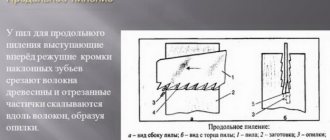
Construction of houses is a responsible matter for every family. You need to think in advance about what to build a house from; the construction time and the costs of building housing depend on this. Today we will not discuss construction with ordinary bricks; we will consider the three most popular types of building materials after brick, log house, blocks and vulture panels.
Log houses
Dwellings have been built with logs since ancient times; they also remain a popular material now. Log houses have good heat resistance in winter and coolness in hot weather, environmental friendliness, and sound insulation.
Disadvantages: flammability, shrinkage, various types of destruction by external environmental factors, for this it needs to be treated every year from rotting and various kinds of rodents. The cost of log house housing will be 18,000 - 80,000 per m2, depending on the type of wood.
Plywood markings: how to read and decipher
Plywood marking is a very interesting topic. Knowing how to decipher the markings, you don’t need any consultant in the store; you yourself can advise anyone.
Instead of a long boring theoretical article, we invite you to learn from a real example. Shall we decipher the label?
Great! Then let's go! We have as many as 19 marking elements ahead of us. But first things first!
Number 1
. At the very top of the marking label there is always information about the plywood manufacturer, its brand and logo. In our case, this is the Syktivkar plywood plant.
Number 2
. Here we see the designation of the type of plywood. It can be birch, coniferous, laminated birch, etc. In our case, it is only indicated that the plywood is laminated.
Number 3
. Next we see the format of the plywood sheet, its length, width and thickness in millimeters.
Number 4
. In this field we see the brand of plywood based on the type of adhesive used. After all, we all remember that plywood is a sandwich consisting of several layers of wood veneer glued together. Main brands:
● FBA
. In the production of this type of plywood, an albumin-casein composition is used.
● FC
. When gluing layers of veneer, urea glue is used.
● FKM
. Melamine adhesive is used in the production of this type of plywood.
● FSF
. The layers of this plywood are held together with phenol-formaldehyde glue.
● FB
. The veneer is impregnated with bakelite varnish.
Number 5
. Next we will find out the type of plywood surface. It can be polished on 1 side - Ш1, or on 2 sides - Ш2. Can be unpolished - NS. In the case of laminated plywood, the designations F and W are used. F is a smooth surface, W is a mesh surface. Accordingly, FF is smooth on both sides, F/W is smooth on one side, etc. In our case, the marking is a little non-standard; it shows the color of the lamination.
Number 6
. Here we see the density of the laminating film on each side through the slash.
Number 7
. This is a manufacturer's barcode, where digital information about it is encrypted.
Number 8
. This is the packing date of the product pack.
Number 9
. Here is the contact information for the plywood manufacturer.
Number 10
. This is a sign of the Russian voluntary certification RSO. This mark confirms the product’s compliance with all GOST requirements.
Number 11
. This is a certification mark of the environmental assessment of the Wilhelm Clauditz Institute (Germany). This mark confirms the product's compliance with all ISO 14025 environmental declaration templates.
Number 12
. VTT is the certification mark of the VTT Institute of Transport and Construction
Number 13
. CE is an administrative marking indicating compliance with health, safety and environmental standards for products sold within the European Economic Area.
Number 14
. FSC is a certification mark confirming that the chain from the procurement of plywood raw materials to the production and sale of plywood is certified according to the FSC system. The plywood is made entirely from forest products that come from licensed forests that are FSC certified.
Number 15
. This shows the type of plywood edge and the number of sides it is applied to. There are the following types of edges:
● P1 – tongue-and-groove edge type.
● P2 – Quarter edge type.
● P3 – chamfered.
In our case, P3*4 means that the plywood is chamfered on all 4 sides.
Number 16
. The number of sheets per package is indicated here.
Number 17
. Designation of plywood grade. B2 here means that the outer layer of plywood on both sides is birch (B - birch, 2 - on 2 sides). And 1/2C is the plywood grade marking. The designation is the same for both sides. 1 is the front layer of plywood of the first (I, B) grade. 2 means that the inner layer of plywood is of the second (II, BB) grade. There are also the following types of plywood:
● E – elite grade
● Third grade - III or CP
● Fourth grade - IV or C
Number 18
. The formaldehyde emission class is indicated here. This indicator indicates the degree of purity of the product and the presence of harmful fumes during its operation.
According to GOST, there are 3 formaldehyde emission classes:
● E1 is a class indicating the purity and safety of the material.
● E2 – indicates that the material has minimal deviations.
