about 10–15 mm between the plates. If the joint between the slabs is not in the area of the rafter leg, fastening through a backing strip 20–25 mm thick is allowed according to the same principle as fastening horizontal joints.
When all the sheets are secured, the joints must be filled with non-hardening bitumen mastic or a special roofing sealant. After sealing, it is recommended to check the plane of the sheathing using a stretched cord, if necessary, installing pads of different thicknesses in the main fastening areas.
The construction of plank sheathing is much simpler. Both edged and unedged boards are suitable for it; it is only important not to use materials that are not calibrated in thickness. The sheathing boards are nailed perpendicular to the rafters. In this case, two factors need to be taken into account:
- The main boards to which the covering of the selected format is attached must be located on the overlap line between the sheets. For these purposes, it is recommended to select the widest boards.
- In the range between the main boards, several additional ones should be installed, taking into account the degree of filling of the sheathing recommended by the manufacturer and the number of intermediate rows of fastening.
If you choose an unedged board, it should be placed with a wider plane upward. For fastening, it is better not to use screws and self-tapping screws; ordinary nails will work better than any other fastener.
Meter: 1 m3 of wood in the structure
10-01-002-01 Installation of rafters
| Resource code | Cost element name | Unit measured | 10-01-002-01 |
| Labor costs of construction workers | person-hour | 24,09 | |
| 1.1 | Average job level | 2,7 | |
| Driver labor costs | person-hour | 0,15 | |
| MACHINES AND MECHANISMS | |||
| Truck-mounted cranes when working on other types of construction 10 t | mach.-h | 0,15 | |
| Saw with carburetor engine | mach.-h | 0,44 | |
| Flatbed vehicles, load capacity up to 5 tons | mach.-h | 0,22 | |
| MATERIALS | |||
| 101-0782 | Forgings from square billets, weight 1.8 kg | T | 0,038 |
| 101-0797 | Hot rolled wire in coils, diameter 6.3-6.5 mm | T | 0,00438 |
| 101-1742 | Roofing felt with coarse-grained coating, waterproofing grade TG-350 | m 2 | 3,38 |
| 101-1805 | Construction nails | T | 0,0072 |
| 102-0024 | Edged softwood bars 4-6.5 m long, 75-150 mm wide, 40-75 mm thick, grade II | m 3 | 0,16 |
| 102-0028 | Edged softwood bars, length 4-6.5 m, width 75-150 mm, thickness 100, 125 mm, grade II | m 3 | 0,06 |
| 102-0059 | Edged softwood boards 4-6.5 m long, 75-150 mm wide, 44 mm thick or more, grade I | m 3 | 0,83 |
| 113-1777 | Antiseptic paste | T | 0,00196 |
Subsection 1.3 COLORS
Table GESN 10-01-023 Laying walking boards
01. Laying running boards on attic floors.
Meter: 100 m strokes
10-01-023-01 Laying walking boards
| Resource code | Cost element name | Unit measured | 10-01-023-01 |
| Labor costs of construction workers | person-hour | 3,8 | |
| 1.1 | Average job level | 2,8 | |
| Driver labor costs | person-hour | 0,08 | |
| MACHINES AND MECHANISMS | |||
| Truck-mounted cranes when working on other types of construction 10 t | mach.-h | 0,08 | |
| Flatbed vehicles, load capacity up to 5 tons | mach.-h | 0,04 | |
| MATERIALS | |||
| 101-1805 | Construction nails | T | 0,00066 |
| 102-0077 | Unedged softwood boards, length 4-6.5 m, all widths, thickness 32-40 mm, grade III | m 3 | 0,3 |
GESN 81-02-12-2001
Part 12
ROOFINGS
Moscow 2009
Table GESN 12-01-007 Construction of roofs of various types
01. Lathing installation. 02. Installation of roofs with lining of ridges, ribs, valleys, pipes, junctions with walls and dormer windows with sealing of gaps with mortar. 03. Sealing of longitudinal and transverse joints between asbestos-cement sheets.