● No grade - this is a highly toxic material and cannot be used.
Number 19
. The mark confirms compliance of the manufacturer’s quality management system with the requirements of the international standard ISO9001-2000.
Blocks
There are many different types of blocks. The most common foam blocks and gas blocks. Gas blocks and foam blocks have gained great popularity in the construction of private houses in a short time. They have a number of advantages, good heat resistance, sound insulation, lightweight in size compared to other materials, due to this, lower costs for the foundation. Disadvantages: quite fragile, they need to be lined as they quickly absorb moisture due to their porous structure. The cost of a house made of foam blocks will be 11,000 - 20,000 rubles. m2.
Plywood varieties
For proper use, it is important to know the grade of the material. Glued veneer sheets are divided into several varieties:
- E (Elite). Old designation - A. High quality version with no flaws on the front surface, minor random deviations may occur. The sheets are used for decorative work and the manufacture of luxury furniture. They are the best base for film cladding and varnishing.
- I grade. Outdated markings are “AB” and “B”. A high-quality variety with a minimum number of defects in the form of cracks up to 2 cm in size per meter of width and visually noticeable fused knots. Wormholes (no more than three per 1 m2) should not exceed 6 mm. The color of the slab is uniform, with possible deviations of about 15%.
- II grade. Previously designated "B" and "BB". Unlike the previous version, it has more flaws. But the surface may contain large fused light and dark knots (up to 15 mm) in the amount of 10 pieces. per 1 m2. Open cracks must be sealed with putty. There may be a lack of veneer (about 2 mm) at the edges.
- III grade. The old markings are “BB” and “SR”. The presence of falling out and large spliced knots, dents, scallops, and torn fibers is allowed (no more than 5% of the area).
- IV grade. Previously designated "C". The product has various and numerous defects, as can be seen in the photo below. The use of such plates is limited to rough work. Despite the shortcomings, the layers are glued together quite well.
Sheets of the highest, first and second grade can be used almost everywhere, the characteristics of grade 3 are also quite high, but the shirt has a small number of defects, and grade 4 is intended exclusively for technical needs
. The sides of the panel may have different quality:
- Grade 1/1. The products have uniform indicators that are precisely specified in GOST 3916.1-96.
- 1/2. The products combine the characteristics of two categories.
- 2/2 and 3/3. The materials fully comply with the second and third quality groups.
- 2/4. One side is second grade, the other is fourth.
Some manufacturers indicate group 5/5, this designation means products for rough construction work.
Application of plywood
The scope of use of the material is quite wide:
- Rough and finishing floor covering with laying of sheets on boards, wooden joists or dry screed.
- All stages of construction of frame houses. Special types are laid as a base before installing the floors. The panels cover the internal and external parts of the walls and the roof.
- Creating smooth surfaces. The material is suitable for installation on lathing or glue.
- You can make various figurines and souvenirs from plywood.
- Decorative cladding of residential and work premises. Laminated options with different textures provide the creation of an individual design.
- Furniture manufacturing. Such interior items look respectable and are of high class.
Plywood has been produced on an industrial scale for more than 100 years and its popularity in various fields is second only to natural solid wood.
In general, there are practically no restrictions on the use of the material; special varieties are used in the transport, shipbuilding and aviation industries.
Peculiarities
There are many options for this material, they all differ in their width, coating and manufacturing features.
In order to choose the optimal product, you need to pay close attention to studying the characteristics. Plywood is a regular sheet that is created using wood
In turn, it goes through several stages of processing, which gives the product its unique properties.
The process of gluing the layers occurs through the use of special compounds, which are usually based on resins. The result is a lightweight material that can also boast of its resistance to temperature changes.
Among the main advantages of such a product are the following.
- Resistance to moisture, so the material can even be used for finishing a bathroom. This can be achieved due to the fact that when in contact with water, the plywood sheets do not delaminate and do not lose their shape.
- Ease of processing and installation. This material is famous for its strength, so you can use any processing tools without fear. Plywood can be cut, sawed or drilled without any problems, which makes it stand out from other materials.
- Possibility to combine with other materials. It should be noted that laminated plywood is very often used as an additional material, so it is perfect for finishing a ceiling, floor or roof. Most experts use this plywood in combination with natural wood.
- Huge scope of application. Laminated plywood can boast of its unique performance characteristics, which allows it to be used in the process of finishing work, in the production of furniture and decorations.
A distinctive feature of moisture-resistant laminated plywood is that during the manufacturing process it is processed much longer and is also covered with thicker paper. This paper is impregnated with a special composition, which makes the finished product durable and allows it not to lose its properties for a long time. In addition, it provides resistance to water.