01. Laying asbestos-cement sheets on finished purlins, installing fasteners, lining ridges, pipes, shafts and connections to walls. 02. Sealing of longitudinal and transverse joints between asbestos-cement sheets.
01. Installation of roofs with lining of ridges, ribs, valleys, pipes, junctions with walls and dormer windows with sealing of gaps with mortar. 02. Primer of the base under the first layer of roofing carpet.
01. Sealing of longitudinal and transverse joints between asbestos-cement sheets. 02. Lathing installation. 03. Installation of roofs with lining of ridges, ribs, valleys, pipes, junctions with walls and dormer windows with sealing of gaps with mortar.
01. Installation of roofs with lining of ridges, ribs, valleys, pipes, junctions with walls and dormer windows with sealing of gaps with mortar.
01. Lathing installation. 02. Installation of roofs with lining of ridges, ribs, valleys, pipes, junctions with walls and dormer windows with sealing of gaps with mortar.
General rules
The attic space or rooms, if they are divided into compartments, are insulated in several ways. The first is that if there is no attic space in the attic, then only the attic floors (the floor of the house) are insulated. Secondly, if there is an attic room in the attic, then the attic roof and floors (the ceiling of the house) are also insulated.
The following can serve as insulation for the attic roof:
- construction felt
- mineral slabs
- rolled mineral wool
The following coatings can serve as floor insulation for the attic:
- foam silicate slabs
- construction felt, mineral boards, rolled mineral wool
- as well as expanded clay, coal slag and hydrophobic ash
Before carrying out work on insulating the attic, you need to go through and check all the joints of the roof and ceiling for the presence of cracks. All cracks must be filled with lime mortar mixed with fibrous substances (tow). All wooden structures must be coated with fire retardant and anti-rot solutions.
Sockets for installing beams must be sealed with bricks. When repairing a coating made of asbestos-cement sheets, it is necessary to pay attention to the gaps formed by the waves of asbestos-cement sheets. If there are any, then they should be filled with lime mortar mixed with fibrous substances.
To seal the junction of asbestos-cement sheets with walls and parapets, it is necessary to check the presence of protective aprons, and galvanized roofing steel collars for pipes. The overlap of dissimilar covering elements on the aprons should be at least 15 cm.
Insulating the attic roof
Work on roof insulation begins with the lining of eaves overhangs, valleys, junctions with walls and proceeds from lower roof levels to higher levels. The slopes of slopes and coverings must be strictly observed.
The overlap of the coating elements at such joining points must be at least 150 mm. The joints of the insulation are made end-to-end. On slopes with a slope of up to 15%, the covering panels are placed parallel, with a greater roof slope - perpendicular to the ridge, laid from the ridge to the overhang.
Each panel of the laid material is cut into panels with a length equal to the length of the slope, adding to the overlap behind the “ridge” and to the lining of the overhangs. Each panel is rolled during installation and fastening. The layer-by-layer order of roof insulation and the thickness of each layer are shown in the figure.
The work on laying the roof insulation layer with rolled materials must meet the following requirements:
- deviations from the staggered position of the seams of the panels when laying and gluing the carpet are not allowed;
- the overlap of the panels one on top of the other should be
- the width in the lower layers is at least 50-70 mm
- and the top ones - at least 70-100 mm
- length in all layers - not less than 100 mm
- The joints of the insulation are made end-to-end
- the joints of layers of panels must be puttied with mastic (or other adhesive material), especially the joints of the top layer of rolled materials
- Dents, air pockets and holes are not allowed
Insulation of the attic floor
If an attic is provided in the attic, then before performing work on insulating the attic space, all work on the construction of walls and partitions of the attic is carried out.
When insulating the ceiling with slag, we lubricate the ceiling with clay sawdust, prepared manually. Lubricating the floor with clay-sand mass is carried out with a layer thickness of 20-25 mm and smoothing the surface.
Clay and sawdust themselves are an insulating layer and can only be replaced with expanded clay concrete (foam concrete is not an insulating material). Then, after the lubricating layer has dried, we fill the ceiling with slag. Backfilling must be done along the running boards so as not to disturb the lubricant layer.
When using sawdust, expanded clay or other materials with a volumetric mass of 300-500 kg/m3 as insulation, the cross-section of the load-bearing beams should be taken the same as for reinforced concrete crossbars with a payload of 150 kg/m3. Slag (fuel or metallurgical) can be used for these purposes in extreme cases and only for spans no more than 3-3.5 m wide.
Before screeding the insulation, it is necessary to construct attic passages from boards or poles so as not to disturb the screed. To do this, the boards are laid and secured to the beams or purlins of the attic. Usually the passages are laid out in three rows of boards and 7 rows of poles.
Protecting attic insulation from fire
For cutting, fire-retardant insulation and lining of chimneys in the attic, solid bricks, asbestos cardboard, asbestos-cement insulating boards, inorganic mineral products on a synthetic basis (mats, semi-rigid boards), construction felt soaked in a clay solution should be used.
Attention! It is strictly prohibited to use mineral products with a bitumen binder for fire retardant insulation of heating pipes.
In places where combustible parts of the building (floors, beams, roof insulation, etc.) will be adjacent to smoke and ventilation ducts, it is necessary to install grooves - see Table 2. Distance (mm) from the internal surfaces of smoke ducts to combustible structures (cuts):
Table 2. Distance (cutting) to combustible structures
| p/p | Furnace devices | Combustible structures | |
| not protected from fire | fire protected | ||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| 1 | Heating stoves or fireplaces of intermittent operation with combustion duration: | ||
| up to 3 hours | 380 | 250 | |
| more than 3 hours | 510 | 380 | |
| 2 | Gas-heated furnaces with a flow rate of more than 2 m3/hour | 380 | 250 |
| 3 | Long-burning heating stoves. Apartment kitchen stoves running on solid fuel. Residential gas water heaters. | 250 | 250 |
| 4 | Combination cookers with built-in boilers and separate apartment heating boilers. | 380 | 250 |
It is not allowed to lay metal chimneys through combustible floors. In exceptional cases, they are removed from combustible roof structures by 700 mm. Moreover, within the attic, such pipes are insulated with a layer of asbestos at least 3 mm thick and plastered over a mesh with cement mortar, and in places where they pass through a combustible roof they are additionally equipped with special devices in the form of sandboxes.
The chimney is plastered with a lime-cement mortar with the addition of asbestos fiber 10-20% of the volume of the solution. The height of the pipe cutting should be 70 mm above the layer of combustible backfill of the roof insulation. The gaps between the ceiling and the pipe cutting must be filled with clay mortar mixed with asbestos.
The ceiling lining and floor should only be finished before cutting. Metal and reinforced concrete beams and slabs must be spaced at least 130 mm from the inner surface of chimneys. The indentations are sealed with brick or other fireproof materials.
An air gap (indent) is left between the pipe and the combustible wall or partition for the entire height of the chimney. Combustible walls, partitions and attic insulation in the indentations are protected with thermal insulation materials - 8 mm thick asbestos cardboard or 25 mm thick plaster.
The protection should be 100mm wider than the overlap of the chimneys on each side. Within the attic space, the surface of the chimneys is rubbed down. And then covered with lime.
Attic prefabricated timber flooring
When installing an attic floor, it is necessary to solve the following main tasks:
- Ensure the strength and rigidity of the floor. The ceiling must withstand the design load with an allowable deflection and not be unstable (not oscillate when moving along the ceiling).
- The heat transfer resistance of the ceiling must be no less than necessary to meet the energy saving requirements in the house. You can learn about energy saving conditions from the article “Heating costs and heat transfer resistance.”