Laminated plywood differs from other materials in that it is almost insensitive to temperature changes, so it can even be used in a bathhouse. The special layer also protects against the effects of cleaning agents, including aggressive abrasives. Another feature of this plywood is that it contains a minimal amount of phenol. This results in a more elastic and durable material, which also has a varnished protective layer of polymer.
Manufacturers and their costs
Manufacturers in Russia
, the Vyatsky Plywood Mill produces FSF plywood . Its specificity is the production of environmentally friendly material, for which they use birch veneer as a raw material. The company produces a product with the following dimensions: 1220x2440, 1250x2500, 1500x3000, 1525x3050 mm. E1 class glue is used for gluing sheets.
To produce products, the plant uses raw materials of legal origin and the highest quality. During all production activities, all measures are taken to preserve forest biological diversity. You can purchase the product for 850 rubles per sheet.
What thickness of plywood is needed for the floor can be read here in this article.
The next enterprise is considered . They also produce high quality FSF plywood from environmentally friendly wood. Production may include the production of laminated, moisture-resistant plywood. The cost of production will be 960 rubles.
Foreign production
But the production of such products is also actively carried out abroad. Finnish products are in great demand today. The leading position is occupied by the company WISA Birch . To obtain FSF plywood, birch veneer is used. This product has found its use in cases where greater loads are required. Softwood plywood is also produced. This product is characterized by light weight, as well as economic efficiency, which has made it possible to gain such popularity in the field of construction. You can buy the product for 1250 rubles.
FSF plywood is a material that is often used today in industrial construction, as well as in home improvement. This product can be used for cladding the external and internal walls of a house, as well as in rooms where there is high humidity. Thanks to its long service life, FSF plywood will delight you with its quality for a long time. And also in our article you can familiarize yourself with what MDF is.
Dimensions
One of the key factors in choosing products is sheet sizes.
Thickness
The thickness of plywood is determined by the number of layers and varies between 4-40 cm:
| Thickness, mm | Purpose |
| 4 | Creativity, packaging, furniture, layout design |
| 6 | Plywood for leveling walls and ceilings that are not exposed to significant loads |
| 8 | Leveling walls, floors and ceilings, manufacturing furniture structures |
| 10 | Can be used as underlayment for flooring |
| 12 | Optimal thickness of flooring, production of furniture structures, elements of car interiors and other equipment |
| 16 or more | Use for critical structures and formwork |
Lenght and width
Manufacturers produce plywood with standardized sheet sizes:
| Length, mm | Width, mm |
| 1525 | 1525 |
| 1475 | |
| 1350 | |
| 1270 | |
| 1220 | |
| 1475 | 1475 |
| 1270 | 1270 |
| 1220 | 1220 |
| 3050 | 1525 |
| 3000 | 1500 |
| 2500 | 1250 |
| 2440 | 1220 |
| 1830 | 1525 |
Acceptance and control methods
Finished products are accepted in batches, which are documented in a metric document with data on the manufacturer's trademark, the country where the product was produced, the volume and dimensions of plywood in the package, the name of the technical documentation in accordance with which the product was produced, and the class of the product.
The batch is accepted and handed over for sale only in cases where the requirements of clauses 6.2, 5.3, 5.4 of GOST 53920-2010 are met.
It is allowed to measure the dimensions of products using tape measures and metal meters, a micrometer and a thickness gauge. The error class of all instruments should be no more than 0.1 mm.
At all stages of production the following parameters must be controlled:
- Current moisture content of the material.
- The product must withstand the effects of cement mortars, moisture, steam, and chemical elements in building mixtures.
- Maintaining strength during bending and stretching in accordance with established parameters.
- The quality of the laminating coating.
- The quality of gluing layers of each sheet.
- The presence of defects with which the product cannot be released must be monitored.
Finished products must be free of swelling, destruction of layers, chips, cracks and other defects.
Technical requirements
The document regulates all necessary stages of production and technical compliance with regulatory requirements, mandatory for all manufacturers. The key positions are the following:
- The main component in manufacturing should be birch veneer, which has higher water-repellent properties.
- The mass of toxic elements released by formaldehyde must correspond to class E-1.
- The material for laminating plywood should be paper impregnated with thermoactive resin.
- If there are defects on the sheets of products, they are eliminated by gluing additional veneer or puttied with a material that does not lose the original color.
- Internal damage that does not affect the strength and general quality of the product can be accepted without rejection, but with a downgrade.