- Sound insulation of the ceiling from airborne noise must meet the established standard. Read what airborne noise is in the article “Floating floors - soundproofing floors.”
- Vapor permeability and air permeability of the ceiling must comply with established standards.
In economy-class houses, the most popular are wooden prefabricated attic floors on wooden beams. Such floors are easy to install, light and inexpensive, and the disadvantages of floors when used as attics are less pronounced.
We list the disadvantages of wooden floors compared to metal and concrete floors:
- Limited load-bearing capacity and length of span to be covered.
- Tendency to unsteadiness - fluctuations when people move or move furniture.
- Flammability, susceptibility to rotting and biodegradation.
- Poor sound insulation of airborne and impact noise. The ceiling structure itself can become a source of noise in the form of creaking.
| Fig.1. Attic floor on wooden beams. 1 - upper skin with windproof backing; 2 - floor beam; 3 — heat and sound insulation; 4 - vapor barrier; 5 - ceiling lining |
A diagram of the construction of a modern wooden floor is shown in Fig. 1.
As wooden beams, timber with a section of 150-250 x 100-200 mm is used. or boards 100-250 x 40-80 mm.
The use of boards makes it possible to reduce the volume of lumber required for the construction of the floor, with a slight decrease in the durability, fire resistance, and sound insulation of the floor.
In the attic floor this decrease is quite tolerable.
When using boards, measures must be taken to prevent the beam from twisting under load.
To do this, the beams are sheathed on both sides - top and bottom - with a layer of rigid sheet or slab materials - plywood, chipboard, DSP or OSB with a thickness of at least 12 mm. (with beam spacing up to 600 mm).
The slabs must be mounted so that the short side of the slabs is perpendicular to the floor beams, and connections parallel to these beams are spaced apart; The sheathing, firmly connected to the beams, forms a load-bearing frame, which prevents the beam from twisting and increases the load-bearing capacity of the floor.
Sheathing sheets are often more convenient to attach to sheathing (bottom) or joists (top).
Sheathing slats with a cross-section of at least 19x89 mm. installed from below perpendicular to the beams with a pitch of no more than 600 mm, convenient for fastening sheathing sheets.
For hemming along the sheathing, you can use less rigid sheets - gypsum plasterboard, gypsum plasterboard with a thickness of at least 12 mm. All edges of sheets or slabs of sheathing must be located above the supports (frame or sheathing elements). Sheathing sheets are fastened with self-tapping screws 40 mm long. greater sheet thickness, in increments of 200 mm.
| Fig.2. Spacer between plank beams |
If logs are attached on top across the beams, then sheathing is not done over the beams. In the absence of upper cladding and joists, with a board height of more than 150 mm. install vertical struts
with a cross section of at least 100x38 mm., Fig. 2.
Vertical braces should be located in the span of beams at a distance of no more than 2100 mm from each beam support and from adjacent vertical braces. It is convenient to make spacers at the joints of sheathing sheets, if the sheathing is attached directly to the beams. The spacers are attached to the beams with nails or special metal brackets.
For timber beams, measures to prevent twisting are not required.
The cross-section of the beams and the spacing of the beams are determined by calculation. For beams, dry lumber with a moisture content of no more than 20% is used.
| Fig.3 Supporting a beam on a wall. 1 - beam; 2 - waterproofing of the beam; 3 - gasket; 4 - waterproofing of the gasket |
Wooden beams made from timber rest on the wall to a depth of 150-200 mm, and from boards - at least 100 mm. The ends of the beams in contact with the brick or block masonry must be impregnated with an antiseptic and wrapped in waterproofing material (roofing felt, waterproofing, plastic film) to a length of 250 mm, and the end of the beam, beveled by 30 mm, must be left open, ensuring an air gap between the end of the beam and wall (Fig. 3).
To level the ends of the beams in height, place a piece of board of the required thickness under them, wrapped in waterproofing. The end of the beam is connected to the wall with a metal connection.
The end of the connection is embedded in the masonry of the wall, the other is nailed to the beam.
To improve fire resistance
sheets of gypsum plasterboard or gypsum board with a thickness of at least 12 mm for 1-2 storey buildings, and at least 15.9 mm, are mounted on the floor from below. for three-story buildings, with a floor area of up to 150 m2.
To access the attic, a hatch measuring at least 500x700 mm is installed in the ceiling.
The construction market offers factory-made wooden beams for prefabricated floors:
- Beams made of laminated veneer lumber
- I-beams made of OSB boards
- Wood-metal beams
The design of floors on such beams is not fundamentally different from the design of floors on beams made of conventional lumber. The use of prefabricated beams allows you to increase the load-bearing capacity of the floor and the length of the covered span.
If this is not necessary, then their use for attic floors, as a rule, is not economically justified.
An attic floor with wooden beams can be an independent structural element of the building, or it can be part of the roof.
In the latter case, the attic floor beams are part of the supporting frame of the roof.
The independent design of the attic floor is more preferable in operation
- easier and more affordable repair of floor and roof parts, better sound insulation of premises.
Combining the slab with the roof structure reduces construction costs.
Thermal insulation of attic floors using wooden beams
Mineral wool insulation of the attic floor is laid in the space between the beams. You can use effective bulk insulation, for example, ecowool.
Insulate with expanded clay, slag, etc. do not do it,
since, with modern standards for thermal insulation, the volume and weight of such insulation for a wooden floor is too large.
The thickness of the insulation is determined by calculation. How to choose the thickness of floor insulation can be found in the article “Calculation of floor insulation.”
To protect the insulation from moisture as a result of condensation of steam from the internal air, a vapor barrier film is laid along the top of the ceiling lining.
Vapor barrier polyethylene film with a thickness of at least 0.15 mm. laid with an overlap of at least 200 mm.
Why steam condenses in the insulation is described in the article “Dew point, vapor barrier and ventilation gap.”
Soundproofing the attic floor
In addition to good thermal protection, attic floors must provide sufficient sound insulation of the upper floor rooms from airborne noise. People sleeping on the top floor should not be awakened by rain or hail hitting the metal roof covering. Therefore, quite stringent requirements for sound insulation are imposed on attic floors.
Rafter system
Since no insulation will be placed between the rafter legs, their pitch and cross-section can be chosen absolutely freely. The kalk.pro service will help in this matter: in the “Roofs” section it is possible to model and calculate load-bearing elements and sheathing for any type of roof.
The most suitable lumber for constructing rafter legs is considered to be a board 50–70 mm thick and 100–200 mm wide. Based on the weight of the roof and the predicted snow load, the pitch between the rafters of this section is adjusted in the range of 60–120 cm. It is imperative to take into account that the rafters during installation are reinforced with a counter-lattice 30–40 mm thick, so it is wise to initially choose a slightly smaller board width.
When installing the rafter system, it is imperative to align the legs in common planes in order to subsequently avoid problems with the alignment of the sheathing. For these purposes, it is recommended to rigidly fasten the outer rafters to the spacers, pull the cords at the top and bottom of the slope, and then place the rest of the legs along them. The rafters must be temporarily fastened from the inside of the roof until the waterproofing and counter-lattice with sheathing are installed on the outside.
Standards for attic walkways
Hello everybody. The essence of the question is this: We bought an apartment on the top floor in a new building. I decided to go to the attic to look at the insulation and saw mineral wool slabs there with a density of at most 30 kg/m3, there were no walking bridges. The laid layer of thermal insulation with a thickness of 200 mm in the places of passages along it turned into a layer of thermal insulation with a thickness of 30-50 mm (the insulation did not regain its shape after walking on it). We asked the developer for documentation - the developer completed everything in accordance with the project (insulation area 30-40 kg/m3, no walkways).