Production
Making plywood sheets is a multi-step process.
- Logs arriving at the plant are soaked in hot water. In this case, a process of natural preservation with tar occurs, which protects the material from subsequent rotting. Also, high temperature helps soften the barrel for ease of further processing. After a few hours, the logs are transferred to the workshop to normalize the temperature and its distribution inside the trunk.
- After uniform heating, the workpieces are sent to a peeling machine, where the bark is removed from the log and the wood is cut layer-by-layer in thin, stable layers using an Archimedean screw in a spiral. The result is veneer.
- Next, the veneer in rolls or sheets goes to the repair shop, where its condition is assessed by automated installations. They identify the presence of knots, cut them out and replace the area with a patch of the same type of wood. It is worth noting that only grades 1 and 2 go through this stage.
- Experts begin gluing the layers. For this purpose, various polymer compositions based on natural or synthetic resins are used. The veneer is laid in layers so that each layer lies perpendicular to the bottom one in the direction of the grain. This makes it possible to provide plywood with high strength to mechanical loads. The result is recorded in an installation with high pressure and steam treatment.
- The finished sheets are cut and sent for storage or to the consumer.
The authors of the video clearly explain and show how plywood is made.
The difference between FC plywood and FSF
For the production of FC plywood, urea resins are used, in particular urea-formaldehyde resin. The manufacturing technology is somewhat similar to that described above, but there are some differences.
The most important aspect is the urea polymer itself, which will fill and hold the veneer sheets together.
It has objective disadvantages:
- Fragility;
- Low water resistance;
- Poor resistance to destructive influences;
- Release of formaldehyde.
These defects are combated and various reagents are introduced into the reaction mass, but the negative characteristics are not eliminated, but only diminished.
FSF plywood is also expected to release free phenol. But after the polymerization reaction, phenol is present in the material only in trace amounts, and it can only be detected in laboratory conditions.
Other comparative characteristics can be found in the table:
| FSF | FC | |
| Water resistance | Exceptionally high | Weak |
| Strength | In any test, the performance is 80-130% higher than that of FC | Inferior to FSF |
| Biosecurity | Maximum, can be damaged by rodents | Without additional processing it is very weak. |
| Environmental friendliness | Detection of traces of phenol possible | Capable of releasing free formaldehyde |
| Appearance | With the same quality, they are practically no different. The difference can only be seen in the cut. | |
But by external signs it is also possible to distinguish FSF plywood from FC. In order to 100% guarantee to separate one type of material from another, you need to carefully examine the end.
In FSF plywood, phenol-formaldehyde resin after polymerization gives the layers a red-brownish tint. And FC plywood, being treated with urea-formaldehyde resins, has end layers of a yellowish tint.
FIG 1. End of FSF plywood
FIG 2. End face of FC plywood
The depth and saturation of the color depends on the presence of certain reagents, but the tonality will help to identify the material.
Classification according to the composition of the adhesive impregnation
Technical characteristics, sanitary safety, directions of use are largely determined by the composition of the means used to glue the veneer sheets.
Plywood is a long-known material, for the production of which both historically established gluing technologies and innovative methods and composites are used. In addition to traditional types, decorative plywood is produced using expensive types of wood or paper with a texture pattern. According to the method and material of gluing layers, five main groups and several subgroups can be distinguished.
FBA
FBA products have the safest adhesive impregnation, consisting of two protein fractions:
- albumin;
- casein
The environmental friendliness of plywood comes with insufficient water resistance, because protein substances tend to swell in the presence of water. Sheet products are not recommended for use in rooms containing damp vapors; they can be used for the production of furniture and the manufacture of decorative elements for finishing dry rooms.
FC
Products with the abbreviation FC in the marking are produced by joining veneer with urea adhesives that do not emit harmful fumes into the surrounding space. The material is relatively resistant to moisture and can be used for finishing rooms with moderate concentrations of water vapor.
FKM
The products of this group demonstrate good resistance to moisture and have confirmed their absolute safety for the surrounding air. The melamine adhesive with which the veneer is joined is non-reactive and does not become a source of harmful fumes, which makes it possible to use FCM products for interior decoration of any premises and furniture manufacturing.
FSF
Plywood with the FSF designation has increased resistance to moisture, which is due to the use of phenol-formaldehyde resinous polymers for gluing sheets. The glue may contain a residual amount of monomeric aldehyde, which evaporates during use of the material. The regulations allow the use of FSF sheets of different sizes for exterior finishing and the production of street furniture.