Accordingly, the questions that have become urgent are: 1. Is there a document that specifies standards for the construction of walking walkways when laying low-density insulation in the attic? 2. Are there standards for the density of attic insulation coatings?
Construction pricing reform should have been completed
Tell me, please, I need to calculate an estimate for the installation of the roof. And the question is, what are walking boards?
OSkirta, ordinary boards so that workers can walk on them and not press on the roof
OSkirta, as well as engineering communications located in the attic.
= plank flooring over attic fill (insulation) for passage through attic rooms
You need to know what type of roofing is needed - slate or metal flooring is needed, take it as the manufacture of wooden structures, for example E 10-01-083-3 or something similar.
FOR WHAT. According to which document, WALKING boards are required ON THE ROOF.
go clean the chimney.
POT R O-14000-004-98 “Regulation. Technical operation of industrial buildings and structures"
slavalit, this is already VZiS..at the expense of HP
slavalit, thank you, I like your answers, they are always on topic!
SNiP II-26-76 “Roofs”
The document is very simple - norms and rules for the operation of the housing stock, clause 4.6.1.5
=if the project provides...then you can build an attic for temporary shelter from rain for service personnel...but THESE are not WALKING boards in the definition according to Sat. 10..read the scope of work..
SNiP 12-03-2001 LABOR SAFETY IN CONSTRUCTION:
Walking boards are used when constructing a thermal insulation backfill for an attic space made of expanded clay or its analogues for the subsequent operation of the under-roof space (according to the technical part of the collection), and the application of prices for other needs (obviously necessary for the operation of over-roof structures) is the responsibility of each estimator.
but then there are the attic floors. and I need these on earth. also on metal corners
and for what if it’s not a secret?
In recreational areas, sometimes in the forest, paths are installed to make walking more convenient
Kareniina, 9 Sat. - purlins for the corner. 11 each - plank flooring. although to be honest, God knows what that means. what is the question - this is the answer
Something like this
Kareniina, I think this price will suit you TER27-07-004-01
Yes, thank you very much - it looks like the truth))) sharpen it a little - and there will be walking boards on the corners)
Kareniina, and I think the cost of the corner can simply be added to the price
Is laying walking boards included in HP or not? metal roof
Tell me, how to calculate the number of running boards when installing a gable roof?
Eva77, why doesn’t the statement say how many m.p.?
It’s not in the statement, I decided to include it in the estimate myself, but I don’t know how to calculate it correctly, can you tell me? In what places are they laid and what width?
Eva77, the width has nothing to do with it, the price includes 1.2 m3 of boards per 100 m.p. (if you want, calculate it yourself). And I would estimate the length like this: one “path” in the middle = the long side of the building; from it there are “paths to the dormer windows and what else is needed (hatches, bottling, equipment).
Eva77, if it’s not on the statement, then you don’t need to add it. Don’t be creative - they won’t appreciate it. this needs to be decided on site
I need these boards to mount the roof (installation of rafters, installation of sheathing, installation of waterproofing, etc.), so as not to trample on the ceiling
Other publications in the “Online Forum” section
Answer: Parking of cars in the courtyards of apartment buildings is regulated by the Code of Rules SP 42.13330.2011 “Urban planning. Planning and development of urban and rural settlements. Updated version of SNiP 2.07.01-89*" clause 11.25. table No. 10. If the parking lot can accommodate up to 10 cars.
Answer: Based on paragraph 32, paragraph 1, Article 264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, other costs include costs associated with production and sales, as well as costs for the maintenance of temporary and rotational camps for the accommodation of workers, as well as all housing and communal facilities for social and welfare purposes. This also includes.
Answer: Parking of cars in the courtyards of apartment buildings is regulated by the Code of Rules SP 42.13330.2011 “Urban planning. Planning and development of urban and rural settlements. Updated version of SNiP 2.07.01-89*" clause 11.25. table No. 10. If the parking lot near the house can accommodate up to 10 av.